Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geography - Marking Key
Geography - Marking Key
Uploaded by
waqas.butt.1525Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Tratado de Ifa Uso Exclusivo de BabalawoDocument22 pagesTratado de Ifa Uso Exclusivo de BabalawoAndersonAguiarOdéIfé0% (3)
- Environmental Systems and Societies Paper 2 SL MarkschemeDocument18 pagesEnvironmental Systems and Societies Paper 2 SL MarkschemeAfra LamisaNo ratings yet
- Dockside Green: The Story of the Most Sustainable Development in the WorldFrom EverandDockside Green: The Story of the Most Sustainable Development in the WorldNo ratings yet
- Minerals, Metals, Mercury and Miracles - UsmanDocument43 pagesMinerals, Metals, Mercury and Miracles - UsmanuiderschenNo ratings yet
- ServiceDocument1,146 pagesServiceEmanuel Nicolas VillarruelNo ratings yet
- Informatica FunctionsDocument46 pagesInformatica FunctionsManoj Krishna100% (1)
- 0680 Environmental Management: MARK SCHEME For The March 2015 SeriesDocument6 pages0680 Environmental Management: MARK SCHEME For The March 2015 Seriesnng.uyenchuoiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Pakistan Studies 2059/02 October/November 2021Document24 pagesCambridge O Level: Pakistan Studies 2059/02 October/November 2021Bilal Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- © UCLES 2023 Page 4 of 24Document21 pages© UCLES 2023 Page 4 of 2467140No ratings yet
- Geo Mineral ResourcesDocument6 pagesGeo Mineral ResourcesRevolt 2.0No ratings yet
- Env ProblemsDocument7 pagesEnv Problemsimon.landageNo ratings yet
- 2059 Pakistan Studies: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2014 SeriesDocument11 pages2059 Pakistan Studies: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2014 Seriesmuhammad saleemNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Pakistan Studies 2059/02Document28 pagesCambridge O Level: Pakistan Studies 2059/02aqsabatool.2708No ratings yet
- Institute of Architecture Department: ArchitectureDocument13 pagesInstitute of Architecture Department: ArchitectureJasjot SinghNo ratings yet
- T. E. Civil: A Seminar Report OnDocument17 pagesT. E. Civil: A Seminar Report OnAlisha mullaNo ratings yet
- JudeDocument54 pagesJudeBranchi IkyureNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 Solid Industrial Waste and Land Degradation-BDocument30 pagesLecture 16 Solid Industrial Waste and Land Degradation-BMuhammad Saad KhokharNo ratings yet
- Coal Mining: A Synopsis BY Aloke GangulyDocument37 pagesCoal Mining: A Synopsis BY Aloke GangulyALOKE GANGULYNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 - DAHUYLADocument14 pagesActivity 6 - DAHUYLAJef Michael L. DahuylaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Pakistan Studies 0448/02Document28 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Pakistan Studies 0448/02zainab.fatima1150No ratings yet
- Management of Mining Wastes White Slag From Steel Mills 1682553851Document6 pagesManagement of Mining Wastes White Slag From Steel Mills 1682553851hjqsdbxh dbhcxNo ratings yet
- Department of Public Works: Addendum To PW 371Document97 pagesDepartment of Public Works: Addendum To PW 371larushkanNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Maximum Mark: 75: Gce O LevelDocument6 pagesMark Scheme Maximum Mark: 75: Gce O Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- Effect of Fly Ash On Geotechnical Properties and Stability of Coal Mine Overburden Dump: An OverviewDocument9 pagesEffect of Fly Ash On Geotechnical Properties and Stability of Coal Mine Overburden Dump: An OverviewVisal SasidharanNo ratings yet
- Transaction Highlights: Krugold Resources, IncDocument5 pagesTransaction Highlights: Krugold Resources, IncAamir AzizNo ratings yet
- Minerals 13 00090Document18 pagesMinerals 13 00090janhvi muleNo ratings yet
- Application of Remotely Sensed Data andDocument10 pagesApplication of Remotely Sensed Data andRonaldo MutepaireNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Geography Mock - Salman HashmiDocument14 pagesMark Scheme Geography Mock - Salman HashmiSarim AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Geography S-8 MSDocument4 pagesGeography S-8 MSdawoodtab23No ratings yet
- 2059 w04 Ms 2Document10 pages2059 w04 Ms 2api-3807993No ratings yet
- 2059 w12 Ms 2Document11 pages2059 w12 Ms 2mstudy123456No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentKirankumar Rohit264No ratings yet
- 06 May 2022 MININGDocument28 pages06 May 2022 MININGSamantha Cabugon0% (1)
- 2059 November 2015 Paper 2 Mark Scheme PDFDocument15 pages2059 November 2015 Paper 2 Mark Scheme PDFareebNo ratings yet
- Mining Geology, Midexam NoteDocument11 pagesMining Geology, Midexam NoteAbu NaeemNo ratings yet
- EIAR Limestone PELICAN-1 FINALDocument30 pagesEIAR Limestone PELICAN-1 FINALZubair KhanNo ratings yet
- Envi SciDocument5 pagesEnvi Scinuebemadethis432No ratings yet
- Written Report - Auditing Mining Industry (Group 4)Document33 pagesWritten Report - Auditing Mining Industry (Group 4)rachel banana hammockNo ratings yet
- Group 26 PlublishedReserch PaperDocument7 pagesGroup 26 PlublishedReserch PaperDaily FunNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 5014/12 October/November 2017Document12 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 5014/12 October/November 2017Jhon CenaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Mine Waste Leachates On Aquatic Environment: A ReviewDocument7 pagesImpact of Mine Waste Leachates On Aquatic Environment: A ReviewKadek Nando setiawanNo ratings yet
- Aba Lakew Residence Aba Yikuno Bridge To University RoadDocument9 pagesAba Lakew Residence Aba Yikuno Bridge To University RoadAsmerom MosinehNo ratings yet
- © Ucles 2008Document2 pages© Ucles 2008PC AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- Indian Small-Scale Mining With Special Emphasis On Environmental ManagementDocument7 pagesIndian Small-Scale Mining With Special Emphasis On Environmental ManagementCarlos MaroveNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabi MinE PDFDocument113 pagesCourse Syllabi MinE PDFgirmay kasayeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/21 May/June 2022Document6 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/21 May/June 2022Tapiwa MT (N1c3isH)No ratings yet
- Ways On How Separating Mixtures Like in MiningDocument11 pagesWays On How Separating Mixtures Like in MiningBENJ AMINNo ratings yet
- Tailings Dam Design. TechnologyUpdate SecuredDocument12 pagesTailings Dam Design. TechnologyUpdate SecuredJavierNo ratings yet
- Status of CoalL and Lignite Resources in IndiaDocument121 pagesStatus of CoalL and Lignite Resources in IndiaAnkon MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Impacto AmbientalDocument11 pagesImpacto AmbientalSeguridad MarvannssNo ratings yet
- Ug Mining Methods - Part 1 2014 - 2015Document130 pagesUg Mining Methods - Part 1 2014 - 2015Ambrose AugenNo ratings yet
- 2059 w19 Ms 2 PDFDocument18 pages2059 w19 Ms 2 PDFZubairHassanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - MINE WASTE MATERIALS AND HANDLING (80 Slides 1 HR 30 Min)Document77 pagesCHAPTER 1 - MINE WASTE MATERIALS AND HANDLING (80 Slides 1 HR 30 Min)mhdnazminorNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics II - Muayad Al-SharradDocument85 pagesSoil Mechanics II - Muayad Al-SharradHumamNo ratings yet
- Published Answer Marks 3: © UCLES 2019 Page 3 of 19Document3 pagesPublished Answer Marks 3: © UCLES 2019 Page 3 of 19PC AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- 5014 Environmental Management: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument10 pages5014 Environmental Management: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of Teachersmstudy123456No ratings yet
- G 2Document183 pagesG 2vpmohammedNo ratings yet
- © UCLES 2019 Page 4 of 17Document3 pages© UCLES 2019 Page 4 of 17Hassan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2006 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International Examinations GCE O LevelDocument9 pagesMARK SCHEME For The May/June 2006 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International Examinations GCE O Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- Guidelines of Restoration After Washout (GE-G-7)Document22 pagesGuidelines of Restoration After Washout (GE-G-7)js kalyana ramaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Reclamation of Low Lying AreasDocument32 pagesGuidelines For Reclamation of Low Lying AreasAyaanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2Saye B.DoloNo ratings yet
- Green energy? Get ready to dig.: Environmental and social costs of renewable energies.From EverandGreen energy? Get ready to dig.: Environmental and social costs of renewable energies.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ABB - Motor-StartersDocument10 pagesABB - Motor-StartersMac WaseemNo ratings yet
- MBA (3 Semester Program) : Financial EconometricsDocument4 pagesMBA (3 Semester Program) : Financial EconometricsNaqeeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Cross Country - Issue 242, August 2023Document92 pagesCross Country - Issue 242, August 2023ธนวัฒน์ ปิยะวิสุทธิกุลNo ratings yet
- Poetic DictionDocument25 pagesPoetic DictionTalha100% (1)
- 1000 Important SAT WordsDocument70 pages1000 Important SAT WordsArifRahman100% (1)
- Amateur Musical Societies and Sports Clubs in Provincial France 1848 1914 Harmony and Hostility 1st Edition Alan R. H. Baker (Auth.)Document54 pagesAmateur Musical Societies and Sports Clubs in Provincial France 1848 1914 Harmony and Hostility 1st Edition Alan R. H. Baker (Auth.)foster.wright732100% (23)
- Hand Hygiene and HandwashingDocument7 pagesHand Hygiene and HandwashingFaith Dianasas RequinaNo ratings yet
- 725SSM Boiler Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument30 pages725SSM Boiler Operation and Maintenance Manualmochamad umarNo ratings yet
- Secret CodesDocument6 pagesSecret CodesUMANo ratings yet
- Group 70 - COMPONENT LOCATIONS - Mitsubishi Outlander III - Wiring DiagramsDocument19 pagesGroup 70 - COMPONENT LOCATIONS - Mitsubishi Outlander III - Wiring DiagramsandreslionNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Treatment in The Management of Cleft Lip and PalateDocument13 pagesOrthodontic Treatment in The Management of Cleft Lip and PalatecareNo ratings yet
- Alcuin of YorkDocument6 pagesAlcuin of YorkemeokeNo ratings yet
- Cisco CBR Series Converged Cable Access Datasheet-C78-738847Document4 pagesCisco CBR Series Converged Cable Access Datasheet-C78-738847irfaneng76No ratings yet
- Jane Eyre Bertha Mason Teachers Notes UpdatedDocument4 pagesJane Eyre Bertha Mason Teachers Notes Updated04. Phan Thi Huyen Trang K17 HLNo ratings yet
- CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701)Document405 pagesCompTIA Security+ (SY0-701)Calisto Junior100% (1)
- Superman All StarsDocument31 pagesSuperman All StarsDaniel CostaNo ratings yet
- Ignou Assignment Wala Ehi 1 Solved Assignment 2018-19Document7 pagesIgnou Assignment Wala Ehi 1 Solved Assignment 2018-19NEW THINK CLASSES100% (1)
- Efm Cip UfDocument6 pagesEfm Cip UfDaneAoneNo ratings yet
- Reading 15 Analysis of Dividends and Share Repurchases - AnswersDocument31 pagesReading 15 Analysis of Dividends and Share Repurchases - AnswersNeerajNo ratings yet
- GVC To IVC To SVC (Ganges Valley Civilization To Indus Valley Civilization To Sarasvati Valley Civilization) PDFDocument28 pagesGVC To IVC To SVC (Ganges Valley Civilization To Indus Valley Civilization To Sarasvati Valley Civilization) PDFanjanaNo ratings yet
- Concept NoteDocument4 pagesConcept NoteAfanie Mae Romero EstepaNo ratings yet
- ExamplesDocument1 pageExamplesSwordhamza KyatNo ratings yet
- About Pets and AnimalsDocument5 pagesAbout Pets and AnimalsMatej JanakievNo ratings yet
- Laptop Repair Course OutlineDocument1 pageLaptop Repair Course Outlineredant21ltd100% (1)
- Literature Review On KudumbasreeDocument9 pagesLiterature Review On Kudumbasreeafdtaeczo100% (1)
- Characteristics of LDCsDocument22 pagesCharacteristics of LDCstinsaeres100% (2)
Geography - Marking Key
Geography - Marking Key
Uploaded by
waqas.butt.1525Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geography - Marking Key
Geography - Marking Key
Uploaded by
waqas.butt.1525Copyright:
Available Formats
1
Beaconhouse School System
MOCK EXAMINATIONS 2024
(ANSWER KEY)
BSS / X GRADE (ANSWER KEY) 2059/02/MOCK/2024 [TURNOVER
2
QUESTION ANSWER MARKS
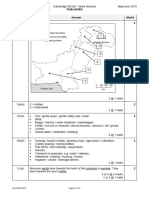
Landform U = Safed Koh
City V = Karachi
1 (a) (i) Line of longitude W = 64°E 4
Plateau X = Balochistan Plateaus
4@1 mark
Gypsum = construction / cement making / plaster / fertilizer / conditioner etc.
Rock Salt = managing ice on roads / food preservative / dyeing clothes etc.
Coal = fuel / cement making / tar / carbon fiber and foam etc.
1 (a) (ii) 4
Mineral Oil = electricity / lubricant / food and laxatives etc.
Lime stone = cement making / reducing salinity / building material etc.
4@1 mark
rugged/uneven ground – so it is difficult to get (large) machinery into
the area;
badland topography – more expensive to reach the minerals/ expensive
to build roads
Barren land – difficult to construct roads; Etc.
1 (b) 4
Note: Any identified idea must link to a feature of topography.
Note: One mark for identification of appropriate idea and a further mark for
development.
Note: Max. 2 marks if no development
4@2 marks
Vegetation cut down/deforestation as land is cleared for mining;
Soil erosion by exposure of soils to rains as land is cleared;
Habitats/ecosystem lost due to clearance of land;
Mining waste produces land pollution;
Water supplies polluted from mineral waste/chemicals from mining
processes seep into groundwater and rivers/sea;
1 (c) (i) 3
Air pollution from machinery/explosives/dust and smoke;
Noise pollution from machinery/extraction processes e.g. blasting;
Subsidence due to collapse of underground tunnels;
Landslides due to explosions
Depressions/deep holes which fill with rainwater.
3@1 mark
Ensure that health, safety and environmental protections are addressed
Process for exploration, mine development, operating procedures and
reclamation and closure activities.
Identify economic and social sustainable development opportunities in
surrounding communities.
Strive to maximize the Sustainable Development benefits and mitigate
1 (c) (ii) the impacts of mining activities on the economic, environmental and 4
social needs of the surrounding communities.
Support education and research pertaining to the most effective and
efficient ways in which mining can and does contribute to Sustainable
Development.
4@1 mark
BSS / X GRADE (ANSWER KEY) 2059/02/MOCK/2024 [TURNOVER
3
QUESTION ANSWER MARKS
Levels marking
No valid response 0
Level 1 1–2
Simple point referring to one view (1)
Simple points referring to any view (2)
Level 2 3–4
Developed point referring to one view (3)
Developed points referring to both views (4)
Level 3 5–6
Developed points referring to both views with evaluation or relevant example
(5)
Developed points referring to both views with evaluation and relevant
example (6)
Content Guide
Answers are likely to refer to:
Possibilities
loans for equipment/hiring experts from abroad with technical
expertise;
sustainable mining techniques reduce environmental damage/allow
safe disposal of waste;
provides employment opportunities in remote rural regions;
large mineral reserves - extraction allows long-term development;
1 (d) wages in mining often higher than in farming etc; 6
transport and power infrastructure developed in remote areas
encourages growth in industries using the minerals e.g. steel industry
near coal and iron ore;
improves the balance of payments/reduces imports and increases
exports;
producing more minerals means more income and increased GDP;
more industrial development brings jobs, means increase in tax revenue
for Pakistan can be spent on education/health;
ETC.
Problems
environmental damage can be irreversible;
better to develop other sectors of the economy e.g. agriculture to fulfil
the demand from an increasing population;
jobs may be low paid and dangerous;
the financial cost of exploitation may not be fully recovered from the
sale/use of the raw materials;
cost of levelling the land after mining activity to avoid land
deformation;
cost of treatment of mining waste and fumes;
cost of technology/machines/experts to make the industry competitive;
some minerals are technically challenging/expensive to extract e.g.
deep underground mining;
BSS / X GRADE (ANSWER KEY) 2059/02/MOCK/2024 [TURNOVER
4
QUESTION ANSWER MARKS
limited pool of workers with skill to operate advanced mining
technology;
some minerals are low quality/may not be worth extracting - if the iron
content of iron ore is less than 60%, it is not suitable for high-quality
steel production e.g. coal from the Thar coalfield contains too many
Sulphur and lime impurities to be used in power stations;
cost of transporting minerals out/bringing workers in may discourage
mineral extraction in remote areas e.g. deserts, mountain regions;
Oil pipelines are expensive to build/maintain.
ETC.
birth rate = 43 – 45
death rate = 27 – 28
2 (a) (i) 3
increases/rises/goes up/gets bigger
3@1 mark
Stage 3
2 (a) (ii) 1
1@1 mark
Shade Stage 2 or Stage 3 or both
2 (a) (iii) 1
1@1 mark
Improvements in hygiene or examples of that, e.g. clean/drinking water
Improved sanitation/introduction of sewage systems
Improved housing/shelter or examples of that, e.g. electricity
Improvements in diet/food intake/safer food storage/better access to
food, e.g. shops/markets
Improved/more/better access to healthcare/medical facilities or
examples of that, e.g. hospitals
2 (a) (iv) More/better/educated/improved access to medical workers or examples 3
of that, e.g. doctors
Vaccinations
Cures for diseases/medicines/medical procedures
Fewer people doing dangerous jobs/improved working conditions
Healthier lifestyle choices/more health conscious or examples of that,
e.g. exercise/not smoking
3@1 mark
Higher paid jobs / better working conditions / more opportunity /
variety of work
Better / higher education / colleges
More reliable sources of food
Expectation of better quality of life
Greater access to healthcare / hospitals / more hospitals / doctors
2 (b) (i) Better healthcare / improved medicines / vaccinations 2
Constant supply / availability of water / electricity / gas / telephone
More entertainment
Better / more housing
Better road / rail / bus links
Better law and order
2@1 mark
BSS / X GRADE (ANSWER KEY) 2059/02/MOCK/2024 [TURNOVER
5
QUESTION ANSWER MARKS
Greater workforce
Increased competition for jobs / more unemployment
Greater variety of skills
Larger local market
Overcrowding / shortage of housing / shanty development
Overpopulation / densely populated
Shortage of food / lack of food
Strain / pressure on named services e.g. need more schools
Strain on named utilities e.g. water, power
2 (b) (ii) Crime increases / increase in violence 4
Growth in informal sector
Urban sprawl / unplanned urban growth
Traffic congestion / jam
Increase in social and psychological problems
Air / water / land / noise pollution / dumping untreated waste /
damage to aquatic life
Increased incidence of named health hazard – dysentery, cholera /
disease spreads more quickly
4@1 mark
Leaving own country
2 (b) (iii) Moving abroad 1
1@1 mark
Densely populated cities put a strain on network due to high numbers
of users; so connections are not always available;
Topography makes some parts of Pakistan inaccessible; so
2 (c) infrastructure cannot be developed there/lack of signal; 4
Extreme weather event/thunderstorms/heavy rainfall; this can
interrupt signal/damage towers and wires;
4@1 mark
Levels marking
No valid response 0
Level 1 1–2
Simple point referring to one view (1)
Simple points referring to any view (2)
Level 2 3–4
Developed point referring to one view (3)
Developed points referring to both views (4)
2 (d) Level 3 5–6 6
Developed points referring to both views with evaluation or relevant example
(5)
Developed points referring to both views with evaluation and relevant
example (6)
Content Guide
Reducing the infant mortality will slow the population growth rate because:
with a reduction in infant mortality people will choose/need to have
fewer children
BSS / X GRADE (ANSWER KEY) 2059/02/MOCK/2024 [TURNOVER
6
QUESTION ANSWER MARKS
pressure on healthcare services will be reduced and more babies will
survive
pressure on education services will be reduced so more of the
population will be well-educated/literate
population growth will slow down as people have more confidence in
healthcare systems and that their children will survive
Reducing the infant mortality will not slow the population growth rate because:
some people will still have large families so that their children can work
for them/send money home/look after them in old age
high cost of pre/anti-natal care
more doctors/nurses needed to help reduce the infant mortality rate
to begin with population will grow, it will take time for people to react
to a lower infant mortality rate and have fewer children
education to be improved before infant mortality rate can be reduced;
to train more midwives/doctors/so the birth rate falls due to higher
literacy
improved nutrition is needed to help reduce the infant mortality rate
and some families cannot afford better diets
living conditions for some families require further improvement, e.g.
sewerage/reliable power supply
Increasing family planning will help slow the population growth rate because:
more access to family planning clinics/centres will inform people
(especially women) of the options available to them
educating women about family planning will help them to make
informed choices about how many children to have
availability and use of contraception can be improved through more
widespread access
educating girls from a young age about sexual health and career
opportunities will encourage them to delay having families and choose
to have fewer children
Increasing family planning will not help slow the population growth rate
because:
males are still the decision makers in some families
religious beliefs/cultural traditions mean some couples continue to
want large families
many poorer families want a large family to help look after them
financially and/or in old age
family planning is not widely available in remote rural areas
investment in education is needed to ensure everyone attends school
Evaluations could include ideas such as:
view A will be achieved by implementing view B, therefore view B is
a better starting point for slowing population growth
BSS / X GRADE (ANSWER KEY) 2059/02/MOCK/2024 [TURNOVER
7
QUESTION ANSWER MARKS
view B challenges cultural/religious beliefs; so there may be resistance
to it, whereas view A would be acceptable to all
education is key to both views which work best if used together ETC.
Buffalo
3 (a) (i) 1
1@1 mark
large number of buffaloes
large scale/large/husbandries
densely packed/crowded/close together
(artificial) fodders /containers of food / organic farming
3 (a) (ii) mass production/commercial scale 3
man-made/non-natural environment/indoor
separate milking areas
Water availability. ETC
3@1 mark
Product
Meat / milk / leather / dung / waste etc.
Use
food/cooking/baking/to eat/consumption/for protein/diet
3 (a) (iii) waste as fertilizers/manure 2
Leather for clothing/jackets
Bones for medicinal purpose
Hides for fur coats etc.
2@1 mark
Subsistence arable farming
3 (b) (i) 1
1@1 mark
Inputs:
manual labour/(mainly)family members working
(mainly) depend on nature/climate conditions/soil/land/relief/rainfall/
underground water/flooding/sunshine
inherited/passed down/traditional knowledge (of farming)
some inputs are obtained during the process of farming, e.g. natural
manure/seeds/animal offspring
small scale/small amount of land/area
tools/named examples, e.g. plough
Processes:
3 (b) (ii) 4
manual labour/(mainly)family members working
Any given example of work done on the farm, e.g. Ploughing/
sowing/weeding/fertilizing/irrigating/harvesting/etc.
Outputs:
outputs are small/little amount
output varies/depends on climate and pests
waste products generated/can be used on the farm
(rarely) there is produce to sell
(rarely) small profits are made to re-invest in the farm
crops/animal products or named example, e.g. rice/milk
BSS / X GRADE (ANSWER KEY) 2059/02/MOCK/2024 [TURNOVER
8
QUESTION ANSWER MARKS
Note: manual labour/(mainly) family members working credited only once
Note: 1 mark reserved for each of inputs, processes and outputs.
4@1 mark
accurate drawing of line at either 75% or 85% (1)
3 (c) (i) correct shading (diagonal) to match the key (1) 2
2@1 mark
sensitive to frost / cold weather conditions / sudden drop in
temperature
3 (c) (ii) 2
usually attacked by pest / locust / attack on lint
2@1 mark
weeding
preparing field
irrigation
fertilization
3 (c) (iii) Drainage of rice fields. 4
Transplanting seedlings.
Harvesting / Polishing ETC.
.
4@1 mark
Levels marking
No valid response 0
Level 1 1–2
Simple point referring to one view (1)
Simple points referring to any view (2)
Level 2 3–4
Developed point referring to one view (3)
Developed points referring to both views (4)
Level 3 5–6
Developed points referring to both views with evaluation or relevant example
(5)
Developed points referring to both views with evaluation and relevant
example (6)
3 (d) Content Guide 6
It is possible to improve agricultural practices and water management to
prevent waterlogging and salinity by:
leaving parts of the land fallow – preventative measure
building more dams/reservoirs to store more water
lining/temporary closure of canals to reduce water leakages
installing tube wells to flush the salt out of the soil/so flow of water
for irrigation can be controlled
planting eucalyptus trees to take in excess water when land is badly
waterlogged
digging surface/sub-surface drains
removing salts by adding gypsum/by reducing fertilizer use
Salinity Control and Reclamation Projects (SCARP)
government legislation, e.g. water quotas
BSS / X GRADE (ANSWER KEY) 2059/02/MOCK/2024 [TURNOVER
9
QUESTION ANSWER MARKS
cultivating salt tolerant crops
using high-yielding varieties which require less irrigation
using saline land for livestock farming
It is not possible to improve agricultural practices and water
management to prevent waterlogging and salinity due to:
cost/time taken for farmers to maintain canals/tunnels
lack of investment in methods
replacing traditional methods with tube wells lowers the water table
and provides water for fewer farmers
literacy/education levels may mean some farmers continue to over-
irrigate
SCARP projects date from 1958 and large public tube wells are
deteriorating/reaching end of their life
lack of access to/cannot afford high yielding varieties
traditional irrigation systems are communally owned, change requires
agreement/may generate disagreement
Line of Latitude A = 28°N
River B = Dasht river
4 (a) (i) 3
City C = Hyderabad
3@1 mark
General
Provides employment
Industrial linkages
Supply of raw materials
To make use of government incentives
Specific
Good road connection
4 (a) (ii) 4
Close to domestic airport at Hyderabad
Close to Karachi/Port Qasim for exports / imported raw materials/
trade in semi-finished goods
Near JENCO thermal power plant.
Close to large domestic market in Karachi and Hyderabad
Large labour force available form Karachi and Hyderabad.
4@2 marks
Value of Imports
1 100 000 million rupees (1 mark)
Value of Exports
780 000 million rupees (1mark)
4 (b) (i) Trade Balance 4
Value of Export – Value of import
780 000 – 1 100 000 = (negative) ‒320 000 million rupees (2 marks)
Note: 1 mark for working and 1 mark for correct value
4@1 mark
Exports:
4 (b) (ii) miscellaneous textiles/worn clothing; 4
cotton (yarn) (medium staple);
BSS / X GRADE (ANSWER KEY) 2059/02/MOCK/2024 [TURNOVER
10
QUESTION ANSWER MARKS
knit or crochet clothing/accessories;
clothing/accessories (not knit or crochet);
cereals/rice;
leather/animal gut articles;
copper
sugar/sugar confectionery;
mineral fuels including oil;
beverages/spirits/vinegar;
salt/Sulphur/stone/cement;
fruit, nuts;
medical/surgical/optical/weapons and ammo/technical apparatus;
sports goods;
carpets and rugs; ETC
Imports:
mineral fuels including coal/oil/petroleum/oil products;
machinery/electronics/electrical equipment;
iron/steel
chemicals/chemical products;
vehicles/cars;
plastics/plastic articles;
animal/vegetable fats/oils/waxes;
oil seeds;
cotton;
wheat: ETC
2@1 mark
Accurate completion of percentage bar chart.
4 (c) 4
4@1 mark
Levels marking
No valid response 0
Level 1 1–2
Simple point referring to one view (1)
Simple points referring to any view (2)
Level 2 3–4
Developed point referring to one view (3)
Developed points referring to both views (4)
Level 3 5–6
4 (d) Developed points referring to both views with evaluation or relevant example 6
(5)
Developed points referring to both views with evaluation and relevant
example (6)
Content Guide
Agree with View A:
Pakistan could manufacture many of the products that it imports
creating jobs;
More chances of employment opportunities
BSS / X GRADE (ANSWER KEY) 2059/02/MOCK/2024 [TURNOVER
11
QUESTION ANSWER MARKS
Industrialization
Improved quality of export products and standards.
Pakistan can educate people on the impact of consumerism on the
environment;
By focusing on local industry e can improve standards of goods can
be improved e.g. by working with PTEC (Pakistan Technical and
Educational Council) for training. Etc.
disagree with View A:
Pakistan does not have resources to manufacture goods that it
imports;
It would cost too much to make the products/cheaper to import them;
it is costly to develop infrastructure and to train and educate people;
It may be difficult to support the domestic demand for products that
are no longer imported.
Importing cheap goods does not affect the balance of trade
significantly; Etc.
Agree with View B:
Pakistan has many natural and cultural attractions
provides a wider range of job opportunities for local people
improvements to transport and/or services for tourism will benefit local
people too
improve relations/cultural links with other countries
contributes to Pakistan’s global image
high-end/adventure/mass tourism will bring in large amounts of
revenue
Pakistan Tourism Development Corporation (PTDC) have already
done work to promote tourism
Disagree with View B:
tourism tends to be seasonal/no money generated out of season
transport/communications infrastructure would need to be further
improved to meet tourist needs
accommodation for tourists would require further improvement
international tourism may lead to dilution of traditional culture
Evaluation may argue:
That both ideas are necessary for improving Pakistan’s GDP.
Y = Punjab
5 (a) (i) Z = Balochistan 2
2@1 mark
1. India
5 (a) (ii) 2. Iran 2
2@1 mark
Northern Pakistan / FATA has no / few rail networks;
Dense network in Punjab;
5 (a) (iii) Sparse network in Balochistan / South / Southwest / one line in 4
Balochistan;
There are two lines in central KPK;
BSS / X GRADE (ANSWER KEY) 2059/02/MOCK/2024 [TURNOVER
12
QUESTION ANSWER MARKS
Medium / moderate network in Sindh;
More around major cities;
More railways in East / more railways in North East (or opposites)
4@1 mark
China / UAE
5 (b) (i) 1
1@1 mark
Any named country – increased sales/markets/market share/enlarge
market share;
China/Afghanistan – neighbouring countries with land links;
China – to maintain relations/political ties with regional superpower;
Afghanistan – foodstuffs such as rice, sugar;
Malaysia – palm oil and mineral oil
5 (b) (ii) UAE/Kuwait/Saudi Arabia – source of crude oil; 2
UAE – nearby country via sea/Arabian Sea/Makran Coast;
USA/Germany/UK – developed economies raw materials, e.g. cotton
yarn/woven cloth or manufactured goods, e.g. sports goods, linen,
suits.
Note: Country must be named plus import or export.
Note: No additional countries allowed.
X = Quetta
Y = Multan
5 (c) (i) 3
Z = Sukkur
3@1 mark
A = Khunjerab Pass
5 (c) (ii) B = Khyber Pass 1
1@1 mark
Identification of Lahore – Islamabad Motorway (M2)
2 large centres of population passed by other populated areas
to promote growth of industrial estate
5 (c) (iii) large volume of traffic / ease congestion / save other road 4
better for lorries / large vehicles
link from Lahore to Karakoram Highway
4@2 marks
Levels marking
No valid response 0
Level 1 1–2
Simple point referring to one view (1)
Simple points referring to any view (2)
Level 2 3–4
5 (d) Developed point referring to one view (3) 6
Developed points referring to both views (4)
Level 3 5–6
Developed points referring to both views with evaluation or relevant example
(5)
Developed points referring to both views with evaluation and relevant
example (6)
BSS / X GRADE (ANSWER KEY) 2059/02/MOCK/2024 [TURNOVER
13
QUESTION ANSWER MARKS
Content Guide
Answers are likely to refer to:
Possibilities
Airways are the fastest, most comfortable and prestigious mode of
transport in recent times.
They can easily cross over geographical boundaries and vast stretches
of seas and oceans.
They can negotiate over difficult terrain like high mountains,
dissected terrain, dreary desert, dense forests with great ease, within
short period of time.
Fast international travel between different countries of the world have
been possible because of the development of airways.
Airways play a vital role during natural and man-made calamities like
floods, famines, earthquake, epidemics and war.
They help in rescue operations and providing relief to the people in
affected areas within short time. ETC.
Problems:
High cost
Large land required for construction of new airports
Non – cooperated Staff / employees
Outdated aero planes
Huge investment required
Inadequate training facilities
Maximized risk factor due to crime, violence and hijacking etc.
BSS / X GRADE (ANSWER KEY) 2059/02/MOCK/2024 [TURNOVER
You might also like
- Tratado de Ifa Uso Exclusivo de BabalawoDocument22 pagesTratado de Ifa Uso Exclusivo de BabalawoAndersonAguiarOdéIfé0% (3)
- Environmental Systems and Societies Paper 2 SL MarkschemeDocument18 pagesEnvironmental Systems and Societies Paper 2 SL MarkschemeAfra LamisaNo ratings yet
- Dockside Green: The Story of the Most Sustainable Development in the WorldFrom EverandDockside Green: The Story of the Most Sustainable Development in the WorldNo ratings yet
- Minerals, Metals, Mercury and Miracles - UsmanDocument43 pagesMinerals, Metals, Mercury and Miracles - UsmanuiderschenNo ratings yet
- ServiceDocument1,146 pagesServiceEmanuel Nicolas VillarruelNo ratings yet
- Informatica FunctionsDocument46 pagesInformatica FunctionsManoj Krishna100% (1)
- 0680 Environmental Management: MARK SCHEME For The March 2015 SeriesDocument6 pages0680 Environmental Management: MARK SCHEME For The March 2015 Seriesnng.uyenchuoiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Pakistan Studies 2059/02 October/November 2021Document24 pagesCambridge O Level: Pakistan Studies 2059/02 October/November 2021Bilal Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- © UCLES 2023 Page 4 of 24Document21 pages© UCLES 2023 Page 4 of 2467140No ratings yet
- Geo Mineral ResourcesDocument6 pagesGeo Mineral ResourcesRevolt 2.0No ratings yet
- Env ProblemsDocument7 pagesEnv Problemsimon.landageNo ratings yet
- 2059 Pakistan Studies: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2014 SeriesDocument11 pages2059 Pakistan Studies: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2014 Seriesmuhammad saleemNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Pakistan Studies 2059/02Document28 pagesCambridge O Level: Pakistan Studies 2059/02aqsabatool.2708No ratings yet
- Institute of Architecture Department: ArchitectureDocument13 pagesInstitute of Architecture Department: ArchitectureJasjot SinghNo ratings yet
- T. E. Civil: A Seminar Report OnDocument17 pagesT. E. Civil: A Seminar Report OnAlisha mullaNo ratings yet
- JudeDocument54 pagesJudeBranchi IkyureNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 Solid Industrial Waste and Land Degradation-BDocument30 pagesLecture 16 Solid Industrial Waste and Land Degradation-BMuhammad Saad KhokharNo ratings yet
- Coal Mining: A Synopsis BY Aloke GangulyDocument37 pagesCoal Mining: A Synopsis BY Aloke GangulyALOKE GANGULYNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 - DAHUYLADocument14 pagesActivity 6 - DAHUYLAJef Michael L. DahuylaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Pakistan Studies 0448/02Document28 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Pakistan Studies 0448/02zainab.fatima1150No ratings yet
- Management of Mining Wastes White Slag From Steel Mills 1682553851Document6 pagesManagement of Mining Wastes White Slag From Steel Mills 1682553851hjqsdbxh dbhcxNo ratings yet
- Department of Public Works: Addendum To PW 371Document97 pagesDepartment of Public Works: Addendum To PW 371larushkanNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Maximum Mark: 75: Gce O LevelDocument6 pagesMark Scheme Maximum Mark: 75: Gce O Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- Effect of Fly Ash On Geotechnical Properties and Stability of Coal Mine Overburden Dump: An OverviewDocument9 pagesEffect of Fly Ash On Geotechnical Properties and Stability of Coal Mine Overburden Dump: An OverviewVisal SasidharanNo ratings yet
- Transaction Highlights: Krugold Resources, IncDocument5 pagesTransaction Highlights: Krugold Resources, IncAamir AzizNo ratings yet
- Minerals 13 00090Document18 pagesMinerals 13 00090janhvi muleNo ratings yet
- Application of Remotely Sensed Data andDocument10 pagesApplication of Remotely Sensed Data andRonaldo MutepaireNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Geography Mock - Salman HashmiDocument14 pagesMark Scheme Geography Mock - Salman HashmiSarim AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Geography S-8 MSDocument4 pagesGeography S-8 MSdawoodtab23No ratings yet
- 2059 w04 Ms 2Document10 pages2059 w04 Ms 2api-3807993No ratings yet
- 2059 w12 Ms 2Document11 pages2059 w12 Ms 2mstudy123456No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentKirankumar Rohit264No ratings yet
- 06 May 2022 MININGDocument28 pages06 May 2022 MININGSamantha Cabugon0% (1)
- 2059 November 2015 Paper 2 Mark Scheme PDFDocument15 pages2059 November 2015 Paper 2 Mark Scheme PDFareebNo ratings yet
- Mining Geology, Midexam NoteDocument11 pagesMining Geology, Midexam NoteAbu NaeemNo ratings yet
- EIAR Limestone PELICAN-1 FINALDocument30 pagesEIAR Limestone PELICAN-1 FINALZubair KhanNo ratings yet
- Envi SciDocument5 pagesEnvi Scinuebemadethis432No ratings yet
- Written Report - Auditing Mining Industry (Group 4)Document33 pagesWritten Report - Auditing Mining Industry (Group 4)rachel banana hammockNo ratings yet
- Group 26 PlublishedReserch PaperDocument7 pagesGroup 26 PlublishedReserch PaperDaily FunNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 5014/12 October/November 2017Document12 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 5014/12 October/November 2017Jhon CenaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Mine Waste Leachates On Aquatic Environment: A ReviewDocument7 pagesImpact of Mine Waste Leachates On Aquatic Environment: A ReviewKadek Nando setiawanNo ratings yet
- Aba Lakew Residence Aba Yikuno Bridge To University RoadDocument9 pagesAba Lakew Residence Aba Yikuno Bridge To University RoadAsmerom MosinehNo ratings yet
- © Ucles 2008Document2 pages© Ucles 2008PC AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- Indian Small-Scale Mining With Special Emphasis On Environmental ManagementDocument7 pagesIndian Small-Scale Mining With Special Emphasis On Environmental ManagementCarlos MaroveNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabi MinE PDFDocument113 pagesCourse Syllabi MinE PDFgirmay kasayeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/21 May/June 2022Document6 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/21 May/June 2022Tapiwa MT (N1c3isH)No ratings yet
- Ways On How Separating Mixtures Like in MiningDocument11 pagesWays On How Separating Mixtures Like in MiningBENJ AMINNo ratings yet
- Tailings Dam Design. TechnologyUpdate SecuredDocument12 pagesTailings Dam Design. TechnologyUpdate SecuredJavierNo ratings yet
- Status of CoalL and Lignite Resources in IndiaDocument121 pagesStatus of CoalL and Lignite Resources in IndiaAnkon MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Impacto AmbientalDocument11 pagesImpacto AmbientalSeguridad MarvannssNo ratings yet
- Ug Mining Methods - Part 1 2014 - 2015Document130 pagesUg Mining Methods - Part 1 2014 - 2015Ambrose AugenNo ratings yet
- 2059 w19 Ms 2 PDFDocument18 pages2059 w19 Ms 2 PDFZubairHassanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - MINE WASTE MATERIALS AND HANDLING (80 Slides 1 HR 30 Min)Document77 pagesCHAPTER 1 - MINE WASTE MATERIALS AND HANDLING (80 Slides 1 HR 30 Min)mhdnazminorNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics II - Muayad Al-SharradDocument85 pagesSoil Mechanics II - Muayad Al-SharradHumamNo ratings yet
- Published Answer Marks 3: © UCLES 2019 Page 3 of 19Document3 pagesPublished Answer Marks 3: © UCLES 2019 Page 3 of 19PC AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- 5014 Environmental Management: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument10 pages5014 Environmental Management: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of Teachersmstudy123456No ratings yet
- G 2Document183 pagesG 2vpmohammedNo ratings yet
- © UCLES 2019 Page 4 of 17Document3 pages© UCLES 2019 Page 4 of 17Hassan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2006 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International Examinations GCE O LevelDocument9 pagesMARK SCHEME For The May/June 2006 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International Examinations GCE O Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- Guidelines of Restoration After Washout (GE-G-7)Document22 pagesGuidelines of Restoration After Washout (GE-G-7)js kalyana ramaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Reclamation of Low Lying AreasDocument32 pagesGuidelines For Reclamation of Low Lying AreasAyaanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2Saye B.DoloNo ratings yet
- Green energy? Get ready to dig.: Environmental and social costs of renewable energies.From EverandGreen energy? Get ready to dig.: Environmental and social costs of renewable energies.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ABB - Motor-StartersDocument10 pagesABB - Motor-StartersMac WaseemNo ratings yet
- MBA (3 Semester Program) : Financial EconometricsDocument4 pagesMBA (3 Semester Program) : Financial EconometricsNaqeeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Cross Country - Issue 242, August 2023Document92 pagesCross Country - Issue 242, August 2023ธนวัฒน์ ปิยะวิสุทธิกุลNo ratings yet
- Poetic DictionDocument25 pagesPoetic DictionTalha100% (1)
- 1000 Important SAT WordsDocument70 pages1000 Important SAT WordsArifRahman100% (1)
- Amateur Musical Societies and Sports Clubs in Provincial France 1848 1914 Harmony and Hostility 1st Edition Alan R. H. Baker (Auth.)Document54 pagesAmateur Musical Societies and Sports Clubs in Provincial France 1848 1914 Harmony and Hostility 1st Edition Alan R. H. Baker (Auth.)foster.wright732100% (23)
- Hand Hygiene and HandwashingDocument7 pagesHand Hygiene and HandwashingFaith Dianasas RequinaNo ratings yet
- 725SSM Boiler Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument30 pages725SSM Boiler Operation and Maintenance Manualmochamad umarNo ratings yet
- Secret CodesDocument6 pagesSecret CodesUMANo ratings yet
- Group 70 - COMPONENT LOCATIONS - Mitsubishi Outlander III - Wiring DiagramsDocument19 pagesGroup 70 - COMPONENT LOCATIONS - Mitsubishi Outlander III - Wiring DiagramsandreslionNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Treatment in The Management of Cleft Lip and PalateDocument13 pagesOrthodontic Treatment in The Management of Cleft Lip and PalatecareNo ratings yet
- Alcuin of YorkDocument6 pagesAlcuin of YorkemeokeNo ratings yet
- Cisco CBR Series Converged Cable Access Datasheet-C78-738847Document4 pagesCisco CBR Series Converged Cable Access Datasheet-C78-738847irfaneng76No ratings yet
- Jane Eyre Bertha Mason Teachers Notes UpdatedDocument4 pagesJane Eyre Bertha Mason Teachers Notes Updated04. Phan Thi Huyen Trang K17 HLNo ratings yet
- CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701)Document405 pagesCompTIA Security+ (SY0-701)Calisto Junior100% (1)
- Superman All StarsDocument31 pagesSuperman All StarsDaniel CostaNo ratings yet
- Ignou Assignment Wala Ehi 1 Solved Assignment 2018-19Document7 pagesIgnou Assignment Wala Ehi 1 Solved Assignment 2018-19NEW THINK CLASSES100% (1)
- Efm Cip UfDocument6 pagesEfm Cip UfDaneAoneNo ratings yet
- Reading 15 Analysis of Dividends and Share Repurchases - AnswersDocument31 pagesReading 15 Analysis of Dividends and Share Repurchases - AnswersNeerajNo ratings yet
- GVC To IVC To SVC (Ganges Valley Civilization To Indus Valley Civilization To Sarasvati Valley Civilization) PDFDocument28 pagesGVC To IVC To SVC (Ganges Valley Civilization To Indus Valley Civilization To Sarasvati Valley Civilization) PDFanjanaNo ratings yet
- Concept NoteDocument4 pagesConcept NoteAfanie Mae Romero EstepaNo ratings yet
- ExamplesDocument1 pageExamplesSwordhamza KyatNo ratings yet
- About Pets and AnimalsDocument5 pagesAbout Pets and AnimalsMatej JanakievNo ratings yet
- Laptop Repair Course OutlineDocument1 pageLaptop Repair Course Outlineredant21ltd100% (1)
- Literature Review On KudumbasreeDocument9 pagesLiterature Review On Kudumbasreeafdtaeczo100% (1)
- Characteristics of LDCsDocument22 pagesCharacteristics of LDCstinsaeres100% (2)