Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sci M.2-Mixture-Key
Sci M.2-Mixture-Key
Uploaded by
Pupae WaranyaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sci M.2-Mixture-Key
Sci M.2-Mixture-Key
Uploaded by
Pupae WaranyaCopyright:
Available Formats
Mixtures
A mixture is made up of two or more than two
components that are mixed physically either by stirring,
shaking or dissolving.
However, the physical properties of the mixture may be different from the
physical properties of the components
such as the boiling point, melting point, color and physical state.
Examples of mixtures : sugar solution, salt water, smoke, marbles in water.
However, mixing of vinegar and baking soda does not produce a mixture.
They react and produce carbon dioxide and water.
Mixing an acid and a base also does not produce a mixture also.
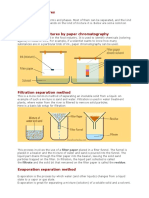
1. Separating Mixtures
The components in a mixture can be separated by physical means
because they are not united by a chemical bond.
In order to separate the components of a mixture,
we need to know the differences in the properties of the components.
Then, we can choose a suitable separation method to separate them.
There are some separation methods such as:
(a) evaporation (d) paper chromatography
(b) crystallization (e) solvent extraction
(c) simple distillation. (f) steam distillation
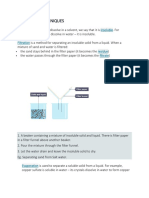
1a). Evaporation
Evaporation is the process of a substance in
a liquid state changing to its gaseous state
due to an increase in temperature.
Evaporation is a way to separate a soluble solid
from a liquid.
For example, salt is soluble in water to form salt water.
During evaporation, the water evaporates away leaving the solid salt behind.
2a). Crystallization
Crystallization is a method to obtain a pure solid from an impure solid.
An impure solid is dissolved in a liquid (solvent) to produce a solution.
The solution is then heated up.
When most of the solvent is evaporated, the hot solution is left to cool down.
The dissolved solid will appear as pure crystals.
The impurities remain in the solvent. Then, the cold solvent is poured off to
obtain the crystals.
Filtration followed by crystallization is often used to obtain pure salts
such as copper(I I ) sulfate. .Sugar is obtained by this way too.
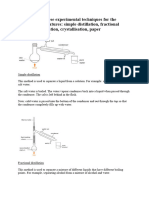
3a). Simple distillation
Simple distillation is used to purify liquids with very different boiling points.
In this process, the mixture of liquids is heated up and the liquid with the
lower boiling point evaporates and escapes as a vapor.
Remember that different liquids have different boiling points.
At this moment, the temperature of the vapor is constant.
The vapor is then cooled and condensed into its pure liquid
which is called distillate.
In the lab, usually a Liebig condenser is used to condense the vapor .
If more than one liquid in a mixture of liquids is needed to be separated ,
fractional distillation is used.
Fractional distillation uses a fractionating column to separate the different
liquids with different boiling points.
For example : Crude oil is separated by this way.
4a). Paper chromatography
Paper chromatography is usually used to separate the different colored
components in dyes or inks.
Example : It is often used in forensic science and food industry.
A drop of ink is placed onto the chromatography paper.
Then, the paper is dipped into a suitable solvent.
The solvent travels up the paper.
The ink dissolves in the solvent and moves up with it.
Different colored components travel at different rate and get spepatrate.
Therefore the colored components’ll appear at different locations on the pp
The movement of a component of an ink or dye during chromatography,
relative to the moment of the solvent , is measured by calculating its
retention factor (Rf) that can be calculated using this formula:
The Rf value of the above component of
the dye = 5 cm / 10 cm = 0.5
Calculating the Rf value allows scientists to identify unknown substances
because it can be compared with the Rf values of known substances under
the same conditions. . The Rf values are always between 0 and 1.
F.) Solvent extraction
Solvent extraction is also known as liquid-liquid extraction.
It involves the separation of two or more components due to their unequal
solubilities in two immiscible (not mixed) liquid phases.
A solvent dissolving only that particular component that needs to be
separated from the mixture is used.
Therefore, choosing the right solvent is important in order to dissolve that
particular component and it must not be miscible (able to mix freely)
with the other solvent.
For example, in order to extract iodine from the mixture of salt and iodine
in water, tetrachloromethane is added. Water is immiscible with
tetrachloromethane.
Salt does not dissolve in tetra chlaromethane but iodine does .
Therefore, a purple solution of iodine in tetra cholera methane is formed.
These two solution do not mix . By using a separating funnel, these two
solutions can be separated . The solvent are the evaporated to obtain the
salt and iodine off separately.
f.) Steam distillation
Steam distillation is used mainly to separate out components that are sensitive
to high temperatures and immiscible with water such as essential oils.
These components decompose at high temperatures.
Steam distillation works similar to simple distillation.
Simple distillation requires direct heat to evaporate the contents.
However, in steam distillation, steam is used instead of direct heat.
The volatile component together with water is distilled out as the distillate.
Upon settling, the extracted component will float on the water and
later is separated by filtering out the water from below.
You might also like
- IGCSE Chemistry - States of Matter and Separation TechniquesDocument12 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - States of Matter and Separation TechniquesChemistryKlipz100% (24)
- A Level Chemistry: Epic Acids, Bases and Buffers Cheat SheetDocument23 pagesA Level Chemistry: Epic Acids, Bases and Buffers Cheat Sheetgemmaandjude6951No ratings yet
- Chemistry Handout How Solubility Changes With Temperature SolubilityDocument16 pagesChemistry Handout How Solubility Changes With Temperature SolubilityAnderson MichelleNo ratings yet
- Color Mixing GuideDocument88 pagesColor Mixing GuideJohn Johnson100% (4)
- Sci M.2-MixtureDocument6 pagesSci M.2-MixturePupae WaranyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part 2 Element, Compound and MixtureDocument38 pagesUnit 1 Part 2 Element, Compound and MixtureI LOVE JAKENo ratings yet
- 2.1 C6 Separation Techniques - Teacher (27 July 2011)Document27 pages2.1 C6 Separation Techniques - Teacher (27 July 2011)ronnie_gohNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument30 pagesSeparation TechniquesSindhu SanthoshNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Japan Part 1Document73 pagesStudy Guide Japan Part 1Janzu SalazarNo ratings yet
- 0particles and MixturesDocument10 pages0particles and Mixturesamacovei_3No ratings yet
- 1.chemistry Form OneDocument53 pages1.chemistry Form Oneaxmed qaseNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes 2Document8 pagesChemistry Notes 2QfkjfksNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds and Mixtures PowerpointDocument13 pagesElements, Compounds and Mixtures PowerpointMaxime Van ElslanderNo ratings yet
- Separation Techniques 1Document8 pagesSeparation Techniques 1Kaylo KganyakoNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Note On Separating TechniquesDocument8 pagesGrade 7 Note On Separating TechniquesBadass PolapainNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument24 pagesPhysical and Chemical ChangesTanesha JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument35 pagesSeparation Techniquesali AbbasNo ratings yet
- Study Material - Separation MethodsDocument7 pagesStudy Material - Separation MethodsSahil NarkhedeNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument11 pagesSeparation TechniqueselizabethNo ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures PDFDocument4 pagesSeparating Mixtures PDFDenise Adriene ParanNo ratings yet
- Separation Techniques - Chromatography, Filtration, DistillationDocument3 pagesSeparation Techniques - Chromatography, Filtration, DistillationamaarshajahanNo ratings yet
- Identify The Difference Between Elements, Compounds and Mixtures in Terms of Particle TheoryDocument17 pagesIdentify The Difference Between Elements, Compounds and Mixtures in Terms of Particle TheoryBenjamin PangNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document11 pagesLab 1ron971No ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures: Techniques and Applications: Evaporation, Distillation and FiltrationDocument4 pagesSeparating Mixtures: Techniques and Applications: Evaporation, Distillation and FiltrationAndrea SobredillaNo ratings yet
- Separating MixturesDocument4 pagesSeparating MixturesRoxette RoseteNo ratings yet
- Element, Compound or MixtureDocument22 pagesElement, Compound or MixturehahaNo ratings yet
- Separation NotesDocument3 pagesSeparation NotesMeetaDeviNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Pure?Document8 pagesIs Matter Pure?Aarti JainNo ratings yet
- Mixtures: Omar Alqinneh 9D.IGCSEDocument10 pagesMixtures: Omar Alqinneh 9D.IGCSEOmar AlqinnehNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us Pure? Separation TechniquesDocument15 pagesIs Matter Around Us Pure? Separation TechniquesAradhya RaiNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument17 pagesSeparation Techniquesdenise adrieneNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument39 pagesOrganic Chemistryh2312416No ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument25 pagesIs Matter Around Us PureGaurav MehndirattaNo ratings yet
- Separating Acids and Neutral Compounds by Solvent Extraction 705Document11 pagesSeparating Acids and Neutral Compounds by Solvent Extraction 705irohanihoheto12350% (2)
- O Level Biology NotesDocument221 pagesO Level Biology NotesKhaled Elshamanhory89% (19)
- Example of Chemical ChangeDocument7 pagesExample of Chemical ChangeRamel OñateNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument45 pagesIs Matter Around Us PuresabirafrinNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Separation TechniquesDocument16 pagesCH 4 Separation TechniquestanhuikuanNo ratings yet
- Experimental ChemistryDocument45 pagesExperimental ChemistryabdullahminhasNo ratings yet
- Lab Skills and Separating Methods: ElementsDocument5 pagesLab Skills and Separating Methods: ElementschiragjogiNo ratings yet
- Separation Techniques: Composed With Epsilon Notes in AndroidDocument7 pagesSeparation Techniques: Composed With Epsilon Notes in AndroidBrãñdøn DzîñgáíNo ratings yet
- Methods of Purification and Analysis TeachDocument20 pagesMethods of Purification and Analysis Teachhafizhapni91% (11)
- Separation Techniques (Chapter21)Document5 pagesSeparation Techniques (Chapter21)M.zuhair asifNo ratings yet
- Classification of MatterDocument38 pagesClassification of MatterNR AdawiyahNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure - Class 9th ScienceDocument9 pagesNotes of CH 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure - Class 9th SciencepjatinNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - 3 - Mixtures & SeparationDocument3 pagesWeek 2 - 3 - Mixtures & SeparationJenmar HemmingsNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument5 pagesSolutionsRuwandi BandaraNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Group 1Document5 pagesLab Report Group 1elfranz franciscoNo ratings yet
- Separating Solids From LiquidsDocument4 pagesSeparating Solids From LiquidsLei Yin100% (1)
- Power Point PresentationDocument18 pagesPower Point PresentationMuntaha SabirNo ratings yet
- Separating MixturesDocument4 pagesSeparating Mixturesulanrain311No ratings yet
- Separating MixturesDocument6 pagesSeparating MixturesKylie AlmarezNo ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry Chapter 2 - Separations and MixturesDocument14 pagesCsec Chemistry Chapter 2 - Separations and Mixtureschelsea AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- Elements Compounds MixturesDocument0 pagesElements Compounds MixturesAdnan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Classification of MatterDocument16 pagesClassification of MattermerielleshanedNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Lab Skills and Separating MethodsDocument9 pagesTopic 2 Lab Skills and Separating MethodsCHIO SHEUNG YONGNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 B Separation - TechniquesDocument64 pagesUnit 2 B Separation - TechniquesTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry o Level NotesDocument11 pagesChemistry o Level NotesThaboooNo ratings yet
- Oil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandOil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- The Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- CUNJCSSP 9 1 Question Paper CSIR UGC NET JRF December 2014 Chemical ScienceDocument45 pagesCUNJCSSP 9 1 Question Paper CSIR UGC NET JRF December 2014 Chemical Scienceayan chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Paper About CdODocument11 pagesPaper About CdOanamNo ratings yet
- NCERT Practice SheetDocument3 pagesNCERT Practice Sheetbajrangkashyap2020No ratings yet
- Nano-Clay Particle As Textile Coating: Ghosh 1Document4 pagesNano-Clay Particle As Textile Coating: Ghosh 1Mastura FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen BondingDocument16 pagesHydrogen BondingBalen I. MohammedNo ratings yet
- I S 3024Document9 pagesI S 3024Hariprasad gantyala100% (1)
- Acids and BasesDocument57 pagesAcids and Basesapi-263909505No ratings yet
- BEU11403 Biomaterials - Lecture 2 PDFDocument40 pagesBEU11403 Biomaterials - Lecture 2 PDFKin HamzahNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structure PDFDocument51 pagesCrystal Structure PDFKUSHAGRA MANIKNo ratings yet
- KHATTAB Abd EssamadDocument11 pagesKHATTAB Abd Essamadabdessamad khattabNo ratings yet
- Medical-Grade Silicone Lubricants For Medical Devices: White PaperDocument6 pagesMedical-Grade Silicone Lubricants For Medical Devices: White PaperrogiegonzNo ratings yet
- Cat KGV 07 17Document16 pagesCat KGV 07 17GILBERTO YOSHIDANo ratings yet
- H2 Biology - Notes On Cell Structure - Cell OrganellesDocument5 pagesH2 Biology - Notes On Cell Structure - Cell OrganellesSefLRho100% (1)
- Foggler - Wire Gauze ReactorDocument7 pagesFoggler - Wire Gauze ReactorJoshita KusumadewiNo ratings yet
- Photoelectrochemical Cells Based On Photosynthetic Systems: A ReviewDocument9 pagesPhotoelectrochemical Cells Based On Photosynthetic Systems: A ReviewMaryam SabouriNo ratings yet
- Water Analysis ReportDocument4 pagesWater Analysis ReportAamirMalikNo ratings yet
- Internship Report in Textile Wet Processing 2023Document6 pagesInternship Report in Textile Wet Processing 2023Uzair AftabNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Questions and Answers: Waxa Diyariyey: Hassan Honest Tell:0616 76 82 04Document4 pagesChemistry Questions and Answers: Waxa Diyariyey: Hassan Honest Tell:0616 76 82 04Abaas MuuseNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Oxides Removal With Liquid SolutionsDocument10 pagesNitrogen Oxides Removal With Liquid SolutionsPravin PatilNo ratings yet
- Special Stains and Its Applications in HistopathologyDocument18 pagesSpecial Stains and Its Applications in HistopathologyIJAR JOURNAL100% (2)
- Bahir Dar University Ethiopian Institute of Textile and Fashion TechnologyDocument21 pagesBahir Dar University Ethiopian Institute of Textile and Fashion TechnologyAndebet KassawNo ratings yet
- MEPP 457 Hydrogen TechnologiesDocument88 pagesMEPP 457 Hydrogen TechnologiesAshim LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Liquid - Liquid ExtractionDocument19 pagesLiquid - Liquid ExtractionApurba Sarker ApuNo ratings yet
- Catalyst ActivityDocument14 pagesCatalyst ActivityMUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ii RRLDocument2 pagesChapter Ii RRLQueendelyn MuycoNo ratings yet
- Master Organic Chemistry SubstitutionDocument43 pagesMaster Organic Chemistry SubstitutionArsalan Khan GhauriNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids Fin Sbu 2020Document70 pagesAlkaloids Fin Sbu 2020Bokhtear UddinNo ratings yet
- Food Drug & Cosmetic Colors (All)Document2 pagesFood Drug & Cosmetic Colors (All)Helpimalive Bass LineNo ratings yet