Professional Documents
Culture Documents
COMPUTING
COMPUTING
Uploaded by
ajetunmobi ayodejiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
COMPUTING
COMPUTING
Uploaded by
ajetunmobi ayodejiCopyright:
Available Formats
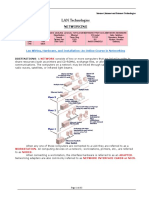
NETWORKING
Definition of network
A computer network often simply referred to as network, is a collection of computers and
devices interconnected by communications channels that facilitate communications among
users and allows users to share resources.
A computer network allows sharing of resources and information among interconnected
devices.
Network exists for one major reason: to share information and resources.
Types of networks
Ethernet
Token ring
Arcnet
Arcnet
An acronym from Attached Resource Computer Network is a star LAN network. It was the first
widely available networking system for microcomputers and became popular in the 1980s for
office automation tasks. Arcnet was developed by John Murphy at Datapoint Corporation in
1976.
Token ring
Token ring local Area network(LAN) technology is a ring topology network.
It uses a special three-byte frame called a token that travels around the ring. Physically, when
implemented, the computers are connected through cables to a “HUB”.
It is the hub that manages the network in a ring topology manner. An example of a token ring
network is the IBM Token Ring.
Ethernet
Ethernet is a bus topology LAN network system. Ethernet LANs use coaxial or twisted pair
cables to connect computer systems
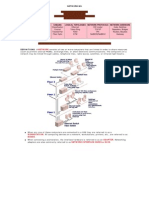
Network Topology
In computer networking, topology refers to the layout of connected devices. There are two
types of network topology, a physical topology and a logical topology.
The physical topology of a network refers to the layout of the cables and network devices; and
logical topology refers to the method of communication of the network devices.
1ST TERM E-LEARNING/ SS3/ICT Page 1
Network topologies are categorized into the following basic types:
1. Star topology
2. Bus topology
3. Ring topology
Star topology: the network devices are connected to central like a Star.
The central point may be a hub, a switch or a router. All the individual network devices
communicate with the central point.
Thus once the hub fails, the whole network is grounded but if any other network decice
fails, the network will be operating without the failed device.
Also, the star topology requires more cables because cables are laid from all the network
devices to the hub.
A star topology is designed with each node(file server, workstations, and peripheral(s)
connected directly to a central network hub, switch, or concentrator.
Data on a star network passes through the hub, switch, or concentrator before continuing
to its destination. The hub, switch, or concentrator manages and controls all functions of
the network.
It also acts as a reapeater for the data flow. This configuration is common with twisted pair
cable, coaxial cable or fiber optic cable. An example of star network is the ARCNET.
Advantages of a Star Topology
Easy to install and wire
No disruptions to the network when connecting or removing devices.
Easy to detect faults and to remove parts.
Disadvantages of a Star Topology
Requires more cable length than a linear topology
If the hub , switch or concentrator fails, nodes attached are disable.
More expensive than linear bus topologies because of the cost of the hubs, switches or
concentrators.
1ST TERM E-LEARNING/ SS3/ICT Page 2
You might also like
- Dokumen - Pub - Computer Systems An Integrated Approach To Architecture and Operating Systems 0321486137 9780321486134Document705 pagesDokumen - Pub - Computer Systems An Integrated Approach To Architecture and Operating Systems 0321486137 9780321486134Enrique González Carrillo100% (1)
- 19 3 RTU560 Training 3Document8 pages19 3 RTU560 Training 3shaidraniNo ratings yet
- 4335 NetworkingemisDocument4 pages4335 NetworkingemisFavour JamesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-2-Introduction Computer NetworkingDocument14 pagesLesson 1-2-Introduction Computer NetworkingMorn TheaNo ratings yet
- Networking BasicsDocument102 pagesNetworking Basicssan1507No ratings yet
- Topology in Network DesignDocument12 pagesTopology in Network Designsaurabh278No ratings yet
- Network: Chapter 2: Types of NetworkDocument8 pagesNetwork: Chapter 2: Types of NetworksweetashusNo ratings yet
- DCCChapter 5Document13 pagesDCCChapter 5Getnete degemuNo ratings yet
- Computer Network For COCDocument20 pagesComputer Network For COCEwunetu DejeneNo ratings yet
- Adama Poly Technique Colleg1Document32 pagesAdama Poly Technique Colleg1Mahdi ZeynNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument12 pagesLab ManualRai HessyNo ratings yet
- IT Web TechnologyDocument79 pagesIT Web TechnologyDale BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Networking in DMRCDocument16 pagesNetworking in DMRCaanchalbahl62100% (1)
- Computer Communication: Unit Viii LanDocument30 pagesComputer Communication: Unit Viii LanleensNo ratings yet
- Core 2Document30 pagesCore 2keanee simbajonNo ratings yet
- Networking BasicsDocument23 pagesNetworking Basicscool.tba100% (2)
- Amie Nbcafe Student Forum: Network TopologyDocument8 pagesAmie Nbcafe Student Forum: Network TopologySomnath LahaNo ratings yet
- Dav Institute of Engineering and Technology: Computer Networks Practical FileDocument25 pagesDav Institute of Engineering and Technology: Computer Networks Practical FileNavpreet Singh Dhillon0% (1)
- Definition - What Does Computer Networking Mean?Document3 pagesDefinition - What Does Computer Networking Mean?Kenneth Jed Solomo100% (1)
- Intro To Comp NetwksDocument1,765 pagesIntro To Comp NetwksManu DibangoNo ratings yet
- Network Topology ICF 8Document9 pagesNetwork Topology ICF 8Gianan JPNo ratings yet
- Cns Practical 2Document10 pagesCns Practical 2How to download AnythingNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument351 pagesComputer NetworkRanjan Saini100% (2)
- Network TopologyDocument2 pagesNetwork TopologyJason CuarentaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Setup Computer NetworkDocument73 pagesUnit 3 - Setup Computer NetworkGioSanBuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- C PPPPPP PPP PPDocument9 pagesC PPPPPP PPP PPahils100% (1)
- Network TopologiesDocument7 pagesNetwork TopologiesraidenNo ratings yet
- IIIT Network Design D.deepak IIIT HyderabadDocument9 pagesIIIT Network Design D.deepak IIIT HyderabadHarshit PahujaNo ratings yet
- Star Topology Many Home Networks Use The Star Topology. A Star Network Features ADocument6 pagesStar Topology Many Home Networks Use The Star Topology. A Star Network Features AsabahafzalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks-4Document6 pagesIntroduction To Networks-4deepheat_008No ratings yet
- Course Contents: Data Communications Grade Prof. Dr. Hassan H. Soliman Dr. Mostafa ElgayarDocument11 pagesCourse Contents: Data Communications Grade Prof. Dr. Hassan H. Soliman Dr. Mostafa Elgayarsaher waleedNo ratings yet
- Work TopologyDocument20 pagesWork Topologyporanchakma514No ratings yet
- This Article Tells About, Bus and Ring Topologies With Advantages and Disadvantages of EachDocument13 pagesThis Article Tells About, Bus and Ring Topologies With Advantages and Disadvantages of EachDesai MehulNo ratings yet
- Network Topology 1Document10 pagesNetwork Topology 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- PC Hardware and NetworkingDocument93 pagesPC Hardware and NetworkingPrince DeuelNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument4 pagesNetwork TopologyAnish VeettiyankalNo ratings yet
- Computer Application: Surbhi Goel 12455 Bcom Hons A Pgdav College DuDocument17 pagesComputer Application: Surbhi Goel 12455 Bcom Hons A Pgdav College DuManish YadavNo ratings yet
- Ics 2306: Computer Networks: Network Topology and ArchitectureDocument54 pagesIcs 2306: Computer Networks: Network Topology and ArchitecturePeter KamauNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Networking: Prepared By: Mr. Maverick Rovie S. LagmanDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networking: Prepared By: Mr. Maverick Rovie S. LagmanLenoverNo ratings yet
- Computer TopologyDocument14 pagesComputer TopologytamnumakamseuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document15 pagesLesson 3Kean Rafael MarianoNo ratings yet
- Network PDFDocument66 pagesNetwork PDFq_riusNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Second Term NoteDocument21 pagesGrade 8 Second Term NoteThiseni De SilvaNo ratings yet
- What Is TopologyDocument7 pagesWhat Is TopologyManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Networking Concepts and Telecommunications: Figure 8-1Document23 pagesNetworking Concepts and Telecommunications: Figure 8-1Ngonidzashe ZanamweNo ratings yet
- What Is Computer Networks?Document8 pagesWhat Is Computer Networks?Katrina Mae VillalunaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-1.3: Network Topologies Network Infrastructure DevicesDocument21 pagesCHAPTER-1.3: Network Topologies Network Infrastructure DevicesAsfikRahmanNo ratings yet
- Presentation of NetworkingDocument27 pagesPresentation of Networkingkamal jamal0% (1)
- Associate ComNetBasOve EN v3Document87 pagesAssociate ComNetBasOve EN v3jonathanharripersadNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Computer Networks: Network TopologyDocument25 pagesBasic Concepts of Computer Networks: Network TopologyAmritansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies: Lecture # 2Document21 pagesNetwork Topologies: Lecture # 2Monika RehmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 DCC NotesDocument11 pagesUnit 4 DCC NoteskharateojasNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument9 pagesNetworkingalmightyfavouriteNo ratings yet
- Basic Networking: Different Types of Network TopologyDocument9 pagesBasic Networking: Different Types of Network TopologySRGiramNo ratings yet
- Computer Network - Lab ManualDocument13 pagesComputer Network - Lab ManualPatel SahilNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument104 pagesNetworkingMahesh ParabNo ratings yet
- Learn The Basic Networking and TopologyDocument16 pagesLearn The Basic Networking and TopologyROSE TASINo ratings yet
- Old Acn FileDocument38 pagesOld Acn FileAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- May Cse 1Document9 pagesMay Cse 1الملاك الابيضNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking Bootcamp: Routing, Switching And TroubleshootingFrom EverandComputer Networking Bootcamp: Routing, Switching And TroubleshootingNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyFrom EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Bacnet Notifier, Rede.Document62 pagesBacnet Notifier, Rede.Thales DiasNo ratings yet
- Interview Preparation Session 4-Dec-2021 - VLSI GuruDocument33 pagesInterview Preparation Session 4-Dec-2021 - VLSI Gurudvlsi dvlsiNo ratings yet
- F5 Customer Demo: BIG-IP AFM - Use AFM in Network Firewall ModeDocument11 pagesF5 Customer Demo: BIG-IP AFM - Use AFM in Network Firewall ModeAries Raf OndisNo ratings yet
- Publish Applications - Linux Virtual Delivery Agent 2106Document2 pagesPublish Applications - Linux Virtual Delivery Agent 2106rameshgmorayNo ratings yet
- Deploy Container Applications Using Kubernetes Implementations With Microk8S and Aws Eks Shiva Subramanian Full ChapterDocument51 pagesDeploy Container Applications Using Kubernetes Implementations With Microk8S and Aws Eks Shiva Subramanian Full Chaptereugene.rucker420100% (6)
- VMCEDocument4 pagesVMCEPastor CaicedoNo ratings yet
- Santosh V Hegde-2022HT01035-ESZG553 RTSDocument7 pagesSantosh V Hegde-2022HT01035-ESZG553 RTSsantosh vighneshwar hegdeNo ratings yet
- Aws Ec2 PDFDocument1,113 pagesAws Ec2 PDFjosephNo ratings yet
- Install Ubuntu Dual WindowDocument5 pagesInstall Ubuntu Dual WindowThành CôngNo ratings yet
- TAFJ tLockManagerDocument24 pagesTAFJ tLockManagersajibarafatsiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Illuminated FDocument3 pagesComputer Science Illuminated Fpearl042008No ratings yet
- Automation Studio Installation and Administration GuideDocument123 pagesAutomation Studio Installation and Administration GuideAlexandre MarchioteNo ratings yet
- Especificaciones Técnicas IBM System x3650 M4Document2 pagesEspecificaciones Técnicas IBM System x3650 M4josealinarezNo ratings yet
- commandsBUC AppnoteDocument48 pagescommandsBUC AppnoteradamNo ratings yet
- dh67cl Techprodspec04 PDFDocument91 pagesdh67cl Techprodspec04 PDFJhrvc7No ratings yet
- Chap 3 OSI ModelDocument33 pagesChap 3 OSI ModelZubair45 Baloch302No ratings yet
- CCNP Encore Part 1 Lab Guide 2022Document16 pagesCCNP Encore Part 1 Lab Guide 2022momoNo ratings yet
- Find Serial Number of Computer in Windows 10Document2 pagesFind Serial Number of Computer in Windows 10GabbarNo ratings yet
- DE2-115 Computer NiosIIDocument63 pagesDE2-115 Computer NiosIITran Quang Thai B1708908No ratings yet
- CHDK Sx120is HowtoDocument8 pagesCHDK Sx120is HowtoBulea EmilianNo ratings yet
- Firebird 3.0.0 Alpha2 ReleaseNotesDocument105 pagesFirebird 3.0.0 Alpha2 ReleaseNotesAnonymous IGsDhuNo ratings yet
- TC290 97 98 99Document476 pagesTC290 97 98 99jinwenjieNo ratings yet
- NFS Server ConfigurationDocument4 pagesNFS Server Configurationnitin desaiNo ratings yet
- Word Count Exercise InstructionsDocument3 pagesWord Count Exercise InstructionsAshwin AjmeraNo ratings yet
- Methods To Bypass Cloudflare and Obtain Website Real IPDocument6 pagesMethods To Bypass Cloudflare and Obtain Website Real IPTrickster 420No ratings yet
- A Semantic Approach To English Grammar 2nd EditionDocument67 pagesA Semantic Approach To English Grammar 2nd EditionAkshay BabbarNo ratings yet
- MicroGuard 540 - New BackgroundDocument21 pagesMicroGuard 540 - New Backgroundjulio cesarNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Bringing Up A Hardware PlatformDocument47 pagesThe Basics of Bringing Up A Hardware PlatformchrismorleyNo ratings yet