Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsDrug Book
Drug Book
Uploaded by
garamalzhrani34Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Guidelines Switching Antidepressants - A3 PDFDocument1 pageGuidelines Switching Antidepressants - A3 PDFP̷s̷ʏ̷ᴄ̷ʜ̷ᴏ̷ᴛ̷ɪ̷ᴄ̷ R̷ᴀ̷ɪ̷ɴ̷ʙ̷ᴏ̷ᴡ̷ᴢ̷50% (2)
- Psychopharmacology 2 AntidepressantsDocument7 pagesPsychopharmacology 2 AntidepressantsBea Samonte100% (2)
- LabetalolDocument3 pagesLabetalolTri Purma Sari50% (2)
- Drug CardsDocument10 pagesDrug CardsMaria Robustelli100% (3)
- Aripiprazole AbilifyDocument2 pagesAripiprazole AbilifyKristi Wray100% (2)
- Drug Study of SchizophreniaDocument17 pagesDrug Study of SchizophreniaCLOYD MARVINNo ratings yet
- Amlo Cloni PregaDocument4 pagesAmlo Cloni PregaKym Karla PatrizyahNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic Drugs: Conventional AntipsychoticsDocument16 pagesAntipsychotic Drugs: Conventional AntipsychoticsApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument106 pagesDrug StudyBlessie Mae Guinanghan AbuanNo ratings yet
- Sertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of ActionDocument11 pagesSertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of Actionkarl montanoNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotics: Dr. Pagan Pambudi, M.Si, SP.SDocument47 pagesAntipsychotics: Dr. Pagan Pambudi, M.Si, SP.SSharah Stephanie IINo ratings yet
- CCMH Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCCMH Drug StudyJoy JarinNo ratings yet
- Risperidone: Group 1 Bobias de Vera Laput Saagundo Siazon UriarteDocument9 pagesRisperidone: Group 1 Bobias de Vera Laput Saagundo Siazon UriarteChresia Schae MondejarNo ratings yet
- RisperidoneDocument4 pagesRisperidoneJay Lemuel BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Withdrawal Topic DiscussionDocument4 pagesAlcohol Withdrawal Topic Discussionapi-734449276No ratings yet
- V. Norepinephrine &dopamine ReuptakeDocument2 pagesV. Norepinephrine &dopamine ReuptakeChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug Analysiskristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyJaessa Feliciano50% (2)
- V. Atypical AntipsychoticsDocument2 pagesV. Atypical AntipsychoticsChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- CNS: Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia, Confusion, Paradoxic RageDocument4 pagesCNS: Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia, Confusion, Paradoxic RageYanna N. CuakiNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-12-12 at 7.31.29 PMDocument16 pagesScreenshot 2022-12-12 at 7.31.29 PMshreshta reddy PalleNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument2 pagesDrugmmmartinez1583No ratings yet
- Levodopa Card#4Document2 pagesLevodopa Card#4USMCDOCNo ratings yet
- PhenobarbitalDocument5 pagesPhenobarbitalapi-3797941100% (1)
- TemazepamDocument1 pageTemazepamCris TanNo ratings yet
- LorazepamDocument4 pagesLorazepamapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreNo ratings yet
- V. DihydroindolonesDocument2 pagesV. DihydroindolonesChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For AMCDocument3 pagesDrug Study For AMCTrixia RiveraNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic MedicationsDocument17 pagesPsychotropic MedicationsMJ Torralba100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyJohn LesterNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol Drug StudyDocument3 pagesHaloperidol Drug StudyAysaaa DCNo ratings yet
- Labetalol Card#8Document1 pageLabetalol Card#8USMCDOC100% (1)
- Requirement Drug Study PsycheDocument6 pagesRequirement Drug Study PsycheRegine Lorenzana Mey-AngNo ratings yet
- AntipsychoticsDocument51 pagesAntipsychoticsShailja SharmaNo ratings yet
- DIAZEPAMDocument4 pagesDIAZEPAMCay SevillaNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine: Brands If It WorksDocument6 pagesChlorpromazine: Brands If It WorksAnonymous cwlpSlReUYNo ratings yet
- Clorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Document2 pagesClorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- Methylphenidate Card#6Document2 pagesMethylphenidate Card#6USMCDOCNo ratings yet
- Drug Presentation: Manisha M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year Con IlbsDocument57 pagesDrug Presentation: Manisha M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year Con IlbsManisha ShakyaNo ratings yet
- SeroquelDocument2 pagesSeroquelNinoska Garcia-Ortiz100% (2)
- CLOZAPINEDocument5 pagesCLOZAPINEMar OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage Action Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Chlorpro MazineDocument2 pagesDrug Dosage Action Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Chlorpro MazineJohn Michael FernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HaldolDocument2 pagesDrug Study HaldolGracia EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Metoclopromide Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoclopromide Drug Studymarklesterdeguzman087No ratings yet
- Pharmacology and ECT: Melvin Issac Zaitul Ilham Wen TzienDocument65 pagesPharmacology and ECT: Melvin Issac Zaitul Ilham Wen TzienayunisallehNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document8 pagesDrug Study 2rey_tengNo ratings yet
- OB MedicationsDocument8 pagesOB MedicationsKathleenNo ratings yet
- XanaxDocument2 pagesXanaxJackie FreyNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Fundamentals Care Plan 1Document12 pagesRunning Head: Fundamentals Care Plan 1Xe StrmNo ratings yet
- PSYC - Medication TemplateDocument15 pagesPSYC - Medication TemplateM Henry100% (1)
- Edited Psyche DrugsDocument49 pagesEdited Psyche Drugsa_lavina02No ratings yet
- HALOPERIDOLDocument3 pagesHALOPERIDOLSonny Dizon PareñasNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol PDFDocument4 pagesHaloperidol PDFfatimahNo ratings yet
- HaloperidolDocument4 pagesHaloperidolKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Modafinil. A Legit Smart Pill That Improves Cognitive FunctionFrom EverandModafinil. A Legit Smart Pill That Improves Cognitive FunctionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Drugs Used For Affective DisordersDocument36 pagesDrugs Used For Affective DisordersSeherKhanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guideline 1Document10 pagesClinical Guideline 1klysmanu93No ratings yet
- 50 Item Psychiatric Exam Answers and RationalesDocument9 pages50 Item Psychiatric Exam Answers and RationalesJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Depresia - Olaru (Lungu) GabrielaDocument24 pagesDepresia - Olaru (Lungu) GabrielaCorina StefanNo ratings yet
- S 002 LBLDocument35 pagesS 002 LBLRDZENNo ratings yet
- Commonly Prescribed Psychotropic MedicationsDocument2 pagesCommonly Prescribed Psychotropic MedicationsDragutin Petrić100% (1)
- Videbeck Psychiatric NSG HandoutsDocument32 pagesVidebeck Psychiatric NSG Handoutskishor100% (4)
- A Cost-Utility Analysis of Pregabalin Versus Venlafaxine XR in The Treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder in PortugalDocument8 pagesA Cost-Utility Analysis of Pregabalin Versus Venlafaxine XR in The Treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder in PortugalNadia KrismandaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology in PsychiatryDocument33 pagesPharmacology in PsychiatryKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument51 pagesPharmacologyAndy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Top-200-Drug ETSYDocument31 pagesTop-200-Drug ETSYBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Jetlax's CNS Pharmacology Cheat Sheet For The Philippines v5.0 - See Bit - Ly - CNSHandouts For CorrectionsDocument43 pagesJetlax's CNS Pharmacology Cheat Sheet For The Philippines v5.0 - See Bit - Ly - CNSHandouts For CorrectionsJor GarciaNo ratings yet
- Neuro (Part1) ATIDocument12 pagesNeuro (Part1) ATIGie Lane Ayuyu100% (8)
- Drugs During PregnancyDocument120 pagesDrugs During Pregnancymanishpankaj123100% (1)
- NCM105 13th PsychopharmacologyDocument17 pagesNCM105 13th PsychopharmacologyKamx MohammedNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants UpdateDocument24 pagesAntidepressants Updatedrsayis2No ratings yet
- Antidepressant MCQs Group 2Document4 pagesAntidepressant MCQs Group 2Ayesha Ayesha100% (1)
- Gangguan CemasssDocument6 pagesGangguan CemasssbNo ratings yet
- Anti Anxiety MedicationsDocument2 pagesAnti Anxiety MedicationsjhgkhgkhgNo ratings yet
- PsihiatrieDocument20 pagesPsihiatrieRoxy RoxzyNo ratings yet
- Park, 2019 - NEJM - DepressionDocument10 pagesPark, 2019 - NEJM - DepressionFabian WelchNo ratings yet
- Management of Depression in Children and Adolescents: ReviewDocument6 pagesManagement of Depression in Children and Adolescents: ReviewResidentes dieciocho veintidósNo ratings yet
- Nonhormonal Therapy For Hot Flashes: Pharmacist'S Letter / Prescriber'S LetterDocument5 pagesNonhormonal Therapy For Hot Flashes: Pharmacist'S Letter / Prescriber'S Letterthomson_70No ratings yet
- Journal of Medicinal Chemistry ArticleDocument63 pagesJournal of Medicinal Chemistry ArticleJudy UgwuegbuNo ratings yet
- Maladaptive Patterns of Behavior A. AnxietyDocument19 pagesMaladaptive Patterns of Behavior A. AnxietyTeal OtterNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsDocument35 pagesLecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsakramuddaulaNo ratings yet
- Psych Drugs Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesPsych Drugs Cheat SheetSuha Abdullah100% (4)
- Depresion in The ElderlyDocument9 pagesDepresion in The ElderlyGuzman RubenNo ratings yet
Drug Book
Drug Book
Uploaded by
garamalzhrani340 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views12 pagesOriginal Title
Drug book
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views12 pagesDrug Book
Drug Book
Uploaded by
garamalzhrani34Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 12
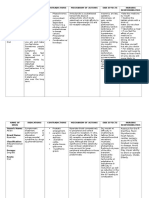
Generic name: Haloperidol
Brand name: Haldol
Classification: Antipsychotics, 1st Generation
Route: PO, IM injection
Does:
PO:
◦Moderate disease, 0.5-2 mg q8-12hr initially
◦Severe disease, 3-5 mg q8-12hr initially; not to
exceed 30 mg/day.
IM injection lactate (prompt-acting):
◦2-5 mg q4-8hr PRN; may require q1hr in acute
agitation; not to exceed 20 mg/day
IM injection decanoate (depot):
◦Initial: IM dose 10-20 times daily PO dose administered monthly; not to exceed 100 mg;
if conversion requires initial dose >100 mg, administer in 2 injections (eg, 100 mg
initially, then remainder in 3-7 days)
◦Maintenance: Monthly dose 10-15 times daily PO dose.
Action:
block dopamine D2 receptors in the brain and exert its antipsychotic action.
Indications:
◦Schizophrenia, psychosis/sedation
◦Tourette syndrome
◦Intractable hiccup
◦Persistent nausea
◦Behavioural disorders
◦Acute agitation
Contraindications:
Contraindicated in severe toxic central nervous system depression or comatose states from
any cause and in individuals who are hypersensitive to this drug or have Parkinson disease.
Do not use in patients with known hypersensitivity to phenothiazines.
Side effects:
◦Anticholinergic effects
◦Sedation
◦Weight gain
◦Erectile dysfunction
◦Oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea
Nursing implementation:
◦Assess patient level of conscious
◦Monitor patient blood pressure, heart rate and ECG rhythm
◦Supervise suicidal risk during early therapy
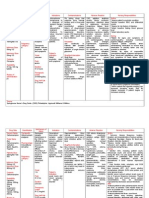
Generic name: Quetiapine
Brand name: Seroquel
Classification: Antipsychotics, 2nd Generation
Route: PO
Does:
Immediate release
◦Day 1: 50 mg/day PO divided q12hr
◦Days 2-3: Dose increased daily in increments of 25-50 mg q8-12hr to 300-400 mg by
day 4; further adjustments can be made in increments of 25-50 mg q12hr at intervals ≥2
days
◦Dosage range: 150-750 mg/day
Extended release
◦Day 1: 300 mg/day PO; subsequently, may be increased by up to 300 mg/day at intervals
≥1 day
◦Maintenance (monotherapy): 400-800 mg/day
Action:
It works by balancing the levels of dopamine and serotonin in your brain, hormones that
help regulate mood, behaviors, and thoughts.
Indications:
◦Schizophrenia
◦For the acute treatment of mania and for maintenance therapy following stabilization
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity, Hypokalemia, Hypomagnesemia, Congenital QT prolongation,
Arrhythmia hx, Avoid abrupt withdrawal
Side effects:
◦Suicidal tendency
◦Exacerbation of depression
◦Extrapyramidal symptoms
◦Hyperthermia, hypothermia
◦Dizziness
◦Hypotension
◦Tachycardia
◦Constipation
◦Weight gain
◦Increased appetite
Nursing implementation:
◦Assess motor function, and be alert for extrapyramidal symptoms
◦Monitoring electrolytes level
◦Instruct the patient to take the medication in evening without food or with light meal
Generic name: Risperidone
Brand name: Risperdal, Risperdal Consta
Classification: Antipsychotics, 2nd Generation; Antimanic Agents
Route: PO, IM injection
Does:
Schizophrenia
PO:
◦2 mg/day initially; may increase in increments of 1-2 mg/day at intervals ≥24 hr
◦Recommended target dosage: 2-8 mg/day once daily or divided q12hr (efficacy follows
bell-shaped curve; 4-8 mg/day more effective than 12-16 mg/day).
IM injection:
◦25 mg IM q2Weeks initially
◦If unresponsive, may benefit from a higher dose of 37.5 or 50 mg
◦Not to exceed 50 mg every 2 weeks
Bipolar Mania
PO (Risperdal or Risperidal M-Tabs)
2-3 mg/day initially; may be increased if necessary in increments of 1 mg/day at intervals of
24 hours to 6 mg/day
Bipolar Disorder
IM (Risperdal Consta):
Monotherapy or in combination with lithium or valproate: 25 mg IM q2Weeks; some
patients may benefit from a higher dose of 37.5 mg or 50 mg
Action:
The primary action of risperidone is to decrease dopaminergic and serotonergic pathway
activity in the brain, therefore decreasing symptoms of schizophrenia and mood disorders.
Indications:
◦Schizophrenia
◦Aggressive behaviour
◦Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
◦Tourette syndrome
◦Bipolar Mania
◦Autism
Contraindications:
Do not use in patients with known hypersensitivity to phenothiazines. Do not use in
comatose states or in the presence of large amounts of central nervous system depressants
like alcohol, barbiturates and narcotics.
Side effects:
◦Somnolence
◦Agitation
◦Anxiety
◦Akathisia
◦Agitation
◦Rhinitis
◦Parkinsonism
◦Dyspepsia
◦Constipation
◦Dry mouth
◦Fatigue
◦Weight increase.
Nursing implementation:
◦Maintain seizure precautions, especially when initiating therapy and increasing dosage
◦Monitor patient regularly for signs and symptoms of diabetes mellitus
◦Monitor the patient If fever occurs, rule out underlying infection, and consult physician
for appropriate comfort measures
Generic name: Lithium carbonate
Brand name: Lithobid, Lithium
Classification: Antimanic agents (Mood stabilizers)
Route: PO
Does:
◦Immediate release: 900-2400 mg/day orally divided every 6-8 hours
◦Extended release: 900-1800 mg/day orally divided every 12 hours
Action:
It works to stabilize the mood and reduce extremes in behavior by restoring the balance of
certain natural substances (neurotransmitters) in the brain.
Indications:
◦Acute manic disorder
◦Bipolar disorder
Contraindications:
Use with caution in renal insufficiency, thyroid disease and adrenocortical deficiency. Do
not prescribe unless monitoring available. Check blood pressure, electrolytes, renal and
thyroid function before commencing treatment and 6 monthly thereafter.
Side effects:
◦Fine hand tremor
◦Plyuria
◦Mild thirst
◦Nausea
◦General discomfort during initial treatment
Nursing implementation:
◦Monitor for lithium toxicity and metabolic acidosis
◦Hypercalcemia and Hyperparathyroidism: Associated with long-term lithium use.
Monitor serum calcium And thyroid function regularly
◦Encephalopathic Syndrome: Increased risk in patients treated with lithium and an
antipsychotic. Monitor routinely for changes to cognitive function
Generic name: Lorazepam
Brand name: Ativan
Classification: Benzodiazepines
Route: PO
Does:
◦Initial: 2-3 mg PO q8-12hr PRN; not to exceed 10 mg/day
◦Maintenance: 2-6 mg/day PO divided q8-12hr
Action:
Binds to benzodiazepine receptors on the postsynaptic GABA-A ligand-gated chloride
channel neuron at several sites within the central nervous system (CNS).
Indications:
◦Anxiety
◦Psychosomatic Disorders
◦Premedication
◦Insomnia due to anxiety
◦Acute panic attacks
◦Status epilepticus
Contraindications:
Lorazepam is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to benzodiazepines or to any
components of the formulation, in acute narrow-angle glaucoma, pre-existing CNS
depression, coma, acute pulmonary insufficiency or sleep apnea. Encephalopathy may be
precipitated in patients with severe hepatic insufficiency.
Side effects:
◦Drowsiness
◦Dizziness
◦Tiredness
◦Muscle weakness
◦Headache
◦Blurred vision
◦Sleep problems (insomnia)
◦Loss of balance or coordination
◦Forgetfulness or amnesia
◦Difficulty concentrating
◦Nausea
◦Vomiting
◦Constipation
◦Changes in appetite
◦Skin rash
Nursing implementation:
◦Periodically reassess the usefulness for individual patients
◦Monitor respirations q5-15min and before each repeated dose
Generic name: fluoxetine
Brand name: Prozac
Classification: Anti-depressant, SSRIs
Route: PO
Does:
◦Initial: 25 mg/6 mg PO qDay in evening
◦If needed, may titrate with 25-50 mg fluoxetine/6-12 mg; not to exceed 75 mg/18 mg per
day
Action:
Its effects by blocking the reuptake of serotonin into presynaptic serotonin neurons by
blocking the reuptake transporter protein located in the presynaptic terminal.
Indications:
◦Depression
◦Obsessive compulsive disorder
Contraindications:
Concomitant use in patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and pimozide is
contraindicated. Also contraindicated in patients with a hypersensitivity to fluoxetine,
hepatic or renal insufficiency.
Side effects:
◦Anxiety
◦Headache
◦Nervousness
◦Drowsiness
◦Sedation
◦Insomnia
◦Dzziness
◦Fatigue
Nursing implementation:
◦Assessment of depression and suicidal risk, particularly at the beginning of therapy or
when doses are changed, anxiety/panic attacks, social functioning, mania/mood lability,
and features of serotonin syndrome
◦Monitor blood glucose and liver function tests
Generic name: Venlafaxine
Brand name: Effexor
Classification: Antidepressants, SNRIs
Route: PO
Does:
Major Depressive Disorder
-Indicated for treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD)
Immediate-release tablets:
◦75 mg/day PO divided q8-12hr initially; may be increased by ≤75 mg/day not faster than
every 4 days
◦Moderate: Up to 225 mg/day PO divided q8-12hr
◦Severe: Up to 375 mg/day PO divided q8-12h
Extended-release tablets or capsules (HCl salt):
◦37.5-75 mg PO once daily initially; may be increased by 75 mg/day every 4 days; not to
exceed 225 mg/day
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
-Indicated for treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
◦Extended-release tablets or capsules (HCl salt) 37.5-75 mg PO once daily initially; may
be increased by 75 mg/day every 4-7 days; not to exceed 225 mg/day
Action:
Venlafaxine works by increasing serotonin levels, norepinephrine, and dopamine in the
brain by blocking transport proteins and stopping their reuptake at the presynaptic terminal.
Indications:
◦Major depressive disorder
◦Generalized anxiety disorder
Contraindications:
Uncontrolled hypertension, high risk of serious ventricular arrhythmias.
Side effects:
◦Nausea
◦Vomiting
◦Vnorexia
◦Dry mouth
◦Constipation
◦Dspepsia
◦Orthostatic hypotension
◦Tremor
◦Sweating
◦Anxiety
◦Dzziness
◦Ftigue
◦Headache
◦Syncope
Nursing implementation:
◦Assess BP and compare to normal values
◦Assess heart rate, ECG, and heart sounds, especially during exercise
Generic name: Amitriptyline
Brand name: Elavil, Levate
Classification: Anti-depressant, TCAs
Route: PO
Does:
◦Outpatient: 25-50 mg PO qHS initially; increase by 25 mg every 5-7 days to 100-200
mg/day (may divide doses throughout day or give at bedtime); if needed, may increase to
300 mg/day
Action:
Acts by blocking the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine neurotransmitters.
Indications:
◦Treatment of depression
Contraindications:
Do not use trazodone if you have taken a MAO inhibitor in the past 14 days;
Hypersensitivity; Some young people have thoughts about suicide when first taking an
antidepressant.
Side effects:
◦Headache
◦Confusion
◦Dizziness
◦Dry mouth
◦Nausea
◦Vomiting
◦Fatigue
◦Constipation
◦Blurred vision
Nursing implementation:
◦Notify physician or mental health professional immediately if patient exhibits worsening
depression or other changes in mood and behaviour
Generic name: Penelzine
Brand name: Nardil
Classification: Antidepressants, MAO Inhibitors
Route: PO
Does:
◦Initial 15 mg PO q8hr, increase not to exceed 20-30 mg q8hr
◦Dosage should be increased to at least 60 mg/day at a fairly rapid pace consistent with
patient tolerance; may be necessary to increase dosage up to 90 mg/day to obtain
sufficient MAO inhibition; many patients do not show a clinical response until treatment
at 60 mg has been continued for at least 4 weeks
◦After maximum benefit from drug is achieved, decrease dose after maximum response
(2-6 weeks) over 2-6 week period to maintain dose as low as 15 mg qDay or every other
day
Action:
phenelzine irreversibly these enzymes, preventing serotonin, norepinephrine, and
dopamine from being broken down, allowing these neurotransmitters to have a more
prolonged effect on their target receptors.
Indications:
◦Resistant depression
◦Panic disorder
◦Social anxiety disorder
Contraindications:
Phenelzine is contraindicated in patients who exhibit hypersensitivity to the drug or who
have pheochromocytoma, congestive heart failure, severe renal impairment or renal
pathology, abnormal LFTs, or a history of liver disease.
Side effects:
◦Dizziness
◦Feeling light-headed
◦Drowsiness
◦Sleep problems
◦Headache
◦Feeling weak or tired
◦Muscle twitching
◦Dry mouth
◦Stomach discomfort
◦Constipation
◦Swelling
◦Weight gain
Nursing implementation:
◦Monitor blood pressure, heart rate, mood (when treating depressive symptoms), weight,
dietary considerations, and suicidal ideation (particularly when initiating therapy or
implementing dose increases
◦Monitor blood glucose levels in patients with diabetes who take phenelzine
Generic name: Lisdexamfetamine
Brand name: Vyvanse
Classification: Stimulants; ADHD Agents
Route: PO
Does:
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder:
◦Starting/switching treatment: 30 mg PO qAM
◦Dose adjustment: Increase by 10- to 20-mg/day increments approximately qWeek
◦Not to exceed 70 mg qDay
Binge Eating Disorder:
◦Indicated for moderate-to-severe binge eating disorder (BED) in adults
◦Starting dose: 30 mg/day PO, THEN
◦Target dose: Titrate in increments of 20 mg at ~1 week intervals to achieve the
recommended target dose of 50-70 mg/day
◦Not to exceed 70 mg/day
Action:
It works primarily by inducing the release of the neurotransmitters dopamine and
norepinephrine from their storage areas in nerve terminals.
Indications:
◦Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
◦Binge eating disorder
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity to amphetamine products or any component of the formulation;
concurrent use of MAO inhibitor, or within 14 days of the last MAO inhibitor dose. Known
hypersensitivity or idiosyncrasy to sympathomimetic amines; advanced arteriosclerosis;
symptomatic cardiovascular disease; moderate-to-severe hypertension; hyperthyroidism;
glaucoma; agitated states; history of drug abuse.
Side effects:
◦Insomnia
◦Xerostomia
◦Upper abdominal pain
◦Tchycardia
◦Hypertension
◦Palpitations
◦Irritability
◦Anxiety
◦Agitation
◦Hyperhidrosis
◦Skin rash
◦Weight loss
Nursing implementation:
◦Prior to treatment, assess for presence of cardiac disease (eg, a careful history, family
history of sudden death or ventricular arrhythmia, and physical exam)
◦monitor for signs of abuse and overdose
You might also like
- Guidelines Switching Antidepressants - A3 PDFDocument1 pageGuidelines Switching Antidepressants - A3 PDFP̷s̷ʏ̷ᴄ̷ʜ̷ᴏ̷ᴛ̷ɪ̷ᴄ̷ R̷ᴀ̷ɪ̷ɴ̷ʙ̷ᴏ̷ᴡ̷ᴢ̷50% (2)
- Psychopharmacology 2 AntidepressantsDocument7 pagesPsychopharmacology 2 AntidepressantsBea Samonte100% (2)
- LabetalolDocument3 pagesLabetalolTri Purma Sari50% (2)
- Drug CardsDocument10 pagesDrug CardsMaria Robustelli100% (3)
- Aripiprazole AbilifyDocument2 pagesAripiprazole AbilifyKristi Wray100% (2)
- Drug Study of SchizophreniaDocument17 pagesDrug Study of SchizophreniaCLOYD MARVINNo ratings yet
- Amlo Cloni PregaDocument4 pagesAmlo Cloni PregaKym Karla PatrizyahNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic Drugs: Conventional AntipsychoticsDocument16 pagesAntipsychotic Drugs: Conventional AntipsychoticsApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument106 pagesDrug StudyBlessie Mae Guinanghan AbuanNo ratings yet
- Sertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of ActionDocument11 pagesSertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of Actionkarl montanoNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotics: Dr. Pagan Pambudi, M.Si, SP.SDocument47 pagesAntipsychotics: Dr. Pagan Pambudi, M.Si, SP.SSharah Stephanie IINo ratings yet
- CCMH Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCCMH Drug StudyJoy JarinNo ratings yet
- Risperidone: Group 1 Bobias de Vera Laput Saagundo Siazon UriarteDocument9 pagesRisperidone: Group 1 Bobias de Vera Laput Saagundo Siazon UriarteChresia Schae MondejarNo ratings yet
- RisperidoneDocument4 pagesRisperidoneJay Lemuel BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Withdrawal Topic DiscussionDocument4 pagesAlcohol Withdrawal Topic Discussionapi-734449276No ratings yet
- V. Norepinephrine &dopamine ReuptakeDocument2 pagesV. Norepinephrine &dopamine ReuptakeChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug Analysiskristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyJaessa Feliciano50% (2)
- V. Atypical AntipsychoticsDocument2 pagesV. Atypical AntipsychoticsChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- CNS: Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia, Confusion, Paradoxic RageDocument4 pagesCNS: Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia, Confusion, Paradoxic RageYanna N. CuakiNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-12-12 at 7.31.29 PMDocument16 pagesScreenshot 2022-12-12 at 7.31.29 PMshreshta reddy PalleNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument2 pagesDrugmmmartinez1583No ratings yet
- Levodopa Card#4Document2 pagesLevodopa Card#4USMCDOCNo ratings yet
- PhenobarbitalDocument5 pagesPhenobarbitalapi-3797941100% (1)
- TemazepamDocument1 pageTemazepamCris TanNo ratings yet
- LorazepamDocument4 pagesLorazepamapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreNo ratings yet
- V. DihydroindolonesDocument2 pagesV. DihydroindolonesChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For AMCDocument3 pagesDrug Study For AMCTrixia RiveraNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic MedicationsDocument17 pagesPsychotropic MedicationsMJ Torralba100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyJohn LesterNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol Drug StudyDocument3 pagesHaloperidol Drug StudyAysaaa DCNo ratings yet
- Labetalol Card#8Document1 pageLabetalol Card#8USMCDOC100% (1)
- Requirement Drug Study PsycheDocument6 pagesRequirement Drug Study PsycheRegine Lorenzana Mey-AngNo ratings yet
- AntipsychoticsDocument51 pagesAntipsychoticsShailja SharmaNo ratings yet
- DIAZEPAMDocument4 pagesDIAZEPAMCay SevillaNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine: Brands If It WorksDocument6 pagesChlorpromazine: Brands If It WorksAnonymous cwlpSlReUYNo ratings yet
- Clorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Document2 pagesClorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- Methylphenidate Card#6Document2 pagesMethylphenidate Card#6USMCDOCNo ratings yet
- Drug Presentation: Manisha M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year Con IlbsDocument57 pagesDrug Presentation: Manisha M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year Con IlbsManisha ShakyaNo ratings yet
- SeroquelDocument2 pagesSeroquelNinoska Garcia-Ortiz100% (2)
- CLOZAPINEDocument5 pagesCLOZAPINEMar OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage Action Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Chlorpro MazineDocument2 pagesDrug Dosage Action Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Chlorpro MazineJohn Michael FernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HaldolDocument2 pagesDrug Study HaldolGracia EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Metoclopromide Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoclopromide Drug Studymarklesterdeguzman087No ratings yet
- Pharmacology and ECT: Melvin Issac Zaitul Ilham Wen TzienDocument65 pagesPharmacology and ECT: Melvin Issac Zaitul Ilham Wen TzienayunisallehNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document8 pagesDrug Study 2rey_tengNo ratings yet
- OB MedicationsDocument8 pagesOB MedicationsKathleenNo ratings yet
- XanaxDocument2 pagesXanaxJackie FreyNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Fundamentals Care Plan 1Document12 pagesRunning Head: Fundamentals Care Plan 1Xe StrmNo ratings yet
- PSYC - Medication TemplateDocument15 pagesPSYC - Medication TemplateM Henry100% (1)
- Edited Psyche DrugsDocument49 pagesEdited Psyche Drugsa_lavina02No ratings yet
- HALOPERIDOLDocument3 pagesHALOPERIDOLSonny Dizon PareñasNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol PDFDocument4 pagesHaloperidol PDFfatimahNo ratings yet
- HaloperidolDocument4 pagesHaloperidolKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Modafinil. A Legit Smart Pill That Improves Cognitive FunctionFrom EverandModafinil. A Legit Smart Pill That Improves Cognitive FunctionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Drugs Used For Affective DisordersDocument36 pagesDrugs Used For Affective DisordersSeherKhanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guideline 1Document10 pagesClinical Guideline 1klysmanu93No ratings yet
- 50 Item Psychiatric Exam Answers and RationalesDocument9 pages50 Item Psychiatric Exam Answers and RationalesJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Depresia - Olaru (Lungu) GabrielaDocument24 pagesDepresia - Olaru (Lungu) GabrielaCorina StefanNo ratings yet
- S 002 LBLDocument35 pagesS 002 LBLRDZENNo ratings yet
- Commonly Prescribed Psychotropic MedicationsDocument2 pagesCommonly Prescribed Psychotropic MedicationsDragutin Petrić100% (1)
- Videbeck Psychiatric NSG HandoutsDocument32 pagesVidebeck Psychiatric NSG Handoutskishor100% (4)
- A Cost-Utility Analysis of Pregabalin Versus Venlafaxine XR in The Treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder in PortugalDocument8 pagesA Cost-Utility Analysis of Pregabalin Versus Venlafaxine XR in The Treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder in PortugalNadia KrismandaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology in PsychiatryDocument33 pagesPharmacology in PsychiatryKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument51 pagesPharmacologyAndy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Top-200-Drug ETSYDocument31 pagesTop-200-Drug ETSYBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Jetlax's CNS Pharmacology Cheat Sheet For The Philippines v5.0 - See Bit - Ly - CNSHandouts For CorrectionsDocument43 pagesJetlax's CNS Pharmacology Cheat Sheet For The Philippines v5.0 - See Bit - Ly - CNSHandouts For CorrectionsJor GarciaNo ratings yet
- Neuro (Part1) ATIDocument12 pagesNeuro (Part1) ATIGie Lane Ayuyu100% (8)
- Drugs During PregnancyDocument120 pagesDrugs During Pregnancymanishpankaj123100% (1)
- NCM105 13th PsychopharmacologyDocument17 pagesNCM105 13th PsychopharmacologyKamx MohammedNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants UpdateDocument24 pagesAntidepressants Updatedrsayis2No ratings yet
- Antidepressant MCQs Group 2Document4 pagesAntidepressant MCQs Group 2Ayesha Ayesha100% (1)
- Gangguan CemasssDocument6 pagesGangguan CemasssbNo ratings yet
- Anti Anxiety MedicationsDocument2 pagesAnti Anxiety MedicationsjhgkhgkhgNo ratings yet
- PsihiatrieDocument20 pagesPsihiatrieRoxy RoxzyNo ratings yet
- Park, 2019 - NEJM - DepressionDocument10 pagesPark, 2019 - NEJM - DepressionFabian WelchNo ratings yet
- Management of Depression in Children and Adolescents: ReviewDocument6 pagesManagement of Depression in Children and Adolescents: ReviewResidentes dieciocho veintidósNo ratings yet
- Nonhormonal Therapy For Hot Flashes: Pharmacist'S Letter / Prescriber'S LetterDocument5 pagesNonhormonal Therapy For Hot Flashes: Pharmacist'S Letter / Prescriber'S Letterthomson_70No ratings yet
- Journal of Medicinal Chemistry ArticleDocument63 pagesJournal of Medicinal Chemistry ArticleJudy UgwuegbuNo ratings yet
- Maladaptive Patterns of Behavior A. AnxietyDocument19 pagesMaladaptive Patterns of Behavior A. AnxietyTeal OtterNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsDocument35 pagesLecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsakramuddaulaNo ratings yet
- Psych Drugs Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesPsych Drugs Cheat SheetSuha Abdullah100% (4)
- Depresion in The ElderlyDocument9 pagesDepresion in The ElderlyGuzman RubenNo ratings yet