Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1901-Article Text-7125-2-10-20211018
1901-Article Text-7125-2-10-20211018
Uploaded by
Romi Lennon NaibahoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- NX CAD CAM CAE - Bundle - Quick Reference (Jun2020)Document2 pagesNX CAD CAM CAE - Bundle - Quick Reference (Jun2020)Thanakorn VichiensamuthNo ratings yet
- Vendor Exit Strategy TemplateDocument10 pagesVendor Exit Strategy TemplateDarija Gojčeta100% (3)
- API 580 Training Course TWIDocument50 pagesAPI 580 Training Course TWIMohammad Danish100% (18)
- Asset Integrity ManagementDocument2 pagesAsset Integrity ManagementGobin Sookram100% (2)
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Testing ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Testing ProcessRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- School Management System SrsDocument21 pagesSchool Management System SrsRana Ali100% (5)
- M/s Ram Krishna CNC Shop Problem Statement: Group AssignmentDocument7 pagesM/s Ram Krishna CNC Shop Problem Statement: Group AssignmentMoidin AfsanNo ratings yet
- GB921P Process Framework Primer R18.0.1Document31 pagesGB921P Process Framework Primer R18.0.1Mark BequilloNo ratings yet
- Artigo - RBIDocument17 pagesArtigo - RBIIelson FreireNo ratings yet
- Api 580Document6 pagesApi 580Fernando ArévaloNo ratings yet
- HSE - Best Practice For RBI PDFDocument186 pagesHSE - Best Practice For RBI PDFDanie-Els100% (4)
- Risk-Based Inspection - Wikipedia PDFDocument15 pagesRisk-Based Inspection - Wikipedia PDFEndhy Wisnu NovindraNo ratings yet
- 6 Planning The RBI AssessmentDocument9 pages6 Planning The RBI AssessmentMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- API 580 Training CoDocument7 pagesAPI 580 Training Cohs.hs20187720No ratings yet
- Storage Tank Risk Based Inspection / Management: 1.1 ConsequenceDocument11 pagesStorage Tank Risk Based Inspection / Management: 1.1 ConsequenceCostin IlincaNo ratings yet
- A Risk-Based Tool To Support The Inspection Management Inchemical PlantsDocument29 pagesA Risk-Based Tool To Support The Inspection Management Inchemical PlantsThanh Dat DoanNo ratings yet
- RBI - A Transparent Process ?Document11 pagesRBI - A Transparent Process ?Vinícius EstevesNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Risk-Based Inspection MethodologyDocument12 pagesDynamic Risk-Based Inspection Methodologynovendi eko nugrohoNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Condition Management - COMADEM2011Document8 pagesA Framework For Condition Management - COMADEM2011ManeeshSinghNo ratings yet
- RBI Best PracticesDocument13 pagesRBI Best PracticesFroylán Ernesto Pompa García100% (1)
- Risk Based Inspection: Ramesh J. PatelDocument7 pagesRisk Based Inspection: Ramesh J. PatelbassamNo ratings yet
- RBI Korean 5xDocument5 pagesRBI Korean 5xQuekchNo ratings yet
- Risk Based InspectionDocument3 pagesRisk Based InspectionZHNo ratings yet
- XIV Paper 38Document11 pagesXIV Paper 38Zenon KociubaNo ratings yet
- Study Notes Video 2 580 Scope Rev 1Document3 pagesStudy Notes Video 2 580 Scope Rev 1majidNo ratings yet
- Risk-Based Inspection in The Context of Nuclear Power PlantsDocument13 pagesRisk-Based Inspection in The Context of Nuclear Power PlantsMohamed ElotmaniNo ratings yet
- Determination of Maintenance Priority Index (Mpi) For Components On Rsg-Gas Safety SystemDocument13 pagesDetermination of Maintenance Priority Index (Mpi) For Components On Rsg-Gas Safety SystemiqbalsetionugrohoNo ratings yet
- Tugas Perbaikan Analisa Kegagalan MaterialDocument18 pagesTugas Perbaikan Analisa Kegagalan MaterialkusmariantoNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Methods and Tools Used For Reliability Evaluation of SscsDocument4 pagesA Survey of Methods and Tools Used For Reliability Evaluation of SscsStefanos DiamantisNo ratings yet
- RiskBased RBI WPLDocument13 pagesRiskBased RBI WPLLuis Carlos BalcazarNo ratings yet
- A Risk Based Inspection (Rbi) Preventive Maintanance Programme: A Case StudyDocument2 pagesA Risk Based Inspection (Rbi) Preventive Maintanance Programme: A Case StudyAchraf BouzianeNo ratings yet
- Paper294606 PDFDocument14 pagesPaper294606 PDFkirandevi1981No ratings yet
- SPE 87030 Development and Implementation of Risk Based Inspection Methodology in Managing Inspection of Pressurized Production FacilitiesDocument10 pagesSPE 87030 Development and Implementation of Risk Based Inspection Methodology in Managing Inspection of Pressurized Production FacilitiesmsmsoftNo ratings yet
- AI-PS Element Guide No 13Document10 pagesAI-PS Element Guide No 13rwerwerwNo ratings yet
- Definition of Risk Based Inspection (Rbi)Document5 pagesDefinition of Risk Based Inspection (Rbi)Akbar HartawanNo ratings yet
- 2 Risk Based InspectionDocument3 pages2 Risk Based Inspectional0% (1)
- Risk Based Inspection Best Practice-The Technical Specification Ron Selva PP Simtech Keynote Paper-1 13th Icpvt 2012 LondonDocument20 pagesRisk Based Inspection Best Practice-The Technical Specification Ron Selva PP Simtech Keynote Paper-1 13th Icpvt 2012 LondonRichard KoehlerNo ratings yet
- Jurnal RCM 1Document9 pagesJurnal RCM 1teguhNo ratings yet
- Process Safety Metrics: Guide For Selecting Leading and Lagging IndicatorsDocument63 pagesProcess Safety Metrics: Guide For Selecting Leading and Lagging IndicatorsDiego100% (1)
- Chap 16Document3 pagesChap 16hs.hs20187720No ratings yet
- AI-PS Element Guide No 7Document11 pagesAI-PS Element Guide No 7alokcNo ratings yet
- Risk Base Inspection Programs For Pressus EquipementDocument13 pagesRisk Base Inspection Programs For Pressus Equipementanys tekNo ratings yet
- LifeTech-Engineering-Services - Asset Integrity ManagementDocument14 pagesLifeTech-Engineering-Services - Asset Integrity Managementyogolain100% (1)
- Risk Based Inspection Study of Slaughter Gas Plants PVP 2000 - Seattle, Washington July 2000Document6 pagesRisk Based Inspection Study of Slaughter Gas Plants PVP 2000 - Seattle, Washington July 2000Mahmoud RefaatNo ratings yet
- AI-PS Element Guide No 7Document10 pagesAI-PS Element Guide No 7Asad KhanNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and Asset Integrity Management in Oil and Gas Production, Process, Transportation and Storage FacilitiesDocument12 pagesCorrosion and Asset Integrity Management in Oil and Gas Production, Process, Transportation and Storage FacilitiesRASHEED YUSUF100% (1)
- Risk Based InspectionDocument2 pagesRisk Based InspectionyogolainNo ratings yet
- Keywords:-5R, PDCA, RCA, Likert Scale Index,, Why Why: AnalysisDocument5 pagesKeywords:-5R, PDCA, RCA, Likert Scale Index,, Why Why: AnalysisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Contractors' Hse Performance: Pragmatic Evaluation, Benchmarking and Ways For ImprovementDocument8 pagesContractors' Hse Performance: Pragmatic Evaluation, Benchmarking and Ways For ImprovementABF ETSNo ratings yet
- Study of A Risk-Based Piping Inspection Guideline System: Shiaw-Wen Tien, Wen-Tsung Hwang, Chih-Hung TsaiDocument8 pagesStudy of A Risk-Based Piping Inspection Guideline System: Shiaw-Wen Tien, Wen-Tsung Hwang, Chih-Hung Tsaikhevin jionaldoNo ratings yet
- RBI Assessment Recommended Work-Ing ProcessDocument1 pageRBI Assessment Recommended Work-Ing ProcessRicardoNo ratings yet
- Interrelationships Between PSM Elements 3-14-18Document18 pagesInterrelationships Between PSM Elements 3-14-18Jinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- AI-PS Element Guide No 6Document10 pagesAI-PS Element Guide No 6rwerwerwNo ratings yet
- Reliability Centered Maintenance and RbiDocument5 pagesReliability Centered Maintenance and RbiDarkmatter DarkmatterrNo ratings yet
- Damage Mechanism Hazard ReviewDocument17 pagesDamage Mechanism Hazard ReviewBobby VonnNo ratings yet
- Risk Based Inspection Jacketed PlatformsDocument19 pagesRisk Based Inspection Jacketed PlatformsronfrendNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Study and Evaluation of Controls ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Study and Evaluation of Controls ProcessRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- The Duty for Sponor Oversight in Clinical Trials: Practical Guide: 2nd Edition Clinical Data ReviewFrom EverandThe Duty for Sponor Oversight in Clinical Trials: Practical Guide: 2nd Edition Clinical Data ReviewNo ratings yet
- Audit Risk Alert: Government Auditing Standards and Single Audit Developments: Strengthening Audit Integrity 2018/19From EverandAudit Risk Alert: Government Auditing Standards and Single Audit Developments: Strengthening Audit Integrity 2018/19No ratings yet
- Mastering Opportunities and Risks in IT Projects: Identifying, anticipating and controlling opportunities and risks: A model for effective management in IT development and operationFrom EverandMastering Opportunities and Risks in IT Projects: Identifying, anticipating and controlling opportunities and risks: A model for effective management in IT development and operationNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Reporting ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Reporting ProcessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Planning ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Planning ProcessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Effective Business Communication Case StudyDocument8 pagesEffective Business Communication Case StudyamritaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document77 pagesLecture 1Divyansh Singh SengarNo ratings yet
- Job Description - Director - Business DevelopmentDocument2 pagesJob Description - Director - Business DevelopmentGovind DesikanNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual-Routine Operation VolumeDocument247 pagesOperation Manual-Routine Operation VolumeSajadShaykhanNo ratings yet
- Verdantix Green Quadrant Enterprise Carbon Management Software 2022 - REPRINT SweepDocument21 pagesVerdantix Green Quadrant Enterprise Carbon Management Software 2022 - REPRINT SweepAdrian Tudoran100% (1)
- TASSS Activity 4Document1 pageTASSS Activity 4Moses TamondongNo ratings yet
- Week 2 ERP ArchitectureDocument35 pagesWeek 2 ERP Architecturesan marco100% (1)
- Capstone Project VFinalDocument8 pagesCapstone Project VFinalCesar FongNo ratings yet
- Midbs Unit 4 Full UnitDocument31 pagesMidbs Unit 4 Full UnitChintoo KalyanadurgamNo ratings yet
- AcumaticaERP InvMgmtDocument247 pagesAcumaticaERP InvMgmtcrudbugNo ratings yet
- Personal Software Process (PSP) Concept Applied To Beginning EngineersDocument5 pagesPersonal Software Process (PSP) Concept Applied To Beginning EngineersAlina KhanNo ratings yet
- JD - Project Procurement Planning EngineerDocument2 pagesJD - Project Procurement Planning EngineerSanjay RamuNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 Security in CloudsDocument41 pagesUNIT-4 Security in Cloudssaradaganerchukundham45No ratings yet
- Process Identification Part 2Document16 pagesProcess Identification Part 2hover.dragon16No ratings yet
- Oracle Apps HRMS Interview Questions and Answers Guide.: Global GuidelineDocument6 pagesOracle Apps HRMS Interview Questions and Answers Guide.: Global GuidelineKhan IsKhanNo ratings yet
- Get Your Dream Client in The Next 90 Days GuideDocument37 pagesGet Your Dream Client in The Next 90 Days GuideinGrill MediaNo ratings yet
- Maxym Gryn CVDocument3 pagesMaxym Gryn CVaminatjenius71No ratings yet
- Merce and B.commumication NotesDocument58 pagesMerce and B.commumication NotesAnshul BajajNo ratings yet
- With 3 Years ExperienceDocument2 pagesWith 3 Years ExperienceGanesh PeketiNo ratings yet
- Motadata ServiceOps Asset Management - 1612524617 - 1622610559Document31 pagesMotadata ServiceOps Asset Management - 1612524617 - 1622610559abc576666No ratings yet
- Srikanth ResumeDocument3 pagesSrikanth Resumehimanshu.kashyap.etcNo ratings yet
- Harnessing The Potential of Data in InsuranceDocument13 pagesHarnessing The Potential of Data in InsuranceSRINIVAS RAONo ratings yet
- Veeam SAP Avilability GuideDocument64 pagesVeeam SAP Avilability Guidemummy206No ratings yet
- Many Enterprise Software Applications That Support IT Services Are Characterised by The Need For High Computing CapabilityDocument7 pagesMany Enterprise Software Applications That Support IT Services Are Characterised by The Need For High Computing CapabilityhimanshusangaNo ratings yet
- Statement of Work (Sow) : White PaperDocument3 pagesStatement of Work (Sow) : White PaperKo Lin TunNo ratings yet
1901-Article Text-7125-2-10-20211018
1901-Article Text-7125-2-10-20211018
Uploaded by
Romi Lennon NaibahoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1901-Article Text-7125-2-10-20211018
1901-Article Text-7125-2-10-20211018
Uploaded by
Romi Lennon NaibahoCopyright:
Available Formats
Volume 5, Nomor 2, Oktober 2021 ISSN2623-1581 (Online)
ISSN 2623-1573 (Print)
GAP ANALYSIS ON RISK BASED INSPECTION (RBI)
IMPLEMENTATION AT PT.XYZ
Atta Rizky Suharto1, Fatma Lestari2
Department of Occupational Health and Safety, Faculty of Public Health, Universitas Indonesia,
attarizkysuharto@gmail.com1, fatma@ui.ac.id2
ABSTRACT
Inspection methodologies have evolved in exploring optimal inspection intervals. The latest approach is
the Risk Based Inspection method, referring to API-580 and API-581. Risk Based Inspection (RBI) has
been implemented mainly in oil and gas industry to manage the risk of aging facilities. The RBI plan has
also been introduced for new facilities and become part of the design requirements, making it the right
time for PT. XYZ to improve their RBI implementation to support the Facility Risk Integrity
Management System. In general, this study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of the ongoing RBI
implementation at PT. XYZ in general while specifically identify the part of RBI and related Asset
Integrity Management already implemented and those that still need further improvement. This study is a
semi-quantitative study on primary data collected through focus group discussion using the 15 evaluation
parameters of RBI based on API 580, API 581, and field observation and secondary data from previous
RBI reports, maintenance program, and inspection program. The results of this study show that the overall
score is 106 out of 150, this indicates a good implementation of RBI but after further analysis there is the
largest gap from the maximum score = 10.0 which is identified as RBI on specific equipment (score=3.0),
documented RBI management policy and strategy (score=3.8), risk target and risk acceptable level
(score=4.0), and specific damage mechanism components (score=5.3). This will assist a more focused
approach to the parts that need improvement while maintaining the industry standards needed to ensure
safe operation with low uncertainty.
Keywords : Inspection, RBI, Risk, Safety
ABSTRAK
Metodologi inspeksi telah berkembang dalam mengeksplorasi interval inspeksi yang optimal. Pendekatan
terbaru adalah dengan metode Risk Based Inspection, mengacu pada API-580 dan API-581. Risiko
Berbasis Inspeksi (RBI) telah diterapkan terutama di industri minyak dan gas untuk mengelola risiko
fasilitas yang sudah menua. Rencana RBI juga telah diperkenalkan untuk fasilitas baru dan menjadi
bagian dari persyaratan desain, menjadikannya waktu yang tepat bagi PT. XYZ untuk meningkatkan
implementasi RBI mereka untuk mendukung Sistem Manajemen Integritas Risiko Fasilitas. Secara umum
studi ini bertujuan untuk mengevaluasi efektivitas implementasi RBI yang berjalan di PT. XYZ sedangkan
secara khusus untuk mengidentifikasi bagian RBI dan Manajemen Integritas Aset yang sudah diterapkan
dan yang masih perlu perbaikan lebih lanjut. Studi ini adalah studi semi-kuantitatif dari data primer
yang dikumpulkan melalui diskusi kelompok terfokus menggunakan 15 parameter evaluasi RBI
berdasarkan API 580, API 581, dan observasi lapangan serta data sekunder dari laporan RBI
sebelumnya, program pemeliharaan, dan program inspeksi. Hasil studi ini menunjukkan skor
keseluruhan adalah 106 dari 150, hal ini menunjukkan implementasi RBI yang baik namun setelah
dianalisis lebih lanjut ada kesenjangan terbesar dari maksimum skor=10,0 yang teridentifikasi adalah
RBI pada peralatan tertentu (skor=3,0), kebijakan dan strategi manajemen RBI yang terdokumentasi
(skor=3,8), target risiko dan tingkat risiko yang dapat diterima (skor=4,0), dan komponen mekanisme
kerusakan spesifik (skor=5,3). Ini akan membantu pendekatan yang lebih fokus ke bagian-bagian yang
perlu ditingkatkan sambil mempertahankan standar industri yang diperlukan untuk memastikan operasi
yang aman dengan ketidakpastian yang rendah.
Kata kunci : Inspeksi, Keselamatan, RBI, Risiko
PREPOTIF Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Page 624
Volume 5, Nomor 2, Oktober 2021 ISSN2623-1581 (Online)
ISSN 2623-1573 (Print)
INTRODUCTION throughout the whole life cycle of the assets.
The integrity life cycle is presented in
PT. XYZ is designed to process Crude Figure 1.
Oil and the first units, consisting of a Risk Based Inspection and
100,000 BPSD (Barrel Per Stream Day) maintenance methodology integrates the
Crude Distillation Unit, a Naphtha Splitter Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM)
and a 6,300 BPSD Fixed Bed Platformer, analysis with takes into consideration not
which were commissioned in 1973. This only reliability and economic aspects, but
refinery is currently in the state of aging also the company’s reputation and
facility that it requires the implementation of environmental impact (Bertolini, M., et.al.,
Risk Based Inspection (RBI), which has 2009).
been implemented since 2007. Risk based
inspection (RBI) is a decision-making tool
that deals with integrity management of
static equipment and piping through focus
on prioritizing inspection based on the risk.
The RBI is primarily designed to evaluate
the risk of pressurized system or static
equipment (piping, pressure vessels, tanks,
and pipelines) exposed to some possible
damage mechanism, damage rates, and
failure modes (Khan, et.al., 2003). The
implementation of risk-based inspection
involves a large number of data, requiring Figure 1. Mechanical Integrity Life Cycle
the use of the RBI Software. This study aims
to evaluate the effectiveness of the RBI
implementation in PT XYZ through a gap For static equipment, i.e. piping,
analysis. pressure vessel, tank, heat exchanger, and
Risk-based inspection technology was other pressurized system (American
successfully implemented in crude Petroleum Institute), the backbone of AIMS
distillation units of Abadan Oil Refinery and is RBI. The risk of the equipment is
Esfahan Oil Refinery. Only a small evaluated to determine the next inspection
percentage of equipment items, 12% and and monitoring plan (Khan, et.al., 2004).
15% respectively for EORC and AORC Upon inspection, all data are evaluated and
plants, were categorized as high risk or high- if anomaly or defect is found, Fitness for
medium risk (Shishesaz et al., 2013). Service (FFS) is conducted to determine the
Asset integrity management system remaining life and Maximum Allowable
(AIMS) involves planning, organizing, Working Pressure (MAWP). Proper
executing, and controlling all process asset recommendations for corrective actions are
risk and integrity through inspection, then given, proposing whether an equipment
monitoring, and maintenance programs in should be repaired, replaced, or down-rated.
order to operate equipment safely and Since RBI becomes a central role in AIMS,
reliably, as well as to operate oil and gas it is of critical important to evaluate the
facilities in the most cost-effective way effectiveness of RBI implementation in PT.
(Khan, et.al., 2006). AIMS are implemented XYZ so that the overall AIMS purposes for
to manage the risks to the acceptable level the static equipment can be achieved
PREPOTIF Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Page 625
Volume 5, Nomor 2, Oktober 2021 ISSN2623-1581 (Online)
ISSN 2623-1573 (Print)
.
METHODS excellent, 106 to 135 = good, 76 to 105 =
average, 46 to 75 = basic, and <45 = poor.
Based on API 580, RBI can be
performed in qualitative, quantitative and
semi-quantitative. The results of each
method are almost the same, but by
qualitative method a unit can be evaluated
quickly. Quantitative method involves us in
more detail and calculation, but with more
accuracy.
This is a semi-quantitative study using
primary and secondary data. Data used were
primary data that were collected through
focus group discussions using RBI
evaluation parameters and field observation, Figure 2. Gap analysis results
and secondary data obtained from reviewing The recommended actions would be
RBI reports and maintenance and inspection planned according to the level of importance
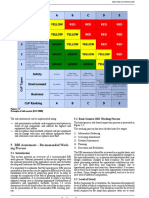
programs. based on the priority matrix in Figure 3, if
The 15 RBI evaluation parameters some findings fall into the low score in the
(American Petroleum Institute, 580 and 581) evaluation and the priority is high, the
are developed and discussed with panel actions should be executed within 1 to 2
experts including with the key site personnel years.
to evaluate the implementation of RBI from On the other hand, if the finding obtains
various aspects, such as organization and a high score and the priority is low, actions
management; administration and paper may be executed in more than 3 years. The
works; inspection activities; method and matrix and color indicated have nothing to
technology; software and database do with the risk level or criticality; it only
application; and human resources shows the level of priority or importance for
availability and competency. Moreover, future follow up in the case when a gap is
specific methods used to follow up defect or found.
failure found were also evaluated, such
fitness for service (FFS) assessment for
defect and root cause failure analysis
(RCFA) for failure. All parameters that
reflect the components of AIMS cycle
shown in Figure 1.
The individual parameters consisted of
more detail evaluation parameters with
particular scores to signify the identified
actual conditions. The parameter was then
plotted in the form of spider graph (Figure
2) in order to visually understand the gap Figure 3. Matrix to indicate level of
width between the actual conditions and the importance and priority actions
ideal condition. Scoring was then performed
with the following categories: >135 =
PREPOTIF Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Page 626
Volume 5, Nomor 2, Oktober 2021 ISSN2623-1581 (Online)
ISSN 2623-1573 (Print)
RESULT implementation of RBI. However, upon
further analysis, shown on Table 1 indicates
The further purpose of gap analysis in the largest gaps as follows, in the respective
this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of order: i) RBI on the specific equipment
the ongoing RBI implementation at PT. (score=3 point), ii) Documented RBI
XYZ. The results of the gap analysis are Management Policy & Strategy (score=3.8
summarized in the spider graph in Figure 2, points), iii) Risk target and risk acceptable
presenting 15 evaluation parameters or level (score=4 points), and iv) Specific
components. Results show an overall score damage mechanism (score=5.3 points).
of 106 of 150, showing a good
Table 1. Gap Analysis Spreadsheet
Max Evaluated Action
No Evaluation Parameters Criticality
Score Score Priority
1 Documented RBI Management Policy & Strategy 10 3.8 H 1
2 Risk Target & Risk Acceptable Level 10 4.0 H 1
3 Organization. Structure and Responsibility 10 9.0 M 7
4 Asset Register and Management 10 10.0 M 7
5 Inspection Plan & Implementation 10 6.2 M 5
6 Fluid Monitoring & Trend Analysis 10 7.0 M 5
7 RBI Software Application 10 8.0 M 7
8 Specific Damage Mechanism Assessment 10 5.3 H 2
9 FFS Assessment and Integrity Performance Indicator 10 9.0 H 4
10 Reporting. Documentation and Knowledge Sharing 10 8.0 M 7
11 Data Management and Information System 10 6.5 M 5
12 RBI on Specific Equipment 10 3.0 M 1
13 Root Cause Failure Analysis (RCFA) 10 10.0 L 9
14 Certification Program 10 8.0 M 7
15 Audit Program on Integrity and Risk 10 8.0 M 7
Table 2. Evaluation Parameter and First Priority Recommended Actions
Due
Action
Evaluation Evaluated Date
No Priorit Recommended Action Plan
Parameter Score (Years
y
)
Documented RBI PT. XYZ, Stat - Eng Department is
1 Management 3.8 1 recommended to develop an RBI Manual or
Policy & Strategy Guideline.
It is recommended for PT. XYZ to develop
Within 1
the RBI for Organizational Work Progam - 2 Years
Risk Target &
(Tata Kerja Organisasi, TKO) or similar
2 Risk Acceptable 4.0 1
RBI Procedure. It is recommended to define
Level
the risk target (USD/year) as an alternate
criterion /baseline for next inspection plan.
PREPOTIF Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Page 627
Volume 5, Nomor 2, Oktober 2021 ISSN2623-1581 (Online)
ISSN 2623-1573 (Print)
It is strongly recommended for PT. XYZ to
evaluate the risk of static equipment
(pressure vessel, heat exchanger, piping,
etc) that is suceptible to HTHA damage
Specific Damage mechanism considering that there are many
3 Mechanism 5.3 2 cases in refinery worldwide that expirience
Assessment catastrophic failure, leading to major-fatal-
accident caused by HTHA. To be more
focused, this assessemnt should be
separated from the on-going RBI
assessment.
To be effective, it is recommended to plan
RBI on Specific PSV inspection and test according to the
4 3.0 1
Equipment risk category as shown by the oil and gas
industry trend worldwide.
Actions that will be recommended methodology for effective plant
should be planned according to the level of maintenance. It helps to achieve operational
importance as listed in the priority matrix in excellence and maximum asset performance
Figure 3. For example, if findings fall into a by using inspection resources more cost-
low score category of evaluation and the effectively and with confidence (TWI, 2009)
priority is high, the actions should be In this parameter, evaluation was
executed within 1 year. conducted to assess the availability of
On the other hand, if the finding obtains specific RBI Management policies (e.g. well
a medium score, the action can be executed documented in manuals or guidelines) and
within 2 years while for those with low documented RBI strategies for the assets.
scores the action may be executed within 3 Evaluation was also performed to assess the
years. The findings of this study have led to presence of evidence of the awareness on
recommendations to fill the gap based on the RBI in all levels of the organization (senior
priority scale starting from high priority management, engineer and technicians).
actions as shown in Table 2. Finally, an evaluation was also conducted to
assess whether the RBI management
DISCUSSION strategy has been integrated to the safety and
asset management; inspection, testing, and
A system failure is rarely caused by a single monitoring; and operation strategies.
cause, but rather the result of a combination or It was reported that RBI has been
series of interacting events. As a result, Risk conducted since 2007 in PT. XYZ for all
Based Inspection & Maintenance should not be unit. However, the previous RBI software
considered as a static exercise that is only done
owned by this company is currently expired
once. It is a dynamic process, which should be
continuously updated as additional information and, as a result, the RBI was not fully
becomes available. implemented at the time of the study.
However, during the site visit, it was
Documented RBI Policy and Strategy understood that the company had just
purchased a new RBI software and they
Analysis using a RBI approach can were in the process of data migration from
increase the effectiveness of the mechanical the previous software. The same is true for
integrity inspection program while the inspection plan. Nevertheless, the role
minimizing risk to health, safety, and the and importance of the RBI Concept has been
environment plus maximizing resource fully understood by the management,
utilization. RBI offers established a engineers, and supervisors, albeit no formal
PREPOTIF Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Page 628
Volume 5, Nomor 2, Oktober 2021 ISSN2623-1581 (Online)
ISSN 2623-1573 (Print)
documents indicated this condition. exists and, if yes, whether the chart
Practically, RBI concept has been integrated elaborates the clear responsibilities and
to the safety and integrity of the assets, but reporting path for the RBI management
the formal document of this integration is system, including the clear statements of
still lacking. It is necessary to develop this roles and responsibilities of the engineers
high-level document so that all levels of involved. This parameter also evaluates
personnel in PT. XYZ have the same whether qualification, experience, and
perception and understanding on RBI expertise available appropriate to the role for
concept and implementation. people in charge. It also determines whether
training is available for the individuals in the
Risk Target and Risk Acceptable Level area of RBI and inspection plan.
Risk targets should be defined by From documents available and from the
management in consultation with all the results of the focus group discussions, it was
team and stake holders. This needs to be evident that the organization for RBI was
done before proceeding to RBI assessments. well established in PT. XYZ and that the
Risk target is considered as maximum role and responsibility of each person was
degree of tolerable risk for continued stated, meaning that the job description and
operation without requiring a mitigation scope of work were clearly defined,
action. Once the target has been met or including for the contractor who performed
exceeded, an activity such as inspection is the actual inspection and RBI assessment.
triggered (Ali & Sabry, 2019). The expertise for RBI-related field was
In this section, the availability of the reasonably adequate and training related to
RBI procedure was evaluated and a risk inspection and RBI was also available.
target or maximum risk acceptable level had However, at the time the study was
been defined. Moreover, whether the conducted, no corrosion engineer was
financial risk was considered in the last RBI available.
assessment in addition to the safety aspect Since RBI is a team-based process, it
was also evaluated. requires a proficient team consisting of
From the results of the evaluation thus individuals with relative experiences and
far, no RBI procedure was in place and no from various departments. A good team can
risk target was defined by the Company. The be formed by including specialists from
risk acceptable level used only followed the process, operations, production,
automatic RBI Software recommendations. maintenance/reliability, corrosion and
No reference to the financial risk was made inspection, knowledgeable and expert in the
in the RBI assessment. plant site conditions and history. This team
shall be led by an RBI engineer or specialist
(from the plant site or outsourced external
Organization, Structure and Responsibility consultant) having expertise in RBI
methodology and previous experiences with
The corporate dimension is reflected in RBI projects (Ali & Sabry, 2019).
the organization’s policies, work procedures,
management systems, control systems, and Asset Register and Management
communication flows (Lestari, Fatma, et.al.,
2020). There is a widespread belief that In this parameter, evaluation was made
safety culture is an important contributor to on whether individual equipment had a tag
operational safety. This parameter evaluates number/ID number attached and was well
whether the company’s organization chart documented. It also assessed whether P&ID
PREPOTIF Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Page 629
Volume 5, Nomor 2, Oktober 2021 ISSN2623-1581 (Online)
ISSN 2623-1573 (Print)
and PFD were available and revised, It was observed that the actual
including the MOC to identify the inspection plan was still mixed or combined
equipment in the system. between risk-based and time-based, and that
It was shown that all assets and data, the effectiveness criterion was only partially
including the Management of Change implemented. It was also concluded from
(MOC), were fully documented and well- discussion that all equipment was well
managed and, therefore, no issue was identified in P&ID, PFD and Isometric. In
identified in this section. some instance, the advanced NDT had
partially been used depending on the case
Inspection Plan and Implementation (Figure 4). Finally, the internal inspection
was still based on turn-around or shutdown
In this section, the availability of any period for every 4 years. From our point of
plan for inspection based on risk in place is view, unless the risk of some critical
assessed or whether the time based equipment is high, this time-based approach
approached is still used. If the RBI is indeed is still adequate considering the immensity
applied, evaluation is also performed on of vessels or reactors dimension and their
whether the inspection plan is considered to complex nature of operation.
be effectiveness or whether the quality level
complies to the RBI Methodology Fluid Monitoring and Trend Analysis
(American Petroleum Institute 581, 2016).
In addition, evaluation is also made on One of the key roles of RBI is to
whether the on-line monitoring facility understand and know the possible damage
location is well identified in the equipment, rates on the equipment, and, therefore, it is
P&ID, PFD, or isometric drawing, and of interest to know if trend analysis of
whether the inspection involves advanced impurities on fluid/product is monitored and
NDT (e.g. phased array UT, backscattered made regularly, and to make sure whether
UT, etc.). Finally, this section also confirms this trend of the chemical impurities is
whether the internal inspection on plotted against time. Moreover, it is
equipment is planned based on RBI or not. important to know that the trend of the
corrosion rate is plotted against time. It is
also important to confirm whether the
corrosion circuit on the piping is made
available or not in the system.
It was observed that the fluid
composition was monitored periodically.
However, this was only partially plotted
against time. The corrosion rate had been
plotted against time for some Units. The
corrosion circuit module was available in the
RBI Software, but PT XYZ had not yet had
the system for data migration to new RBI
Software from the previous software and
RBI assessment was still being carried out.
Figure 4. Pipe Clamp
PREPOTIF Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Page 630
Volume 5, Nomor 2, Oktober 2021 ISSN2623-1581 (Online)
ISSN 2623-1573 (Print)
RBI Software Application Specific Damage Mechanisms
Software is required to perform RBI for
Since PT. XYZ has entered aging
multiple equipment i.e. several hundreds or
condition, to thinning mechanism due to
thousands of assets generally found in small
metal loss it is critically important to
to large facilities, since manual calculations
evaluate other possible time-dependent
are not practically feasible due to
damage mechanism. It is of interest to know
complexities involved, although it is
whether HTHA has been evaluated for the
possible to do them for few equipment as
equipment and piping, provided that major
shown by Kaley (2009). Software’s can be
and catastrophic accidents have occurred in
used for calculations, keeping records of
refineries worldwide due to HTHA damage
thickness trending and inspection data and
mechanism. Further, SCC, Fatigue, and CUI
most importantly automating the whole
should be evaluated for the equipment and
integrity management system of a facility by
piping.
connecting with enterprise resource planning
To avoid conditions that could cause
(ERP) system or computerized maintenance
HTHA, it is important that actual operating
management system (CMMS).
conditions are known and monitored, and
Since RBI program involves a large
regular HTHA inspections performed. When
number of assets, data, and continues
information, it is desirable to know whether proper safety considerations and controls are
RBI Software is available and utilized in PT. established, the risk of HTHA failures is
greatly reduced in ammonia, refinery, and
XYZ. This may take the form of commercial
chemical plants using tubes, heat
RBI software or Excel spreadsheet-based.
exchangers, and pressure vessels containing
During the discussion and site visit, it
hydrogen at elevated temperatures (Benac &
was evident that the company had just
McAndrew, 2012).
purchased a new software, thus the software
It was identified that HTHA was not
is currently available and used by PT. XYZ
specifically evaluated in PT. XYZ and that
(Figure 5). This new software would be
the Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) and
maintained and updated/upgraded regularly
Fatigue had also not specifically evaluated
or deemed as an “all time license” software.
in PT. XYZ as they only did it on case-by-
At the time of the study, data migration from
the previous system was still ongoing. case basis. The CUI was partially evaluated
and there was no overall plan to inspect
possible CUI attack on piping and vessels.
Figure 5. RBI Software PT XYZ
Figure 6. Window Opening for CUI
Inspection
PREPOTIF Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Page 631
Volume 5, Nomor 2, Oktober 2021 ISSN2623-1581 (Online)
ISSN 2623-1573 (Print)
inspection including visual cleanness and
FFS Assessment and Integrity housekeeping is reported and documented,
Performance Indicator and finally, iv) operational experience
provides feedback into design.
RBI and FFS technologies can be It was observed that the reports related
complementary techniques since both to inspection were partially managed within
provide inputs to each other, as identified by the RBI plan and that there were, up to the
Buchheim (2001). Generally, RBI programs time of the study, formal and non-formal
provide design t-min as a remaining life or ways to share knowledge in the subjects. In
retiring criteria, an asset that has reached its general, the concept and inter-related aspects
design t-min can be assessed by FFS for of reliability, integrity, safety and risk
evaluating a thinner required t-min. If FFS should be understood by all engineers and
study finds the new t-min fit for service, this field inspectors.
reduced t-min can replace the original
design t-min for risk calculations and thus Data Management and Information System
impacting the PoF and resultant risk (Ali &
Sabry, 2019). This section evaluates whether RBI
This parameter is designed to know Data, including the inspection plan, have
whether all information from inspection, been integrated into the existing electronic
test, and monitoring activities are collected data storage system, and whether anomaly
and gathered to enable data assessment. data and status are registered in a database
Furthermore, if FFS is conducted upon all system for tracking.
defect types or anomalies discovered during It was discovered that the inspection
inspection, the next step will be evaluating data was registered and managed through
whether the remaining life and MAWP of the use of an inspection database software
each equipment is evaluated regularly based and then transferred regularly to the RBI
on the most current inspection information. Software for risk assessment. However,
It was observed that the fitness for there was no automatic tracking system
services (FFS) assessment, specifically available at the time of the study.
related to corrosion issues, had been The quality and availability of data is
regularly performed in PT. XYZ on piping one of the most important aspect as the RBI
or vessels containing defects to ensure the process is driven by data. At this stage of the
integrity of the equipment. The remaining project, it is beneficial to do an audit for this
life and MAWP (as product of FFS purpose to find out available vs. minimum
Assessment) were also regularly calculated required data for RBI assessments (Ali &
based on the updated and most recent Sabry, 2019).
inspection data.
RBI on Specific Equipment
Reporting, Documentation, and Knowledge Originally, the old version of RBI is
Sharing intended to evaluate the risk of static
equipment. However, the valves have also
In this section it is important to ensure been considered and included in the API
that; i) the reporting routes are clearly 581. In this section, evaluation is made to
defined and managed effectively within the identify whether the Pressure Safety Valve
RBI strategy, ii) there are systems available (PSV) or Pressure Relief Devices (PRD)
to share reliability knowledge internally have been inspected and tested based on the
within the organization, iii) routine
PREPOTIF Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Page 632
Volume 5, Nomor 2, Oktober 2021 ISSN2623-1581 (Online)
ISSN 2623-1573 (Print)
RBI in PT. XYZ. The same question also against the standard (Mercer, M., 1998).
applies on whether the storage tank has been This section assessed whether self-audit or
inspected based on RBI method. internal audit addressing RBI issues is
It was stated during discussion that the periodically performed and an external audit
PSV/PRD were still inspected and tested addressing equipment integrity issues is also
using time-based approach according to periodically performed.
MIGAS re-certification program (e.g. every It was confirmed that RBI audit was
3 years for PSV). conducted internally as a part of Stat-Eng.
inspection plan and externally as a part of,
Root Cause Failure Analysis (RCFA) or embedded to, the Company Insurance
Audit Program.
As a part of the lessons learned from
any equipment failure or plant accident, it is CONCLUSION
important to know whether RCFA is
conducted on equipment failure (such as The significance of RBI concept and
leak or rupture) to determine the root implementation have been understood by all
cause(s) and contributing cause(s) to failure management level, engineers. and
that similar accidents can be prevented in supervisors in the field of PT XYZ and are
the future. Also, this part aims to understand supported by a good organization structure
whether the RCFA report was well and role and responsibility divisions. Except
documented and easily retrieved. for corrosion engineer who is not available
It was recognized that PT. XYZ at the time of the study, the overall abilities
performed RCFA (called RCPS - Root of engineers and inspectors in dealing with
Cause Problem Solving) internally in case of inspection and RBI are considered to be
equipment failure, and that this process was adequate with some degree of competency.
well-documented and easily retrieved from Furthermore, inspection plan is determined
the system. based on the RBI assessment although in the
inspection execution, due to some
Certification Program consideration, is the assessment is still
performed using two approaches, i.e. risk-
This section seeks to understand based and time-based (according to the turn-
whether static equipment re-certification around schedule). Thus, it is recommended
program is included in the inspection and to have documented RBI policies, RBI
the test plan to fulfill the MIGAS strategy manual or guideline, and RBI
requirement or not. Assessment to identify procedures so that the people involved will
equipment with expired certification is also have the same perception and understanding
made. on RBI. Moreover, it is also recommended
It was stated that all static equipment to run RBI assessment specifically on
(pressure vessels) followed MIGAS re- certain damage mechanisms, namely High
certification program. Some of the Temperature Hydrogen Attack (HTHA),
certifications of the vessels, however, were fatigue, and Corrosion Under Insulation
expired. (CUI). Finally, to be more effective, it is
also suggested to consider the inspection
Audit Program on Integrity and Risk plan of Pressure Relief Devices (PRD) based
on risk-approach instead of time-based
The main function of audit is to identify management.
any gap between the current practices
PREPOTIF Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Page 633
Volume 5, Nomor 2, Oktober 2021 ISSN2623-1581 (Online)
ISSN 2623-1573 (Print)
REFERENCES Khan, F.I., Sadiq, R., and Haddara, M. M.
(2003), Risk-based maintenance
Ali & Sabry, (2019), Implementing a (RBM): a quantitative approach for
Successful Risk Based Inspection maintenance/inspection schedulling
Program. and planning. Journal of loss
American Petroleum Institute (API) 510 prevention in the process industries.
(2018), Pressure Vessel Inspection Khan, F.I., Haddara, M.M., & Bhattacharya,
Code. S.K. (2006), Risk-Based Integrity
American Petroleum Institute (API) 570 and Inspection Modeling (RBIIM) of
(2018), Piping Inspection Code. Process Component/System. Risk
American Petroleum Institute (API) 571 Analysis.
(2003), Damage Mechanism Khan, F.I., Sadiq, R., and Haddara, M. M.
Affecting Fixed Equipment in (2004), Risk-based inspection and
Refining Industry. maintenance (RBIM): multi-attribute
American Petroleum Institute (API) 575 decision-making with aggregative
(2014), Inspection Practices for risk analysis. Process safety and
Atmospheric and Low-Pressure environmental protection.
Storage Tanks. Mercer, M. (1998), Occupational health
American Petroleum Institute (API) 580 audit, Margeret Mercer extols the
(2002), Risk Based Inspection virtues of audit as a management tool
Guideline. in the occupational health service.
American Petroleum Institute (API) 581 Shishesaz et al., (2013), Comparison of API
(2016), Risk Based Inspection 510 pressure vessels inspection
Methodology. planning with API 581 risk-based
American Petroleum Institute (API) 653 inspection planning approaches.
(2014), Tank Inspection, Repair, TWI, (2009). Risk Based Inspection,
Alteration, and Reconstruction. Retrieved from 23th May 2017
Benac & McAndrew, (2012), Reducing the http://www.twi-
Risk of High Temperature Hydrogen global.com/capabilities/integrity-
Attack (HTHA) Failures. management/ risk-based-inspection/
Bertolini, M., et al. (2009), Development of Zhaoyang et al., (2011). Development of
Risk-Based Inspection and Risk-Based Inspection and
Maintenance procedures for an oil Maintenance for an Oil Refiner.
refinery. Journal of Loss Prevention
in the Process Industries.
Lestari, Fatma., et al. (2020), A Safety
Climate Framework for Improving
Health and Safety in the Indonesian
Construction Industry. International
Journal of Environmental Research
and Public Health.
Kaley, L. C., (2009), API RP 581 Risk-
Based Inspection Technology
Demonstrating The Technology
Through A Worked Example
Problem.
PREPOTIF Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Page 634
You might also like
- NX CAD CAM CAE - Bundle - Quick Reference (Jun2020)Document2 pagesNX CAD CAM CAE - Bundle - Quick Reference (Jun2020)Thanakorn VichiensamuthNo ratings yet
- Vendor Exit Strategy TemplateDocument10 pagesVendor Exit Strategy TemplateDarija Gojčeta100% (3)
- API 580 Training Course TWIDocument50 pagesAPI 580 Training Course TWIMohammad Danish100% (18)
- Asset Integrity ManagementDocument2 pagesAsset Integrity ManagementGobin Sookram100% (2)
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Testing ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Testing ProcessRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- School Management System SrsDocument21 pagesSchool Management System SrsRana Ali100% (5)
- M/s Ram Krishna CNC Shop Problem Statement: Group AssignmentDocument7 pagesM/s Ram Krishna CNC Shop Problem Statement: Group AssignmentMoidin AfsanNo ratings yet
- GB921P Process Framework Primer R18.0.1Document31 pagesGB921P Process Framework Primer R18.0.1Mark BequilloNo ratings yet
- Artigo - RBIDocument17 pagesArtigo - RBIIelson FreireNo ratings yet
- Api 580Document6 pagesApi 580Fernando ArévaloNo ratings yet
- HSE - Best Practice For RBI PDFDocument186 pagesHSE - Best Practice For RBI PDFDanie-Els100% (4)
- Risk-Based Inspection - Wikipedia PDFDocument15 pagesRisk-Based Inspection - Wikipedia PDFEndhy Wisnu NovindraNo ratings yet
- 6 Planning The RBI AssessmentDocument9 pages6 Planning The RBI AssessmentMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- API 580 Training CoDocument7 pagesAPI 580 Training Cohs.hs20187720No ratings yet
- Storage Tank Risk Based Inspection / Management: 1.1 ConsequenceDocument11 pagesStorage Tank Risk Based Inspection / Management: 1.1 ConsequenceCostin IlincaNo ratings yet
- A Risk-Based Tool To Support The Inspection Management Inchemical PlantsDocument29 pagesA Risk-Based Tool To Support The Inspection Management Inchemical PlantsThanh Dat DoanNo ratings yet
- RBI - A Transparent Process ?Document11 pagesRBI - A Transparent Process ?Vinícius EstevesNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Risk-Based Inspection MethodologyDocument12 pagesDynamic Risk-Based Inspection Methodologynovendi eko nugrohoNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Condition Management - COMADEM2011Document8 pagesA Framework For Condition Management - COMADEM2011ManeeshSinghNo ratings yet
- RBI Best PracticesDocument13 pagesRBI Best PracticesFroylán Ernesto Pompa García100% (1)
- Risk Based Inspection: Ramesh J. PatelDocument7 pagesRisk Based Inspection: Ramesh J. PatelbassamNo ratings yet
- RBI Korean 5xDocument5 pagesRBI Korean 5xQuekchNo ratings yet
- Risk Based InspectionDocument3 pagesRisk Based InspectionZHNo ratings yet
- XIV Paper 38Document11 pagesXIV Paper 38Zenon KociubaNo ratings yet
- Study Notes Video 2 580 Scope Rev 1Document3 pagesStudy Notes Video 2 580 Scope Rev 1majidNo ratings yet
- Risk-Based Inspection in The Context of Nuclear Power PlantsDocument13 pagesRisk-Based Inspection in The Context of Nuclear Power PlantsMohamed ElotmaniNo ratings yet
- Determination of Maintenance Priority Index (Mpi) For Components On Rsg-Gas Safety SystemDocument13 pagesDetermination of Maintenance Priority Index (Mpi) For Components On Rsg-Gas Safety SystemiqbalsetionugrohoNo ratings yet
- Tugas Perbaikan Analisa Kegagalan MaterialDocument18 pagesTugas Perbaikan Analisa Kegagalan MaterialkusmariantoNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Methods and Tools Used For Reliability Evaluation of SscsDocument4 pagesA Survey of Methods and Tools Used For Reliability Evaluation of SscsStefanos DiamantisNo ratings yet
- RiskBased RBI WPLDocument13 pagesRiskBased RBI WPLLuis Carlos BalcazarNo ratings yet
- A Risk Based Inspection (Rbi) Preventive Maintanance Programme: A Case StudyDocument2 pagesA Risk Based Inspection (Rbi) Preventive Maintanance Programme: A Case StudyAchraf BouzianeNo ratings yet
- Paper294606 PDFDocument14 pagesPaper294606 PDFkirandevi1981No ratings yet
- SPE 87030 Development and Implementation of Risk Based Inspection Methodology in Managing Inspection of Pressurized Production FacilitiesDocument10 pagesSPE 87030 Development and Implementation of Risk Based Inspection Methodology in Managing Inspection of Pressurized Production FacilitiesmsmsoftNo ratings yet
- AI-PS Element Guide No 13Document10 pagesAI-PS Element Guide No 13rwerwerwNo ratings yet
- Definition of Risk Based Inspection (Rbi)Document5 pagesDefinition of Risk Based Inspection (Rbi)Akbar HartawanNo ratings yet
- 2 Risk Based InspectionDocument3 pages2 Risk Based Inspectional0% (1)
- Risk Based Inspection Best Practice-The Technical Specification Ron Selva PP Simtech Keynote Paper-1 13th Icpvt 2012 LondonDocument20 pagesRisk Based Inspection Best Practice-The Technical Specification Ron Selva PP Simtech Keynote Paper-1 13th Icpvt 2012 LondonRichard KoehlerNo ratings yet
- Jurnal RCM 1Document9 pagesJurnal RCM 1teguhNo ratings yet
- Process Safety Metrics: Guide For Selecting Leading and Lagging IndicatorsDocument63 pagesProcess Safety Metrics: Guide For Selecting Leading and Lagging IndicatorsDiego100% (1)
- Chap 16Document3 pagesChap 16hs.hs20187720No ratings yet
- AI-PS Element Guide No 7Document11 pagesAI-PS Element Guide No 7alokcNo ratings yet
- Risk Base Inspection Programs For Pressus EquipementDocument13 pagesRisk Base Inspection Programs For Pressus Equipementanys tekNo ratings yet
- LifeTech-Engineering-Services - Asset Integrity ManagementDocument14 pagesLifeTech-Engineering-Services - Asset Integrity Managementyogolain100% (1)
- Risk Based Inspection Study of Slaughter Gas Plants PVP 2000 - Seattle, Washington July 2000Document6 pagesRisk Based Inspection Study of Slaughter Gas Plants PVP 2000 - Seattle, Washington July 2000Mahmoud RefaatNo ratings yet
- AI-PS Element Guide No 7Document10 pagesAI-PS Element Guide No 7Asad KhanNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and Asset Integrity Management in Oil and Gas Production, Process, Transportation and Storage FacilitiesDocument12 pagesCorrosion and Asset Integrity Management in Oil and Gas Production, Process, Transportation and Storage FacilitiesRASHEED YUSUF100% (1)
- Risk Based InspectionDocument2 pagesRisk Based InspectionyogolainNo ratings yet
- Keywords:-5R, PDCA, RCA, Likert Scale Index,, Why Why: AnalysisDocument5 pagesKeywords:-5R, PDCA, RCA, Likert Scale Index,, Why Why: AnalysisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Contractors' Hse Performance: Pragmatic Evaluation, Benchmarking and Ways For ImprovementDocument8 pagesContractors' Hse Performance: Pragmatic Evaluation, Benchmarking and Ways For ImprovementABF ETSNo ratings yet
- Study of A Risk-Based Piping Inspection Guideline System: Shiaw-Wen Tien, Wen-Tsung Hwang, Chih-Hung TsaiDocument8 pagesStudy of A Risk-Based Piping Inspection Guideline System: Shiaw-Wen Tien, Wen-Tsung Hwang, Chih-Hung Tsaikhevin jionaldoNo ratings yet
- RBI Assessment Recommended Work-Ing ProcessDocument1 pageRBI Assessment Recommended Work-Ing ProcessRicardoNo ratings yet
- Interrelationships Between PSM Elements 3-14-18Document18 pagesInterrelationships Between PSM Elements 3-14-18Jinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- AI-PS Element Guide No 6Document10 pagesAI-PS Element Guide No 6rwerwerwNo ratings yet
- Reliability Centered Maintenance and RbiDocument5 pagesReliability Centered Maintenance and RbiDarkmatter DarkmatterrNo ratings yet
- Damage Mechanism Hazard ReviewDocument17 pagesDamage Mechanism Hazard ReviewBobby VonnNo ratings yet
- Risk Based Inspection Jacketed PlatformsDocument19 pagesRisk Based Inspection Jacketed PlatformsronfrendNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Study and Evaluation of Controls ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Study and Evaluation of Controls ProcessRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- The Duty for Sponor Oversight in Clinical Trials: Practical Guide: 2nd Edition Clinical Data ReviewFrom EverandThe Duty for Sponor Oversight in Clinical Trials: Practical Guide: 2nd Edition Clinical Data ReviewNo ratings yet
- Audit Risk Alert: Government Auditing Standards and Single Audit Developments: Strengthening Audit Integrity 2018/19From EverandAudit Risk Alert: Government Auditing Standards and Single Audit Developments: Strengthening Audit Integrity 2018/19No ratings yet
- Mastering Opportunities and Risks in IT Projects: Identifying, anticipating and controlling opportunities and risks: A model for effective management in IT development and operationFrom EverandMastering Opportunities and Risks in IT Projects: Identifying, anticipating and controlling opportunities and risks: A model for effective management in IT development and operationNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Reporting ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Reporting ProcessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Planning ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Planning ProcessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Effective Business Communication Case StudyDocument8 pagesEffective Business Communication Case StudyamritaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document77 pagesLecture 1Divyansh Singh SengarNo ratings yet
- Job Description - Director - Business DevelopmentDocument2 pagesJob Description - Director - Business DevelopmentGovind DesikanNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual-Routine Operation VolumeDocument247 pagesOperation Manual-Routine Operation VolumeSajadShaykhanNo ratings yet
- Verdantix Green Quadrant Enterprise Carbon Management Software 2022 - REPRINT SweepDocument21 pagesVerdantix Green Quadrant Enterprise Carbon Management Software 2022 - REPRINT SweepAdrian Tudoran100% (1)
- TASSS Activity 4Document1 pageTASSS Activity 4Moses TamondongNo ratings yet
- Week 2 ERP ArchitectureDocument35 pagesWeek 2 ERP Architecturesan marco100% (1)
- Capstone Project VFinalDocument8 pagesCapstone Project VFinalCesar FongNo ratings yet
- Midbs Unit 4 Full UnitDocument31 pagesMidbs Unit 4 Full UnitChintoo KalyanadurgamNo ratings yet
- AcumaticaERP InvMgmtDocument247 pagesAcumaticaERP InvMgmtcrudbugNo ratings yet
- Personal Software Process (PSP) Concept Applied To Beginning EngineersDocument5 pagesPersonal Software Process (PSP) Concept Applied To Beginning EngineersAlina KhanNo ratings yet
- JD - Project Procurement Planning EngineerDocument2 pagesJD - Project Procurement Planning EngineerSanjay RamuNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 Security in CloudsDocument41 pagesUNIT-4 Security in Cloudssaradaganerchukundham45No ratings yet
- Process Identification Part 2Document16 pagesProcess Identification Part 2hover.dragon16No ratings yet
- Oracle Apps HRMS Interview Questions and Answers Guide.: Global GuidelineDocument6 pagesOracle Apps HRMS Interview Questions and Answers Guide.: Global GuidelineKhan IsKhanNo ratings yet
- Get Your Dream Client in The Next 90 Days GuideDocument37 pagesGet Your Dream Client in The Next 90 Days GuideinGrill MediaNo ratings yet
- Maxym Gryn CVDocument3 pagesMaxym Gryn CVaminatjenius71No ratings yet
- Merce and B.commumication NotesDocument58 pagesMerce and B.commumication NotesAnshul BajajNo ratings yet
- With 3 Years ExperienceDocument2 pagesWith 3 Years ExperienceGanesh PeketiNo ratings yet
- Motadata ServiceOps Asset Management - 1612524617 - 1622610559Document31 pagesMotadata ServiceOps Asset Management - 1612524617 - 1622610559abc576666No ratings yet
- Srikanth ResumeDocument3 pagesSrikanth Resumehimanshu.kashyap.etcNo ratings yet
- Harnessing The Potential of Data in InsuranceDocument13 pagesHarnessing The Potential of Data in InsuranceSRINIVAS RAONo ratings yet
- Veeam SAP Avilability GuideDocument64 pagesVeeam SAP Avilability Guidemummy206No ratings yet
- Many Enterprise Software Applications That Support IT Services Are Characterised by The Need For High Computing CapabilityDocument7 pagesMany Enterprise Software Applications That Support IT Services Are Characterised by The Need For High Computing CapabilityhimanshusangaNo ratings yet
- Statement of Work (Sow) : White PaperDocument3 pagesStatement of Work (Sow) : White PaperKo Lin TunNo ratings yet