Professional Documents
Culture Documents
材導作業
材導作業
Uploaded by
林珍伃Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
材導作業
材導作業
Uploaded by
林珍伃Copyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Materials Science and Engineering Homework 3
A set of load-displacement data, acquired from a tensile test of a nickel sample,
is given in this file. The gauge width, thickness and length of the sample are 2.0
mm, 0.2 mm and 10.0 mm, respectively.
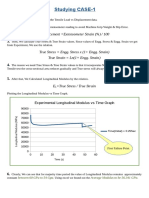
1. Plot an engineering stress-strain curve according to the load-displacement
data.
1000 Stress Strain curve
900
800
700 (0.009273916,776.40075)
600
Stress
500
400
300
y = 112588(x - 0.002)
200
100
0
0 0.005 0.01 Strain
0.015 0.02 0.025 0.03
1800
Stress Strain curve
1600 y = 112588(x - 0.002)
0.380871916 ,1718.21975
1400
1200
1000
Stress
800
600
400
200
0
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 Strain
0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5
2. Plot a true stress-(plastic) strain curve according to the engineering stress-
strain curve.
True stress strain curve
2500
0.344493492,2400.935
2000 169
1500
True stress
1000
500
0
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4
True strain
3. Find the elastic constant of the sample.
112588MPa
4. Find the (engineering) yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, uniform
elongation and total elongation.
yield strength:766.40075MPa
ultimate tensile strength: 1718.21975MPa
uniform elongation: 3.808719164/10≒0.38=38%
total elongation: 4.727439164/10≒0.473=47.3%
5. What is the true tensile stress at the onset of necking?
2400.935169
6. Find the modulus of resilience, Ur, and strain hardening exponent, n, of the
sample.
modulus of resilience, Ur :(766.40075)^2/2*112588≒2.6
strain hardening exponent, n :0.2581
plastic deformation(log)
3.5
y = 0.2581x + 3.3258
log(stress)
R² = 0.1338 2.5
1.5
1
-4 -3.5 -3 -2.5 -2 -1.5 -1
log(strain)
(Accommodate all your plots and answer in one page A4 paper and clearly
indicate your answers. No calculation processes are required. Due date: 10:00,
2nd of May, 2024.)
You might also like
- Whirling Experimental Lab - S2007Document7 pagesWhirling Experimental Lab - S2007Abhinav Bansal100% (2)
- Lab 321 #1 VVVDocument12 pagesLab 321 #1 VVVSamNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Structures HumarDocument1,048 pagesDynamics of Structures Humarali_biscoeat100% (6)
- 7D162B Pressure Drop For Double Pipe Heat Exchanger SiDocument4 pages7D162B Pressure Drop For Double Pipe Heat Exchanger SiparagmhamunkarNo ratings yet
- (Students) Lec#2, StrainDocument18 pages(Students) Lec#2, StrainJubillee Magsino0% (1)
- Practice 3 Mec - MergedDocument11 pagesPractice 3 Mec - MergedMichelle ReynaNo ratings yet
- Solids Lab 2 - 201110737.AL AQEEB FAIQ BIN ROZAIDEDocument14 pagesSolids Lab 2 - 201110737.AL AQEEB FAIQ BIN ROZAIDEpicul 08No ratings yet
- Reinforcement Bars GraphsDocument8 pagesReinforcement Bars GraphsPhanendra Kumar AttadaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 (S11196260)Document9 pagesLab 2 (S11196260)Vasemaca BoladauNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment # 1: Error! No Text of Specified Style in DocumentDocument8 pagesLaboratory Experiment # 1: Error! No Text of Specified Style in DocumentM Asjid SaeedNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Rock Mechanics 6 PDFDocument7 pagesLaboratory Rock Mechanics 6 PDFirsanNo ratings yet
- Mekanika Material Kelompok 5Document10 pagesMekanika Material Kelompok 5fikri wahyu pratamaNo ratings yet
- M.E. 3300 Lab Memo: Table 1. Data TableDocument4 pagesM.E. 3300 Lab Memo: Table 1. Data TableJan YsNo ratings yet
- CE 003 - Week 6Document25 pagesCE 003 - Week 6Kevin PoleNo ratings yet
- Lab RollingDocument26 pagesLab RollingiwaleedwasimNo ratings yet
- PR1 TiDocument4 pagesPR1 TiAsep Ridwan SetiawanNo ratings yet
- StressDocument13 pagesStressLenielle AmatosaNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test 2Document6 pagesTensile Test 2zakariaNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test Lab ReportDocument9 pagesTensile Test Lab ReportTan Xuennie0% (1)
- Lab 1Document5 pagesLab 1muhammad.amir14333No ratings yet
- Book 1Document11 pagesBook 1afiverr903No ratings yet
- Tensile Test Lab Report (For Me)Document15 pagesTensile Test Lab Report (For Me)frentsenNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test ReportDocument12 pagesTensile Test ReportNURUL AINA BINTI MOHAMAD FUAD STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Materials 1 Lab ReportDocument8 pagesMaterials 1 Lab ReportarthurNo ratings yet
- Le Hai Yen - 火災学会Document13 pagesLe Hai Yen - 火災学会Hải YếnNo ratings yet
- Etk Material Curves 20121018Document15 pagesEtk Material Curves 20121018ManuNo ratings yet
- Material Yr1 - Tutorial 6Document16 pagesMaterial Yr1 - Tutorial 6Ahmed TahaNo ratings yet
- CH 4 ExampleDocument9 pagesCH 4 ExampleBishwajit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- CH 4 ExampleDocument9 pagesCH 4 ExampleKevin Nunez HNo ratings yet
- New 1Document9 pagesNew 1Chenthil Kumar KNo ratings yet
- CH 4 ExampleDocument9 pagesCH 4 ExampleMd MamroseNo ratings yet
- Contoh & Latihan Uji TarikDocument9 pagesContoh & Latihan Uji TarikVishnu DevaNo ratings yet
- C1990-EH(HC)ver 1 0英文Document6 pagesC1990-EH(HC)ver 1 0英文顏健軒No ratings yet
- CompressionDocument7 pagesCompressionFaidhi FahmiNo ratings yet
- Studying Case 1Document4 pagesStudying Case 1vivek dasNo ratings yet
- Sample CalculationDocument5 pagesSample CalculationhidayatullahNo ratings yet
- SOM AssignmentDocument5 pagesSOM AssignmentQueenie BaridgeNo ratings yet
- Evaluation and Optimization of Tensile Strength Responses of Copper at Sub Zero Temperatures Using Taguchi Robust Design and Machine LearningDocument17 pagesEvaluation and Optimization of Tensile Strength Responses of Copper at Sub Zero Temperatures Using Taguchi Robust Design and Machine LearningsandeepNo ratings yet
- Closed-Book Practice-Ch 06 (2016!07!31)Document8 pagesClosed-Book Practice-Ch 06 (2016!07!31)JuanNo ratings yet
- Tuesday-2 Tensile Arko Basak 210184Document6 pagesTuesday-2 Tensile Arko Basak 210184Dewanshu JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Module 2Document19 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Module 2eysNo ratings yet
- Non-Destructive Testing For Surface Hardness and Case Depth Research TeamDocument5 pagesNon-Destructive Testing For Surface Hardness and Case Depth Research TeamRITIK SHARMANo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - BeamDocument3 pagesExperiment 1 - BeamRyan SooknarineNo ratings yet
- Buckling Test: Name: Ahmed Sayed ID: SUKD1503838Document12 pagesBuckling Test: Name: Ahmed Sayed ID: SUKD1503838ŸØüsap BasiliNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Helical Spring: Dhaka University of Engineering & Technology, GAZIPUR-1700Document19 pagesPresentation On Helical Spring: Dhaka University of Engineering & Technology, GAZIPUR-1700Md saydul islamNo ratings yet
- Assignment #2: Bsce-2B CE 225Document67 pagesAssignment #2: Bsce-2B CE 225Charlene Mae Edang BagaresNo ratings yet
- Tugas Kelompok 3 - Mekanika MaterialDocument3 pagesTugas Kelompok 3 - Mekanika Materialfikri wahyu pratamaNo ratings yet
- اختبار الشدDocument6 pagesاختبار الشدIhab El-SayedNo ratings yet
- Mae 244 7sep05 Tensile and ImpactDocument9 pagesMae 244 7sep05 Tensile and Impactapi-3730129100% (2)
- FoM - LCF QuestionsDocument5 pagesFoM - LCF Questionsbharath kumarNo ratings yet
- Ciencia de MaterialesDocument2 pagesCiencia de MaterialesEnrique Romero BlancoNo ratings yet
- Tensile TestDocument5 pagesTensile TestzakariaNo ratings yet
- Sir Fawad Najam Assignment No 1 FinalDocument50 pagesSir Fawad Najam Assignment No 1 FinalRajput JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Mom L 2Document5 pagesMom L 2Safwara Ibrahim KhattakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Fatigue Failure TheoriesDocument32 pagesChapter 6 Fatigue Failure TheoriesSuraj ShelarNo ratings yet
- CE242 - Tensile Test - 2023Document25 pagesCE242 - Tensile Test - 2023K K BajpaiNo ratings yet
- SSMDocument7 pagesSSMSurya DewantaraNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document1 pageHW 2Nikos VaxevanidisNo ratings yet
- Cyclic Plasticity of Engineering Materials: Experiments and ModelsFrom EverandCyclic Plasticity of Engineering Materials: Experiments and ModelsNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument81 pagesUnit IMugilNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Falling Ball Viscometry and Its Accuracy: Group R1Document9 pagesInvestigation of Falling Ball Viscometry and Its Accuracy: Group R1Robert HomaiNo ratings yet
- Ch8-Introduction To Magnetic FieldsDocument28 pagesCh8-Introduction To Magnetic Fieldsmehdii.heidary1366100% (3)
- PDF Gate 1991 To 2018Document332 pagesPDF Gate 1991 To 2018sammyNo ratings yet
- Paper AmrDocument41 pagesPaper AmrErfan AZNNo ratings yet
- 4.quantum Mechanics - GATE PDFDocument28 pages4.quantum Mechanics - GATE PDFMridusmita BoruahNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE PAPER Physics XI by S.K. Pandey Principal KV GangraniDocument9 pagesSAMPLE PAPER Physics XI by S.K. Pandey Principal KV GangraniAKASH KUMAR X ANo ratings yet
- Differential Geometry and Its Applications: A. PatákDocument4 pagesDifferential Geometry and Its Applications: A. PatákmiftahchoyNo ratings yet
- Classical Fields: Notes For A Course OnDocument203 pagesClassical Fields: Notes For A Course OnCassianoNo ratings yet
- ADDocument491 pagesADSwagat DasNo ratings yet
- Pulleys and WedgesDocument28 pagesPulleys and WedgesMagesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Speed and Velocity PDFDocument17 pagesSpeed and Velocity PDFWalterVia100% (1)
- 21 Lecture OutlineDocument30 pages21 Lecture OutlineTahir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Design of Equipment FoundationsDocument28 pagesDesign of Equipment Foundationsapi-379773793% (42)
- Deflection of TrussesDocument9 pagesDeflection of TrussesfranckoNo ratings yet
- A Review of Flow and Heat TransferDocument28 pagesA Review of Flow and Heat TransferOssama Bohamd100% (1)
- Glass HoleDocument170 pagesGlass HoleAhsan SattarNo ratings yet
- ELMS Task Weeks 12 13 Dancing Oobleck A Non Newtonian Fluid ExperimentationDocument3 pagesELMS Task Weeks 12 13 Dancing Oobleck A Non Newtonian Fluid ExperimentationLead CanadaNo ratings yet
- Corre CeDocument29 pagesCorre CeKim VeneracionNo ratings yet
- Homework # 4Document2 pagesHomework # 4eniNo ratings yet
- 9702 - s19 - QP - 23 (Dragged)Document2 pages9702 - s19 - QP - 23 (Dragged)Nezza WidarkoNo ratings yet
- 1216 TheoreticalManualSEAWAYDocument290 pages1216 TheoreticalManualSEAWAYolgerrenekoopNo ratings yet
- ASTM D6816-11 (Reapproved 2016)Document9 pagesASTM D6816-11 (Reapproved 2016)anant11235No ratings yet
- Cavitation Effects in Centrifugal Pumps-A Review: Maxime Binama, Alex Muhirwa, Emmanuel BisengimanaDocument12 pagesCavitation Effects in Centrifugal Pumps-A Review: Maxime Binama, Alex Muhirwa, Emmanuel BisengimanaVILLANUEVA_DANIEL2064No ratings yet
- Rotational Inertia Lab ReportDocument8 pagesRotational Inertia Lab Reportbrian100% (1)
- Effect of Geomaterial Variability On Seismic Response Analyses of Earthen DamsDocument16 pagesEffect of Geomaterial Variability On Seismic Response Analyses of Earthen DamsSebastian PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Saeed Book Bank: S.# Isbn/Tag Author Title Cur. PriceDocument20 pagesSaeed Book Bank: S.# Isbn/Tag Author Title Cur. PriceMubeenNo ratings yet