Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CSTP 3 Park 7 15 2023
CSTP 3 Park 7 15 2023
Uploaded by
api-679162830Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Edu 542 Reading Notes - Understanding How We Learn 20 6Document14 pagesEdu 542 Reading Notes - Understanding How We Learn 20 6api-557497068No ratings yet
- Theories of LearningDocument26 pagesTheories of LearningSplendor Hyaline87% (15)
- cstp3 Valdez 7Document9 pagescstp3 Valdez 7api-679125096No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 TricomoDocument9 pagesCSTP 3 Tricomoapi-518371548No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Pollard 05012019Document16 pagesCSTP 3 Pollard 05012019api-378895647No ratings yet
- Fs1-Activity-2 - Mosada, Jersey O.Document12 pagesFs1-Activity-2 - Mosada, Jersey O.John Paul Sarmiento LatojaNo ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Kim 5Document15 pagesCSTP 3 Kim 5api-431376258No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Carnovale 5Document9 pagesCSTP 3 Carnovale 5api-483980310No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Fountain FinalDocument9 pagesCSTP 3 Fountain Finalapi-518367210No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Uchemefuna 4Document9 pagesCSTP 3 Uchemefuna 4api-434100129No ratings yet
- Reinventing School Libraries: Alternatives, Models and Options For The Future Ken HaycockDocument6 pagesReinventing School Libraries: Alternatives, Models and Options For The Future Ken HaycockMarília CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Vivi Khaeronnisa - EidDocument3 pagesVivi Khaeronnisa - EidViviKhaerunnisaNo ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Uchemefuna 4Document8 pagesCSTP 1 Uchemefuna 4api-434100129No ratings yet
- CSTP 3: Understanding and Organizing Subject Matter For Student LearningDocument8 pagesCSTP 3: Understanding and Organizing Subject Matter For Student LearningKaitlyn MillerNo ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Moritz 4Document9 pagesCSTP 3 Moritz 4api-678881681No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Wu 2022springDocument11 pagesCSTP 3 Wu 2022springapi-556974818No ratings yet
- cstp3 2009Document10 pagescstp3 2009api-637118082No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Dow 5Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Dow 5api-414910309No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Dutra 5Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Dutra 5api-417555971No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Oloughlin 4Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Oloughlin 4api-679108380No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Reed 4 28 2022Document13 pagesCSTP 3 Reed 4 28 2022api-557161783No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Park 7 15 2023Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Park 7 15 2023api-679162830No ratings yet
- Smith Fotip PopDocument5 pagesSmith Fotip Popapi-378363663No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Roy 5Document10 pagesCSTP 3 Roy 5api-622216865No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Snyder 04 30 24Document13 pagesCSTP 3 Snyder 04 30 24api-573216944No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Fleischner 423Document12 pagesCSTP 3 Fleischner 423api-570352555No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Luna 12Document8 pagesCSTP 3 Luna 12api-377956533No ratings yet
- 1st Quarter COT 2023-2024Document7 pages1st Quarter COT 2023-2024Anjenneth Castillo-Teñoso FontamillasNo ratings yet
- Plasencia cstp3Document11 pagesPlasencia cstp3api-621922737No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Bispham 5Document10 pagesCSTP 3 Bispham 5api-679014895No ratings yet
- Fs1 Activity 2 Shaira M. Maynigo Ss 4aDocument11 pagesFs1 Activity 2 Shaira M. Maynigo Ss 4aShaira MaynigoNo ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Chavez 5 3 24Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Chavez 5 3 24api-700836871No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Sullivan 7Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Sullivan 7api-621945476No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Sullivan 7Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Sullivan 7api-621945476No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Hoover Warther 4Document12 pagesCSTP 3 Hoover Warther 4api-678703656No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Feigin 4Document13 pagesCSTP 3 Feigin 4api-621922636No ratings yet
- What Do The Different Ecosystems of The World Contain?: By: Jacqueline MedranoDocument4 pagesWhat Do The Different Ecosystems of The World Contain?: By: Jacqueline MedranoJacqueline Medrano100% (1)
- CSTP 3 Meadows 5 4 22Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Meadows 5 4 22api-528348325No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Cervantes 4Document12 pagesCSTP 3 Cervantes 4api-287731576No ratings yet
- cstp3 Stiegler Spring20Document11 pagescstp3 Stiegler Spring20api-432267464No ratings yet
- Spring 2024 Combined Anas Sallam CSTPDocument70 pagesSpring 2024 Combined Anas Sallam CSTPapi-700065294No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 F19Document12 pagesCSTP 3 F19Lauren Williams-HackmanNo ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Moreno Semester4Document10 pagesCSTP 3 Moreno Semester4api-637117229No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Bernstein Semester 3Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Bernstein Semester 3api-483682821No ratings yet
- cstp3 Adler 9 26 21-1Document9 pagescstp3 Adler 9 26 21-1api-572473620No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Vanruyven 3Document14 pagesCSTP 3 Vanruyven 3api-570828996No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Salamone 4.30.24Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Salamone 4.30.24taylornsalamoneNo ratings yet
- TeachingProf1 (Final)Document2 pagesTeachingProf1 (Final)Jeane Mae Boo100% (10)
- CSTP 3 Tan9Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Tan9api-359540985No ratings yet
- cstp3 Sarah Clingan 7Document9 pagescstp3 Sarah Clingan 7api-679242917No ratings yet
- Unit Solar SystemDocument4 pagesUnit Solar Systemapi-643407639No ratings yet
- Teacher Notes: Title Description Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesTeacher Notes: Title Description Learning Outcomesapi-286968161No ratings yet
- cstp3 2009Document8 pagescstp3 2009api-518696763No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Hoffman 10Document9 pagesCSTP 3 Hoffman 10api-556450134No ratings yet
- Living World UnitofworkDocument7 pagesLiving World Unitofworkapi-374402085No ratings yet
- cstp3 Hayek 04Document7 pagescstp3 Hayek 04api-678417409No ratings yet
- cstp3 2009Document7 pagescstp3 2009api-635814181No ratings yet
- cstp3 Kerkhoff FinalDocument7 pagescstp3 Kerkhoff Finalapi-644316184No ratings yet
- cstp3 2009Document8 pagescstp3 2009api-529077418No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Ellenwood 7-25-2021Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Ellenwood 7-25-2021api-557053172No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Aoki 9Document7 pagesCSTP 1 Aoki 9api-572429129No ratings yet
- Teacher Guide for A Girl Called Echo: Learning About the History and Culture of the Métis Nation in Grades 6–8From EverandTeacher Guide for A Girl Called Echo: Learning About the History and Culture of the Métis Nation in Grades 6–8No ratings yet
- From Communicative To Action Oriented - Theory Into PracticeDocument9 pagesFrom Communicative To Action Oriented - Theory Into PracticeUxueNo ratings yet
- Final Unit Learning PlanDocument45 pagesFinal Unit Learning Plancristine joyNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 13 Cantos FlorenceDocument4 pagesLearning Task 13 Cantos FlorenceCantos FlorenceNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories & Materials DevelopmentDocument4 pagesLearning Theories & Materials DevelopmentRJEREENo ratings yet
- Pe 6.3 Sample SLRP - Make Meaning - Totjhs2023Document13 pagesPe 6.3 Sample SLRP - Make Meaning - Totjhs2023laguiamudamalidasNo ratings yet
- Lev Vygotsky - Sociocultural Theory of Cognotive DevelopmentDocument9 pagesLev Vygotsky - Sociocultural Theory of Cognotive DevelopmentRea Hashim100% (2)
- EDUC 5270 WA Unit 3Document10 pagesEDUC 5270 WA Unit 3FRANCISCO ANTONIO DE LEONNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper Joan MarieDocument2 pagesReflection Paper Joan Mariejoan marie PeliasNo ratings yet
- Standard 2 CSTP: Creating and Maintaining Effective Environments For Student LearningDocument7 pagesStandard 2 CSTP: Creating and Maintaining Effective Environments For Student LearningAmy HickeyNo ratings yet
- Literacy and Social Studies Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesLiteracy and Social Studies Lesson Planapi-411494189100% (1)
- Đáp Án Trung Học Thực Hành Đại Học Sư Phạm 2020-2021Document12 pagesĐáp Án Trung Học Thực Hành Đại Học Sư Phạm 2020-2021Chi Vũ LinhNo ratings yet
- English - Year5, Recount, Biography of A Famous AustralianDocument9 pagesEnglish - Year5, Recount, Biography of A Famous Australianmbed2010No ratings yet
- Task 1: Planning Commentary: 1. Central FocusDocument6 pagesTask 1: Planning Commentary: 1. Central FocushasanNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Content and Language Demands For "Reclassified" StudentsDocument7 pagesScaffolding Content and Language Demands For "Reclassified" Studentsapi-506389013No ratings yet
- Aibl Feronica PurbaDocument15 pagesAibl Feronica PurbaNurul Rahmiah FitriNo ratings yet
- Educ 5410 Unit 2 Portfolio ActivityDocument11 pagesEduc 5410 Unit 2 Portfolio ActivityNzangura IreenNo ratings yet
- Integrated Unit Plan Day OneDocument4 pagesIntegrated Unit Plan Day Oneapi-322101445No ratings yet
- Final Report About Learning DisabilitiesDocument32 pagesFinal Report About Learning DisabilitiesDary OngNo ratings yet
- Ncedtl Ecc Curriculum Scope SequenceDocument3 pagesNcedtl Ecc Curriculum Scope SequenceJaynal HussainNo ratings yet
- English-Tagalog Strategic Intervention Materials in BiologyDocument13 pagesEnglish-Tagalog Strategic Intervention Materials in BiologyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Bee-Bots Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesBee-Bots Lesson Planapi-537450355No ratings yet
- Final Unit PlanDocument26 pagesFinal Unit Planapi-253092616No ratings yet
- GIYA Teachers Guides For Instructions Yielding Archetype Teachers KindergartenDocument8 pagesGIYA Teachers Guides For Instructions Yielding Archetype Teachers KindergartenRebeca OrcalesNo ratings yet
- A Guidance Approach For The Encouraging Classroom 6th Edition Test Bank Dan GartrellDocument5 pagesA Guidance Approach For The Encouraging Classroom 6th Edition Test Bank Dan Gartrellmelaniehallwgrqkdtxic100% (48)
- ArtikelDocument15 pagesArtikelIna QueenNo ratings yet
- Online Division Training of Receiving Teachers Handling Learners With Special NeedsDocument43 pagesOnline Division Training of Receiving Teachers Handling Learners With Special NeedsJeferson SardengNo ratings yet
- John Brown Learning SegmentDocument7 pagesJohn Brown Learning Segmentapi-343313917No ratings yet
- Orff Reflection Lesson 3Document2 pagesOrff Reflection Lesson 3Winnie NgNo ratings yet
CSTP 3 Park 7 15 2023
CSTP 3 Park 7 15 2023
Uploaded by
api-679162830Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CSTP 3 Park 7 15 2023
CSTP 3 Park 7 15 2023
Uploaded by
api-679162830Copyright:
Available Formats
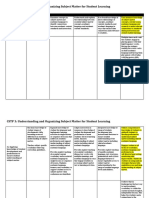
CSTP 3: Understanding and Organizing Subject Matter for Student Learning
Element Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating
Has a foundational Examines concepts in Understands and explains Uses broad knowledge of inter- Uses extensive knowledge
knowledge of subject subject matter and the relationship between relationships of concepts, of subject matter concepts,
matter, related academic academic language to essential subject matter academic content standards, and current issues, academic
3.1 Demonstrating
language, and academic identify connections concepts, academic academic language in ways that language, and research to
knowledge of subject
content standards. between academic content language, and academic ensure clear connections and make relevant connections
matter academic
standards and instruction. content standards. relevance to students. to standards during
content standards
instruction and extend
student learning.
The teacher examines the As a whole class, we utilize Studies The teacher links Earth
lesson and determines Weekly's materials and online Day to the ecosystem,
what to be taught before, platform emphasizing the critical
during and after the (https://www.studiesweekly.com/) role of plants in impacting
to enrich our learning experiences
lesson. both animals and the
in History and Science. We engage
with the platform by watching
planet. Students learn
Assessed July 2023 videos relevant to the subject essential vocabulary such
matter. We also leverage the audio as decomposers and
feature to listen to each section of consumers, deepening
the news, pausing as needed to their understanding of
highlight key information. After our ecological relationships
reading session, we actively and the importance of
participate in whiteboard activities, environmental
with each student equipped with conservation.
their own mini whiteboard to
respond to questions presented on
Assessed April 2024
the website. Furthermore, the
teacher is in the process of creating
individual accounts for all students,
enabling them to complete
assessments at the conclusion of
each weekly study. This
multifaceted approach enhances
our learning and assessment
process as students enjoy
participating for points, our reward
system.
Assessed November 2023
CSTP 3: Understanding and Organizing Subject Matter for Student Learning
Element Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating
Has basic knowledge of Expands knowledge of Adapts instruction in Integrates knowledge of range of Utilizes comprehensive
student stages of student development and response to knowledge of students development into knowledge of students to
development while implements learning student development and instructional decisions to ensure guide all students to
becoming aware of activities in single lessons proficiencies to meet student understanding of the develop proficiencies,
differences in students’ or sequence of lessons students’ diverse learning subject matter including related understand subject matter
understanding of subject that addresses students’ needs. Ensures academic language. including related
matter. proficiencies and support understanding of subject academic language.
understanding of subject matter including related Provides explicit teaching of
3.2 Applying Teaches subject-specific matter including related academic language. specific academic language, text Engages student at all
knowledge of student vocabulary following academic language. structures, grammatical, and levels of vocabulary,
development and curriculum guidelines. Provides explicit teaching stylistic language features to academic language, and
proficiencies to ensure Provides explicit teaching of essential vocabulary, ensure equitable access to subject proficiencies in self-
student of essential content idioms, key words with matter understanding for the range directed goal setting,
understanding of vocabulary and associated multiple meanings, and of student language levels and monitoring, and
subject matter academic language in academic language in abilities. improvement. Guides all
single lessons or sequence ways that engage students students in using analysis
of lessons. Explains in accessing subject strategies that provides
academic language, matter text or learning equitable access and deep
formats, and vocabulary activities. understanding of subject
to support student access matter.
to subject matter when
confusions are identified.
The teacher ask questions In addition to directly instructing The teacher equips
and prepares activities so students on crucial vocabulary, students with key
that students can connect idioms, and key terms during the vocabulary to find
their prior knowledge to lesson, the teacher goes the extra definitions while reading
the context of subject mile by adapting and providing Science and History
matter. support for students in completing newspapers for cross-
the crossword puzzle following the
puzzles. Additionally,
lesson. This support includes
The teacher goes over the students are taught how to
providing them with a word bank
important words to know on a separate sheet of paper and identify cause-and-effect
in prior to the lesson; also, offering assistance in locating and relationships and other
during the lesson the key making connections of the crucial information to
vocabulary are reviewed descriptions and the words. highlight. Encouraging the
with examples. use of recently learned
Assessed July 2023 Assessed November 2023 academic language in
discussions helps students
become comfortable and
proficient in expressing
their understanding.
Assessed April 2024
CSTP 3: Understanding and Organizing Subject Matter for Student Learning
Element Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating
Follows organization of Examines organization of Uses knowledge of Integrates knowledge of Uses extensive knowledge
curriculum as provided by curriculum and considers curriculum and student curriculum and resources to of curriculum and related
site and district to support adjustments in single readiness to organize and organize and adjust instruction resources to flexibly and
student understanding of lessons or sequence of adjust the curriculum to within and across subject matter effectively organize and
3.3 Organizing
the subject matter. lessons to support ensure student to extend student understanding. adjust instruction.
curriculum to
understanding of subject understanding.
facilitate student
matter. Ensures student
understanding of the
comprehension and
subject matter
facilitates student
articulation about what
they do and do not
understand.
The teacher organizes the The teacher has established a structured When teaching division,
curriculum based on weekly routine for the unit. It begins with the teacher offers various
the distribution of a new Spelling Packet
students' levels and with a fresh set of words on Monday. approaches for
highlights the Together as a class, students examine the comprehension, allowing
interrelatedness of phonics and various patterns present in students to choose the
the words. Then, they engage in crossword
subjects. For example, puzzles, which serve the dual purpose of
method that resonates
math problems reinforcing word definitions and with them. This flexible
incorporate real-life expanding their vocabulary instruction strategy
comprehension. This systematic approach
situations, requiring ensures that students not only learn the
demonstrates the teacher's
comprehension before words but also grasp their meanings extensive knowledge of
computation. effectively. Moving on to Tuesday, students curriculum and related
initiate the process of constructing
resources.
sentences that incorporate the newly
Assessed July 2023 learned words, gaining practical
knowledge of their proper usage. Assessed April 2024
Throughout the remainder of the week,
students diligently work through their
Spelling Packets, which entail tasks such as
writing the words, decoding them, and
responding to fill-in-the-blank questions.
On every Friday, students are to turn in
their packets and we conclude it with a
spelling test. This comprehensive
approach allows students to develop a
well-rounded understanding of the words
and their application in various contexts.
Assessed November 2023
CSTP 3: Understanding and Organizing Subject Matter for Student Learning
Element Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating
Uses instructional Gathers and uses Selects and adapts a Integrates instructional strategies Uses an extensive
strategies that are additional instructional variety of instructional appropriate to subject matter to repertoire of instructional
provided in the strategies in single lessons strategies to ensure meet students’ diverse learning, to strategies to develop
3.4 Utilizing
curriculum. or sequence of lessons to student understanding of ensure student understanding of enthusiasm, meta-
instructional
increase student academic language academic language, and guide cognitive abilities, and
strategies that are
understanding of appropriate to subject student in understanding support and challenge the
appropriate to the
academic language matter and that addresses connections within and across full range of student
subject matter
appropriate to subject students’ diverse learning subject matter. towards a deep knowledge
matter. needs. of subject matter.
The teacher incorporates The teacher integrates the real-life The teacher employs both
songs and stories to story of Wonder (a book our class is books and internet
facilitate the development reading), which is based on the resources to teach about
of essential academic experiences of Nathaniel Newman California missions.
language among students. who was born with Treacher Students are assigned a
Additionally, utilizing art Collins Syndrome. This allows specific mission and
students to gain a deeper
activities and related tasked with researching
understanding of not only the main
videos enhances their information about it
character Auggie but also the
understanding of the diverse perspectives portrayed in across 18 topics. They
content, making it more the book. then construct a model
accessible and engaging. and deliver a presentation
based on their findings,
Assessed July 2023 Assessed November 2023 fostering hands-on
learning and
comprehensive
understanding of the
subject matter.
Assessed April 2024
CSTP 3: Understanding and Organizing Subject Matter for Student Learning
Element Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating
Uses available Explores additional Selects, adapts, and Integrates a wide range of adapted Engages students in
instructional materials, instructional materials, utilizes appropriate resources, technologies, and identifying and adapting
resources, and resources, and instructional materials, instructional materials to meet resources, technologies,
technologies for specific technologies to make resources, and identified student needs and make and standards-aligned
3.5 Using and
lessons to make subject subject matter accessible technologies for concept subject matter accessible to instructional materials to
adapting resources,
matter accessible to to students. and skill development in students. extend student
technologies, and
students. subject matter. Resources understanding and critical
standards-aligned
Explores how to make reflect the diversity of the Assists student with equitable thinking about subject
instructional
Identifies technological technological resources classroom and support access to materials, resources, and matter.
materials including
resource needs. available to all students. differentiated learning of technologies. Seeks outside
adopted materials, to
subject matter. resources and support. Ensures that student are
make subject matter
able to obtain equitable
accessible to all
Guides students to use access to a wide range of
students
available print, electronic, technologies through
and online subject matter ongoing links to outside
resources based on resources and support.
individual needs.
The teacher carefully In teaching about California The teacher allocated in-
selects instructional missions, the teacher provides class time for students to
materials that align with books on students' chosen missions present their California
students' comprehension to aid them in writing reports and mission models. Each
levels. Visual and tangible building models. Additionally, student had access to a
aids, as well as physical students are encouraged to use the device and received clear
Internet for further research. If
activities, are effective instructions regarding the
feasible, a field trip to the San Juan
tools for providing content to include in their
Capistrano mission will be planned
differentiated learning to enhance their learning. After presentations.
experiences. building their mission, students will
have options of presenting their Assessed April 2024
Students are motivated to mission using an online platform
enhance their math skills, (either Webquest, Canva or
such as multiplication and Minecraft): presentation slides with
division, through voice recording or a walk-through
enjoyable online games video.
which creates a fun and
engaging learning Assessed November 2023
environment.
Assessed July 2023
CSTP 3: Understanding and Organizing Subject Matter for Student Learning
Element Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating
Is aware of students’ primary Seeks additional information Identifies language Integrates knowledge of English Engages English learners in
language and English describing elements of proficiencies and English language development, English assessment of their progress
language proficiencies based culture and language learner strengths in the study learners’ strengths and assessed needs in English language
on available assessment data. proficiencies in listening, of language and content. into English language and content development and in meeting
speaking, reading, and Differentiates instruction instruction. content standards. Supports
writing. Uses multiple using one or more students to establish and
measures for assessing components of English monitor language and content
3.6 Addressing the English learners’ language development to goals.
needs of English performance to identify gaps support English learners. Develops and adapts instruction to
learners and student Provides adapted materials to in English language provide a wide range of scaffolded
with special needs to help English learners access development. Creates and implements support for language and content for Is resourceful and flexible in
provide equitable content. scaffolds to support the range of English learners. the design, adjustment, and
access to the content Attempts to scaffold content standards-based instruction elimination of scaffolds
using visuals, models, and using literacy strategies, based on English learners’
graphic organizers. SDAIE, and content level proficiencies, knowledge,
English language and skills in the content.
development in order for
students to improve language
proficiencies and understand
content.
The teacher would try to By incorporating something my The teacher prompts
learn how the EL’s student is interested in, the English learners to explain
language might differ engagement in overall academics certain concepts in
from English language. has increased. Spanish, emphasizing
Also, using various form Assessed November 2023 their ability to teach others
of delivery such as props, and highlighting language
videos, and pictures, the as a learned skill.
teacher can demonstrate to
support English Learners. Assessed April 2024
Assessed July 2023
CSTP 3: Understanding and Organizing Subject Matter for Student Learning
Element Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating
Has an awareness of the full Seeks additional information Utilizes information on the Integrates accommodations, Guides and support the full
range of students identified on the full range of students full range of students adaptations, and extensions to range of student with special
with special needs through identified with special needs identified with special needs instruction for the full range of needs to actively engage in
data provided by the school. to address challenges or to assess strengths and students with special needs to ensure the assessment and monitor
supports in single lessons or competencies to provide adequate support and challenge. their own strengths, learning
sequence of lessons. appropriate challenge and needs, and achievement in
accommodations in Communicates and collaborates with accessing content.
instruction. colleagues, support staff, and families
Attends required meeting Cooperates with resource to ensure consistent instruction. Communicates and
3.6 Addressing the with resource personnel and personnel, para-educators, Communicates regularly with Supports families in positive collaborates with resource
needs of English families. and families during meetings resource personnel, para- engagement with school. personnel, para-educators,
learners and student and activities in support of educators, and families to families, leadership, and
with special needs to learning plans and goals. ensure that student services Initiates and monitors referral students in creating a
provide equitable are provided and progress is processes and follow-up meeting to coordinated program to
access to the content made in accessing ensure that students receive support optimize success of the full
appropriate content. and/or extended learning that is range of students with special
integrated into the core curriculum. needs.
Learns about referral Seeks additional information Refers students as needed in
processes for students with on struggling learners and a timely and appropriate Takes leadership at the
special needs. advanced learners to manner supported with site/district and collaborates
determine appropriateness documented data over time, with resource personnel to
for referral. including interventions tried ensure the smooth and
previous to referral. effective implementations of
referral processes.
The teacher would learn the The teacher will start by identifying The teacher adapts
specific needs of the student the specific needs of the students instruction by breaking it
and prepares the lesson that are challenging for them. Based down into smaller,
accordingly- if the student on these needs, the teacher will manageable chunks for
has hard time working in make adjustments to the classroom
groups, he/she would work
students with special
seating arrangement and teaching needs. The teacher
independently with help of strategies. Some examples of
the teacher; if the student regularly check in with
classroom accommodations include
needs more time to complete these students to identify
providing pacing breaks between
any task, he/ she would assignments, breaking down areas of struggle or
receive a reasonable assignments into smaller pieces, success, offering
extended period. immediate feedback.
communicating with families about
The teacher would also log Additionally, the teacher
students' progress, and adapting
the progress of learning and
lessons to suit individual needs. maintains open
collaborate with the student’s
These modifications will create a communication with their
family and whoever should
more supportive and inclusive guardians to ensure
be involved to ensure the
learning environment especially for students receive necessary
progress of the student.
Assessed July 2023 students with special needs. support and to align goals
for their academic
Assessed November 2023 success.
Assessed April 2024
CSTP 3: Understanding and Organizing Subject Matter for Student Learning
Element Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating
You might also like
- Edu 542 Reading Notes - Understanding How We Learn 20 6Document14 pagesEdu 542 Reading Notes - Understanding How We Learn 20 6api-557497068No ratings yet
- Theories of LearningDocument26 pagesTheories of LearningSplendor Hyaline87% (15)
- cstp3 Valdez 7Document9 pagescstp3 Valdez 7api-679125096No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 TricomoDocument9 pagesCSTP 3 Tricomoapi-518371548No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Pollard 05012019Document16 pagesCSTP 3 Pollard 05012019api-378895647No ratings yet
- Fs1-Activity-2 - Mosada, Jersey O.Document12 pagesFs1-Activity-2 - Mosada, Jersey O.John Paul Sarmiento LatojaNo ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Kim 5Document15 pagesCSTP 3 Kim 5api-431376258No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Carnovale 5Document9 pagesCSTP 3 Carnovale 5api-483980310No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Fountain FinalDocument9 pagesCSTP 3 Fountain Finalapi-518367210No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Uchemefuna 4Document9 pagesCSTP 3 Uchemefuna 4api-434100129No ratings yet
- Reinventing School Libraries: Alternatives, Models and Options For The Future Ken HaycockDocument6 pagesReinventing School Libraries: Alternatives, Models and Options For The Future Ken HaycockMarília CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Vivi Khaeronnisa - EidDocument3 pagesVivi Khaeronnisa - EidViviKhaerunnisaNo ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Uchemefuna 4Document8 pagesCSTP 1 Uchemefuna 4api-434100129No ratings yet
- CSTP 3: Understanding and Organizing Subject Matter For Student LearningDocument8 pagesCSTP 3: Understanding and Organizing Subject Matter For Student LearningKaitlyn MillerNo ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Moritz 4Document9 pagesCSTP 3 Moritz 4api-678881681No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Wu 2022springDocument11 pagesCSTP 3 Wu 2022springapi-556974818No ratings yet
- cstp3 2009Document10 pagescstp3 2009api-637118082No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Dow 5Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Dow 5api-414910309No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Dutra 5Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Dutra 5api-417555971No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Oloughlin 4Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Oloughlin 4api-679108380No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Reed 4 28 2022Document13 pagesCSTP 3 Reed 4 28 2022api-557161783No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Park 7 15 2023Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Park 7 15 2023api-679162830No ratings yet
- Smith Fotip PopDocument5 pagesSmith Fotip Popapi-378363663No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Roy 5Document10 pagesCSTP 3 Roy 5api-622216865No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Snyder 04 30 24Document13 pagesCSTP 3 Snyder 04 30 24api-573216944No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Fleischner 423Document12 pagesCSTP 3 Fleischner 423api-570352555No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Luna 12Document8 pagesCSTP 3 Luna 12api-377956533No ratings yet
- 1st Quarter COT 2023-2024Document7 pages1st Quarter COT 2023-2024Anjenneth Castillo-Teñoso FontamillasNo ratings yet
- Plasencia cstp3Document11 pagesPlasencia cstp3api-621922737No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Bispham 5Document10 pagesCSTP 3 Bispham 5api-679014895No ratings yet
- Fs1 Activity 2 Shaira M. Maynigo Ss 4aDocument11 pagesFs1 Activity 2 Shaira M. Maynigo Ss 4aShaira MaynigoNo ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Chavez 5 3 24Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Chavez 5 3 24api-700836871No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Sullivan 7Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Sullivan 7api-621945476No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Sullivan 7Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Sullivan 7api-621945476No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Hoover Warther 4Document12 pagesCSTP 3 Hoover Warther 4api-678703656No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Feigin 4Document13 pagesCSTP 3 Feigin 4api-621922636No ratings yet
- What Do The Different Ecosystems of The World Contain?: By: Jacqueline MedranoDocument4 pagesWhat Do The Different Ecosystems of The World Contain?: By: Jacqueline MedranoJacqueline Medrano100% (1)
- CSTP 3 Meadows 5 4 22Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Meadows 5 4 22api-528348325No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Cervantes 4Document12 pagesCSTP 3 Cervantes 4api-287731576No ratings yet
- cstp3 Stiegler Spring20Document11 pagescstp3 Stiegler Spring20api-432267464No ratings yet
- Spring 2024 Combined Anas Sallam CSTPDocument70 pagesSpring 2024 Combined Anas Sallam CSTPapi-700065294No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 F19Document12 pagesCSTP 3 F19Lauren Williams-HackmanNo ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Moreno Semester4Document10 pagesCSTP 3 Moreno Semester4api-637117229No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Bernstein Semester 3Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Bernstein Semester 3api-483682821No ratings yet
- cstp3 Adler 9 26 21-1Document9 pagescstp3 Adler 9 26 21-1api-572473620No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Vanruyven 3Document14 pagesCSTP 3 Vanruyven 3api-570828996No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Salamone 4.30.24Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Salamone 4.30.24taylornsalamoneNo ratings yet
- TeachingProf1 (Final)Document2 pagesTeachingProf1 (Final)Jeane Mae Boo100% (10)
- CSTP 3 Tan9Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Tan9api-359540985No ratings yet
- cstp3 Sarah Clingan 7Document9 pagescstp3 Sarah Clingan 7api-679242917No ratings yet
- Unit Solar SystemDocument4 pagesUnit Solar Systemapi-643407639No ratings yet
- Teacher Notes: Title Description Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesTeacher Notes: Title Description Learning Outcomesapi-286968161No ratings yet
- cstp3 2009Document8 pagescstp3 2009api-518696763No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Hoffman 10Document9 pagesCSTP 3 Hoffman 10api-556450134No ratings yet
- Living World UnitofworkDocument7 pagesLiving World Unitofworkapi-374402085No ratings yet
- cstp3 Hayek 04Document7 pagescstp3 Hayek 04api-678417409No ratings yet
- cstp3 2009Document7 pagescstp3 2009api-635814181No ratings yet
- cstp3 Kerkhoff FinalDocument7 pagescstp3 Kerkhoff Finalapi-644316184No ratings yet
- cstp3 2009Document8 pagescstp3 2009api-529077418No ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Ellenwood 7-25-2021Document7 pagesCSTP 3 Ellenwood 7-25-2021api-557053172No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Aoki 9Document7 pagesCSTP 1 Aoki 9api-572429129No ratings yet
- Teacher Guide for A Girl Called Echo: Learning About the History and Culture of the Métis Nation in Grades 6–8From EverandTeacher Guide for A Girl Called Echo: Learning About the History and Culture of the Métis Nation in Grades 6–8No ratings yet
- From Communicative To Action Oriented - Theory Into PracticeDocument9 pagesFrom Communicative To Action Oriented - Theory Into PracticeUxueNo ratings yet
- Final Unit Learning PlanDocument45 pagesFinal Unit Learning Plancristine joyNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 13 Cantos FlorenceDocument4 pagesLearning Task 13 Cantos FlorenceCantos FlorenceNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories & Materials DevelopmentDocument4 pagesLearning Theories & Materials DevelopmentRJEREENo ratings yet
- Pe 6.3 Sample SLRP - Make Meaning - Totjhs2023Document13 pagesPe 6.3 Sample SLRP - Make Meaning - Totjhs2023laguiamudamalidasNo ratings yet
- Lev Vygotsky - Sociocultural Theory of Cognotive DevelopmentDocument9 pagesLev Vygotsky - Sociocultural Theory of Cognotive DevelopmentRea Hashim100% (2)
- EDUC 5270 WA Unit 3Document10 pagesEDUC 5270 WA Unit 3FRANCISCO ANTONIO DE LEONNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper Joan MarieDocument2 pagesReflection Paper Joan Mariejoan marie PeliasNo ratings yet
- Standard 2 CSTP: Creating and Maintaining Effective Environments For Student LearningDocument7 pagesStandard 2 CSTP: Creating and Maintaining Effective Environments For Student LearningAmy HickeyNo ratings yet
- Literacy and Social Studies Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesLiteracy and Social Studies Lesson Planapi-411494189100% (1)
- Đáp Án Trung Học Thực Hành Đại Học Sư Phạm 2020-2021Document12 pagesĐáp Án Trung Học Thực Hành Đại Học Sư Phạm 2020-2021Chi Vũ LinhNo ratings yet
- English - Year5, Recount, Biography of A Famous AustralianDocument9 pagesEnglish - Year5, Recount, Biography of A Famous Australianmbed2010No ratings yet
- Task 1: Planning Commentary: 1. Central FocusDocument6 pagesTask 1: Planning Commentary: 1. Central FocushasanNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Content and Language Demands For "Reclassified" StudentsDocument7 pagesScaffolding Content and Language Demands For "Reclassified" Studentsapi-506389013No ratings yet
- Aibl Feronica PurbaDocument15 pagesAibl Feronica PurbaNurul Rahmiah FitriNo ratings yet
- Educ 5410 Unit 2 Portfolio ActivityDocument11 pagesEduc 5410 Unit 2 Portfolio ActivityNzangura IreenNo ratings yet
- Integrated Unit Plan Day OneDocument4 pagesIntegrated Unit Plan Day Oneapi-322101445No ratings yet
- Final Report About Learning DisabilitiesDocument32 pagesFinal Report About Learning DisabilitiesDary OngNo ratings yet
- Ncedtl Ecc Curriculum Scope SequenceDocument3 pagesNcedtl Ecc Curriculum Scope SequenceJaynal HussainNo ratings yet
- English-Tagalog Strategic Intervention Materials in BiologyDocument13 pagesEnglish-Tagalog Strategic Intervention Materials in BiologyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Bee-Bots Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesBee-Bots Lesson Planapi-537450355No ratings yet
- Final Unit PlanDocument26 pagesFinal Unit Planapi-253092616No ratings yet
- GIYA Teachers Guides For Instructions Yielding Archetype Teachers KindergartenDocument8 pagesGIYA Teachers Guides For Instructions Yielding Archetype Teachers KindergartenRebeca OrcalesNo ratings yet
- A Guidance Approach For The Encouraging Classroom 6th Edition Test Bank Dan GartrellDocument5 pagesA Guidance Approach For The Encouraging Classroom 6th Edition Test Bank Dan Gartrellmelaniehallwgrqkdtxic100% (48)
- ArtikelDocument15 pagesArtikelIna QueenNo ratings yet
- Online Division Training of Receiving Teachers Handling Learners With Special NeedsDocument43 pagesOnline Division Training of Receiving Teachers Handling Learners With Special NeedsJeferson SardengNo ratings yet
- John Brown Learning SegmentDocument7 pagesJohn Brown Learning Segmentapi-343313917No ratings yet
- Orff Reflection Lesson 3Document2 pagesOrff Reflection Lesson 3Winnie NgNo ratings yet