Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exit Model by Endeshaw
Exit Model by Endeshaw
Uploaded by
hailomasegede27Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
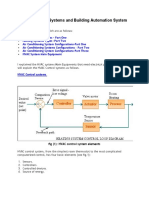
- HVAC Control Systems and Building Automation System PDFDocument19 pagesHVAC Control Systems and Building Automation System PDFStephany Montero100% (5)
- User Manual: Telemetry UnitDocument17 pagesUser Manual: Telemetry UnitChristian Vasquez MedranoNo ratings yet
- MosfetDocument8 pagesMosfetHarshit OjhaNo ratings yet
- Principles and Applications of MOSFET and JFET MosfetDocument5 pagesPrinciples and Applications of MOSFET and JFET MosfetKim KimNo ratings yet
- Example A: Find The Resistance of 6.5 M of Wire, Diameter 0.6 MM, If TheDocument4 pagesExample A: Find The Resistance of 6.5 M of Wire, Diameter 0.6 MM, If TheTara GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 3-PPT MosfetDocument28 pages3-PPT MosfetVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Mosfet Diode TransistorDocument45 pagesUnit3 Mosfet Diode TransistorPriyanshu yadavNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument61 pages1 Introductionfiraol temesgenNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument25 pagesMini Projectcharan524No ratings yet
- ETI 2203 Lesson 7Document10 pagesETI 2203 Lesson 7amash.emillyNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 8Document6 pagesExperiment No. 8LoraineCundangan-medinaNo ratings yet
- Unit - Vi Field Effect TransistorDocument16 pagesUnit - Vi Field Effect TransistorBhavaniPrasadNo ratings yet
- Mosfet SaiDocument35 pagesMosfet SaiDisha GoelNo ratings yet
- BEng FETDocument13 pagesBEng FETJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Field Effect Transistor NotesDocument21 pagesField Effect Transistor NotessaraswatnidhiNo ratings yet
- Mofet - IGBT - SCR - Traic - Snubber CKTDocument17 pagesMofet - IGBT - SCR - Traic - Snubber CKTTejas krishnakanthNo ratings yet
- CMOS Interview QuestionsDocument52 pagesCMOS Interview QuestionsKAMARUDHEEN KP100% (1)
- BEEE NotesDocument23 pagesBEEE Notessonali2408100% (6)
- Observations: Experimental ValuesDocument7 pagesObservations: Experimental ValuesShibeshwar MandalNo ratings yet
- SD 3rd Module MOSFETDocument8 pagesSD 3rd Module MOSFETPranathi GNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Group-B Q&aDocument13 pagesVlsi Group-B Q&aROHAN CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- CMOS Interview QADocument14 pagesCMOS Interview QAarammartNo ratings yet
- Design of Cmos BufferDocument5 pagesDesign of Cmos BufferVarunKaradesaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document39 pagesLecture 1Nuniwal JyotiNo ratings yet
- Leakage CurrentDocument5 pagesLeakage CurrentImam WijayaNo ratings yet
- MOSFET As A SwitchDocument11 pagesMOSFET As A Switchrahul samanta100% (1)
- JFETDocument20 pagesJFETMenzi TabilidNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document7 pagesAssignment 3Arnon PukhrambamNo ratings yet
- The Range of Can Be Specified Over Which The Gain Does Not Deviate More Than 70.7% of The Maximum Gain at Some Reference MidDocument21 pagesThe Range of Can Be Specified Over Which The Gain Does Not Deviate More Than 70.7% of The Maximum Gain at Some Reference MidRiyaz PashaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word Document-1Document4 pagesNew Microsoft Word Document-1Agaba SamuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Field Effect TransistorsDocument48 pagesChapter 10 Field Effect TransistorsanjugaduNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - FET - WatermarkDocument16 pagesMODULE 1 - FET - WatermarkAnupama MohananNo ratings yet
- EI2301-IE - Unit 1 - Part A and Part B - With Answers PDFDocument21 pagesEI2301-IE - Unit 1 - Part A and Part B - With Answers PDFsartpgitNo ratings yet
- Field Effect Transistors (FET) : Comparison Between BJT and FETDocument9 pagesField Effect Transistors (FET) : Comparison Between BJT and FETpranavraikar1No ratings yet
- The Basic Structure: Field Effect TransistorDocument10 pagesThe Basic Structure: Field Effect TransistormokhaladNo ratings yet
- Ece-Research Work 1Document10 pagesEce-Research Work 1Peale ObiedoNo ratings yet
- Tunnel DiodeDocument56 pagesTunnel DiodeNaveed Ramzan100% (2)
- Electronics Hons C3 FET Field Effect TransistorDocument21 pagesElectronics Hons C3 FET Field Effect TransistorGawrav BaishyaNo ratings yet
- VLSI PresentationDocument8 pagesVLSI PresentationKazi MidulNo ratings yet
- Mosfet Lab 2Document11 pagesMosfet Lab 2Jaime Aguilar100% (1)
- Final MosfetDocument33 pagesFinal MosfetabdallaNo ratings yet
- Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Document6 pagesMetal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Yasir KhanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS (FET) EditDocument58 pagesCHAPTER 5 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS (FET) Editruhiyahnazihah_15106No ratings yet
- Technical Examination Level - 7Document37 pagesTechnical Examination Level - 7Madhunath YadavNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Transistor Models and The Feedback Amp - Docmicrosoft Word - Transistor Models and The Feedback Amp - Doctransistor - Models - and - The - FbaDocument14 pagesMicrosoft Word - Transistor Models and The Feedback Amp - Docmicrosoft Word - Transistor Models and The Feedback Amp - Doctransistor - Models - and - The - FbashubhamformeNo ratings yet
- Field Effect TransistorDocument13 pagesField Effect TransistorLORD TNo ratings yet
- MosfetDocument23 pagesMosfetgopikrishna yarlagaddaNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechatronic Engineering: Power DiodeDocument12 pagesDepartment of Mechatronic Engineering: Power DiodeEng King'e FredrickNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Field Effect Transistors: A. Introduction To FetsDocument10 pagesChapter 8: Field Effect Transistors: A. Introduction To FetsBmanNo ratings yet
- Unit III Jfet - MosfetDocument20 pagesUnit III Jfet - Mosfet1akshat341No ratings yet
- Field Effect Transistor (FET) : Department of Physics Guru Jambheshwar University of Science & Technology HisarDocument13 pagesField Effect Transistor (FET) : Department of Physics Guru Jambheshwar University of Science & Technology HisarAnkita Sharma1610No ratings yet
- True FalseDocument5 pagesTrue FalseShuvodip Das50% (2)
- V. Mosfet PDFDocument33 pagesV. Mosfet PDFleeminho_janxiNo ratings yet
- Assignment FET 2Document3 pagesAssignment FET 2shobanraj1995No ratings yet
- Name Ali Muneer Sap Id 70070422 Subject Basic Electronics Section GDocument9 pagesName Ali Muneer Sap Id 70070422 Subject Basic Electronics Section GRana HusnainNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Semi Conductor DevicesDocument4 pagesCH 9 Semi Conductor Devicesscholars learningNo ratings yet
- Field Effect TransistorsDocument6 pagesField Effect TransistorsMunna HossainNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)No ratings yet
- Revised Competency in Computer Science and Engineering 2024Document11 pagesRevised Competency in Computer Science and Engineering 2024hailomasegede27No ratings yet
- No. Name Fname Gfname Request - NoDocument215 pagesNo. Name Fname Gfname Request - Nohailomasegede27100% (1)
- Revised Exit Exam Blue Print For Computer Science and EngineeringDocument16 pagesRevised Exit Exam Blue Print For Computer Science and Engineeringhailomasegede27100% (1)
- No. Name Fname Gfname Request - NoDocument88 pagesNo. Name Fname Gfname Request - Nohailomasegede27No ratings yet
- No. Name Fname Gfname Request - NoDocument86 pagesNo. Name Fname Gfname Request - Nohailomasegede27100% (1)
- No. Name Fname Gfname Request - NoDocument12 pagesNo. Name Fname Gfname Request - Nohailomasegede27No ratings yet
- Evaluation Condition of Transformer Based On Infrared Thermography ResultsDocument4 pagesEvaluation Condition of Transformer Based On Infrared Thermography Resultscarlos patrickNo ratings yet
- Kue Oem Hurm KitsDocument20 pagesKue Oem Hurm KitsChí Khang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Lpcxpresso1115 With Cmsis Dap SCHDocument4 pagesLpcxpresso1115 With Cmsis Dap SCHAnkur SharmaNo ratings yet
- Manual Do Gerador de SinalDocument11 pagesManual Do Gerador de Sinalmanoel seraphimNo ratings yet
- User Manual Capacitor Type GeneratorDocument17 pagesUser Manual Capacitor Type GeneratorUMA AKANDU UCHENo ratings yet
- 800 10684 PDFDocument1 page800 10684 PDFМаксNo ratings yet
- EE 313 - LAB Project - ECD - 2020Document2 pagesEE 313 - LAB Project - ECD - 2020Muhammad YousafNo ratings yet
- Megger Earth TesterDocument3 pagesMegger Earth TesterAhmad RobbyNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Electric Loads PDFDocument1 pageVehicle Electric Loads PDFphoneme79No ratings yet
- Resume of Mohammad YousufDocument2 pagesResume of Mohammad YousufEngr Mohammad YousufNo ratings yet
- Chapter One History and Evolution of Telecommunication NetworksDocument58 pagesChapter One History and Evolution of Telecommunication NetworksTibebu Xibe TeNo ratings yet
- Final Presentation - SanneDocument18 pagesFinal Presentation - SanneAnh TranNo ratings yet
- BMW Transmission Specs 2004Document15 pagesBMW Transmission Specs 2004gabriela sanguinoNo ratings yet
- Measuring Gigaohms With A Simple MultimeterDocument11 pagesMeasuring Gigaohms With A Simple MultimeterZIASY Shesmer100% (1)
- P Series Ciac Service Manual 30,36K FVDocument108 pagesP Series Ciac Service Manual 30,36K FVAnthony Pineda ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Antenna CatalogDocument50 pagesAntenna CatalogashishsinghchouhanNo ratings yet
- Bpe MicroprojectDocument19 pagesBpe Microproject10 Durvesh PathakNo ratings yet
- ISO 26262: Functional Safety Standard For Modern Road VehiclesDocument15 pagesISO 26262: Functional Safety Standard For Modern Road VehiclesH MORENONo ratings yet
- Epson PRO-G7905U - PROD - SPEC - R1Document2 pagesEpson PRO-G7905U - PROD - SPEC - R1DANIEL ALFONSO GREIFF DAVILANo ratings yet
- CH 07Document56 pagesCH 07miathegirl9No ratings yet
- Circuit Builder Acitivity B and CDocument3 pagesCircuit Builder Acitivity B and CSujatha VimalNo ratings yet
- NT68169UFGDocument1 pageNT68169UFGaldinaenNo ratings yet
- Automatic Room ControllerDocument14 pagesAutomatic Room ControllerAbiraja BNo ratings yet
- Mag Pi 119Document100 pagesMag Pi 119Aro2006No ratings yet
- Multi V S (Side Discharge) CatalogDocument1 pageMulti V S (Side Discharge) CatalogKyaw San Oo100% (1)
- Work Instruction: Range/principleDocument3 pagesWork Instruction: Range/principleLim ChsNo ratings yet
- KJ4-M18MB80-ANU: Product Description Inductive Sensor AnalogueDocument2 pagesKJ4-M18MB80-ANU: Product Description Inductive Sensor AnalogueBAHARO ALYAUMA IEDNo ratings yet
- FKEN 604.18GS4 Switch de FlujoDocument1 pageFKEN 604.18GS4 Switch de FlujoRigoberto HerreraNo ratings yet
Exit Model by Endeshaw
Exit Model by Endeshaw
Uploaded by
hailomasegede27Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exit Model by Endeshaw
Exit Model by Endeshaw
Uploaded by
hailomasegede27Copyright:
Available Formats
By: Ayalsew .
1.the main characteristics of a Darlington Amplifier are
a. Low input impedance, low output impedance and low voltage gain.
b. High input impedance, high output impedance and high current gain
C. Low input impedance, low output impedance and high current gain.
d. High input impedance, low output impedance and high current gain.
The correct answer is d. High input impedance, low output impedance and high current gain.
A Darlington Amplifier is a type of transistor amplifier that consists of two bipolar transistors
connected in a configuration such that the current gain of each transistor is multiplied. The first
transistor is a common-emitter amplifier, and the second transistor is a common-collector
amplifier. This configuration provides a high input impedance, low output impedance, and high
current gain.
The high input impedance of the Darlington Amplifier is due to the first transistor being a
common-emitter amplifier, which has a high input impedance. The low output impedance is due
to the second transistor being a common-collector amplifier, which has a low output impedance.
The high current gain is due to the fact that the current gain of the two transistors is multiplied.
Therefore, option d is the most appropriate answer.
2. What configuration is widely preferred in cascading amplifiers?
a. Common Collector
b.Common Base
C.Common source
d. Common Emitter
The configuration that is widely preferred in cascading amplifiers is the Common Emitter
configuration. This is because the Common Emitter configuration provides high voltage gain,
which is necessary for most amplification applications. Additionally, it provides a relatively low
input impedance and a relatively high output impedance, which makes it suitable for cascading
with other amplifier stages.
3.Enhancement mode MOSFETS are more commonly used as
a.Capacitors
b.Buffers
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
c.Resistors
d.Switches
Regarding the second question, Enhancement mode MOSFETs are more commonly used as
switches. This is because an enhancement mode MOSFET can be turned on or off by applying a
voltage to its gate terminal, and when it is on, it has a low resistance between its source and drain
terminals, which makes it suitable for switching applications. While MOSFETs can also be used
as capacitors or buffers in some applications, these are less common applications for
enhancement mode MOSFETs.
4.An n-channel D-MOSFET with a positive VGS is operating in
a.the enhancement mode
b. Saturation
C.cutoff
d. the depletion mode
An n-channel D-MOSFET with a positive VGS is operating in the enhancement mode.
In the enhancement mode of operation, the MOSFET is turned on by applying a positive voltage
to the gate (VGS) with respect to the source (VS). This creates an inversion layer in the channel
between the source and drain, allowing current to flow from the source to the drain.
In contrast, in the depletion mode of operation, the MOSFET is already conducting current even
with zero VGS, and applying a negative voltage to the gate increases the channel resistance,
reducing the current flow.
When the MOSFET is operating in the saturation region, it is conducting the maximum possible
current for a given VDS, and the drain-source voltage is typically smaller than VGS - VTH,
where VTH is the threshold voltage of the MOSFET. This is not the case described in the
question, where it is only stated that VGS is positive, so it is not possible to determine whether
the MOSFET is in saturation or not.
Therefore, option a, the enhancement mode, is the correct answer to the question.
5.The process of emitting photons from a semi-conductive material is called
a.electroluminescence.
b. gallium arsenide.
C gallium phosphide.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
d.photoluminescence
The process of emitting photons from a semiconductive material is called electroluminescence.
When a voltage is applied across a semiconductive material, electrons and holes are injected into
the material, and when they recombine, they can release energy in the form of light. This process
is called electroluminescence.
This process is used in a variety of electronic devices, including light-emitting diodes (LEDs)
and displays. LEDs are made from semiconductive materials such as gallium arsenide or gallium
phosphide, which can emit light when a voltage is applied across them. Therefore, options a, b,
and c are related to the materials that can be used in electroluminescence, but the actual process
of emitting photons from a semiconductive material is known as electroluminescence. Option d,
photoluminescence, is a different process in which a material absorbs light and then emits light
in response, rather than emitting light directly due to the application of voltage.
An n-channel D-MOSFET with a positive VGS is operating in the enhancement mode.
In the enhancement mode of operation, the MOSFET is turned on by applying a positive voltage
to the gate (VGS) with respect to the source (VS). This creates an inversion layer in the channel
between the source and drain, allowing current to flow from the source to the drain.
In contrast, in the depletion mode of operation, the MOSFET is already conducting current even
with zero VGS, and applying a negative voltage to the gate increases the channel resistance,
reducing the current flow.
When the MOSFET is operating in the saturation region, it is conducting the maximum possible
current for a given VDS, and the drain-source voltage is typically smaller than VGS - VTH,
where VTH is the threshold voltage of the MOSFET. This is not the case described in the
question, where it is only stated that VGS is positive, so it is not possible to determine whether
the MOSFET is in saturation or not.
Therefore, option a, the enhancement mode, is the correct answer to the question.
An n-channel D-MOSFET with a positive VGS is operating in the enhancement mode.
In the enhancement mode of operation, the MOSFET is turned on by applying a positive voltage
to the gate (VGS) with respect to the source (VS). This creates an inversion layer in the channel
between the source and drain, allowing current to flow from the source to the drain.
In contrast, in the depletion mode of operation, the MOSFET is already conducting current even
with zero VGS, and applying a negative voltage to the gate increases the channel resistance,
reducing the current flow.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
When the MOSFET is operating in the saturation region, it is conducting the maximum possible
current for a given VDS, and the drain-source voltage is typically smaller than VGS - VTH,
where VTH is the threshold voltage of the MOSFET. This is not the case described in the
question, where it is only stated that VGS is positive, so it is not possible to determine whether
the MOSFET is in saturation or not.
Therefore, option a, the enhancement mode, is the correct answer to the question.
6.When the temperature of a doped semiconductor is increased, its conductivity,
a. Increases.
b.Does not change
c. Increases or decreases depending on whether it is p-or n-type
d. Decreases.
a. Increases.
In a doped semiconductor, the presence of impurities (dopants) modifies the electronic properties
of the material, creating either p-type or n-type semiconductors.
When the temperature of a doped semiconductor is increased, the thermal energy increases the
number of thermally generated charge carriers, either holes (in p-type) or electrons (in n-type),
which increases the conductivity of the material. This is because at higher temperatures, there are
more thermally excited electrons or holes available to participate in conduction.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
7.A signal x(t) and its Hilbert transform is having
a. Same energy spectral density
b.Same amplitude spectrum
C.Same power spectral density
d. Same autocorrelation function
b. Same amplitude spectrum.
The Hilbert transform of a signal x(t) is a mathematical operation that results in a new signal,
called the analytic signal, that is closely related to x(t). The analytic signal has the same
magnitude spectrum as the original signal x(t) but with a phase shift of 90 degrees.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
The amplitude spectrum of a signal refers to the magnitude of its frequency components, while
the energy spectral density and power spectral density refer to the energy or power contained in
the signal at each frequency. The autocorrelation function describes the similarity between a
signal and a delayed version of itself.
Since the Hilbert transform only affects the phase of the signal and not its magnitude, it follows
that the amplitude spectrum of the original signal and its Hilbert transform will be the same.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
8.Which of the following type of arcuits in electrical engineering cannot be analyzed using
Ohm's law
a. Unilateral circuit
b .Conductor circuit
c.Bilateral circuit
d.Linear circuit
a. Unilateral circuit cannot be analyzed using Ohm's law.
Ohm's law states that the current flowing through a conductor between two points is directly
proportional to the voltage across the two points, given a constant temperature and pressure. It is
applicable only to linear circuits, which follow the principle of superposition and have a constant
resistance.
A unilateral circuit, on the other hand, is a circuit that has a non-linear element such as a diode or
a transistor. These elements do not obey Ohm's law and their behavior cannot be described by a
single constant resistance value. Therefore, unilateral circuits cannot be analyzed using Ohm's
law.
Conductor circuit and bilateral circuit are not types of circuits and do not affect the applicability
of Ohm's law. Linear circuits are a type of circuit that can be analyzed using Ohm's law.
a. Increases.
In a doped semiconductor, the presence of impurities (dopants) modifies the electronic properties
of the material, creating either p-type or n-type semiconductors.
When the temperature of a doped semiconductor is increased, the thermal energy increases the
number of thermally generated charge carriers, either holes (in p-type) or electrons (in n-type),
which increases the conductivity of the material. This is because at higher temperatures, there are
more thermally excited electrons or holes available to participate in conduction.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
9.Which of the following techniques is used in determining the time domain response of a linear
time invariant system?
a. Fourier Series
b. Laplace transform
c. Convolution Integral
d. Fourier transform:
c. Convolution Integral.
The time domain response of a linear time-invariant (LTI) system can be determined using the
convolution integral. The convolution integral expresses the output of an LTI system as the
convolution of the input signal with the impulse response of the system.
The Laplace transform and Fourier transform are used to analyze the frequency domain behavior
of LTI systems, while the Fourier series is used to represent periodic signals in terms of a sum of
harmonic components.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
10.In a PNP transistor, the current carriers are
a. acceptor ions
b.holes
c. free electrons
d. donor ions
c. free electrons.
In a PNP transistor, the majority charge carriers are holes, which are present in the P-type
material. However, the minority charge carriers are free electrons, which are injected from the N-
type material into the P-type region when the transistor is forward-biased.
When the base-emitter junction is forward-biased, the injected electrons recombine with holes in
the base region, creating a depletion region and allowing holes to flow from the emitter to the
base. The holes then diffuse across the base region and are swept into the collector by the electric
field created by the reverse-biased collector-base junction.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
11.The data elements in structure are also known as:
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
a. Objects
b. Instruction
c. Members
d. Data
c. Members.
In computer programming, a structure is a composite data type that groups together related data
elements of different data types under a single name. Each data element within a structure is
referred to as a member, and these members are accessed using the dot operator (.) followed by
the member name.
For example, consider a structure named "Person" that contains members such as "name", "age",
and "address". In C programming language, the structure can be defined as follows:
```
struct Person {
char name[50];
int age;
char address[100];
};
```
In this example, "name", "age", and "address" are the members of the "Person" structure.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
12.Which among the following assertions represents a necessary condition for the existence of
Fourier Transform of discrete time
signal (DTFT)?
a. Discrete Time Signal should be absolutely integrable
b. Discrete Time Signal should be absolutely multipliable
c. Discrete Time Signal should be absolutely summable
d. Discrete Time Signal should be absolutely differentiable
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
c. Discrete Time Signal should be absolutely summable.
The Fourier Transform of a discrete time signal (DTFT) exists if the signal is absolutely
summable, meaning that the sum of the absolute values of the signal's samples is finite.
Mathematically, if x[n] is a discrete time signal, its DTFT X(e^(jw)) is defined as the sum from
negative infinity to positive infinity of x[n] multiplied by e^(-jwn), where w is the angular
frequency.
The other options are not necessary conditions for the existence of the DTFT. Option (a) refers to
the condition for the existence of the Fourier transform of a continuous time signal, while option
(b) and (d) are not relevant to the existence of the DTFT.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
13.A type of assembly language instruction that alters the course of the program is called a -
a.flow chart
b. loop and jump
c.loop
d. jump
A jump instruction is a type of assembly language instruction that alters the course of a program
by transferring control to a different part of the program. A jump instruction changes the flow of
execution by transferring control to a different memory location or label in the program.
A flow chart is a graphical representation of a program's logic, which may include jump
instructions. A loop is a control flow statement that allows a program to repeatedly execute a
block of code. A loop and jump statement is a combination of loop and jump instructions, which
are used together to implement complex control structures.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
d. Estimating the area under the square of its amplitude spectrum.
Rayleigh's energy theorem states that the energy of a signal can be determined by integrating the
square of its amplitude over all time. Mathematically, if x(t) is a signal, its energy E is given by:
E = ∫[x(t)]^2 dt from negative infinity to positive infinity
This means that the energy of a signal is proportional to the area under the square of its
amplitude spectrum. The amplitude spectrum of a signal represents the magnitude of its
frequency components.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
Option (a) is related to estimating the power of a signal, which is proportional to the area under
the one-half power of its amplitude spectrum. Option (b) is not a recognized theorem or method
for estimating the energy or power of a signal. Option (c) is related to estimating the magnitude
of a signal's frequency components, not its energy.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
14.According to Rayleigh's theorem, it becomes possible to determine the energy of a signal by:
a. Estimating the area under the one-fourth power of its amplitude spectrum
b Estimating the area exactly half as that of its amplitude spectrum
C. Estimating the area under the square root of its amplitude spectrum.
d. Estimating the area under the square of its amplitude spectrum.
tion
15.Which one of the following is an example of a hardware:
a. Web editor
b. Instruction
C .Memory
d .Program
C. Memory.
Memory is an example of hardware. Hardware refers to the physical components of a computer
system that can be seen and touched. Memory is a hardware component that stores data and
instructions for the computer to access and use.
A web editor, instruction, and program are not examples of hardware. A web editor is a software
application used for creating and editing web pages. An instruction is a command given to the
computer to perform a specific task, which is executed by the computer's processor. A program
is a sequence of instructions that are executed by the computer to perform a specific task.
Therefore, option (C) is the correct answer.
16.How many full adders are required to build a 7-bit ripple carry adder?
a. 7
b. 2 the power of 6
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
c .2 the power of 7
d. 8
c. 2 the power of 7.
A ripple carry adder is a digital circuit that adds two binary numbers by cascading full adders
together. In a full adder, the sum and carry outputs depend on the input bits and the carry input.
To build a 7-bit ripple carry adder, we need to cascade seven full adders together. Each full adder
produces a sum bit and a carry bit, which are then fed as inputs to the next full adder. Therefore,
we need 7 full adders to add the 7 bits of the two binary numbers.
Mathematically, the number of full adders required to build an n-bit ripple carry adder is 2^(n-1),
since each full adder has two inputs and one carry input. For a 7-bit ripple carry adder, this gives
us 2^(7-1) = 2^6 = 64 possible combinations of input bits, and thus 2^6 = 64 full adders would
be required in the worst case scenario.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer, which represents the minimum number of full adders
required to build a 7-bit ripple carry adder.
17.The invalid state of an S-R latch occurs when
a. S=1, R=0
b. S=0, R=1
C.S=0, R=0
d. S= 1, R=1
An S-R latch is a digital circuit that can store one bit of information. It has two inputs, S (set) and
R (reset), and two outputs, Q (the normal output) and Q' (the complement output). The S-R latch
is said to be in an invalid state when both inputs S and R are set to logic 1 (S=1, R=1).
In this state, the outputs Q and Q' will both be set to logic 0, which is an unstable condition. If
either S or R is set to logic 0, the latch will return to a stable state, with either Q or Q' set to logic
1 and the other set to logic 0.
Option (a) represents the normal set state, where S=1 and R=0. Option (b) represents the normal
reset state, where S=0 and R=1. Option (c) represents an undefined state, where both S and R are
set to logic 0.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
18.In which of the following header file is cin and cout defined in C++?
a.<iomanip.h>
b.< iostream. h >
C. <fstream.h>
d. <iocode.h>
19.In an N-type semiconductor, the position of Fermi-level:
a. In conduction Band
b.In valance Band
C.Near valance Band
d.Near Conduction Band
20.A pulse is applied to each input of an Exclusive-OR gate. One pulse goes HIGH at 1-0 and
goes back LOW at t-Ims. The other pulse goes HIGH at t=0.8ms and goes back LOW at t-3ms.
The output pulse can be described as follows:
a. It goes HIGH at t=0 and back LOW at t=3ms
b. It goes HIGH at t=0and back LOW at t-Qems then back to HIGH at t-tms and back low at Jms
c. It goes HIGH at t-0 and back LOW at t-0.8ms
d. Igoes HIGH at t-1ms and back LOW at t-3ms
18. b. <iostream.h>
In C++, the standard input/output library is defined in the "iostream" header file. It provides the
declarations of the standard input/output stream objects, including "cin" for input and "cout" for
output.
Option (a) refers to the "iomanip" header file, which provides functions to manipulate the
input/output formatting of streams. Option (c) refers to the "fstream" header file, which provides
classes to work with files. Option (d) is not a recognized header file in C++.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
19. d. Near Conduction Band.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
In an N-type semiconductor, the majority charge carriers are electrons, which are generated by
doping the semiconductor with impurities such as phosphorus or arsenic. These impurities have
extra electrons that are loosely bound and can easily move through the crystal lattice of the
semiconductor.
The Fermi level is a measure of the energy level at which there is a 50% probability of finding an
electron. In an N-type semiconductor, the Fermi level is located near the conduction band, which
is the band of energy levels in the semiconductor that is partially filled with electrons. This is
because the majority charge carriers in an N-type semiconductor are electrons, which occupy
energy levels in the conduction band.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
20. b. It goes HIGH at t=0 and back LOW at t-0.8ms.
The Exclusive-OR (XOR) gate produces an output that is HIGH (logic 1) only when the inputs
are different, and LOW (logic 0) when the inputs are the same. In the given scenario, one input
pulse goes HIGH at t=1ms and back LOW at t=1.8ms, while the other input pulse goes HIGH at
t=0.8ms and back LOW at t=3ms.
The output pulse will go HIGH only when the inputs are different, which occurs between
t=0.8ms and t=1ms, and between t=1.8ms and t=3ms. Therefore, the output pulse will go HIGH
at t=0 and back LOW at t=0.8ms, then go HIGH again at t=1ms and back LOW at t=3ms.
Option (a) is incorrect because the output pulse does not remain HIGH from t=0 to t=3ms.
Option (c) is incorrect because the output pulse does not go back LOW at t=0.8ms. Option (d) is
incorrect because it describes the timing of one of the input pulses, not the output pulse.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
21.The total gain of a multistage amplifier is less than the product of the gains of individual
stages due to
a. The use of many capacitors
b. Power loss in the coupling device
c. The use of many transistors
d. Loading effect of the next stage
on
22.Int a=5; the word int shows
a. Ty int pe
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
b.Value
C.variable
d. Operator
21. d. Loading effect of the next stage.
In a multistage amplifier, the output of one stage is connected to the input of the next stage. The
gain of each stage is affected by the loading effect of the next stage, which can reduce the overall
gain of the amplifier. When the output of a stage is connected to the input of the next stage, it can
cause a change in the input impedance of the next stage, which can affect the gain of the next
stage.
The loading effect is caused by the input impedance of the next stage, which can act as a load on
the output of the previous stage. This can cause a reduction in the output voltage of the previous
stage, which in turn reduces the gain of the amplifier.
Option (a) is incorrect because the use of capacitors is not related to the reduction in gain of a
multistage amplifier. Option (b) is incorrect because power loss in coupling devices can also be
minimized. Option (c) is incorrect because the use of many transistors may increase the gain of
the amplifier.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
22. a. Type.
In the given statement, "int a=5;", the keyword "int" specifies the type of the variable "a" as an
integer. In C++, variables must be declared with a specific type, which determines the size and
type of data that can be stored in the variable.
Option (b) is incorrect because "5" is the initial value assigned to the variable "a", not its type.
Option (c) is incorrect because "a" is the name of the variable, not a keyword or data type.
Option (d) is incorrect because an operator is a symbol that performs a specific operation on one
or more operands.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
23.What function does booting perform when the computer is switched on?
a. Shut-down test
b. Reliability test
c. Power-on-self test
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
d. Correct functioning test
24.To measure a current out of the second resistor in a series circuit consisting of four resistors,
an Ammeter can be placed
a.At the negative terminal of the source.
b. Between the third and the fourth resistor.
C.Between the second and the third resistor.
d.At any point in the circuit.
23. c. Power-on-self test.
Booting is the process of starting a computer and loading the operating system into its memory.
When a computer is switched on, the system performs a Power-on-self test (POST) as part of the
booting process. The POST is a diagnostic process that checks the hardware components of the
computer to ensure that they are functioning correctly. It verifies the integrity of the basic
input/output system (BIOS), checks the memory and storage devices, and detects and reports any
errors or problems that are found.
Option (a) is incorrect because a shut-down test is not a recognized function performed during
booting. Option (b) is incorrect because a reliability test is not a standard function performed
during booting. Option (d) is incorrect because a correct functioning test is not a standard
function performed during booting.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
24. C. Between the second and the third resistor.
In a series circuit, the current is the same through each component. To measure the current
through a specific resistor, an ammeter must be placed in series with that resistor. It is important
to place the ammeter in the correct location to measure the current accurately.
In the given scenario, the ammeter should be placed between the second and the third resistor to
measure the current through the second resistor. This is because the current flowing through the
circuit is the same, but the voltage drop across each resistor will be different. By placing the
ammeter between the second and third resistor, it will measure the current flowing through the
second resistor only.
Option (a) is incorrect because placing the ammeter at the negative terminal of the source will
measure the total current flowing through the circuit, not the current through a specific resistor.
Option (b) is incorrect because placing the ammeter between the third and fourth resistor will
measure the current flowing through both the third and fourth resistors. Option (d) is incorrect
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
because placing the ammeter at any point in the circuit will not necessarily measure the current
through the second resistor only.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
The domain of the expression ABCD + AB + CD + Bis:
a. A and D
b.B only
c.Conly
d.A, B, C, and D
25.The given expression is:
ABCD + AB + CD + B
To determine the domain of this expression, we need to identify the variables and their possible
values that would make the expression well-defined and meaningful.
In this expression, the variables are A, B, C, and D. Since these variables are not further qualified
or restricted, we can assume that they can take any value within their respective domains.
Therefore, the domain of the expression is all possible combinations of values of A, B, C, and D.
Option (d) is the correct answer.
26. .Which of the following active filters experiences propagation delay at the input type
frequency spectrum?
a.Butterworth filter
b. Elliptical filter
c. chebyshev filter
d. Bessel filter
An active filter is a type of electronic filter that uses active components such as operational
amplifiers (op-amps) to amplify, attenuate, or reshape the input signal. Active filters are widely
used in signal processing applications such as audio processing, telecommunications, and
instrumentation.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
Propagation delay is the time delay experienced by a signal as it passes through a filter. It is
caused by the finite rise time of the filter response and the phase shift of the filter at different
frequencies.
Of the given options, the Bessel filter is the only active filter that experiences minimal
propagation delay at the input type frequency spectrum. This is because the Bessel filter has a
maximally flat group delay response, which means that all frequencies are delayed by the same
amount. This is desirable in applications where the input signal needs to be preserved without
distortion or delay, such as in audio applications or biomedical signal processing.
Option (a) is incorrect because a Butterworth filter has a frequency response that is maximally
flat in the passband, but does not have a flat group delay response. Option (b) is incorrect
because an elliptical filter has a nonlinear phase response that can cause significant propagation
delay at certain frequencies. Option (c) is incorrect because a Chebyshev filter has ripple in both
the passband and stopband, which can cause significant phase distortion and propagation delay.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer
27.An example of a peripheral unit is
a.The video monitor
b. The MPU
c. The address register
d.The interphase adapter
a. The video monitor
A peripheral unit, also known as a peripheral device, is a device that is connected to a computer
and provides additional functionality or input/output capabilities. Examples of peripheral devices
include printers, scanners, keyboards, mice, and monitors.
Of the given options, the video monitor is an example of a peripheral unit because it is a display
device that is connected to a computer and provides visual output. It is an output device that
displays the output of the computer's graphics card, allowing the user to interact with the
computer's graphical user interface (GUI) and view images, videos, and other multimedia content.
Option (b) is incorrect because the MPU (microprocessor unit) is a component within a computer
that performs processing operations, and is not a peripheral device. Option (c) is incorrect
because the address register is a component within a computer's processor that stores memory
addresses, and is not a peripheral device. Option (d) is incorrect because an interface adapter is a
device that enables communication between different devices or systems, and is not a peripheral
device in and of itself.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
28.If three bulbs are connected in parallel and two bulb blows out, what happens to the other
builb?
a. The other bulb blows out as well
b.the other bulb stops glowing
C.The other bulb glows with increased brightness
d. The other bulb continues to glow with the same brightness
29.When the crystal diode current is large, the bias is
a. reverse
b. forward
C.small
d. large
30.What happens to bandwidth if the total gain increased in cascade amplifiers?
a. Increases
b. Infinite
c.Decreases
d.Remain the same
28. d. The other bulb continues to glow with the same brightness.
In a parallel circuit, each component is connected across the same voltage source, and the
voltage across each component is the same. Therefore, if one bulb blows out, the other bulbs will
continue to operate normally because they are still connected to the same voltage source. The
current through the other bulbs will decrease because the total resistance in the circuit has
increased, but this will not necessarily cause any noticeable change in their brightness.
Option (a) is incorrect because the other bulb will not blow out as well. Option (b) is incorrect
because the other bulb will not stop glowing. Option (c) is incorrect because the other bulb will
not glow with increased brightness.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
29. b. Forward.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
A crystal diode is a type of semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction
only. It is used in rectifier circuits to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC).
The bias of a diode refers to the external voltage applied to the diode that determines its forward
or reverse operating characteristics. When the crystal diode current is large, it means that the
diode is operating in the forward bias mode. In this mode, the diode allows current to flow from
its anode to its cathode, and the voltage drop across the diode is typically around 0.7 volts for
silicon diodes.
Option (a) is incorrect because a reverse bias is when the external voltage applied to the diode is
in the opposite direction to its normal operating direction, and very little current flows through
the diode. Option (c) is incorrect because the size of the current does not determine the bias.
Option (d) is incorrect because the bias is determined by the external voltage applied to the diode,
not the current flowing through it.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
30. a. Increases.
In a cascade amplifier, multiple amplifier stages are connected in series to increase the overall
gain of the amplifier. The gain of each stage is determined by the bandwidth and gain of the
individual stage.
When the total gain is increased in a cascade amplifier, it means that the gain of each stage has
been increased. This can lead to an increase in the bandwidth of the amplifier because the
bandwidth of each stage is typically inversely proportional to its gain. As the gain of each stage
is increased, the bandwidth of each stage will also increase, resulting in an overall increase in the
bandwidth of the cascade amplifier.
Option (b) is incorrect because the bandwidth cannot be infinite in a practical amplifier. Option
(c) is incorrect because the bandwidth typically decreases as the gain increases in a single
amplifier stage, but this relationship is reversed in a cascade amplifier. Option (d) is incorrect
because the bandwidth will not remain the same when the gain is increased.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
31.The ratio of the voltage transform at the first port to the voltage transform at the second port
is known as?
a. Transfer admittance
b. Current transfer ratio
c. Voltage transfer ratio
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
d. Transfer impedance
c. Voltage transfer ratio.
In a two-port network, the voltage transfer ratio is the ratio of the output voltage to the input
voltage at each port. It is a measure of how much the voltage is amplified or attenuated as it
passes through the network.
The voltage transfer ratio can be expressed in terms of the open-circuit voltage (Voc) and the
short-circuit current (Isc) at each port. For example, for the first port, the voltage transfer ratio is
given by:
Voltage transfer ratio (port 1) = Voc1 / Vin1
Similarly, for the second port, the voltage transfer ratio is given by:
Voltage transfer ratio (port 2) = Voc2 / Vin2
The ratio of the voltage transfer ratio at the first port to the voltage transfer ratio at the second
port is known as the voltage transfer ratio ratio, or VTRR. It is given by:
VTRR = (Voc1 / Vin1) / (Voc2 / Vin2)
Option (a) is incorrect because transfer admittance is a measure of how much current flows
through the network in response to a voltage input. Option (b) is incorrect because current
transfer ratio is a measure of how much the current is amplified or attenuated as it passes through
the network. Option (d) is incorrect because transfer impedance is a measure of how much the
output voltage is affected by an input current.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
32.Which of the following is correct about the voltage transformation ratio in electrical
engineering?
a. Ratio of secondary current to the primary current.
b.Ratio of induced emf in secondary to induced emf in primary.
c.Ratio of power in primary to power in secondary.
d. Ratio of number of primary turns to the number of secondary turns.
b. Ratio of induced emf in secondary to induced emf in primary.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
In electrical engineering, voltage transformation ratio refers to the ratio of the voltage induced in
the secondary winding of a transformer to the voltage applied to the primary winding. It is a
measure of the voltage transformation capability of the transformer.
The voltage transformation ratio is determined by the turns ratio of the transformer windings.
The turns ratio is the ratio of the number of turns in the secondary winding to the number of
turns in the primary winding.
The induced emf (electromotive force) in the windings is directly proportional to the number of
turns in the winding and the rate of change of the magnetic flux linking the winding. Therefore,
the voltage transformation ratio can also be expressed as the ratio of the induced emf in the
secondary winding to the induced emf in the primary winding.
Option (a) is incorrect because the ratio of secondary current to primary current is known as the
current transformation ratio, which is determined by the turns ratio and the load impedance.
Option (c) is incorrect because the ratio of power in primary to power in secondary is not directly
related to the voltage transformation ratio, although it is related to the turns ratio and the
efficiency of the transformer. Option (d) is incorrect because the turns ratio determines the
voltage transformation ratio, but not directly.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
34.You have an application for a diode to be used in a tuning circuit. A type of diode to use
might be;
a. a Gunn .
b. a Schottky diode.
C.a varactor diode.
d. an LED.
C. A varactor diode.
A tuning circuit is a circuit that is designed to select a specific frequency or range of frequencies
from a signal. A varactor diode, also known as a variable capacitance diode or a varicap diode, is
a type of diode that is commonly used in tuning circuits.
The capacitance of a varactor diode can be varied by changing the reverse voltage across the
diode. This makes it useful for voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs), frequency synthesizers,
and other circuits that require a variable capacitance to tune to a specific frequency.
Option (a) is incorrect because a Gunn diode is a type of diode that is used in microwave
applications as a source of microwave signals. It is not typically used in tuning circuits. Option
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
(b) is incorrect because a Schottky diode is a type of diode that has a low forward voltage drop
and fast switching speed, but is not typically used in tuning circuits. Option (d) is incorrect
because an LED (light-emitting diode) is a type of diode that emits light when current flows
through it, and is not typically used in tuning circuits.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
36.Thevenin's resistance Ruh is found
a. Between any two open terminals.
b.By removing voltage sources along with their internal resistances.
c.By short-circuiting the given two terminals.
d.Between same open terminals as for Eth
37.When analyzing two port networks in parallel, which of the following is more convenient to
use?
a. 2-parameters
b. y-parameters
c.h-parameters
d. T-parameters
38.Which of the following is the correct syntax of including a user defined header files in C++?
a. #include
b. #include [userdefined]
c #include
d.#include 'userdefined"
36. Ruh (Thevenin's resistance) is found:
a. Between any two open terminals.
Thevenin's theorem is used to simplify complex circuits into an equivalent circuit that contains a
single voltage source and a single series resistance. The Thevenin resistance (Rth) is the
equivalent resistance of the circuit as seen from two open terminals where the voltage source has
been removed.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
Option (a) is the correct answer because the Thevenin resistance can be found by calculating the
resistance between any two open terminals in the circuit.
Option (b) is incorrect because removing voltage sources along with their internal resistances is
part of the process of finding the Thevenin voltage, not the Thevenin resistance. Option (c) is
incorrect because short-circuiting the given two terminals is part of the process of finding the
Norton resistance, not the Thevenin resistance. Option (d) is incorrect because the Thevenin
resistance is not necessarily between the same open terminals as the Thevenin voltage.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
37. b. y-parameters.
Two-port network parameters are used to describe the behavior of a circuit that has two
input/output ports. There are several types of two-port network parameters, including z-
parameters (impedance parameters), y-parameters (admittance parameters), h-parameters (hybrid
parameters), and t-parameters (scattering parameters).
When analyzing two-port networks in parallel, it is more convenient to use y-parameters because
they describe the relationship between the current entering and leaving each port, and are
therefore more directly related to parallel connections.
Option (a) is incorrect because 2-parameters are not commonly used in circuit analysis. Option (c)
is incorrect because h-parameters are more commonly used in amplifier analysis, and are less
directly related to parallel connections. Option (d) is incorrect because t-parameters are more
commonly used in high-frequency circuit analysis, and are less directly related to parallel
connections.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
38. a. #include <userdefined>
In C++, header files are used to define the declarations and definitions of functions, classes, and
other objects that are used in a program. Header files can be included in a C++ program using the
#include preprocessor directive.
The correct syntax for including a user-defined header file in C++ is:
#include <userdefined>
Option (a) is the correct answer because it uses angle brackets (< and >) to specify the name of
the header file, which tells the compiler to look for the file in the standard include directories.
Option (b) is incorrect because it uses square brackets instead of angle brackets. Option (c) is
incorrect because it uses double quotes instead of angle brackets, which tells the compiler to look
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
for the file in the current directory. Option (d) is incorrect because it uses single quotes instead of
angle brackets or double quotes.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
38.Tomas is willing to do his final thesis project on high gain and high tuning filter. Depending
on his idear select the appropriate filter for his project title.
a. Passive filter
b.RL filter
c.Active filter
d.RC filter
An active filter is a type of electronic filter that uses one or more active components, such as
transistors or op-amps, to amplify and shape the input signal. Active filters have higher gain and
better tuning capabilities compared to passive filters, which rely on passive components such as
resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
Since Tomas is interested in a high gain and high tuning filter for his thesis project, an active
filter would be the most appropriate choice. Active filters can be designed to have high gain and
precise frequency response characteristics, making them ideal for a wide range of applications,
including audio processing, signal conditioning, and control systems.
Option (a) is incorrect because passive filters have limited gain and tuning capabilities, and may
not be suitable for high gain and high tuning applications. Option (b) is incorrect because RL
filters are a type of passive filter that use resistors and inductors, and may not have the required
gain and tuning characteristics for Tomas's project. Option (d) is also incorrect because RC
filters are a type of passive filter that use resistors and capacitors, and may not have the required
gain and tuning characteristics for Tomas's project.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
39.A Laplace Transform exists when. L The function is piece-wise continuous il. The function is
of exponential order the
function is piecewise discrete iv. The function is of differential order
a. ini & iv
b. i'& iv
c i&il
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
d. li & iii
40.A time domain signal is considered digital if,
a.If it is has countable amplitude levels
b.It is continuous along the time axis
c.If it is discrete along the time axis
d.If it has uncountable amplitude levels
41.Often a common-collector will be the last stage before the load. The main function(s) of this
stage is
a. To provide voltage gain at the loadi
b. To provide phase inversion of the input signal
c. To buffer the voltage amplifiers from the low-resistance load and provide impedance matching
for maximum power
transfer
d. provide a high-frequency path to improve the frequency response
39. b. i' & iv.
A Laplace transform is a mathematical tool used to analyze linear time-invariant systems in the
frequency domain. It is defined for a wide range of functions, but certain conditions must be met
for the Laplace transform to exist.
Option (b) is the correct answer because a Laplace transform exists for functions that are of
exponential order, which means that there exist positive constants A and B such that |f(t)| ≤
Ae^(Bt) for all t ≥ 0. Additionally, a Laplace transform exists for functions that are of differential
order, which means that the function can be expressed as a finite linear combination of
derivatives of continuous functions.
Option (a) is incorrect because piece-wise continuity is not a sufficient condition for the
existence of a Laplace transform. Option (c) is incorrect because piecewise discreteness is not a
condition for the existence of a Laplace transform. Option (d) is incorrect because differential
order is a sufficient condition for the existence of a Laplace transform, but it is not the only
condition.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
40. c. If it is discrete along the time axis.
A time domain signal can be either continuous or discrete. A continuous-time signal is one that is
defined for all values of time, while a discrete-time signal is one that is defined only at specific
times.
In digital signal processing, signals are typically represented as discrete-time signals, which
means that the signal is sampled at specific times. A signal is considered digital if it is discrete
along the time axis.
Option (a) is incorrect because having countable amplitude levels is not a condition for a signal
to be considered digital. Option (b) is incorrect because a continuous signal can still be
considered digital if it is sampled at specific times. Option (d) is incorrect because having
uncountable amplitude levels is not a condition for a signal to be considered digital.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
41. c. To buffer the voltage amplifiers from the low-resistance load and provide impedance
matching for maximum power transfer.
A common-collector amplifier, also known as an emitter follower, is a type of transistor
amplifier that has the collector connected to the input signal, and the emitter connected to a low-
resistance load. This configuration is often used as the last stage before the load because it
provides several key functions.
One of the main functions of the common-collector stage is to buffer the voltage amplifiers from
the low-resistance load. The low-resistance load can cause significant loading effects on the
voltage amplifiers, which can degrade their performance. The common-collector stage isolates
the voltage amplifiers from the load, which helps to minimize these loading effects.
Another important function of the common-collector stage is to provide impedance matching for
maximum power transfer. The low-resistance load can present a significant impedance mismatch
to the voltage amplifiers, which can cause a loss of power transfer. The common-collector stage
is designed to provide a low output impedance, which helps to match the impedance of the
amplifier to the load for maximum power transfer.
Option (a) is incorrect because the common-collector stage typically has a voltage gain of
approximately unity, so it does not provide significant voltage gain at the load. Option (b) is
incorrect because the common-collector stage does not provide phase inversion of the input
signal. Option (d) is incorrect because the common-collector stage is not typically used to
improve the frequency response of the amplifier.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
42.When the temperature of a doped semiconductor is increased, its conductivity
a. does not change
b.increases
C. depending on its p- or n-type
d. decreases
b. Increases.
When the temperature of a doped semiconductor is increased, its conductivity generally
increases. This is because increasing the temperature causes more electrons to be excited from
the valence band to the conduction band, which increases the number of charge carriers available
for conduction.
In an n-type semiconductor, the majority charge carriers are electrons, and increasing the
temperature increases the number of free electrons available for conduction. In a p-type
semiconductor, the majority charge carriers are holes (i.e., the absence of electrons), and
increasing the temperature increases the number of holes available for conduction.
Option (a) is incorrect because the conductivity of a doped semiconductor typically does change
with temperature. Option (c) is incorrect because both p-type and n-type semiconductors exhibit
an increase in conductivity with increasing temperature. Option (d) is incorrect because
increasing the temperature generally increases the number of charge carriers available for
conduction, which leads to an increase in conductivity.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
43.What do the negative frequency components represent after transforming a time domain
signal to the freque
a. The existence of a negative frequency b. Previously sampled frequency components
c. The complex conjugate of the positive frequency components
d. The phase shift in frequency components
44.An LC circuit cannot produce oscillation, when
a. Resistance is low
b.Resistance is large
C.Inductance is large
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
d. Capacitance is large
45.In which of the following header file is cin and cout defined in C++?
a. <iostream. h >
b. <iomanip. h >
c<fstream.h>
d. <iocode. h >
43. c. The complex conjugate of the positive frequency components.
When transforming a time domain signal to the frequency domain using the Fourier transform,
the resulting frequency domain signal will typically contain both positive and negative frequency
components. The negative frequency components represent the complex conjugate of the
positive frequency components.
Specifically, if X(f) is the Fourier transform of a time domain signal x(t), then X(-f) is the
complex conjugate of X(f), where f is the frequency variable.
Option (a) is incorrect because negative frequencies do not represent the existence of a negative
frequency. Option (b) is incorrect because previously sampled frequency components are
represented by the discrete Fourier transform, not the continuous Fourier transform. Option (d) is
incorrect because the phase shift in frequency components is represented by the phase angle of
the complex frequency response.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
44. b. Resistance is large.
An LC circuit, which consists of an inductor and a capacitor connected in parallel or in series,
can produce oscillations when the energy stored in the inductor and capacitor is exchanged back
and forth between them. This exchange of energy results in a sinusoidal waveform with a
specific frequency, known as the resonant frequency of the circuit.
However, an LC circuit cannot produce oscillations when the resistance in the circuit is large.
This is because the resistance dissipates the energy stored in the inductor and capacitor,
preventing the exchange of energy needed for oscillations to occur.
Option (a), (c), and (d) are incorrect because the inductance and capacitance are essential
components of an LC circuit that enable the exchange of energy needed for oscillations to occur.
A large inductance or capacitance may affect the resonant frequency of the circuit, but it does not
prevent oscillations from occurring altogether.Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
45. a. <iostream.h>
The iostream header file is used in C++ to define the cin and cout input/output streams. These
streams allow input and output operations to be performed on the console or other devices.
The correct syntax for including the iostream header file in a C++ program is:
#include <iostream>
Option (a) is the correct answer because it uses the correct header file name, which includes the
".h" extension. Option (b) is incorrect because the iomanip header file is used to define
input/output manipulators, which are used to modify the format of data being read from or
written to a stream. Option (c) is incorrect because the fstream header file is used for file
input/output operations. Option (d) is incorrect because there is no header file named "iocode.h"
in C++.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
46.Digital logic circuits in which the logic states of the inputs at any given instant determine the
state of the output are called
a. Combinational logic circuits
b. Sequential logic circuits
c. Reasonable logic circuits
d. Automated logic circuits
a. Combinational logic circuits.
Combinational logic circuits are digital logic circuits in which the output state is solely
determined by the input state at any given instant of time. In other words, the output depends
only on the current values of the inputs and not on any past input values or the current state of
the circuit.
Combinational logic circuits are constructed using basic logic gates such as AND, OR, NOT, and
XOR gates, and are used to perform arithmetic and logical operations, encode and decode data,
and implement digital signal processing functions.
Option (b) is incorrect because sequential logic circuits depend not only on the current input state
but also on the previous state of the circuit. They contain memory elements such as flip-flops,
which store the previous state of the circuit and enable the circuit to exhibit a state-dependent
behavior. Option (c) is incorrect because there is no such thing as "reasonable logic circuits".
Option (d) is incorrect because there is no such thing as "automated logic circuits".
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
47.The energy of power signal is equivalent to
a.Infinity
b.One
c. Very small
d.Zero
The energy of a power signal is infinite, which is represented by the symbol ∞.
This is because a power signal is defined as a signal whose power is finite, but whose duration is
infinite. Mathematically, the energy of a power signal is given by the integral of the squared
magnitude of the signal over an infinite time interval. Since the time interval is infinite, the
integral diverges to infinity, indicating that the energy is infinite.
Therefore, the answer is (a) Infinity.
48.In superposition theorem, when we consider the effect of one voltage source, all the other
voltage sources are:
a.Removed
b. Opened
c. Undisturbed
d. Shorted
In the superposition theorem, when we consider the effect of one voltage source, all the other
voltage sources are "turned off" or "disabled". This means that they are either removed or
shorted out, depending on whether they are ideal voltage sources or real voltage sources.
If the other voltage sources are ideal voltage sources, they are shorted out. This is because ideal
voltage sources have zero internal resistance and can supply an infinite amount of current, which
would interfere with the analysis of the circuit.
If the other voltage sources are real voltage sources, they are generally removed from the circuit.
This is because real voltage sources have finite internal resistance and can only supply a limited
amount of current. Removing them from the circuit simplifies the analysis and avoids potential
errors in the calculations.
Therefore, the answer is (a) Removed (for ideal voltage sources) or (d) Shorted (for real voltage
sources).
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……..
1) An LC circuit cannot produce oscillation
a.Resistance is low
b.Resistance is large
c.Inductance is large
d.Capacitance is large
An LC (inductor-capacitor) circuit is a type of resonant circuit that can produce oscillations at a
specific frequency. However, the conditions for oscillations to occur depend on the values of the
components in the circuit. The correct answer to the question is (b) Resistance is large.
The condition for oscillations to occur in an LC circuit is that the total energy stored in the circuit
must be conserved and exchanged between the inductor and capacitor. In other words, the energy
must oscillate back and forth between the inductor and capacitor, which causes the oscillations.
However, if the resistance in the circuit is too large, the energy stored in the circuit will be
dissipated as heat instead of being exchanged between the inductor and capacitor. This means
that the circuit will not be able to sustain the oscillations, and the oscillations will die out quickly.
Therefore, if the resistance in an LC circuit is too large, the circuit will not be able to produce
oscillations. The correct answer is (b) Resistance is large.
2)In which of the following header file is cin and cout defined in C++?
a.< iostream. h >
b.< iomanip. h >
C.<fstream. h>
d.<iocode. h>
In modern C++, the header file that defines the standard input/output streams `cin` and `cout` is
`<iostream>`. Therefore, the correct answer is (a) `<iostream.h>`.
The `<iostream>` header file contains the declarations for the standard input/output streams `cin`,
`cout`, `cerr` and `clog`, as well as the necessary functions and operators for input/output
operations, such as `<<` and `>>`.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
It's important to note that in older versions of C++, the header file `<iostream.h>` was used
instead of `<iostream>`. However, the former is now deprecated and the latter is the preferred
header file to use for C++ input/output operations.
The other options listed, `<iomanip.h>`, `<fstream.h>`, and `<iocode.h>`, are header files that
define other functionalities in C++: `<iomanip>` is used for input/output manipulators,
`<fstream>` is used for file input/output operations, and `<iocode>` is not a standard header file
in C++.
3) The signal is said to be
whenever we can define a signal at an instant of time
a. Both deterministic and non-deterministic
b. Deterministic
c. Continues
d. Non-Deterministic
The signal is said to be deterministic whenever we can define a signal at an instant of time.
Therefore, the correct answer is (b) Deterministic.
In signal processing, a deterministic signal is a signal that can be completely described by a
mathematical function or an analytical expression. This means that for any given time, the value
of the signal can be determined with certainty, and there is no randomness or uncertainty
involved.
Examples of deterministic signals include sinusoidal signals, square waves, and triangular waves.
These signals can be described by mathematical functions or formulas that precisely define their
values at any given time.
In contrast, a non-deterministic signal, also known as a stochastic signal, is a signal that has
some degree of randomness or uncertainty involved. Examples of non-deterministic signals
include noise signals and random processes, which cannot be completely described by a
mathematical function or expression.
Therefore, whenever we can precisely define a signal at an instant of time, the signal is said to be
deterministic.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
4)A combinational circuit which is used to change a decimal number into an equivalent BCD:
number is ?
a. Decoder
b. De-multiplexer
c. Multiplexer
d. Encoder
The combinational circuit which is used to change a decimal number into an equivalent BCD
(Binary Coded Decimal) number is an Encoder. Therefore, the correct answer is (d) Encoder.
An Encoder is a combinational circuit that converts an input signal into a coded output signal. In
the case of decimal-to-BCD conversion, the decimal number (consisting of 10 possible digits 0-9)
is the input signal, and the BCD code (consisting of four bits for each decimal digit) is the output
signal.
The BCD code represents each decimal digit with a binary code, where each digit is represented
by a four-bit binary number. For example, the decimal digit 5 is represented by the BCD code
0101.
Therefore, an Encoder is used to convert a decimal number into its equivalent BCD code by
encoding each decimal digit into its corresponding four-bit binary code.
In summary, an Encoder is a combinational circuit that is used to convert an input signal into a
coded output signal, and in the case of decimal-to-BCD conversion, an Encoder is used to
convert a decimal number into its equivalent BCD code.
5) When transistors are used in digital circuits they usually operate in the......
A. saturation and cutoff regions
B.active region
C. linear region
D.breakdown region
When transistors are used in digital circuits, they usually operate in the saturation and cutoff
regions. Therefore, the correct answer is (A) saturation and cutoff regions.
In digital circuits, transistors are commonly used as switches to control the flow of current
between different parts of the circuit. In order to achieve this, the transistor is operated in either
the saturation region or the cutoff region, depending on whether the switch is on or off.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
In the saturation region, the transistor is fully turned on, and there is a large current flowing
between the collector and emitter terminals. This is the "on" state of the switch, and it is used to
represent a logic "1" in digital circuits.
In the cutoff region, the transistor is fully turned off, and there is no current flowing between the
collector and emitter terminals. This is the "off" state of the switch, and it is used to represent a
logic "0" in digital circuits.
Therefore, when transistors are used in digital circuits, they usually operate in the saturation and
cutoff regions. The active region and linear region are used in analog circuits to amplify signals,
but they are not typically used in digital circuits. The breakdown region is a region of operation
that should be avoided, as it can cause damage to the transistor.
6)While Thevenizing a circuit between two terminals Vth is equal to
A) E.M.F. of the battery nearest to the terminals
B) Net voltage available in the circuit
C)Short-circuit terminal voltage
D) open-circuit terminal voltage
While Thevenizing a circuit between two terminals, Vth is equal to the open-circuit terminal
voltage. Therefore, the correct answer is (D) open-circuit terminal voltage.
The Thevenin's theorem states that any linear circuit can be replaced by an equivalent circuit
consisting of a voltage source in series with a resistor, known as the Thevenin equivalent circuit.
The equivalent voltage source is equal to the open-circuit voltage at the terminals of the circuit,
and the equivalent resistance is equal to the resistance seen by the circuit when all the
independent sources are turned off.
To find the Thevenin equivalent circuit, we need to calculate the open-circuit voltage at the
terminals of the circuit. This is the voltage that would be measured across the terminals if we
disconnected any loads connected to the circuit. By doing so, we create an open circuit, and the
voltage measured across the open terminals is the open-circuit terminal voltage.
Therefore, when Thevenizing a circuit between two terminals, Vth is equal to the open-circuit
terminal voltage.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
7) A filter that passes frequency between two designated cut-off frequencies fe and attenuates al
other frequencies greater than
fc is
a. Band elimination filter
b. High pass filter
c Low pass filter
d. Band pass filter
A filter that passes frequency between two designated cut-off frequencies fe and attenuates all
other frequencies greater than fc is a Band Pass Filter. Therefore, the correct answer is (d) Band
Pass Filter.
A Band Pass Filter is a type of filter that allows signals within a certain frequency range (known
as the passband) to pass through the filter while attenuating or blocking signals outside of that
range (known as the stopband). The passband is defined by two cutoff frequencies, fe and fc,
which are the frequencies at which the filter's output is reduced by a certain amount compared to
the maximum output. Frequencies within the passband are amplified or passed through the filter,
while frequencies outside the passband are attenuated or blocked.
In contrast, a Low Pass Filter allows signals with frequencies below a certain cutoff frequency to
pass through the filter, while attenuating signals with frequencies above that cutoff frequency. A
High Pass Filter allows signals with frequencies above a certain cutoff frequency to pass through
the filter, while attenuating signals with frequencies below that cutoff frequency. A Band
Elimination Filter, also known as a Notch Filter, attenuates signals within a specific frequency
range, while passing signals outside of that range.
Therefore, the filter that passes frequencies between two designated cutoff frequencies and
attenuates all other frequencies greater than fc is a Band Pass Filter.
8) Which one of the following is the purpose of a wide band-pass filter?
a. Zero noise
b. Sharp cut-off frequency value
c. Sharp bandwidth value
d. Sharp bandwidth and sharp cut-off frequency value
The purpose of a wide band-pass filter is to have a sharp bandwidth value. Therefore, the correct
answer is (c) Sharp bandwidth value.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
A band-pass filter is a type of electronic filter that allows signals within a certain frequency
range, known as the passband, to pass through the filter, while attenuating or blocking signals
outside of that range, known as the stopband. The bandwidth of a band-pass filter is the range of
frequencies within the passband, and a wide band-pass filter has a larger bandwidth than a
narrow band-pass filter.
A wide band-pass filter is designed to have a broad range of frequencies within the passband,
making it useful for applications that require the transmission or amplification of signals over a
wide range of frequencies. However, a wide band-pass filter still needs to have a sharp
bandwidth value to ensure that only the desired frequencies are passed through the filter, and that
signals outside of the passband are attenuated or blocked.
Sharp bandwidth value means that the filter has a well-defined passband and a steep transition
between the passband and the stopband. This ensures that the filter only passes signals within a
specific frequency range, while attenuating or blocking signals outside of that range. Therefore, a
wide band-pass filter with a sharp bandwidth value is useful for applications such as audio
processing, radio communications, and scientific instrumentation, where signals with a wide
range of frequencies need to be transmitted or analyzed.
8) If Av, Ai, and Ap represents the voltage gain, current gain and power gain ratio of an
amplifier which of the following is correct
expression for the corresponding values in decibel?
a Power gain: (20 log Ap dB
b. Power gain: 20 log Ap dB
c .Voltage gain: (10 log Av dB \)
d. Current gain: 10 log AvdB
The correct expressions for the corresponding values in decibel are:
a) Power gain: 10 log (Ap) dB
b) Voltage gain: 20 log (Av) dB
c) Current gain: 20 log (Ai) dB
In general, the decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two values, such as
power, voltage, or current. The decibel value for a given ratio is calculated as 10 times the
logarithm to base 10 of that ratio.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
By: Ayalsew .F
For power gain, the decibel expression is 10 log (Ap) dB, where Ap is the power gain ratio of the
amplifier. This expression represents the decibel value of the ratio of output power to input
power.
For voltage gain, the decibel expression is 20 log (Av) dB, where Av is the voltage gain ratio of
the amplifier. This expression represents the decibel value of the ratio of output voltage to input
voltage.
For current gain, the decibel expression is 20 log (Ai) dB, where Ai is the current gain ratio of
the amplifier. This expression represents the decibel value of the ratio of output current to input
current.
Therefore, the correct expression for the power gain in decibel is 10 log (Ap) dB, and the correct
expressions for the voltage and current gains in decibel are 20 log (Av) dB and 20 log (Ai) dB,
respectively.
Exit Model pdf Electrical and computer Eng
You might also like
- HVAC Control Systems and Building Automation System PDFDocument19 pagesHVAC Control Systems and Building Automation System PDFStephany Montero100% (5)
- User Manual: Telemetry UnitDocument17 pagesUser Manual: Telemetry UnitChristian Vasquez MedranoNo ratings yet
- MosfetDocument8 pagesMosfetHarshit OjhaNo ratings yet
- Principles and Applications of MOSFET and JFET MosfetDocument5 pagesPrinciples and Applications of MOSFET and JFET MosfetKim KimNo ratings yet
- Example A: Find The Resistance of 6.5 M of Wire, Diameter 0.6 MM, If TheDocument4 pagesExample A: Find The Resistance of 6.5 M of Wire, Diameter 0.6 MM, If TheTara GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 3-PPT MosfetDocument28 pages3-PPT MosfetVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Mosfet Diode TransistorDocument45 pagesUnit3 Mosfet Diode TransistorPriyanshu yadavNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument61 pages1 Introductionfiraol temesgenNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument25 pagesMini Projectcharan524No ratings yet
- ETI 2203 Lesson 7Document10 pagesETI 2203 Lesson 7amash.emillyNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 8Document6 pagesExperiment No. 8LoraineCundangan-medinaNo ratings yet
- Unit - Vi Field Effect TransistorDocument16 pagesUnit - Vi Field Effect TransistorBhavaniPrasadNo ratings yet
- Mosfet SaiDocument35 pagesMosfet SaiDisha GoelNo ratings yet
- BEng FETDocument13 pagesBEng FETJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Field Effect Transistor NotesDocument21 pagesField Effect Transistor NotessaraswatnidhiNo ratings yet
- Mofet - IGBT - SCR - Traic - Snubber CKTDocument17 pagesMofet - IGBT - SCR - Traic - Snubber CKTTejas krishnakanthNo ratings yet
- CMOS Interview QuestionsDocument52 pagesCMOS Interview QuestionsKAMARUDHEEN KP100% (1)
- BEEE NotesDocument23 pagesBEEE Notessonali2408100% (6)
- Observations: Experimental ValuesDocument7 pagesObservations: Experimental ValuesShibeshwar MandalNo ratings yet
- SD 3rd Module MOSFETDocument8 pagesSD 3rd Module MOSFETPranathi GNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Group-B Q&aDocument13 pagesVlsi Group-B Q&aROHAN CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- CMOS Interview QADocument14 pagesCMOS Interview QAarammartNo ratings yet
- Design of Cmos BufferDocument5 pagesDesign of Cmos BufferVarunKaradesaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document39 pagesLecture 1Nuniwal JyotiNo ratings yet
- Leakage CurrentDocument5 pagesLeakage CurrentImam WijayaNo ratings yet
- MOSFET As A SwitchDocument11 pagesMOSFET As A Switchrahul samanta100% (1)
- JFETDocument20 pagesJFETMenzi TabilidNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document7 pagesAssignment 3Arnon PukhrambamNo ratings yet
- The Range of Can Be Specified Over Which The Gain Does Not Deviate More Than 70.7% of The Maximum Gain at Some Reference MidDocument21 pagesThe Range of Can Be Specified Over Which The Gain Does Not Deviate More Than 70.7% of The Maximum Gain at Some Reference MidRiyaz PashaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word Document-1Document4 pagesNew Microsoft Word Document-1Agaba SamuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Field Effect TransistorsDocument48 pagesChapter 10 Field Effect TransistorsanjugaduNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - FET - WatermarkDocument16 pagesMODULE 1 - FET - WatermarkAnupama MohananNo ratings yet
- EI2301-IE - Unit 1 - Part A and Part B - With Answers PDFDocument21 pagesEI2301-IE - Unit 1 - Part A and Part B - With Answers PDFsartpgitNo ratings yet
- Field Effect Transistors (FET) : Comparison Between BJT and FETDocument9 pagesField Effect Transistors (FET) : Comparison Between BJT and FETpranavraikar1No ratings yet
- The Basic Structure: Field Effect TransistorDocument10 pagesThe Basic Structure: Field Effect TransistormokhaladNo ratings yet
- Ece-Research Work 1Document10 pagesEce-Research Work 1Peale ObiedoNo ratings yet
- Tunnel DiodeDocument56 pagesTunnel DiodeNaveed Ramzan100% (2)
- Electronics Hons C3 FET Field Effect TransistorDocument21 pagesElectronics Hons C3 FET Field Effect TransistorGawrav BaishyaNo ratings yet
- VLSI PresentationDocument8 pagesVLSI PresentationKazi MidulNo ratings yet
- Mosfet Lab 2Document11 pagesMosfet Lab 2Jaime Aguilar100% (1)
- Final MosfetDocument33 pagesFinal MosfetabdallaNo ratings yet
- Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Document6 pagesMetal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Yasir KhanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS (FET) EditDocument58 pagesCHAPTER 5 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS (FET) Editruhiyahnazihah_15106No ratings yet
- Technical Examination Level - 7Document37 pagesTechnical Examination Level - 7Madhunath YadavNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Transistor Models and The Feedback Amp - Docmicrosoft Word - Transistor Models and The Feedback Amp - Doctransistor - Models - and - The - FbaDocument14 pagesMicrosoft Word - Transistor Models and The Feedback Amp - Docmicrosoft Word - Transistor Models and The Feedback Amp - Doctransistor - Models - and - The - FbashubhamformeNo ratings yet
- Field Effect TransistorDocument13 pagesField Effect TransistorLORD TNo ratings yet
- MosfetDocument23 pagesMosfetgopikrishna yarlagaddaNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechatronic Engineering: Power DiodeDocument12 pagesDepartment of Mechatronic Engineering: Power DiodeEng King'e FredrickNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Field Effect Transistors: A. Introduction To FetsDocument10 pagesChapter 8: Field Effect Transistors: A. Introduction To FetsBmanNo ratings yet
- Unit III Jfet - MosfetDocument20 pagesUnit III Jfet - Mosfet1akshat341No ratings yet
- Field Effect Transistor (FET) : Department of Physics Guru Jambheshwar University of Science & Technology HisarDocument13 pagesField Effect Transistor (FET) : Department of Physics Guru Jambheshwar University of Science & Technology HisarAnkita Sharma1610No ratings yet
- True FalseDocument5 pagesTrue FalseShuvodip Das50% (2)
- V. Mosfet PDFDocument33 pagesV. Mosfet PDFleeminho_janxiNo ratings yet
- Assignment FET 2Document3 pagesAssignment FET 2shobanraj1995No ratings yet
- Name Ali Muneer Sap Id 70070422 Subject Basic Electronics Section GDocument9 pagesName Ali Muneer Sap Id 70070422 Subject Basic Electronics Section GRana HusnainNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Semi Conductor DevicesDocument4 pagesCH 9 Semi Conductor Devicesscholars learningNo ratings yet
- Field Effect TransistorsDocument6 pagesField Effect TransistorsMunna HossainNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)No ratings yet
- Revised Competency in Computer Science and Engineering 2024Document11 pagesRevised Competency in Computer Science and Engineering 2024hailomasegede27No ratings yet
- No. Name Fname Gfname Request - NoDocument215 pagesNo. Name Fname Gfname Request - Nohailomasegede27100% (1)
- Revised Exit Exam Blue Print For Computer Science and EngineeringDocument16 pagesRevised Exit Exam Blue Print For Computer Science and Engineeringhailomasegede27100% (1)
- No. Name Fname Gfname Request - NoDocument88 pagesNo. Name Fname Gfname Request - Nohailomasegede27No ratings yet
- No. Name Fname Gfname Request - NoDocument86 pagesNo. Name Fname Gfname Request - Nohailomasegede27100% (1)
- No. Name Fname Gfname Request - NoDocument12 pagesNo. Name Fname Gfname Request - Nohailomasegede27No ratings yet
- Evaluation Condition of Transformer Based On Infrared Thermography ResultsDocument4 pagesEvaluation Condition of Transformer Based On Infrared Thermography Resultscarlos patrickNo ratings yet
- Kue Oem Hurm KitsDocument20 pagesKue Oem Hurm KitsChí Khang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Lpcxpresso1115 With Cmsis Dap SCHDocument4 pagesLpcxpresso1115 With Cmsis Dap SCHAnkur SharmaNo ratings yet
- Manual Do Gerador de SinalDocument11 pagesManual Do Gerador de Sinalmanoel seraphimNo ratings yet
- User Manual Capacitor Type GeneratorDocument17 pagesUser Manual Capacitor Type GeneratorUMA AKANDU UCHENo ratings yet
- 800 10684 PDFDocument1 page800 10684 PDFМаксNo ratings yet
- EE 313 - LAB Project - ECD - 2020Document2 pagesEE 313 - LAB Project - ECD - 2020Muhammad YousafNo ratings yet
- Megger Earth TesterDocument3 pagesMegger Earth TesterAhmad RobbyNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Electric Loads PDFDocument1 pageVehicle Electric Loads PDFphoneme79No ratings yet
- Resume of Mohammad YousufDocument2 pagesResume of Mohammad YousufEngr Mohammad YousufNo ratings yet
- Chapter One History and Evolution of Telecommunication NetworksDocument58 pagesChapter One History and Evolution of Telecommunication NetworksTibebu Xibe TeNo ratings yet
- Final Presentation - SanneDocument18 pagesFinal Presentation - SanneAnh TranNo ratings yet
- BMW Transmission Specs 2004Document15 pagesBMW Transmission Specs 2004gabriela sanguinoNo ratings yet
- Measuring Gigaohms With A Simple MultimeterDocument11 pagesMeasuring Gigaohms With A Simple MultimeterZIASY Shesmer100% (1)
- P Series Ciac Service Manual 30,36K FVDocument108 pagesP Series Ciac Service Manual 30,36K FVAnthony Pineda ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Antenna CatalogDocument50 pagesAntenna CatalogashishsinghchouhanNo ratings yet
- Bpe MicroprojectDocument19 pagesBpe Microproject10 Durvesh PathakNo ratings yet
- ISO 26262: Functional Safety Standard For Modern Road VehiclesDocument15 pagesISO 26262: Functional Safety Standard For Modern Road VehiclesH MORENONo ratings yet
- Epson PRO-G7905U - PROD - SPEC - R1Document2 pagesEpson PRO-G7905U - PROD - SPEC - R1DANIEL ALFONSO GREIFF DAVILANo ratings yet
- CH 07Document56 pagesCH 07miathegirl9No ratings yet
- Circuit Builder Acitivity B and CDocument3 pagesCircuit Builder Acitivity B and CSujatha VimalNo ratings yet
- NT68169UFGDocument1 pageNT68169UFGaldinaenNo ratings yet
- Automatic Room ControllerDocument14 pagesAutomatic Room ControllerAbiraja BNo ratings yet
- Mag Pi 119Document100 pagesMag Pi 119Aro2006No ratings yet
- Multi V S (Side Discharge) CatalogDocument1 pageMulti V S (Side Discharge) CatalogKyaw San Oo100% (1)
- Work Instruction: Range/principleDocument3 pagesWork Instruction: Range/principleLim ChsNo ratings yet
- KJ4-M18MB80-ANU: Product Description Inductive Sensor AnalogueDocument2 pagesKJ4-M18MB80-ANU: Product Description Inductive Sensor AnalogueBAHARO ALYAUMA IEDNo ratings yet
- FKEN 604.18GS4 Switch de FlujoDocument1 pageFKEN 604.18GS4 Switch de FlujoRigoberto HerreraNo ratings yet