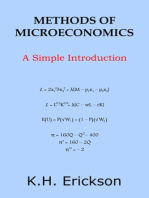
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hsslive XII CH 2 Addnl Notes
Hsslive XII CH 2 Addnl Notes
Uploaded by
BabaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Microeconomics Chapter 4Document15 pagesMicroeconomics Chapter 4Ian Jowmariell GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Cardinal UtilityDocument6 pagesCardinal UtilityShadowNo ratings yet
- EQUI Marginal Concept-WordDocument4 pagesEQUI Marginal Concept-Wordnithinsdn100% (2)
- R Micro-1Document44 pagesR Micro-1Täð Œvê MîðNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior BsaDocument9 pagesConsumer Behavior Bsaamosoundo59No ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Theory of Consumer BehaviorDocument58 pagesChapter Two: Theory of Consumer BehaviorOromay EliasNo ratings yet
- Chapter I Consumer Behavior Page ofDocument30 pagesChapter I Consumer Behavior Page oftegegn mogessieNo ratings yet
- Consumers EquilibriumDocument52 pagesConsumers EquilibriumabdanNo ratings yet
- Eco PDFDocument52 pagesEco PDF203 596 Reuben RoyNo ratings yet
- Consumer Equalibrium - Unit 3Document19 pagesConsumer Equalibrium - Unit 3JEHAN mNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Consumer BevaviourDocument65 pagesUnit 2 Consumer BevaviourSangam KarkiNo ratings yet
- Utility Analysis - Engineering EconomicsDocument15 pagesUtility Analysis - Engineering EconomicsPankaj Gill100% (2)
- Screenshot 2023-01-12 at 11.39.38 AMDocument44 pagesScreenshot 2023-01-12 at 11.39.38 AMfebinpaulk4uNo ratings yet
- Unit One: Theory of Consumer Behavior and DemandDocument33 pagesUnit One: Theory of Consumer Behavior and DemandmilkesomidaksaNo ratings yet
- Null 3Document9 pagesNull 3preciouskazvita7No ratings yet
- Consumer's EquilibriumDocument34 pagesConsumer's Equilibriumkcsujan8No ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviorDocument9 pagesConsumer Behaviortitusjunior23No ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument4 pagesConsumer Behavioursid.samir2203No ratings yet
- Concept of Utility (TU, MU)Document10 pagesConcept of Utility (TU, MU)Tanya MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Consumer's Equilibrium: PsychologicalDocument1 pageConsumer's Equilibrium: PsychologicalGT ANUPNo ratings yet
- Utility AnalysisDocument15 pagesUtility AnalysisRahul RamchandaniNo ratings yet
- Assignmemt: Subject: Submitted To: Submitted By: Registration No: Date: DepartmentDocument8 pagesAssignmemt: Subject: Submitted To: Submitted By: Registration No: Date: DepartmentShadowNo ratings yet
- The Theory of ConsumerDocument31 pagesThe Theory of ConsumerMahendra ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument29 pagesChapter OneLakachew GetasewNo ratings yet
- Assignment of EconomicsDocument2 pagesAssignment of Economicsm_a_n_oNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument22 pagesConsumer Behaviouryai giniNo ratings yet
- Consumer Equilibrium 1Document14 pagesConsumer Equilibrium 1ovaisamjad720No ratings yet
- Principles of Economics BBA 103 NDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Economics BBA 103 NPritee SinghNo ratings yet
- Utility AnalysisDocument9 pagesUtility AnalysisJulfikar asifNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2Document14 pagesUnit - 2hoioljmmbhpgmryaheNo ratings yet
- CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR. BBSdocxDocument14 pagesCONSUMER BEHAVIOUR. BBSdocxkatana zamNo ratings yet
- Micro I Notes (Up To End)Document129 pagesMicro I Notes (Up To End)yimerNo ratings yet
- UtilityDocument15 pagesUtilityrupeshdahake8586No ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument17 pagesEconomicssyedasadanwer3290No ratings yet
- Unit 2 RevisedDocument24 pagesUnit 2 Revisedyai giniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5. Consumer BehaviorDocument9 pagesLecture 5. Consumer BehaviorJhon PerezNo ratings yet
- Theory of Consumer BehaviourDocument11 pagesTheory of Consumer BehaviourRaphinos VakachaNo ratings yet
- Micro Chap 1Document44 pagesMicro Chap 1GuNo ratings yet
- Demand Under Consumer BehaviorDocument18 pagesDemand Under Consumer BehaviorGhulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Economics Chapter - 3?!?Document27 pagesEconomics Chapter - 3?!?Eliyas BeniyamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Consumer Demand TheoryDocument40 pagesChapter 5. Consumer Demand Theoryhurricane2010100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document34 pagesChapter 3josephyoseph97No ratings yet
- Consumers EquilibriumDocument11 pagesConsumers EquilibriumYash MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 EconomicsDocument22 pagesChapter 3 EconomicsAbdi TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Eco 123 Topic 2 Consumer Behaviour-1Document142 pagesEco 123 Topic 2 Consumer Behaviour-1raphael shingishaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Theory of Consumer BehaviorDocument34 pagesChapter Three: Theory of Consumer BehaviorWaaqoo Guutuu Waaqoo GuutuuNo ratings yet
- Eoc 5Document12 pagesEoc 5Maiwand BabakarkhailNo ratings yet
- Utility AnalysisDocument13 pagesUtility AnalysisRohika K.C.No ratings yet
- Utility Analysis EcontentDocument11 pagesUtility Analysis EcontentMRS.NAMRATA KISHNANI BSSSNo ratings yet
- Cardinal Utility RevisedDocument22 pagesCardinal Utility Revisedfe23samarthNo ratings yet
- Theory of Consumer BehaviorDocument11 pagesTheory of Consumer BehaviorTamar Y.No ratings yet
- Class 12 Micro Economics Chapter 2 - Revision NotesDocument23 pagesClass 12 Micro Economics Chapter 2 - Revision NotesSachin PalNo ratings yet
- H.P National Law University, Shimla: Assignment of "Economics" (Assignment Second)Document20 pagesH.P National Law University, Shimla: Assignment of "Economics" (Assignment Second)tarun chhapolaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 - Consumer EquilibriumDocument17 pagesUnit - 3 - Consumer Equilibriumsaravanan100% (1)
- Law of Diminishing Marginal UtilityDocument15 pagesLaw of Diminishing Marginal Utilitypoudelsandesh12345678No ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument32 pagesConsumer Behaviourgrouprocks4No ratings yet
- UtilityDocument7 pagesUtilitysn nNo ratings yet
- Wa0033.Document3 pagesWa0033.zb77338No ratings yet
- Methods of Microeconomics: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMethods of Microeconomics: A Simple IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
Hsslive XII CH 2 Addnl Notes
Hsslive XII CH 2 Addnl Notes
Uploaded by
BabaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hsslive XII CH 2 Addnl Notes
Hsslive XII CH 2 Addnl Notes
Uploaded by
BabaCopyright:
Available Formats
Micro economics Theory of consumer behaviour
UTILITY
Utility of a commodity is defined its want-satisfying capacity.
Cardinal Utility Analysis
Cardinal utility analysis assumes that level of utility can be expressed in numbers. It can be measure with the
unit Utile.
Total Utility(TU): Total utility of a commodity is the total satisfaction derived from consuming the given
amount of the commodity. Consumption of More units of a commodity provides more satisfaction to the
consumer. Total Utility depends on the quantity of the commodity consumed. Therefore, TUn refers to total
utility derived from consuming n units of a commodity.
Marginal Utility: Marginal utility (MU) is the change in total utility due to consumption of one additional unit
of a commodity. In general, MUn = TUn – TU(n-1), here n refers to the nth unit of the commodity
In other way we can say that Total utility the sum total of marginal utility. Total utility and marginal utility can
also be related in the following way.
TUn = MU1 + MU2 + … + MU(n-1) + MUn
LAW OF DIMINISHING MARGINAL UTILITY
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility states that marginal utility from consuming each additional unit
of a commodity declines as its consumption increases, while keeping consumption of other commodities
constant. The following table and diagram shows the law of diminishing marginal utility.
Total Marginal
Units
utility utility
1 12 12
2 18 6
3 22 4
4 24 2
5 24 0
6 22 -2
The above table and diagram show that the total utility increases but at a diminishing rate. The marginal
utility diminishes with increase in consumption of the commodity from 12 to 6, 6 to 4 and so on. This follows
from the law of diminishing marginal utility. MU becomes zero at a level when TU remains constant. In the
example, TU does not change at 5th unit of consumption and therefore MU = 0. Thereafter, TU starts falling
and MU becomes negative.
Ordinal Utility Analysis
Under this analysis the consumer cannot measure utility, but he can able to rank the utility obtained from
the consumption of different bundles. We use Indifference curves to represent this.
PREPARED BY RAJESH.S, K.T.C.T.E.M.H.S.S KADUVAYIL, THIRUVANANTHAPURAM
You might also like
- Microeconomics Chapter 4Document15 pagesMicroeconomics Chapter 4Ian Jowmariell GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Cardinal UtilityDocument6 pagesCardinal UtilityShadowNo ratings yet
- EQUI Marginal Concept-WordDocument4 pagesEQUI Marginal Concept-Wordnithinsdn100% (2)
- R Micro-1Document44 pagesR Micro-1Täð Œvê MîðNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior BsaDocument9 pagesConsumer Behavior Bsaamosoundo59No ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Theory of Consumer BehaviorDocument58 pagesChapter Two: Theory of Consumer BehaviorOromay EliasNo ratings yet
- Chapter I Consumer Behavior Page ofDocument30 pagesChapter I Consumer Behavior Page oftegegn mogessieNo ratings yet
- Consumers EquilibriumDocument52 pagesConsumers EquilibriumabdanNo ratings yet
- Eco PDFDocument52 pagesEco PDF203 596 Reuben RoyNo ratings yet
- Consumer Equalibrium - Unit 3Document19 pagesConsumer Equalibrium - Unit 3JEHAN mNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Consumer BevaviourDocument65 pagesUnit 2 Consumer BevaviourSangam KarkiNo ratings yet
- Utility Analysis - Engineering EconomicsDocument15 pagesUtility Analysis - Engineering EconomicsPankaj Gill100% (2)
- Screenshot 2023-01-12 at 11.39.38 AMDocument44 pagesScreenshot 2023-01-12 at 11.39.38 AMfebinpaulk4uNo ratings yet
- Unit One: Theory of Consumer Behavior and DemandDocument33 pagesUnit One: Theory of Consumer Behavior and DemandmilkesomidaksaNo ratings yet
- Null 3Document9 pagesNull 3preciouskazvita7No ratings yet
- Consumer's EquilibriumDocument34 pagesConsumer's Equilibriumkcsujan8No ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviorDocument9 pagesConsumer Behaviortitusjunior23No ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument4 pagesConsumer Behavioursid.samir2203No ratings yet
- Concept of Utility (TU, MU)Document10 pagesConcept of Utility (TU, MU)Tanya MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Consumer's Equilibrium: PsychologicalDocument1 pageConsumer's Equilibrium: PsychologicalGT ANUPNo ratings yet
- Utility AnalysisDocument15 pagesUtility AnalysisRahul RamchandaniNo ratings yet
- Assignmemt: Subject: Submitted To: Submitted By: Registration No: Date: DepartmentDocument8 pagesAssignmemt: Subject: Submitted To: Submitted By: Registration No: Date: DepartmentShadowNo ratings yet
- The Theory of ConsumerDocument31 pagesThe Theory of ConsumerMahendra ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument29 pagesChapter OneLakachew GetasewNo ratings yet
- Assignment of EconomicsDocument2 pagesAssignment of Economicsm_a_n_oNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument22 pagesConsumer Behaviouryai giniNo ratings yet
- Consumer Equilibrium 1Document14 pagesConsumer Equilibrium 1ovaisamjad720No ratings yet
- Principles of Economics BBA 103 NDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Economics BBA 103 NPritee SinghNo ratings yet
- Utility AnalysisDocument9 pagesUtility AnalysisJulfikar asifNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2Document14 pagesUnit - 2hoioljmmbhpgmryaheNo ratings yet
- CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR. BBSdocxDocument14 pagesCONSUMER BEHAVIOUR. BBSdocxkatana zamNo ratings yet
- Micro I Notes (Up To End)Document129 pagesMicro I Notes (Up To End)yimerNo ratings yet
- UtilityDocument15 pagesUtilityrupeshdahake8586No ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument17 pagesEconomicssyedasadanwer3290No ratings yet
- Unit 2 RevisedDocument24 pagesUnit 2 Revisedyai giniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5. Consumer BehaviorDocument9 pagesLecture 5. Consumer BehaviorJhon PerezNo ratings yet
- Theory of Consumer BehaviourDocument11 pagesTheory of Consumer BehaviourRaphinos VakachaNo ratings yet
- Micro Chap 1Document44 pagesMicro Chap 1GuNo ratings yet
- Demand Under Consumer BehaviorDocument18 pagesDemand Under Consumer BehaviorGhulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Economics Chapter - 3?!?Document27 pagesEconomics Chapter - 3?!?Eliyas BeniyamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Consumer Demand TheoryDocument40 pagesChapter 5. Consumer Demand Theoryhurricane2010100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document34 pagesChapter 3josephyoseph97No ratings yet
- Consumers EquilibriumDocument11 pagesConsumers EquilibriumYash MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 EconomicsDocument22 pagesChapter 3 EconomicsAbdi TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Eco 123 Topic 2 Consumer Behaviour-1Document142 pagesEco 123 Topic 2 Consumer Behaviour-1raphael shingishaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Theory of Consumer BehaviorDocument34 pagesChapter Three: Theory of Consumer BehaviorWaaqoo Guutuu Waaqoo GuutuuNo ratings yet
- Eoc 5Document12 pagesEoc 5Maiwand BabakarkhailNo ratings yet
- Utility AnalysisDocument13 pagesUtility AnalysisRohika K.C.No ratings yet
- Utility Analysis EcontentDocument11 pagesUtility Analysis EcontentMRS.NAMRATA KISHNANI BSSSNo ratings yet
- Cardinal Utility RevisedDocument22 pagesCardinal Utility Revisedfe23samarthNo ratings yet
- Theory of Consumer BehaviorDocument11 pagesTheory of Consumer BehaviorTamar Y.No ratings yet
- Class 12 Micro Economics Chapter 2 - Revision NotesDocument23 pagesClass 12 Micro Economics Chapter 2 - Revision NotesSachin PalNo ratings yet
- H.P National Law University, Shimla: Assignment of "Economics" (Assignment Second)Document20 pagesH.P National Law University, Shimla: Assignment of "Economics" (Assignment Second)tarun chhapolaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 - Consumer EquilibriumDocument17 pagesUnit - 3 - Consumer Equilibriumsaravanan100% (1)
- Law of Diminishing Marginal UtilityDocument15 pagesLaw of Diminishing Marginal Utilitypoudelsandesh12345678No ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument32 pagesConsumer Behaviourgrouprocks4No ratings yet
- UtilityDocument7 pagesUtilitysn nNo ratings yet
- Wa0033.Document3 pagesWa0033.zb77338No ratings yet
- Methods of Microeconomics: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMethods of Microeconomics: A Simple IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)