Professional Documents
Culture Documents
F-38 Gajanan Bonde Mind Map Optical Fibre
F-38 Gajanan Bonde Mind Map Optical Fibre
Uploaded by
udaygiripunjeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F-38 Gajanan Bonde Mind Map Optical Fibre
F-38 Gajanan Bonde Mind Map Optical Fibre
Uploaded by
udaygiripunjeCopyright:
Available Formats
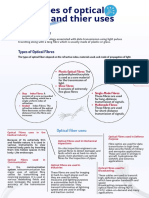
Optical Fibre Is A Thin, Flexible, Transparent Fibre That
Can Transmit Pulses Of Light.
Optical Fibres Form The Backbone Of Moder.
Telecommunication Networks.
It Is Made Up Of Optically Pure Glass Or Plastic And
Introduction Used For High Speed Data Transmission.
They Are Used To Transmitt Voice, Data, And Video
Signals Over Long Distances. Telecommunication
Optical Fibre Are Used In Telecommunication
Networks, Medical Imaging And Internet Connections.
Optical Fibre Cables Are Laid Underground In The
Ocean And Across Continents To Connect Different
Core Is The Central Region Of The Fibre Where Light Is
Parts Of The World.
Transmitted.
Optical Fibres Are Used In Medical Imaging
It Is Made Of Hight Refractive Index Material To
Techniques Such As Endoscopy And Minimal Invasive Core
Ensure Efficient Transmission.
Surgeries.
The Core Is Surrounded By Cladding To Confine The
They Enable Doctors To Visualise Internal Organs And
Medical Imaging Light Within The Fibre.
Perform Procedures With Minimal Invasiveness . Applications Of Optical Fibre
Cladding Is A Layer Of Material That Surrounds The
Fibre Optic Probes And Catheters Are Used To Deliver
Core.
Light To The Desired Areas For Imaging And
Treatment.
Structure Of Optical Fibre It Has A Lower Refractive Index To Help Reflect The
Cladding
Light Back Into The Core.
Optical Fibre Are Used For Hight Speed Internet
Connections, Particularly In Fibre To The Home
Networks. The Cladding Protects The Core And Reduces Optical
Losses.
They Provide Fast, Reliable, And Hight Band Width
Intenet Access To Residential And Business Internet Connectivity Coating Is A Protective Layer Outside The Cladding.
Premises.
It Provides Mechanical Strength And Protects The
Coating
Fibre Optics Internet Offers Faster Download And
Upload Speeds Compared To Traditional Broadband
Optical Fibre Fibre From External Elements.
Connections. The Coating Can Be Made Of Plastic Or Other
Materials.
Optical Fibre Have A Much Higher Bandwidth
Compared To Traditional Copper Cables. Light Signals Enter The Core And Travel Throught It.
They Can Transmit Lage Amount Of Data At High When The Light Hite The Boundary Of The Core And
Hight Bandwidth
Speed. Cladding, It Is Reflected Back Into The Core Due To
Total Internal Reflection
Total Internal Reflection.
This Make Them Suitable For Hight Speed Internet
Connections And Data Intensive Applications. The Reflection Allows The Light To Propogate
Through The Fibre Without Significant Loss.
They Are Used For Long Haul Telecommunications
And Undersea Cables. Modal Diapersion Occurs When Different Light Rays
Take Different Paths Through The Fibre.
Optical Fibers Can Transmit Signals Over Long
Distances Without Significant Loss Of Signal Quality. Long Distance Transmission Advantages Of Optical Fibre It Can Cause The Light Pulses To Spread And Overlap,
Modal Diapersion
Working Principle Of Optical Fibre Resulting In Signal Degradation.
The Low Attenuation Of Light In The Fiber Allows It To
Travel Long Distances Without The Need For Frequent Modal Diapersion Can Be Reduced By Using Single
Signal Regeneration. Mode Fibres Or Dispersion Shifted Fibres.
Unlike Copper Cables, Optical Fibers Are Not Affected As The Light Travels Throught The Fibre, It Can
By Electromagnetic Interference. Weaken And Lose Its Clarity.
This Makes Them More Reliable And Less Susceptible Signal Regeneration Devices Are Used To Amplify And
Immune To Electromegnetic Interference
To Data Loss Or Interruption. Reshape The Signal To Maintain The Quality Of
Signal Regeneration
Transmission.
They Are Immune To Radio Frequency Interference,
Electrical Noise, And Crosstalk. Repeaters And Amplifiers Are Example Of Signal
Regeneration Devices Used In Optical Fibre
Communication Systems.
You might also like
- Writing A Proposal For Feasibility StudyDocument18 pagesWriting A Proposal For Feasibility StudyJerrelyn Segayo100% (5)
- Mid OBEDocument4 pagesMid OBEShuvo Dip RoyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 F2019105036Document5 pagesAssignment 1 F2019105036BILAL HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- Sp&em IEEE Batch 01Document3 pagesSp&em IEEE Batch 01thushikareddyNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05 Dec 2023Document14 pagesAdobe Scan 05 Dec 2023hurrytj6No ratings yet
- Physics PosterDocument1 pagePhysics Postermuntasirtoqi555No ratings yet
- Optical Fiber and Their UsesDocument1 pageOptical Fiber and Their UsesRoman AyubNo ratings yet
- Submitted To Submitted By: Manmohan Singh Roll No-07EAIAI027Document17 pagesSubmitted To Submitted By: Manmohan Singh Roll No-07EAIAI027Manmohan SinghNo ratings yet
- MTNL Power Point Presentation - 3Document20 pagesMTNL Power Point Presentation - 3Varun SachdevaNo ratings yet
- OC Unit 1Document76 pagesOC Unit 1VarshiniNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber CommunicationDocument6 pagesOptical Fiber CommunicationShuvo Dip RoyNo ratings yet
- OFC CharacteristicsDocument27 pagesOFC CharacteristicsABCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (Fiber Optics)Document15 pagesChapter 6 (Fiber Optics)Sri TharanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Photonics Principles and The MostDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Photonics Principles and The Mostmahmoud khedrNo ratings yet
- Acsnano 2c01989Document11 pagesAcsnano 2c01989Uğur Berkay ÇalışkanNo ratings yet
- Opticalfibertutor PDFDocument8 pagesOpticalfibertutor PDFchristal MIAKOUKILANo ratings yet
- Future Trends in Fiber Optics Communication: Francis Idachaba, Dike U. Ike, and Orovwode HopeDocument5 pagesFuture Trends in Fiber Optics Communication: Francis Idachaba, Dike U. Ike, and Orovwode HopeHelloNo ratings yet
- BSNL Training ReportDocument33 pagesBSNL Training ReportAnil KamathNo ratings yet
- Optical FibreDocument19 pagesOptical FibreShashank ChauhanNo ratings yet
- The Abcs of Ethernet Fiber OpticsDocument4 pagesThe Abcs of Ethernet Fiber OpticsAlan GallagherNo ratings yet
- Fiber To Home, Fiber To PremisesDocument17 pagesFiber To Home, Fiber To PremisesBikash Ranjan RamNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic TutorialDocument7 pagesFiber Optic TutorialJulio MalquiheyroNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To Optical Fiber Communication Systems: February 2021Document18 pagesA Brief Introduction To Optical Fiber Communication Systems: February 2021mariyappanNo ratings yet
- Overview of Fiber Optic Sensors For NDT ApplicationsDocument11 pagesOverview of Fiber Optic Sensors For NDT ApplicationsSri RamNo ratings yet
- Optical Network Security Technical Analysis of Fiber Tapping MecDocument6 pagesOptical Network Security Technical Analysis of Fiber Tapping MecSteven MuñozNo ratings yet
- Pnas 1611740113Document6 pagesPnas 1611740113Mark Nelson MagnoNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communication: PrefaceDocument11 pagesOptical Fiber Communication: PrefaceSushanth reddyNo ratings yet
- Abstract of Fiber Optic SensorsDocument6 pagesAbstract of Fiber Optic SensorsKamal UniyalNo ratings yet
- Fiber-Optic Sensing A Historical PerspectiveDocument15 pagesFiber-Optic Sensing A Historical PerspectiveAnonymous Shv3RwsWnrNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To Optical Fiber Communication Systems: February 2021Document18 pagesA Brief Introduction To Optical Fiber Communication Systems: February 2021Ahmed ShdedNo ratings yet
- Fibra Optica - 095804Document4 pagesFibra Optica - 095804antonybernal650No ratings yet
- Optical Fibers-Principles and Applications: M. Harinath ReddyDocument4 pagesOptical Fibers-Principles and Applications: M. Harinath ReddysathiyamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Sensors and Their Applications: Conference PaperDocument7 pagesFiber Optic Sensors and Their Applications: Conference Paperpaolo.baraldiNo ratings yet
- TE (FE) 01 Optical CommunicationsDocument62 pagesTE (FE) 01 Optical CommunicationsKaushik AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics: Mr. Aditya GuptaDocument4 pagesFiber Optics: Mr. Aditya GuptaAditya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Engg Phy-Unit 4 - FIBRE OPTICSDocument2 pagesEngg Phy-Unit 4 - FIBRE OPTICSPhantom's NetworkNo ratings yet
- EDFA Chapman PDFDocument10 pagesEDFA Chapman PDFLevis AckermanNo ratings yet
- Future Trends in Fiber Optics CommunicationDocument6 pagesFuture Trends in Fiber Optics CommunicationKoustav MondalNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To Optical Fiber Communication Systems: February 2021Document18 pagesA Brief Introduction To Optical Fiber Communication Systems: February 2021Dejan NNo ratings yet
- 2 Fiber Optic BasicsDocument11 pages2 Fiber Optic BasicsDheeraj Yadav100% (1)
- Measurement of The Attenuation of The OpDocument9 pagesMeasurement of The Attenuation of The OpsuryaNo ratings yet
- OFC & OFS ConceptsDocument27 pagesOFC & OFS ConceptsKaushal PatelNo ratings yet
- Tech Note 13Document2 pagesTech Note 13meteohrNo ratings yet
- Nphoton 2012 15Document1 pageNphoton 2012 15arkoprobho235No ratings yet
- Applications Optical Fiber Communication: Optical Time-Domain ReflectometerDocument11 pagesApplications Optical Fiber Communication: Optical Time-Domain Reflectometertotoestbeau100% (2)
- The Basics of FTTHDocument36 pagesThe Basics of FTTHFanny TampubolonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Optical CommunicationDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Optical Communicationrajeev91No ratings yet
- Wa0029. 1Document30 pagesWa0029. 1Angelina BennyNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communication: Mitali.R.shindeDocument16 pagesOptical Fiber Communication: Mitali.R.shindeprathamesh nerkarNo ratings yet
- An Integrated Optical Transceiver Circuit For Power Delivery and Bi-Directional Data Communication in A Medical Catheter DeviceDocument4 pagesAn Integrated Optical Transceiver Circuit For Power Delivery and Bi-Directional Data Communication in A Medical Catheter DeviceasifnewazuccNo ratings yet
- History and Vision of Optical Fiber Fusion Splicing TechnologyDocument4 pagesHistory and Vision of Optical Fiber Fusion Splicing TechnologyCHARLES ROBERTNo ratings yet
- Fibre Used in Telecom & Their CharacteristicsDocument35 pagesFibre Used in Telecom & Their CharacteristicsVinay MehtaNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument25 pagesPhysics ProjectShraddha KhaleNo ratings yet
- Fibre OpticsDocument3 pagesFibre Optics18danbykNo ratings yet
- Applications of Optical FiberDocument4 pagesApplications of Optical FiberQalb e WajahatNo ratings yet
- Ofc NotesDocument9 pagesOfc Notesshameem v.pNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpfDocument18 pagesFiber Opfvipinchauhan247No ratings yet
- Photonic Crystal Fiber For Minimizing The Intermodal Dispersion and Enhancing The Transmission ProfileDocument5 pagesPhotonic Crystal Fiber For Minimizing The Intermodal Dispersion and Enhancing The Transmission ProfileMekhla duttaNo ratings yet
- Indoor Wireless InterconnectDocument4 pagesIndoor Wireless InterconnectViet Nam Trong ToiNo ratings yet
- Flexible Neural Electrodes: Revolutionizing Brain-Computer InterfacesFrom EverandFlexible Neural Electrodes: Revolutionizing Brain-Computer InterfacesNo ratings yet
- 9 10 Curve Fitting and Interpolation Part 2Document32 pages9 10 Curve Fitting and Interpolation Part 2Marshall james G. RamirezNo ratings yet
- Guhan Mahalingam: Assembly EngineerDocument2 pagesGuhan Mahalingam: Assembly EngineerGuhan MNo ratings yet
- RAC GRADE 9 Q1 W 4 M 4 FINAlDocument11 pagesRAC GRADE 9 Q1 W 4 M 4 FINAlOviya EikoNo ratings yet
- Measures of Dispersion (Part 2)Document13 pagesMeasures of Dispersion (Part 2)BS Accoutancy St. SimonNo ratings yet
- Distributed File SystemDocument49 pagesDistributed File SystemRicha SinghNo ratings yet
- IC Quality Assurance Audit Checklist 11546 - WORDDocument2 pagesIC Quality Assurance Audit Checklist 11546 - WORDnafis2uNo ratings yet
- DX100 Field Maintenance Guide: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocument24 pagesDX100 Field Maintenance Guide: Downloaded From Manuals Search Engine조장현No ratings yet
- Mathematics 9Document5 pagesMathematics 9Van Mark TejadaNo ratings yet
- CAT1000P: Program To Create A GEOPAK Part Program With The Help of CAD DataDocument39 pagesCAT1000P: Program To Create A GEOPAK Part Program With The Help of CAD DataYnomata RusamellNo ratings yet
- Class Test II 2008-2009Document1 pageClass Test II 2008-2009api-3728136No ratings yet
- Sample Letter of AuthorizationDocument1 pageSample Letter of AuthorizationevanaannNo ratings yet
- SPTVE CSS 10 Quarter 4 Week 1 2Document10 pagesSPTVE CSS 10 Quarter 4 Week 1 2Sophia Colleen Lapu-osNo ratings yet
- Is Reading A Wonderful Human Activity?: Chrizza May Sabarre Meth5 Mrs. BradyDocument3 pagesIs Reading A Wonderful Human Activity?: Chrizza May Sabarre Meth5 Mrs. BradyLulu BritanniaNo ratings yet
- 26071-100-V1A-J001-10619 - 001 HIPPS SYSTEM INTERNAL WIRING DIAGRAM FOR ISH-106 - Code1Document14 pages26071-100-V1A-J001-10619 - 001 HIPPS SYSTEM INTERNAL WIRING DIAGRAM FOR ISH-106 - Code1widionosucipto29No ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mobile PhonesDocument12 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Mobile PhonesMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networking: Lecture 5 - Addressing in NetworkingDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Networking: Lecture 5 - Addressing in NetworkingSamuel SilasNo ratings yet
- A Multilevel Consideration of Service Design ConditionsDocument24 pagesA Multilevel Consideration of Service Design ConditionsLiza LayaNo ratings yet
- CHAP 3.2 Protection Against Malicious SoftwareDocument22 pagesCHAP 3.2 Protection Against Malicious SoftwareFirdausNo ratings yet
- Pump Selection Rev 03Document9 pagesPump Selection Rev 03orode franklynNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Y1x1aa3k1bs256#wrDocument1 pageData Sheet Y1x1aa3k1bs256#wrLuke FosterNo ratings yet
- Database Programming With SQL 2-3: Comparison Operators Practice ActivitiesDocument2 pagesDatabase Programming With SQL 2-3: Comparison Operators Practice Activitiesstenly94No ratings yet
- Com Power Lvmkt215enDocument70 pagesCom Power Lvmkt215enCbdtxd PcbtrNo ratings yet
- ABB Capability Guide - LRDocument60 pagesABB Capability Guide - LRtobyNo ratings yet
- MCQ'S Product Design and DevelopmentDocument14 pagesMCQ'S Product Design and Developmentchiku khade100% (5)
- Lecture 3 CADDocument10 pagesLecture 3 CADdesubie bireNo ratings yet
- Consensus Assessments Initiative Questionnaire v3 1Document104 pagesConsensus Assessments Initiative Questionnaire v3 1RANA SNo ratings yet
- Odyssey Catalog USAH105fDocument68 pagesOdyssey Catalog USAH105ffelipeffcNo ratings yet
- Computers: Game Consoles vs. PersonalDocument10 pagesComputers: Game Consoles vs. PersonalRazvan Julian PetrescuNo ratings yet
- Management PracticesDocument2 pagesManagement PracticesGwyneth MendozaNo ratings yet