Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Research Iii: Quarter 3 Week 2.2
Research Iii: Quarter 3 Week 2.2
Uploaded by
John Miles SerneoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Research Iii: Quarter 3 Week 2.2
Research Iii: Quarter 3 Week 2.2
Uploaded by
John Miles SerneoCopyright:
Available Formats
FOR ZAMBOANGA CITY DIVISION USE ONLY
NOT FOR SALE
9
RESEARCH III
QUARTER 3
Week 2.2
Capsulized Self-Learning Empowerment
Toolkit
Schools Division Office of Zamboanga City
Region IX, Zamboanga Peninsula
Zamboanga City
“Unido, Junto avanza con el EduKalidad Cree, junto junto puede!”
Prepared by: RIZZA EARL VEVERLY T. ANGELES, SST-III
Don Pablo Lorenzo Memorial High School - JHS
1
SUBJECT & Grade 9
QUARTER 3 WEEK 2 DATE _
GRADE/LEVEL RESEARCH III DD/MM/YYYY
TOPIC Statistical Tests
1. Utilizes appropriate statistical tools in analyzing data.
LEARNING (SSP-RS9-AID-III-q-t-7)
COMPETENCIES 2. Interprets data/ statistical results. (SSP-RS9-AID-III-u-v-8)
3. Test hypothesis (SSP-RS9-AID-III-v-w-9)
IMPORTANT: Do not write anything on this material. Write your answer on a
separate sheet of paper and don not forget to answer all SAQs.
UNDERSTAND
Statistical Tests
There are different statistical tests or tools available for you to use to
analyze your data. But the question is, which one will you use for your
study? This lesson will help you determine which statistical test is
appropriate for your study.
What is a statistical test?
Statistical tests are used in hypothesis testing. They can be used to:
determine whether a predictor variable (independent variable) has a statistically
significant relationship with an outcome variable (dependent variable).
estimate the difference between two or more groups.
Statistical tests are based on the null hypothesis that there is no correlation or
difference between groups. Then they determine if the observed data fall outside of the
null hypothesis's predicted range of values.
What does a statistical test do?
A test statistic is a number that describes how much the relationship between
variables in your test differs from the null hypothesis of no relationship. The P-value is
then calculated (probability value). If the null hypothesis of no relationship were true,
the p-value estimates how likely it is that you would see the difference described by the
test statistic.
You can infer a statistically significant relationship between the predictor
(independent) and outcome (dependent) variables if the test statistic's value
is more extreme than the null hypothesis's statistic. If the test statistic's
value is less extreme than the null hypothesis's, you can conclude that there
is no statistically significant relationship between the predictor
(independent) and the outcome (dependent).
When to perform a statistical test?
Statistical tests can be performed on data that has been collected in a statistically
valid manner, such as through an experiment or observations made using probability
Prepared by: RIZZA EARL VEVERLY T. ANGELES, SST-III
Don Pablo Lorenzo Memorial High School - JHS
2
sampling methods. Your sample size must be large enough to approximate the true
distribution of the population being studied for a statistical test to be valid.
You need to know the following to determine which statistical test to use:
Whether your data meets certain assumptions.
The types of variables that you’re dealing with.
What are the statistical assumptions?
Statistical tests make some common assumptions about the data they are testing:
1. Independence of observations (a.k.a. no autocorrelation): The
observations/variables you include in your test are not related (for example,
multiple measurements of a single test subject are not independent, while
measurements of multiple different test subjects are independent).
2. Homogeneity of variance: the variance within each group being compared is
similar among all groups. If one group has much more variation than others, it
will limit the test’s effectiveness.
3. Normality of data: the data follows a normal distribution (a.k.a. a bell curve).
This assumption applies only to quantitative data.
You can infer a statistically significant relationship between the
independent and dependent variables if the test statistic's value is more
extreme than the null hypothesis's statistic. If the test statistic's value is
less extreme than the null hypothesis's, you can infer that there is no
statistically significant relationship between the independent and
dependent variables.
What are the types of variables?
What type of statistical test you can use is usually determined by the types of
variables you have.
Quantitative variables represent amounts of things (e.g. the number of trees in
a forest). Types of quantitative variables include:
Continuous (can be Ratio or Interval Scale): represent measures and can
usually be divided into units smaller than one (e.g. 0.75 grams).
Discrete (a.k.a integer variables): represent counts and usually can’t be
divided into units smaller than one (e.g. 1 tree).
Categorical variables represent groupings of things (e.g. the different tree
species in a forest). Types of categorical variables include:
Ordinal: represent data with an order (e.g. rankings).
Nominal: represent group names (e.g. brands or species names).
Binary: represent data with a yes/no or 1/0 outcome (e.g. win or lose).
Select a test that is appropriate for the types of predictor and outcome
variables you have gathered. Since you are doing an experiment, these are
the independent and dependent variables.
Prepared by: RIZZA EARL VEVERLY T. ANGELES, SST-III
Don Pablo Lorenzo Memorial High School - JHS
3
You can use the given tables below to help you determine which statistical test best
matches your variables.
What is a parametric test?
Parametric tests usually have stricter requirements than nonparametric tests, and
are able to make stronger inferences from the data. They can only be conducted with
data that adheres to the common assumptions of statistical tests.
The most common types of parametric test include regression tests, comparison
tests, and correlation tests.
Regression tests
Regression tests are used to test cause-and-effect relationships. They look for
the effect of one or more continuous variables on another variable.
Predictor variable Outcome variable
Statistical Sample research
(Independent (Dependent
Test question
variable) variable)
Simple linear Continuous Continuous What is the effect of
regression 1 IV* 1 DV** income on longevity?
Continuous Continuous What is the effect of
Multiple
2 or more IVs 1 DV income and minutes of
linear
exercise per day on
regression
longevity?
Continuous Binary What is the effect of
Logistic drug dosage on the
regression survival of a test
subject?
*IV refers to Independent Variable **DV refers to Dependent Variable
Comparison tests
Comparison tests look for differences among group means. They can be used
to test the effect of a categorical variable on the mean value of some other
characteristic.
t tests are used when comparing the means of precisely two groups (e.g. the
average heights of men and women). ANOVA and MANOVA tests are used when
comparing the means of more than two groups (e.g. the average heights of children,
teenagers, and adults).
Predictor variable Outcome variable
Statistical Sample research
(Independent (Dependent
Test question
variable) variable)
Categorical Quantitative What is the effect of two
Paired t-test 1 IV* Groups come different test prep
(t test for from the same programs on the
dependent population average exam scores for
samples) students from the same
class?
Prepared by: RIZZA EARL VEVERLY T. ANGELES, SST-III
Don Pablo Lorenzo Memorial High School - JHS
4
Independent Categorical Quantitative What is the difference in
t-test (t test 1 IV* Groups come average exam scores for
for from the different students from two
independent populations different schools?
samples)
Categorical Quantitative What is the difference in
ANOVA 1 or more IVs 1 DV** average pain levels
(Analysis of among post-surgical
Variance) patients given three
different painkillers?
MANOVA Categorical Quantitative What is the effect of
(Multivariate 1 or more IVs 2 or more DVs flower species on petal
Analysis of length, petal width, and
Variance) stem length?
*IV refers to Independent Variable **DV refers to Dependent Variable
Correlation tests
Correlation tests check whether two variables are related without assuming
cause-and-effect relationships.
These can be used to test whether two variables you want to use in (for example)
a multiple regression test are autocorrelated.
Predictor variable Outcome variable
Statistical Sample research
(Independent (Dependent
Test question
variable) variable)
How are latitude and
Pearson’s r Continuous Continuous
temperature related?
What is a nonparametric test?
Non-parametric tests don’t make as many assumptions about the data, and are
useful when one or more of the common statistical assumptions are violated. However,
the inferences they make aren’t as strong as with parametric tests.
Predictor variable Outcome variable
Statistical
(Independent (Dependent Use in place of
Test
variable) variable)
Spearman’s r Quantitative Quantitative Pearson’s r
Chi square of Categorical Categorical Pearson’s r
independence
Sign Test Categorical Quantitative One sample t test
Categorical Quantitative
Kruskal–
3 or more IVs or ANOVA
Wallis H
groups
Categorical Quantitative
ANOSIM 3 or more IVs or 2 or more DVs MANOVA
groups
Prepared by: RIZZA EARL VEVERLY T. ANGELES, SST-III
Don Pablo Lorenzo Memorial High School - JHS
5
Categorical Quantitative
Wilcoxon
2 IVs or groups Groups come
Rank-Sum Independent t test
from different
test
populations
Categorical Quantitative
Wilcoxon
2 IVs or groups Groups come
Signed-rank Paired t test
from the same
test
population
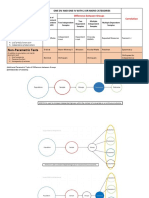
Here is a flowchart to help you choose among parametric tests. For
nonparametric alternatives, please check the table above.
Figure 1 Choosing a statistical test.
SAQ-1: What will help you determine the appropriate statistical test for your
study? Explain briefly.
SAQ-2: Why is it important to use appropriate statistical test for your study?
Prepared by: RIZZA EARL VEVERLY T. ANGELES, SST-III
Don Pablo Lorenzo Memorial High School - JHS
6
You are done with this lesson. You may now proceed to Let’s Practice
section.
Let’s Practice! (Write your answer on your answer sheet.)
Direction: Read the given situation below and answer the given questions.
Proponents: Students of Megan Dehning’s class, Innovations Public Charter School
(HI-SEES, 2011-2012)
Title: “A Comparison of the Abundance and Diversity of Fish Species at Kahalu’u Bay”
Research Question:
Is there a difference in the abundance and diversity of fish close to shore and further from
shore at Kahalu’u Bay?
Hypothesis:
We think there will be more fish species in the water farther from shore because there is less
human activity and more coral, providing a greater food source.
Procedure:
The materials were collected and were split into two groups. A 50 meter transect line was
laid down in water that is close to shore and in water a further distance from shore. Being
careful not to hurt the coral reef while doing this. Give the fish a minute or two to get used to
the transect line. All the fish that are within 3 feet of the transect line were counted by putting
a tally mark next to that species on the data sheet. these steps were repeated until everyone
in the group has collected data. After all the data were collected, the transect line was
carefully picked up.
Results:
Conclusion:
Our hypothesis regarding the total number of fish observed in waters farther from shore
versus closer to shore was supported because 54.2% of all fish surveyed were found in
waters further from shore.
GUIDE QUESTIONS:
1. What type of research question is the example asking (e.g., descriptive, measuring
associations, measuring differences)?
2. Can you identify all of the variables measured by the research project?
3. How many variables are there? Is there a distinction between the independent
variable(s) (IV) and the dependent variable(s) (DV)?
4. What type of data is the measurement collecting (e.g., ordinal, nominal, interval)?
5. Using the available resources, can you determine what type of statistical analysis
to apply?
Prepared by: RIZZA EARL VEVERLY T. ANGELES, SST-III
Don Pablo Lorenzo Memorial High School - JHS
7
You will learn more about each statistical tests as we go through the
quarter. For now, you are done with this lesson. But before you
evaluate how much you have learned today, let’s go back to a few key
points.
REMEMBER
Key Points
Statistical tests are used in hypothesis testing to help the researchers analyze
and interpret the data collected.
To help you determine which statistical test to use for your study, you need to
know (1) whether your data meets certain assumptions and (2) the type of
variables that you have (nature of your independent and dependent variables).
Parametric statistical procedures rely on assumptions about the shape of the
underlying population's distribution as well as the shape or parameters of the
assumed distribution. Nonparametric statistical methods make no or few
assumptions about the shape or parameters of the population distribution from
which the sample was taken.
Parametric tests includes simple linear regression, multiple linear regression,
logistic regression, Pearson’s r, paired t test, independent t test, ANOVA, and
MANOVA.
Nonparametric tests includes Chi square for independent sample, Spearman’s
r, Sign test, Kruskal–Wallis H, ANOSIM, Wilcoxon Rank-Sum test, and Wilcoxon
Sign-Sum test.
TRY
Let’s see how much you have learned today!
Read each question carefully. Choose the best answer and write the CAPITAL
LETTER of the choice corresponding to your answer on your answer sheet.
1. Which of the following is NOT TRUE about statistical tests?
A. It is an estimate of the difference between two or more groups.
B. It determine whether the independent variable has a statistical signifincant
relationship with the dependent variable.
C. Statistical tests are solely based on the alternative hypothesis.
D. It determines if the observed data fall outside of the null hypothesis’s predicted
range of values.
2. Which of the following is NOT TRUE about the common assumptions about the data
when doing a statistical test?
A. The observations you include in your test are not related.
B. The data follows a normal distribution.
C. The variance within each group being compared is similar among all groups.
D. It is only used when the researcher is only interested in conitnuous type of data.
3. A sample of people where grouped into an omnivore, vegetarian, vegan, or fruitarian.
What type of data is the given grouping?
A. Continuous B. Nominal C. Ordinal D. Ratio
4. Which of the following refers to the type of variable which represent groupings of
things?
A. Quantitative B. Continuous C. Categorical D. Discrete
Prepared by: RIZZA EARL VEVERLY T. ANGELES, SST-III
Don Pablo Lorenzo Memorial High School - JHS
8
5. What statistical test is appropriate for the given research question: “What is the effect
of two different feeding management system on the weight of 45 days old chicken?”
A. Paired t test B. Independent t test C. MANOVA D. z test
6. Using figure 1 as a basis, what it the appropriate statistical test for a study with a
categorical type of independent variable and a quantitative type of dependent
variable; and where you compare the means of the groups with one dependent
variable (outcome variable)?
A. Chi square B. t test C. ANOVA D. ANOVA
7. What would be the alternative statistical test for ANOVA when you use a
nonparametric test?
A. ANOSIM C. Spearman’s r
B. Wilcoxon Rank-Sum test D. Kruskal–Wallis H
8. What is the appropriate statistical test for a study that would use a nonparametric
test which has two or more independent variables that are categorical in nature, has
a continuous type of dependent variable and where groups come from the same
population?
A. Wilcoxon Signed-rank test C. Spearman’s r
B. Wilcoxon Rank-Sum test D. Kruskal–Wallis H
9. Which of the following statistical tests is appropriate for this research question: “How
are the number of cars a company owns and its revenue related?
A. ANOVA B. Independent t test C. Pearson’s r D. Paired t test
10. For study which will use a parametric test with 2 independent variables (categorical
type in nature) and 1 quantitative dependent variable, what is the appropriate
statistical to analyze the data collected from this study?
A. ANOVA B. Simple linear regression C. MANOVA D. Pearson’s r
Bevans, Rebecca. “Statistical Tests: Which One Should You Use?,”
December 28, 2020.
https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/statistical-tests/.
REFERENCE
Figure:
Figure 1- https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/statistical-tests/
This learning resource contains copyrighted materials. The use of
which has not been specifically authorized by the copyright owner.
We are developing this CapSLET in our efforts to provide printed
references to the learning continuity plan of this division in this time of
DISCLAIMER pandemic.
This material is not intended for uploading nor for commercial use
but purely for educational purposes and for the utilization of
Zamboanga City Division only.
Prepared by: RIZZA EARL VEVERLY T. ANGELES, SST-III
Don Pablo Lorenzo Memorial High School - JHS
You might also like
- Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 10th Edition Gravetter Solutions ManualDocument13 pagesStatistics For The Behavioral Sciences 10th Edition Gravetter Solutions Manualjerryperezaxkfsjizmc100% (15)
- Presentation T TestDocument31 pagesPresentation T TestEe HAng Yong0% (1)
- Multiple+Choice+Questions ForecastingDocument3 pagesMultiple+Choice+Questions Forecastingjackywen102486% (7)
- R Q& ADocument24 pagesR Q& Aalene100% (1)
- Choosing The Right Statistical Test - Types and ExamplesDocument14 pagesChoosing The Right Statistical Test - Types and ExamplesRizwanNo ratings yet
- Statistical TreatmentDocument7 pagesStatistical TreatmentIvy Frias JapaNo ratings yet
- Choosing The Right Statistical TestDocument6 pagesChoosing The Right Statistical Testlehalinh.119No ratings yet
- SCRIBBR - Choosing The Right Statistical TestDocument14 pagesSCRIBBR - Choosing The Right Statistical TestmllabateNo ratings yet
- What Does A Statistical Test DoDocument16 pagesWhat Does A Statistical Test DoRenato PanesNo ratings yet
- Technical Codes.Document68 pagesTechnical Codes.Levi Lico PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12.1 MA SR GuidelinesDocument43 pagesLecture 12.1 MA SR GuidelinesArokiasamy JairishNo ratings yet
- Statistical ToolsDocument3 pagesStatistical ToolsReizhelle AbisNo ratings yet
- Statistics Project GuideDocument7 pagesStatistics Project GuideShubham UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans in Urdu SubjectDocument10 pagesLesson Plans in Urdu SubjectNoor Ul AinNo ratings yet
- Which TESTDocument9 pagesWhich TESTfasilistheoNo ratings yet
- Summary StatisticsDocument2 pagesSummary StatisticsMarck SuyomNo ratings yet
- Theory Hypothesis Design Data: To Answer / To Test Research Study CollectDocument44 pagesTheory Hypothesis Design Data: To Answer / To Test Research Study CollectCharlyn KeithNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistical Tools (Inset Iis 2023)Document64 pagesBasic Statistical Tools (Inset Iis 2023)walden habanaNo ratings yet
- Stat Sa ResearchDocument2 pagesStat Sa ResearchLhiana Mari PeñaredondoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 NotesDocument6 pagesLecture 1 NotesSerenaNo ratings yet
- Prof. Hilaria M. Barsabal Cagayan State UniversityDocument35 pagesProf. Hilaria M. Barsabal Cagayan State UniversityDarlene Andres PonceNo ratings yet
- T-Test (Independent & Paired) 1Document7 pagesT-Test (Independent & Paired) 1መለክ ሓራNo ratings yet
- Presentation ARM Week10Document27 pagesPresentation ARM Week10lilywhite786No ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics: Paper #6Document11 pagesAdvanced Statistics: Paper #6Precious NosaNo ratings yet
- Q. 1 How Is Mode Calculated? Also Discuss Its Merits and Demerits. AnsDocument13 pagesQ. 1 How Is Mode Calculated? Also Discuss Its Merits and Demerits. AnsGHULAM RABANINo ratings yet
- Introduction of StatisticsDocument14 pagesIntroduction of StatisticsKarl Andrei PeñaNo ratings yet
- Statistics Supplement McEvoyDocument10 pagesStatistics Supplement McEvoyMujahed LaswiNo ratings yet
- Handout Stat Week 10 Ind Samples T TestDocument6 pagesHandout Stat Week 10 Ind Samples T TestIsa IrawanNo ratings yet
- 2802 Key PointsDocument34 pages2802 Key PointssethtwardNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Writing Thesis and Dissertation 1Document72 pagesA Guide To Writing Thesis and Dissertation 1louella repolloNo ratings yet
- 8 Data Management - Treatment of Data For Quantitative StudiesDocument31 pages8 Data Management - Treatment of Data For Quantitative StudiesGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- ExP Psych 07 The Basics of ExperimentationDocument32 pagesExP Psych 07 The Basics of ExperimentationLouise L.No ratings yet
- Saghar 8612-2Document22 pagesSaghar 8612-2Anila zafarNo ratings yet
- 8614 22Document13 pages8614 22Muhammad NaqeebNo ratings yet
- Non-Parametric TestsDocument13 pagesNon-Parametric TestsDiana Jean Alo-adNo ratings yet
- 1 Prepared by Drashti JasaniDocument60 pages1 Prepared by Drashti JasaniBHAVIK RATHODNo ratings yet
- Julie Ann A. Analista February 2014Document67 pagesJulie Ann A. Analista February 2014Julie AnalistaNo ratings yet
- ValidityDocument23 pagesValidityfarheenchaudhryNo ratings yet
- Q3 W4 Basic Statistics in Experimental ResearchDocument30 pagesQ3 W4 Basic Statistics in Experimental ResearchjohnbenedickbNo ratings yet
- ANOVADocument4 pagesANOVAAiyemity Astrid EscarlanNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 2 Hypothesis Testing and Test of DifferencesDocument13 pagesUnit 7 2 Hypothesis Testing and Test of Differencesedselsalamanca2No ratings yet
- 10-11 T-Test & ANOVADocument15 pages10-11 T-Test & ANOVAMuhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF WATER QUALITY DATADocument14 pagesLecture Notes On STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF WATER QUALITY DATAtony frankNo ratings yet
- MBS659 Anova and T-TestsDocument8 pagesMBS659 Anova and T-Testsromanaaz1990No ratings yet
- R M HandoutDocument13 pagesR M HandoutGaurav Gangwar SuryaNo ratings yet
- Steps Quantitative Data AnalysisDocument4 pagesSteps Quantitative Data AnalysisShafira Anis TamayaNo ratings yet
- 14 Experimental Psych SummaryDocument3 pages14 Experimental Psych SummaryYvonne SipalayNo ratings yet
- Statistics in Title StructuringDocument18 pagesStatistics in Title Structuringjohn goocoNo ratings yet
- 408 MidDocument7 pages408 Midshishirar.12No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Data AnalysisRevisedDocument33 pagesChapter 5 Data AnalysisRevisedBantamkak FikaduNo ratings yet
- Assumptions IDocument50 pagesAssumptions IEmrullah SürücüNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Experiments QBDocument11 pagesDesign and Analysis of Experiments QBÃÑŠHÜNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in MAED Stat Part 1Document15 pagesLecture Notes in MAED Stat Part 1Jose Espino100% (1)
- Q2 PR2-Weeks-7-8-CONCLUSIONDocument12 pagesQ2 PR2-Weeks-7-8-CONCLUSIONmacristinaisabel.talladorNo ratings yet
- Local Media1419236475208910846Document36 pagesLocal Media1419236475208910846Maria Khristina Buera BongalaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Basic StatisticsDocument7 pagesLesson 1 Basic StatisticsRoxette Turingan TalosigNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Statistics and Research: John Ian Wilzon T. DizonDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Statistics and Research: John Ian Wilzon T. DizonAbdu MohammedNo ratings yet
- ExP Psych 14Document29 pagesExP Psych 14Jhaven MañasNo ratings yet
- Ch11 Experimental Design One Way Independent Samples DesignDocument14 pagesCh11 Experimental Design One Way Independent Samples DesignMahesh JadaNo ratings yet
- T TEST LectureDocument26 pagesT TEST LectureMax SantosNo ratings yet
- Statistical TreatmentDocument16 pagesStatistical TreatmentMaria ArleneNo ratings yet
- 2019 - Van Aert - Publication Bias Examined in Meta-Analyses From Psychology and Medicine - A Meta-Meta-AnalysisDocument32 pages2019 - Van Aert - Publication Bias Examined in Meta-Analyses From Psychology and Medicine - A Meta-Meta-AnalysisLim Kok PingNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Penerapan Akuntansi Sektor Publik Dan Pengawasan Internal Terhadap Kualitass Laporan Keuangan Dinas Perhubungan Kota SemrangDocument16 pagesPengaruh Penerapan Akuntansi Sektor Publik Dan Pengawasan Internal Terhadap Kualitass Laporan Keuangan Dinas Perhubungan Kota SemrangSitti MarhamaNo ratings yet
- PF Intro 2014 AndreasSvenssonDocument71 pagesPF Intro 2014 AndreasSvenssontempat filemNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eleven: Sampling: Design and ProceduresDocument28 pagesChapter Eleven: Sampling: Design and Proceduresnazmur_2007No ratings yet
- Generalized Linear Models: Simon Jackman Stanford UniversityDocument7 pagesGeneralized Linear Models: Simon Jackman Stanford UniversityababacarbaNo ratings yet
- Data Statistik F TestDocument2 pagesData Statistik F TestDwiNo ratings yet
- Inferential Statistics Problem SheetDocument3 pagesInferential Statistics Problem Sheetyoshita takalkhedeNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis ExcelDocument3 pagesData Analysis ExcelMohammad HannaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Results & DiscussionDocument4 pagesChapter 4 - Results & DiscussionJM NoynayNo ratings yet
- Assessment in Learning 1 Standard Scores I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesAssessment in Learning 1 Standard Scores I. ObjectivesSymon FeolinoNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document37 pagesModule 2Mae AstovezaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Elementary Statistics 6Th Edition Allan Bluman Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument46 pagesEbook Elementary Statistics 6Th Edition Allan Bluman Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDouglasRileycnji100% (12)
- EE325 Introductory EconometricsDocument2 pagesEE325 Introductory EconometricscrampingpaulNo ratings yet
- Horne and Ostberg Morningness - Eveningness Questionnaire: A Reduced ScaleDocument14 pagesHorne and Ostberg Morningness - Eveningness Questionnaire: A Reduced ScaleAndres OliveriNo ratings yet
- 1 Point Estimation: Parameter Estimation Kaustav Banerjee Decision Sciences Area, IIM LucknowDocument4 pages1 Point Estimation: Parameter Estimation Kaustav Banerjee Decision Sciences Area, IIM LucknowRajiv KumarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentos para La Aplicación de Bioestadística en Odontología (Parte 2)Document8 pagesFundamentos para La Aplicación de Bioestadística en Odontología (Parte 2)Evl UesixNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document3 pagesHomework 1Yeily Guzman CastroNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Amongst Customer Satisfaction, Loyalty, Demographic and Tripographic1 Attributes: A Case of Star Rated Hotel Guests in EthiopiaDocument15 pagesThe Relationship Amongst Customer Satisfaction, Loyalty, Demographic and Tripographic1 Attributes: A Case of Star Rated Hotel Guests in EthiopiaMammta ShresthaNo ratings yet
- 1 Statistical Quality Control, 7th Edition by Douglas C. MontgomeryDocument65 pages1 Statistical Quality Control, 7th Edition by Douglas C. MontgomeryMohammed AlamriNo ratings yet
- Box and Whisker Plots (D3.2.15)Document11 pagesBox and Whisker Plots (D3.2.15)gomzj005No ratings yet
- MM Pretest PDFDocument6 pagesMM Pretest PDFJophie AndreilleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6. Techniques in Testing Reliability of Assessment Method: Split - Half and Internal Consistency MethodsDocument8 pagesLesson 6. Techniques in Testing Reliability of Assessment Method: Split - Half and Internal Consistency Methodspixie02No ratings yet
- FORECAST ACCURACY - Supply Chain ManagementDocument29 pagesFORECAST ACCURACY - Supply Chain ManagementTrisha Nicole SanidadNo ratings yet
- Statistical Package For The Social SciencesDocument5 pagesStatistical Package For The Social SciencesMohammad Alamgir KabirNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distribution and EstimationDocument46 pagesSampling Distribution and EstimationPrinceNo ratings yet
- Test of Significance: Made By: 404 Tanushree D. 405 Swati Dhoke 406 Husain SaifyDocument16 pagesTest of Significance: Made By: 404 Tanushree D. 405 Swati Dhoke 406 Husain SaifyHusain SaifyNo ratings yet
- ReliabilityDocument8 pagesReliabilitysaheer100% (1)
- Variance and Standard DeviationDocument17 pagesVariance and Standard DeviationPuja GahatrajNo ratings yet