Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.1 Physical Quantities Notes
1.1 Physical Quantities Notes
Uploaded by
Izzati Anuar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOriginal Title
1.1 Physical quantities Notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 page1.1 Physical Quantities Notes
1.1 Physical Quantities Notes
Uploaded by
Izzati AnuarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
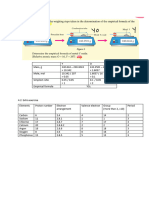
Physical quantities
Examples: time, length, speed, frequency, momentum, force, temperature
Physical quantities = consist of:
Base quantities Derived quantities
Physical quantity that cannot be derived from Physical quantity that can be derived from
another physical quantity another physical quantity
Length : metre, m Volume : length x length x length = m3
Mass : kilogram, kg Velocity : length / time = m/s
Time : second, s Density : mass / volume = kg/ m3
Temperature : kelvin, K Acceleration: velocity / time = m/s2
Electric Current : ampere, A Force : mass x acceleration = kg m / s2
Note: single unit Note: unit can be combined
Quantity Symbol Unit Symbol
Length l Metre m
Volume V Metre cube M3
Physical quantity: magnitude and unit
: magnitude = number
Example: length = 100 m (magnitude: 100, unit: m)
Time = 4 hours (magnitude: 4, unit: h)
Area = 10.2 m2 (magnitude: 10.2, unit: m2)
Physical quantities can be divided into two categories:
Scalar quantities Vector quantities
Physical quantities that have magnitude only Physical quantities that have magnitude and
direction
Distance temperature Displacement
Time speed Velocity
Area energy Force
Length density Acceleration
Momentum
Unit: metric unit and imperial unit
- Metric unit : universal unit (s, m, K)
- Imperial unit : gallons, miles, feet, yards
You might also like
- Base Quantity Name Symbol: Fundamentals of Mechanical EngineeringDocument39 pagesBase Quantity Name Symbol: Fundamentals of Mechanical Engineeringlukhman100% (1)
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Physics NotesDocument2 pagesPhysics Notesredz45No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 StudentDocument38 pagesChapter 1 StudentM HisyamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - System of Units UpdatedDocument16 pagesChapter 1 - System of Units UpdatedRN Builder IpohNo ratings yet
- P-9-T1 - 01 Measurement Units - Dimensions PDFDocument32 pagesP-9-T1 - 01 Measurement Units - Dimensions PDFriddhiNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 WEEK 2Document42 pagesGeneral Physics 1 WEEK 2Reynier BatallerNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument6 pagesPhysicsmmhftn4ffjNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument7 pagesPhysicsLouis WilsonNo ratings yet
- LatihanDocument4 pagesLatihanrachman daniNo ratings yet
- Physics Learning MaterialDocument128 pagesPhysics Learning MaterialMukesh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Physics Learning Material 1 13Document13 pagesPhysics Learning Material 1 13Rehab RamadanNo ratings yet
- LCT 1Document27 pagesLCT 1Umair AsifNo ratings yet
- Notebook 1 FinalDocument4 pagesNotebook 1 Finalapi-339050167No ratings yet
- Chapter One PDFDocument12 pagesChapter One PDFMohamed AbdelghanyNo ratings yet
- Physical Measurement1Document13 pagesPhysical Measurement1Gaber HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 2020Document27 pagesChapter 1 2020mariaNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities and Measurement STD 7 Physics NotesDocument6 pagesPhysical Quantities and Measurement STD 7 Physics NotesMyScribd_ieltsNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2023 Revision Notes for Mechanics - Free PDF DownloadDocument26 pagesJEE Advanced 2023 Revision Notes for Mechanics - Free PDF DownloadVenayak SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and Measurement Lecturer Only1Document45 pagesChapter 1 Physical Quantities and Measurement Lecturer Only1Jerome FizzowNo ratings yet
- Measurement TechniqueDocument27 pagesMeasurement TechniquejidopawNo ratings yet
- Physics Course Outline Topic One: Units and MeasurementsDocument40 pagesPhysics Course Outline Topic One: Units and MeasurementsMwanza MaliiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Measurement Adge 104Document12 pagesModule 2 Measurement Adge 104alexandrearebucasNo ratings yet
- A Lingo of MeasurementsDocument18 pagesA Lingo of MeasurementsdarwinsagucioNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities and MeasurementsDocument4 pagesPhysical Quantities and MeasurementskhuwajaabbasrohaanNo ratings yet
- History of MeasurementsDocument13 pagesHistory of MeasurementsShubhenduGuptaNo ratings yet
- PW 01 - 25.02-1.03.2019 - Physical Quantities and Error Calculations PDFDocument53 pagesPW 01 - 25.02-1.03.2019 - Physical Quantities and Error Calculations PDFLiviu LucaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Units of MeasurementDocument34 pagesChapter 1-Units of MeasurementDn ZackNo ratings yet
- Makalah Units of MeasurementDocument10 pagesMakalah Units of MeasurementRaihan WibawaNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroDocument26 pages1 IntroJerry PratamaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 12 Physics PamphletDocument131 pagesGrade 10 12 Physics PamphletBryanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 f4 MeasurementDocument28 pagesChapter 1 f4 Measurementsuniza ahmadNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 MesureDocument22 pagesLec 3 Mesurezbadizbadi04No ratings yet
- Grade 10 To 12 Physics in DetailsDocument131 pagesGrade 10 To 12 Physics in DetailsXavier100% (2)
- 2021 Units & MeasurementDocument9 pages2021 Units & MeasurementSora RoseNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula-Book JeeDocument115 pagesPhysics Formula-Book JeePritish Jaiswal82% (17)
- Formulae - 2Document35 pagesFormulae - 2A.BensonNo ratings yet
- 1.units and MeasurementsDocument27 pages1.units and Measurementsahmed khanNo ratings yet
- B S G S Lecture Part 1 - CollabDocument16 pagesB S G S Lecture Part 1 - CollabNeo GarceraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument13 pagesChapter 1 PDFR Yone OoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slide Week 1 20222 PDFDocument19 pagesLecture Slide Week 1 20222 PDFMUHAMMAD LUQMAN HAKIMI MOHD ZAMRINo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 f4 Measurement (1)Document26 pagesChapter 1 f4 Measurement (1)suniza ahmadNo ratings yet
- Physics in Details g10-12Document131 pagesPhysics in Details g10-12Andrea Maluba100% (2)
- Phys 110 CH 1Document17 pagesPhys 110 CH 1Mamdoh Al-QuthamiNo ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument2 pagesMeasurementSav OliNo ratings yet
- L, d m t A V ρ F f: Table 2: Physical Quantities and Their UnitsDocument1 pageL, d m t A V ρ F f: Table 2: Physical Quantities and Their Unitsμαστρο ΜήτσοςNo ratings yet
- Units and DimensionsDocument15 pagesUnits and DimensionspokhralikanchhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Measurement: 1.1 Physical QuantitiesDocument16 pagesChapter 1: Measurement: 1.1 Physical QuantitiesLeejing LimNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of CETDocument20 pagesBasic Concepts of CETAtharvNo ratings yet
- EEd 16Document2 pagesEEd 16Rishel AlamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Unit and MeasurementDocument25 pagesChapter 1 Unit and MeasurementAmar Danial100% (1)
- Tyhjmnf 767Document6 pagesTyhjmnf 767sneha sharmaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 101 Measurment & Units - LECTURE1Document2 pagesPHYSICS 101 Measurment & Units - LECTURE1Hassan AideedNo ratings yet
- Fundamental QuantityDocument18 pagesFundamental Quantityaries triwidajati100% (2)
- Unit 1 ADocument18 pagesUnit 1 Aapi-3699866100% (1)
- Topic 1: Unit and MeasurementDocument23 pagesTopic 1: Unit and MeasurementUmar ShahNo ratings yet
- 1242023061712303998Document6 pages1242023061712303998akshithreddy101No ratings yet
- Physics 2Document6 pagesPhysics 2mathiasshereni243No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in ChemistryDocument124 pagesBasic Concepts in Chemistryara_anjo100% (1)
- Hydrocarbon IGCSEDocument1 pageHydrocarbon IGCSEIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- Specialized Cell For Animal CellDocument2 pagesSpecialized Cell For Animal CellIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- MT F5 P1 ExtraDocument4 pagesMT F5 P1 ExtraIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- Formative Practice 1.1Document2 pagesFormative Practice 1.1Izzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- System in Human BodyDocument1 pageSystem in Human BodyIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- Specialized Cell For PlantDocument1 pageSpecialized Cell For PlantIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- Type of GraphsDocument1 pageType of GraphsIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- Rotations AnswersDocument15 pagesRotations AnswersIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument1 pageHomeworkIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- Self Practice 2.1c F5Document2 pagesSelf Practice 2.1c F5Izzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- Extra Class Phy F4Document5 pagesExtra Class Phy F4Izzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- F5 Math Revision MYDocument23 pagesF5 Math Revision MYIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- Formative Pactice 2.3Document1 pageFormative Pactice 2.3Izzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- Activity Book 2.1 PhyDocument1 pageActivity Book 2.1 PhyIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document7 pagesChapter 6Izzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- AdaptationDocument1 pageAdaptationIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- Specific Latern HeatDocument9 pagesSpecific Latern HeatIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Waves NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Waves NotesIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- 2-Properties - Ai State of Matter NotesDocument1 page2-Properties - Ai State of Matter NotesIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet