Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6
6
Uploaded by
Alexandrew charle RimocalCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Barcode Project ProposalDocument22 pagesBarcode Project Proposalapi-297065332100% (2)
- Online Blood Bank Management SystemDocument21 pagesOnline Blood Bank Management SystemYallaling Goudar59% (27)
- Lean and JIT McdonaldsDocument10 pagesLean and JIT McdonaldsHarshal Naik100% (2)
- Shezan - Strategic Analysis & PlanningDocument90 pagesShezan - Strategic Analysis & PlanningZohaib H. Shah90% (40)
- Jio MartDocument6 pagesJio Martayushi100% (2)
- Blockchain SystemDocument12 pagesBlockchain Systemkhairina100% (1)
- Digitization AssignmentDocument8 pagesDigitization Assignmentlaveenanorona555No ratings yet
- Research Paper in ProcessDocument9 pagesResearch Paper in ProcessakanshaNo ratings yet
- AmirLatif2020 Article ARemixIDESmartContract-basedFrDocument24 pagesAmirLatif2020 Article ARemixIDESmartContract-basedFrDivya KandpalNo ratings yet
- Big Data in HealthcareDocument16 pagesBig Data in Healthcareadohadwala3955No ratings yet
- BEHR - Review (1) - For MergeDocument59 pagesBEHR - Review (1) - For MergeBhanu RoyalNo ratings yet
- AiramForeign RRLDocument2 pagesAiramForeign RRLjenny adlaoNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument3 pagesResearchJehira OcampoNo ratings yet
- Medchain: A Design of Blockchain-Based System For Medical Records Access and Permissions ManagementDocument19 pagesMedchain: A Design of Blockchain-Based System For Medical Records Access and Permissions ManagementThangavel MuruganNo ratings yet
- Health Systems and Technology: Course Number: CIS 1200 Dowling CollegeDocument11 pagesHealth Systems and Technology: Course Number: CIS 1200 Dowling CollegecleodeesNo ratings yet
- A Secure Cloud-Based Patient Electronic Medical Records System Using Two-Factor AuthenticationDocument6 pagesA Secure Cloud-Based Patient Electronic Medical Records System Using Two-Factor AuthenticationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Kailash ProjectDocument13 pagesKailash ProjectNarendra Kumar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Smart HealthcareDocument9 pagesSmart HealthcareRohit RajNo ratings yet
- Securing and Authenticating Healthcare RecordsDocument17 pagesSecuring and Authenticating Healthcare Recordssayali pawarNo ratings yet
- ABSTRAC1Document2 pagesABSTRAC1Kishen KumarNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce's Important Role in The Medical Sector: Luzanna Fung Lok Chee and Rashad YazdanifardDocument8 pagesEcommerce's Important Role in The Medical Sector: Luzanna Fung Lok Chee and Rashad YazdanifardAsora Yasmin snehaNo ratings yet
- Project PPTDocument36 pagesProject PPTGARVIN CHOWDHARY 20BCE2239No ratings yet
- Clinicappchain: A Low-Cost Blockchain Hyperledger Solution For HealthcareDocument9 pagesClinicappchain: A Low-Cost Blockchain Hyperledger Solution For HealthcareNafiul AlamNo ratings yet
- Smart HealthcareDocument6 pagesSmart HealthcarepharezeNo ratings yet
- Foreign and Local LiterarureDocument6 pagesForeign and Local Literarurepia espanilloNo ratings yet
- Synopsis On Patient Record Management System (1) - 1Document8 pagesSynopsis On Patient Record Management System (1) - 1Sagar KasanaNo ratings yet
- A Blockchain Framework To Secure Personal Health RDocument19 pagesA Blockchain Framework To Secure Personal Health RpersonneNo ratings yet
- Smarter Smart ContractsDocument15 pagesSmarter Smart ContractsBen JacobsNo ratings yet
- Universal Dashboard To Track Medical RecordsDocument14 pagesUniversal Dashboard To Track Medical RecordsBhargav RajNo ratings yet
- BTP-Report RoughDocument7 pagesBTP-Report RoughSudir SinghNo ratings yet
- Big Data Health Care Using ToolsDocument18 pagesBig Data Health Care Using ToolsGEETHA RANI 218003946No ratings yet
- Cloud MRM-A Bio-IT Tool For Correlative Studies in Dermatology 30.08.2011Document11 pagesCloud MRM-A Bio-IT Tool For Correlative Studies in Dermatology 30.08.2011Aimoldina AlmaNo ratings yet
- Modul Cloud Computing Dan Hl7 Dalam Pelayanan Kesehatan (HIM750)Document27 pagesModul Cloud Computing Dan Hl7 Dalam Pelayanan Kesehatan (HIM750)stellaNo ratings yet
- Official Lecture#4 - Overview of Health InformaticsDocument3 pagesOfficial Lecture#4 - Overview of Health InformaticsLYKA ANTONETTE ABREGANANo ratings yet
- An Edge Computing Based Smart Healthcare Framework PDFDocument22 pagesAn Edge Computing Based Smart Healthcare Framework PDFSidheeque FasalNo ratings yet
- Implementing A Personal Health Record Cloud Platform Using Ciphertext-Policy Attribute-Based EncryptionDocument8 pagesImplementing A Personal Health Record Cloud Platform Using Ciphertext-Policy Attribute-Based EncryptionAyeni AyomideNo ratings yet
- Information Systems For ManagerDocument6 pagesInformation Systems For ManagerLavina AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Final 2Document11 pagesFinal 2Thunder BangNo ratings yet
- 20bce2239 ProjectDocument36 pages20bce2239 ProjectGARVIN CHOWDHARY 20BCE2239No ratings yet
- Advancement of Blockchain Technology in Healthcare Student Name: University: Course: LecturerDocument7 pagesAdvancement of Blockchain Technology in Healthcare Student Name: University: Course: Lecturercofoje9006No ratings yet
- Thesis Statement On Electronic Medical RecordsDocument7 pagesThesis Statement On Electronic Medical Recordsgjgm36vk100% (1)
- TQM Intro 097,081,063,045Document2 pagesTQM Intro 097,081,063,045Talha MughalNo ratings yet
- BlockChain ProjectDocument10 pagesBlockChain ProjectAshu jadhavNo ratings yet
- Ieeesem: E-Health System Security Issues and Block Chain Technology in KenyaDocument8 pagesIeeesem: E-Health System Security Issues and Block Chain Technology in KenyasisayNo ratings yet
- Moroccan Electronic Health Record System: Houssam BENBRAHIM, Hanaâ HACHIMI and Aouatif AMINEDocument8 pagesMoroccan Electronic Health Record System: Houssam BENBRAHIM, Hanaâ HACHIMI and Aouatif AMINESouhaïla MOUMOUNo ratings yet
- InCITe-2022 Paper 116Document16 pagesInCITe-2022 Paper 116akttripathiNo ratings yet
- Digitalization in Omnichannel Healthcare Supply Chain B - 2023 - Journal of BusiDocument20 pagesDigitalization in Omnichannel Healthcare Supply Chain B - 2023 - Journal of BusiTariqNo ratings yet
- gjmbsv3n3spl 14Document25 pagesgjmbsv3n3spl 14areeb khanNo ratings yet
- (IJIT-V7I3P12) :mrs. Shilpa Pimpalkar, Yash Shende, Tanvi Patil, Pratik Nath, Aditi YadavDocument5 pages(IJIT-V7I3P12) :mrs. Shilpa Pimpalkar, Yash Shende, Tanvi Patil, Pratik Nath, Aditi YadavIJITJournalsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Tics Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesNursing Tics Lecture NotesMichael Gustilo100% (1)
- Med RecDocument6 pagesMed RecSasi KumarNo ratings yet
- Role of Information Technology in MedicineDocument7 pagesRole of Information Technology in MedicineFahadghaznavi100% (1)
- Big Data Analytics in Medical ApplicationsDocument17 pagesBig Data Analytics in Medical ApplicationsGaurav VatsNo ratings yet
- Midpresentation Report-2024Document21 pagesMidpresentation Report-2024raghudatheshNo ratings yet
- ISM - AssignmentDocument8 pagesISM - AssignmentAkshatNo ratings yet
- Medicine Tracking SystemDocument11 pagesMedicine Tracking Systemshinderushi.eduNo ratings yet
- Development of Medibiometric in Healthcare SystemDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Medibiometric in Healthcare SystemajextopeNo ratings yet
- De La Salle University - Dasmariñas: Graduate ProgramDocument8 pagesDe La Salle University - Dasmariñas: Graduate ProgramZejkeara ImperialNo ratings yet
- Hgrid: An Economical Model For Mass-Health Care System Using Latest Technology (Grid Computing)Document5 pagesHgrid: An Economical Model For Mass-Health Care System Using Latest Technology (Grid Computing)IJMERNo ratings yet
- Computer Science & Engineering: Experiment-3.2Document2 pagesComputer Science & Engineering: Experiment-3.2Shantanu RaiNo ratings yet
- Implementation Considerations For Blockchain in Healthcare InstitutionsDocument9 pagesImplementation Considerations For Blockchain in Healthcare InstitutionstdeviyanNo ratings yet
- Health informatics: Improving patient careFrom EverandHealth informatics: Improving patient careBCS, The Chartered Institute for ITRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Digital Health Transformation: Harnessing ICT for Better Patient Outcomes.From EverandDigital Health Transformation: Harnessing ICT for Better Patient Outcomes.No ratings yet
- JIT Inventory ManagementDocument25 pagesJIT Inventory ManagementPendyalaHariKrishnaNo ratings yet
- Modeling The Interrelationships Among Barriers To Sustainable Supply ChainDocument57 pagesModeling The Interrelationships Among Barriers To Sustainable Supply ChainMathiyazhagan KaliyanNo ratings yet
- DLP - Grade 7 (Procedure in Storing and Receiving Tools and Materials)Document6 pagesDLP - Grade 7 (Procedure in Storing and Receiving Tools and Materials)colleen100% (1)
- Ecommerce Module 1Document34 pagesEcommerce Module 1Blaze 2021No ratings yet
- (53 Pages) Sent - Lecture 2 & 3 - Incoterms 2020 - (Updated On Sep 2021)Document53 pages(53 Pages) Sent - Lecture 2 & 3 - Incoterms 2020 - (Updated On Sep 2021)Tâm Lê Hồ HỒNGNo ratings yet
- Name: Anshima Gupta Nidhi Kumari Prita Dhawan Shilpi Awasthi Taufique AhmadDocument49 pagesName: Anshima Gupta Nidhi Kumari Prita Dhawan Shilpi Awasthi Taufique AhmadTaufique AhmadNo ratings yet
- Maersk Container Guarantee Permanent LetterDocument2 pagesMaersk Container Guarantee Permanent Lettermelantikapardosi15No ratings yet
- স্পেশাল_পিডিএফ_একাউন্টিংDocument11 pagesস্পেশাল_পিডিএফ_একাউন্টিংMuhammad Rakib HossenNo ratings yet
- Tema 4-1 - Techniques For Optimizing of Transportation Logistics NetworkDocument44 pagesTema 4-1 - Techniques For Optimizing of Transportation Logistics NetworkRaluca AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Inventory ManagementDocument51 pagesInventory ManagementMay Jovi JalaNo ratings yet
- Kargaindia Roadways Private Limited Company ProfileDocument21 pagesKargaindia Roadways Private Limited Company ProfileBhavyassh AgarwaalNo ratings yet
- A Conceptual Model For Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) : Information Management & Computer Security April 2005Document13 pagesA Conceptual Model For Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) : Information Management & Computer Security April 2005Paul MacoveiNo ratings yet
- Capture Tow Literature Review: 2. Just in TimeDocument67 pagesCapture Tow Literature Review: 2. Just in TimeA'del JummaNo ratings yet
- Retail MGTDocument29 pagesRetail MGTKasiraman RamanujamNo ratings yet
- Tugas AKBDocument8 pagesTugas AKBRizkiNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document18 pagesModule 5Sarthak YadavNo ratings yet
- Q4 Applied Entrepreneurship 11 12 WEEK 2Document4 pagesQ4 Applied Entrepreneurship 11 12 WEEK 2Jierroe Evangelista0% (1)
- Akuntansi 3Document4 pagesAkuntansi 3Icha Novia R.No ratings yet
- Introduction & Importance of Supply Chain ManagementDocument8 pagesIntroduction & Importance of Supply Chain ManagementRiddhi ShahNo ratings yet
- Vendor Selection A Literature ReviewDocument14 pagesVendor Selection A Literature ReviewNecat SönmezNo ratings yet
- Summer 2022-2023 - Course Outline - Introduction To BusinessDocument10 pagesSummer 2022-2023 - Course Outline - Introduction To BusinessShoaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit 9Document43 pagesUnit 9Abhijeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementDocument15 pagesLogistics and Supply Chain ManagementAbout life and lessonsNo ratings yet
- MN3197 Operations ManagementDocument2 pagesMN3197 Operations Managementandrewbarrett0No ratings yet
- Designing Distribution NetwrokDocument45 pagesDesigning Distribution NetwrokMayank PrakashNo ratings yet
- The Magic of Levelled SchedulingDocument10 pagesThe Magic of Levelled SchedulingAnonymous GNxRzFNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Cost Classification)Document13 pagesChapter 2 (Cost Classification)Najia MuktaNo ratings yet
6
6
Uploaded by
Alexandrew charle RimocalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
6
6
Uploaded by
Alexandrew charle RimocalCopyright:
Available Formats
o The big four accounting firms (Deloitte, Pricewaterhouse Coopers (PwC), Ernst & young
(EY), and KPMG) and many financial institutions have already recognized the importance
of blockchain and thus have launched several projects.
I. SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT APPLICATIONS
Supply Chain Management- refers to controlling the entire production flow, from acquiring
raw materials to delivering the final product/service at the destination.
Benefits of Blockchain on Supply Chain Management
o holds complete provenance details,
o enhances transparency and accountability in supply chain systems (all suppliers can track
shipments, deliveries, and progress),
o increases trust between suppliers in the chain,
o eliminates middleman auditors (can carry out their own checks and balances at any time),
o effectively and securely helpful to logistics management (smart contracts),
o ensures the genuineness and quality of products (result in reduction in processing times,
management costs, and human errors),
o enables better quality, outcomes, and performance of effective supply chain management
(SCM) processes (improves in facilitating planning, scheduling, coordinating, monitoring,
and validating these activities).
International Business Machine (IBM)- a supply chain consulting services that presently has a
fleet of 1,000 trucks that make over 25,000 deliveries each week on a project combining
blockchain technology with innovative internet of things (IoT) solutions.
IBM Food Trust- blockchain-based food-traceability platform since 2018; modular solution
built on blockchain, benefiting all network participants with a safer, smarter, and more
sustainable food. Nestle, McCormick, and Dole use this IBM food trust in their businesses.
Examples:
o Maersk- a Danish shipping company, is using blockchain to track all its shipments across
the world.
o Provenance- which piloted a traceability project in Indonesia's fishing industry through
mobile phones, blockchain, and smart tagging.
II. HEALTHCARE APPLICATIONS
Electronic Medical Record (EMR)- where patient data and records are digitized and stored;
exposed to patient-privacy violations, outdated data, and incomplete data.
Benefits of Blockchain on Healthcare
o common database of health data and information (doctors, hospitals, patients, and all other
stakeholders can access; doctors can spend less time in doing administrative tasks,
providing more time for patient care, and more research can be shared for new treatments),
o holds the complete medical history for each patient, with multiple granularities of control,
o tamper-resistant means of storing medical history,
o increased efficiency in providing insurance quotes (minimizing claim and billing fraud),
o precise drug recommendations and drug development (more accessible and ready for
research).
Zhang et al. (2018) identified seven potential blockchain use cases in healthcare:
1. prescription tracking to detect opioid overdose and over-prescription,
2. data sharing to incorporate telemedicine with traditional care,
3. sharing cancer data with providers using patient-authorized access,
4. cancer registry sharing to aggregate observations in cancer cases,
5. patient digital identity management for better patient record matching,
6. personal health records for accessing and controlling complete health history,
7. and health insurance claim adjudication automation to surface error and fraud.
Angeles (2018) discussed in detail three promising healthcare use cases:
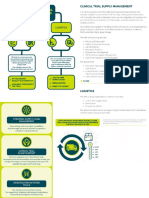
1. healthcare data exchange and interoperability,
2. drug supply chain integrity and remote auditing,
3. clinical trials and population health research.
Examples:
o Patientory- a software and service company, offers a blockchain-based application that
securely stores and manages health information in real time, giving patients control of their
own health data.
You might also like
- Barcode Project ProposalDocument22 pagesBarcode Project Proposalapi-297065332100% (2)
- Online Blood Bank Management SystemDocument21 pagesOnline Blood Bank Management SystemYallaling Goudar59% (27)
- Lean and JIT McdonaldsDocument10 pagesLean and JIT McdonaldsHarshal Naik100% (2)
- Shezan - Strategic Analysis & PlanningDocument90 pagesShezan - Strategic Analysis & PlanningZohaib H. Shah90% (40)
- Jio MartDocument6 pagesJio Martayushi100% (2)
- Blockchain SystemDocument12 pagesBlockchain Systemkhairina100% (1)
- Digitization AssignmentDocument8 pagesDigitization Assignmentlaveenanorona555No ratings yet
- Research Paper in ProcessDocument9 pagesResearch Paper in ProcessakanshaNo ratings yet
- AmirLatif2020 Article ARemixIDESmartContract-basedFrDocument24 pagesAmirLatif2020 Article ARemixIDESmartContract-basedFrDivya KandpalNo ratings yet
- Big Data in HealthcareDocument16 pagesBig Data in Healthcareadohadwala3955No ratings yet
- BEHR - Review (1) - For MergeDocument59 pagesBEHR - Review (1) - For MergeBhanu RoyalNo ratings yet
- AiramForeign RRLDocument2 pagesAiramForeign RRLjenny adlaoNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument3 pagesResearchJehira OcampoNo ratings yet
- Medchain: A Design of Blockchain-Based System For Medical Records Access and Permissions ManagementDocument19 pagesMedchain: A Design of Blockchain-Based System For Medical Records Access and Permissions ManagementThangavel MuruganNo ratings yet
- Health Systems and Technology: Course Number: CIS 1200 Dowling CollegeDocument11 pagesHealth Systems and Technology: Course Number: CIS 1200 Dowling CollegecleodeesNo ratings yet
- A Secure Cloud-Based Patient Electronic Medical Records System Using Two-Factor AuthenticationDocument6 pagesA Secure Cloud-Based Patient Electronic Medical Records System Using Two-Factor AuthenticationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Kailash ProjectDocument13 pagesKailash ProjectNarendra Kumar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Smart HealthcareDocument9 pagesSmart HealthcareRohit RajNo ratings yet
- Securing and Authenticating Healthcare RecordsDocument17 pagesSecuring and Authenticating Healthcare Recordssayali pawarNo ratings yet
- ABSTRAC1Document2 pagesABSTRAC1Kishen KumarNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce's Important Role in The Medical Sector: Luzanna Fung Lok Chee and Rashad YazdanifardDocument8 pagesEcommerce's Important Role in The Medical Sector: Luzanna Fung Lok Chee and Rashad YazdanifardAsora Yasmin snehaNo ratings yet
- Project PPTDocument36 pagesProject PPTGARVIN CHOWDHARY 20BCE2239No ratings yet
- Clinicappchain: A Low-Cost Blockchain Hyperledger Solution For HealthcareDocument9 pagesClinicappchain: A Low-Cost Blockchain Hyperledger Solution For HealthcareNafiul AlamNo ratings yet
- Smart HealthcareDocument6 pagesSmart HealthcarepharezeNo ratings yet
- Foreign and Local LiterarureDocument6 pagesForeign and Local Literarurepia espanilloNo ratings yet
- Synopsis On Patient Record Management System (1) - 1Document8 pagesSynopsis On Patient Record Management System (1) - 1Sagar KasanaNo ratings yet
- A Blockchain Framework To Secure Personal Health RDocument19 pagesA Blockchain Framework To Secure Personal Health RpersonneNo ratings yet
- Smarter Smart ContractsDocument15 pagesSmarter Smart ContractsBen JacobsNo ratings yet
- Universal Dashboard To Track Medical RecordsDocument14 pagesUniversal Dashboard To Track Medical RecordsBhargav RajNo ratings yet
- BTP-Report RoughDocument7 pagesBTP-Report RoughSudir SinghNo ratings yet
- Big Data Health Care Using ToolsDocument18 pagesBig Data Health Care Using ToolsGEETHA RANI 218003946No ratings yet
- Cloud MRM-A Bio-IT Tool For Correlative Studies in Dermatology 30.08.2011Document11 pagesCloud MRM-A Bio-IT Tool For Correlative Studies in Dermatology 30.08.2011Aimoldina AlmaNo ratings yet
- Modul Cloud Computing Dan Hl7 Dalam Pelayanan Kesehatan (HIM750)Document27 pagesModul Cloud Computing Dan Hl7 Dalam Pelayanan Kesehatan (HIM750)stellaNo ratings yet
- Official Lecture#4 - Overview of Health InformaticsDocument3 pagesOfficial Lecture#4 - Overview of Health InformaticsLYKA ANTONETTE ABREGANANo ratings yet
- An Edge Computing Based Smart Healthcare Framework PDFDocument22 pagesAn Edge Computing Based Smart Healthcare Framework PDFSidheeque FasalNo ratings yet
- Implementing A Personal Health Record Cloud Platform Using Ciphertext-Policy Attribute-Based EncryptionDocument8 pagesImplementing A Personal Health Record Cloud Platform Using Ciphertext-Policy Attribute-Based EncryptionAyeni AyomideNo ratings yet
- Information Systems For ManagerDocument6 pagesInformation Systems For ManagerLavina AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Final 2Document11 pagesFinal 2Thunder BangNo ratings yet
- 20bce2239 ProjectDocument36 pages20bce2239 ProjectGARVIN CHOWDHARY 20BCE2239No ratings yet
- Advancement of Blockchain Technology in Healthcare Student Name: University: Course: LecturerDocument7 pagesAdvancement of Blockchain Technology in Healthcare Student Name: University: Course: Lecturercofoje9006No ratings yet
- Thesis Statement On Electronic Medical RecordsDocument7 pagesThesis Statement On Electronic Medical Recordsgjgm36vk100% (1)
- TQM Intro 097,081,063,045Document2 pagesTQM Intro 097,081,063,045Talha MughalNo ratings yet
- BlockChain ProjectDocument10 pagesBlockChain ProjectAshu jadhavNo ratings yet
- Ieeesem: E-Health System Security Issues and Block Chain Technology in KenyaDocument8 pagesIeeesem: E-Health System Security Issues and Block Chain Technology in KenyasisayNo ratings yet
- Moroccan Electronic Health Record System: Houssam BENBRAHIM, Hanaâ HACHIMI and Aouatif AMINEDocument8 pagesMoroccan Electronic Health Record System: Houssam BENBRAHIM, Hanaâ HACHIMI and Aouatif AMINESouhaïla MOUMOUNo ratings yet
- InCITe-2022 Paper 116Document16 pagesInCITe-2022 Paper 116akttripathiNo ratings yet
- Digitalization in Omnichannel Healthcare Supply Chain B - 2023 - Journal of BusiDocument20 pagesDigitalization in Omnichannel Healthcare Supply Chain B - 2023 - Journal of BusiTariqNo ratings yet
- gjmbsv3n3spl 14Document25 pagesgjmbsv3n3spl 14areeb khanNo ratings yet
- (IJIT-V7I3P12) :mrs. Shilpa Pimpalkar, Yash Shende, Tanvi Patil, Pratik Nath, Aditi YadavDocument5 pages(IJIT-V7I3P12) :mrs. Shilpa Pimpalkar, Yash Shende, Tanvi Patil, Pratik Nath, Aditi YadavIJITJournalsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Tics Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesNursing Tics Lecture NotesMichael Gustilo100% (1)
- Med RecDocument6 pagesMed RecSasi KumarNo ratings yet
- Role of Information Technology in MedicineDocument7 pagesRole of Information Technology in MedicineFahadghaznavi100% (1)
- Big Data Analytics in Medical ApplicationsDocument17 pagesBig Data Analytics in Medical ApplicationsGaurav VatsNo ratings yet
- Midpresentation Report-2024Document21 pagesMidpresentation Report-2024raghudatheshNo ratings yet
- ISM - AssignmentDocument8 pagesISM - AssignmentAkshatNo ratings yet
- Medicine Tracking SystemDocument11 pagesMedicine Tracking Systemshinderushi.eduNo ratings yet
- Development of Medibiometric in Healthcare SystemDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Medibiometric in Healthcare SystemajextopeNo ratings yet
- De La Salle University - Dasmariñas: Graduate ProgramDocument8 pagesDe La Salle University - Dasmariñas: Graduate ProgramZejkeara ImperialNo ratings yet
- Hgrid: An Economical Model For Mass-Health Care System Using Latest Technology (Grid Computing)Document5 pagesHgrid: An Economical Model For Mass-Health Care System Using Latest Technology (Grid Computing)IJMERNo ratings yet
- Computer Science & Engineering: Experiment-3.2Document2 pagesComputer Science & Engineering: Experiment-3.2Shantanu RaiNo ratings yet
- Implementation Considerations For Blockchain in Healthcare InstitutionsDocument9 pagesImplementation Considerations For Blockchain in Healthcare InstitutionstdeviyanNo ratings yet
- Health informatics: Improving patient careFrom EverandHealth informatics: Improving patient careBCS, The Chartered Institute for ITRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Digital Health Transformation: Harnessing ICT for Better Patient Outcomes.From EverandDigital Health Transformation: Harnessing ICT for Better Patient Outcomes.No ratings yet
- JIT Inventory ManagementDocument25 pagesJIT Inventory ManagementPendyalaHariKrishnaNo ratings yet
- Modeling The Interrelationships Among Barriers To Sustainable Supply ChainDocument57 pagesModeling The Interrelationships Among Barriers To Sustainable Supply ChainMathiyazhagan KaliyanNo ratings yet
- DLP - Grade 7 (Procedure in Storing and Receiving Tools and Materials)Document6 pagesDLP - Grade 7 (Procedure in Storing and Receiving Tools and Materials)colleen100% (1)
- Ecommerce Module 1Document34 pagesEcommerce Module 1Blaze 2021No ratings yet
- (53 Pages) Sent - Lecture 2 & 3 - Incoterms 2020 - (Updated On Sep 2021)Document53 pages(53 Pages) Sent - Lecture 2 & 3 - Incoterms 2020 - (Updated On Sep 2021)Tâm Lê Hồ HỒNGNo ratings yet
- Name: Anshima Gupta Nidhi Kumari Prita Dhawan Shilpi Awasthi Taufique AhmadDocument49 pagesName: Anshima Gupta Nidhi Kumari Prita Dhawan Shilpi Awasthi Taufique AhmadTaufique AhmadNo ratings yet
- Maersk Container Guarantee Permanent LetterDocument2 pagesMaersk Container Guarantee Permanent Lettermelantikapardosi15No ratings yet
- স্পেশাল_পিডিএফ_একাউন্টিংDocument11 pagesস্পেশাল_পিডিএফ_একাউন্টিংMuhammad Rakib HossenNo ratings yet
- Tema 4-1 - Techniques For Optimizing of Transportation Logistics NetworkDocument44 pagesTema 4-1 - Techniques For Optimizing of Transportation Logistics NetworkRaluca AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Inventory ManagementDocument51 pagesInventory ManagementMay Jovi JalaNo ratings yet
- Kargaindia Roadways Private Limited Company ProfileDocument21 pagesKargaindia Roadways Private Limited Company ProfileBhavyassh AgarwaalNo ratings yet
- A Conceptual Model For Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) : Information Management & Computer Security April 2005Document13 pagesA Conceptual Model For Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) : Information Management & Computer Security April 2005Paul MacoveiNo ratings yet
- Capture Tow Literature Review: 2. Just in TimeDocument67 pagesCapture Tow Literature Review: 2. Just in TimeA'del JummaNo ratings yet
- Retail MGTDocument29 pagesRetail MGTKasiraman RamanujamNo ratings yet
- Tugas AKBDocument8 pagesTugas AKBRizkiNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document18 pagesModule 5Sarthak YadavNo ratings yet
- Q4 Applied Entrepreneurship 11 12 WEEK 2Document4 pagesQ4 Applied Entrepreneurship 11 12 WEEK 2Jierroe Evangelista0% (1)
- Akuntansi 3Document4 pagesAkuntansi 3Icha Novia R.No ratings yet
- Introduction & Importance of Supply Chain ManagementDocument8 pagesIntroduction & Importance of Supply Chain ManagementRiddhi ShahNo ratings yet
- Vendor Selection A Literature ReviewDocument14 pagesVendor Selection A Literature ReviewNecat SönmezNo ratings yet
- Summer 2022-2023 - Course Outline - Introduction To BusinessDocument10 pagesSummer 2022-2023 - Course Outline - Introduction To BusinessShoaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit 9Document43 pagesUnit 9Abhijeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementDocument15 pagesLogistics and Supply Chain ManagementAbout life and lessonsNo ratings yet
- MN3197 Operations ManagementDocument2 pagesMN3197 Operations Managementandrewbarrett0No ratings yet
- Designing Distribution NetwrokDocument45 pagesDesigning Distribution NetwrokMayank PrakashNo ratings yet
- The Magic of Levelled SchedulingDocument10 pagesThe Magic of Levelled SchedulingAnonymous GNxRzFNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Cost Classification)Document13 pagesChapter 2 (Cost Classification)Najia MuktaNo ratings yet