Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsEls Plan
Els Plan
Uploaded by
julliennePLAN
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- TBDY 2018 EnglishDocument608 pagesTBDY 2018 EnglishaygunbayramNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument4 pagesEarth and Life ScienceArmelin AlipayoNo ratings yet
- PE11 - MELC 4 Module 4 - Week7 For Teacher PDFDocument24 pagesPE11 - MELC 4 Module 4 - Week7 For Teacher PDFRommel Cando80% (5)
- MELCS UnpackingDocument2 pagesMELCS UnpackingTawagin Mo Akong Merts100% (5)
- MELCs in Earth and Life ScienceDocument5 pagesMELCs in Earth and Life ScienceAdonis Besa100% (14)
- AGoT2 Illustrated Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAGoT2 Illustrated Cheat SheetIgor Silva100% (1)
- M. Ashraf Adeel - Epistemology of The Quran - Elements of A Virtue Approach To Knowledge and Understanding-Springer Internati PDFDocument141 pagesM. Ashraf Adeel - Epistemology of The Quran - Elements of A Virtue Approach To Knowledge and Understanding-Springer Internati PDFimreadingNo ratings yet
- Bow ElsDocument15 pagesBow ElsMarilyn TabuenaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science 11 Module (Week 1-5)Document38 pagesEarth Science 11 Module (Week 1-5)Hilary Grace Sumbi GargarNo ratings yet
- 3rd Grade Science SyllabusDocument6 pages3rd Grade Science Syllabusepetadavid41No ratings yet
- First Semester Syllabus in Earth Science 11 First QuarterDocument11 pagesFirst Semester Syllabus in Earth Science 11 First QuarterElvie CalinisanNo ratings yet
- ELS and G10 ScienceDocument8 pagesELS and G10 ScienceJadeNo ratings yet
- WEEK5Document5 pagesWEEK5Marianne Joy Flormata AlulodNo ratings yet
- SHS Core Subjects MELC Earth and LIfe ScienceDocument6 pagesSHS Core Subjects MELC Earth and LIfe ScienceBaby Yanyan100% (3)
- Ahs13 Filipino Sa Piling Larangan Akademik Week 2 PDFDocument6 pagesAhs13 Filipino Sa Piling Larangan Akademik Week 2 PDFJoy RamosNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science 11Document4 pagesEarth and Life Science 11deborah dumapeNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science 11Document4 pagesEarth and Life Science 11DEBORAH DUMAPENo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Slem q1Document69 pagesEarth and Life Slem q1Kenji YamaguchiNo ratings yet
- DLL 5Document5 pagesDLL 5jullienneNo ratings yet
- Science 10 BowDocument10 pagesScience 10 BowGERRY CHEL LAURENTENo ratings yet
- Learning Continuity Plan SY 2020 - 2021Document5 pagesLearning Continuity Plan SY 2020 - 2021allanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Modular 2Document1 pageEarth Science Modular 2Prasann KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science - BCO - MELCDocument12 pagesGrade 10 Science - BCO - MELCMarfe Montelibano0% (1)
- DLL 1Document2 pagesDLL 1jullienneNo ratings yet
- DLL 2Document2 pagesDLL 2jullienneNo ratings yet
- Proposed Budget of WorkDocument3 pagesProposed Budget of WorkMarilou DuqueNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Water Worlds in The Solar System PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Water Worlds in The Solar System PDFmatthew.robertson769100% (27)
- SHS Core Subjects MELC Earth CienceDocument6 pagesSHS Core Subjects MELC Earth CienceBaby Yanyan67% (3)
- Water Worlds in The Solar System Antony Joseph All ChapterDocument67 pagesWater Worlds in The Solar System Antony Joseph All Chapterjamie.mcneal448100% (6)
- CH 23-6 Earth History FoldableDocument1 pageCH 23-6 Earth History Foldabletownsenr94No ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument5 pagesEarth ScienceVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- TOS sCIENCE 1ST Quarter 1st Sem 20 21Document13 pagesTOS sCIENCE 1ST Quarter 1st Sem 20 21Arjune PantallanoNo ratings yet
- ESCIDocument5 pagesESCIGenesis AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- DLL 1Document4 pagesDLL 1jullienneNo ratings yet
- MELCS Unpacking2Document2 pagesMELCS Unpacking2Tawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- MELCS UnpackingDocument2 pagesMELCS UnpackingTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Budget-of-Work-Earth and Life ScienceDocument5 pagesBudget-of-Work-Earth and Life Sciencejoei Arquero100% (1)
- Quarter 1 Lesson 1Document3 pagesQuarter 1 Lesson 1Lester EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Flexible Assessment Activities and Flexible Learning StrategiesDocument5 pagesFlexible Assessment Activities and Flexible Learning StrategiesAisa EdzaNo ratings yet
- DLL 2Document5 pagesDLL 2jullienneNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesAndrie Vonn Perocho NerpiolNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity in Science 10 Group 1Document2 pagesLearning Activity in Science 10 Group 1NikkoOdejarNo ratings yet
- Earth Science IntroDocument25 pagesEarth Science IntroMiku BinondoNo ratings yet
- 1module 2 - Lesson 2 - Activity 2Document3 pages1module 2 - Lesson 2 - Activity 2JESSA SUMAYANGNo ratings yet
- 1module 2 - Lesson 2 - Activity 2Document3 pages1module 2 - Lesson 2 - Activity 2JESSA SUMAYANGNo ratings yet
- Week One DLLDocument4 pagesWeek One DLLKlarissa LomibaoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument113 pagesEarth and Life ScienceDo Lai NabNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide SampleDocument11 pagesLearning Guide Samplelj BoniolNo ratings yet
- Els W6Document11 pagesEls W6renliejanepNo ratings yet
- Distance Learning Activity Plan: Subject: Earth & Life ScienceDocument6 pagesDistance Learning Activity Plan: Subject: Earth & Life ScienceCatherine De LunaNo ratings yet
- Ii. Content Iii. Learning ResourcesDocument3 pagesIi. Content Iii. Learning ResourcesAq Nga ToNo ratings yet
- Science10 q1 WLP Week1Document2 pagesScience10 q1 WLP Week1Kristine Mae TaboyNo ratings yet
- Earth Science TMDocument64 pagesEarth Science TMMary Vi D. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Ciencias 5 3 Per ModDocument6 pagesCiencias 5 3 Per ModWill ChoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science ModuleDocument112 pagesEarth and Life Science ModuleLeidi Mae S. TugayNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science ModuleDocument117 pagesEarth and Life Science ModuleGlenda AstodilloNo ratings yet
- Earth As The Habitable Planet DAY 1Document47 pagesEarth As The Habitable Planet DAY 1ehlie canlasNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Syllabus SY 11 12 PDFDocument5 pagesEarth Science Syllabus SY 11 12 PDFGeneris SuiNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusJaquilin JosephNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science ModuleDocument114 pagesEarth and Life Science ModuleMax LiaraNo ratings yet
- DLL June 3-7-19-ElsDocument4 pagesDLL June 3-7-19-ElsCristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Atmospheric Science: Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandHandbook of Atmospheric Science: Principles and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- The Stromboli Volcano: An Integrated Study of the 2002 - 2003 EruptionFrom EverandThe Stromboli Volcano: An Integrated Study of the 2002 - 2003 EruptionSonia CalvariNo ratings yet
- Extreme Events and Natural Hazards: The Complexity PerspectiveFrom EverandExtreme Events and Natural Hazards: The Complexity PerspectiveA. Surjalal SharmaNo ratings yet
- School-Summary_JHS_v2.0Document34 pagesSchool-Summary_JHS_v2.0jullienneNo ratings yet
- School-Summary_SHS_v2.0 GRADE 12 V1Document10 pagesSchool-Summary_SHS_v2.0 GRADE 12 V1jullienneNo ratings yet
- TVL 11 FAIRMONT RAM SCORESHEETSDocument22 pagesTVL 11 FAIRMONT RAM SCORESHEETSjullienneNo ratings yet
- Class-Scoresheet_SHS_v2.0-1NEON-RAMDocument28 pagesClass-Scoresheet_SHS_v2.0-1NEON-RAMjullienneNo ratings yet
- School-Form-1-SF-1-35Document6 pagesSchool-Form-1-SF-1-35jullienneNo ratings yet
- School-Summary_SHS_v2.0 GRADE 12Document30 pagesSchool-Summary_SHS_v2.0 GRADE 12jullienneNo ratings yet
- 2ND 23-24 LLS NewDocument1 page2ND 23-24 LLS NewjullienneNo ratings yet
- Pe Exam Ist Sem 2024 - 024007Document2 pagesPe Exam Ist Sem 2024 - 024007jullienneNo ratings yet
- 1ST 23-24 LLS NewDocument1 page1ST 23-24 LLS NewjullienneNo ratings yet
- LR Action Plan 23-24Document2 pagesLR Action Plan 23-24jullienneNo ratings yet
- LR Action Plan 23-24 FinalDocument2 pagesLR Action Plan 23-24 FinaljullienneNo ratings yet
- MID-MRF-JGADocument13 pagesMID-MRF-JGAjullienneNo ratings yet
- PD 3RD 23-24 LLS NewDocument1 pagePD 3RD 23-24 LLS NewjullienneNo ratings yet
- M and e Tool LRMSDocument6 pagesM and e Tool LRMSjullienneNo ratings yet
- Ram MPSDocument3 pagesRam MPSjullienneNo ratings yet
- Mid Year AccomplishmentDocument2 pagesMid Year AccomplishmentjullienneNo ratings yet
- 4TH 23-24 LLS NewDocument1 page4TH 23-24 LLS NewjullienneNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report SHS ClinicDocument4 pagesAccomplishment Report SHS ClinicjullienneNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report For Grade Level Chairmanship & Shs Math Coor Sy 2023-2024.Document9 pagesAccomplishment Report For Grade Level Chairmanship & Shs Math Coor Sy 2023-2024.jullienneNo ratings yet
- Yes-O Ar 24Document1 pageYes-O Ar 24jullienneNo ratings yet
- Molecular PolarityDocument13 pagesMolecular PolarityjullienneNo ratings yet
- Cot 1-Taleon 2023Document6 pagesCot 1-Taleon 2023jullienneNo ratings yet
- Cot 2 - Nedy 2023Document5 pagesCot 2 - Nedy 2023jullienneNo ratings yet
- PPG 18-Mar 4 EMPTYDocument4 pagesPPG 18-Mar 4 EMPTYjullienneNo ratings yet
- PS Q2 Tos-23-24Document4 pagesPS Q2 Tos-23-24jullienneNo ratings yet
- PPG 17-Mar 4Document5 pagesPPG 17-Mar 4jullienneNo ratings yet
- PPG 17Document4 pagesPPG 17jullienneNo ratings yet
- PPG 18-Mar 4Document5 pagesPPG 18-Mar 4jullienneNo ratings yet
- Sci 10 4TH ExamDocument6 pagesSci 10 4TH ExamjullienneNo ratings yet
- Subsystem of EarthDocument2 pagesSubsystem of EarthjullienneNo ratings yet
- Love Song For A VampireDocument1 pageLove Song For A VampireVivianamorteccinaNo ratings yet
- PKM Full C.V. Sept 2021Document11 pagesPKM Full C.V. Sept 2021aopera87No ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Stroke-Associated PneumoniaDocument16 pagesDiagnosis of Stroke-Associated PneumoniaCecilia Casandra UneputtyNo ratings yet
- Malunggay Oleifera As Cleaning AgentDocument2 pagesMalunggay Oleifera As Cleaning AgentMackieNo ratings yet
- Subcontract Agreement (Jenesis) V.1.1Document4 pagesSubcontract Agreement (Jenesis) V.1.1sigit l.prabowoNo ratings yet
- Driscoll WordsDocument55 pagesDriscoll WordsMatthew James DriscollNo ratings yet
- 20120-Article Text-29342-1-10-20200625Document5 pages20120-Article Text-29342-1-10-20200625Min PuNo ratings yet
- 080930-Antarctica TourismDocument15 pages080930-Antarctica TourismVân PhươngNo ratings yet
- Linda Hutcheon - Historiographic MetafictionDocument30 pagesLinda Hutcheon - Historiographic Metafictiongrebucko100% (2)
- Karachi: List of Valid Licence Holder of Banaspati (Ps:221-2003®) July 2014Document76 pagesKarachi: List of Valid Licence Holder of Banaspati (Ps:221-2003®) July 2014Okita MiraningrumNo ratings yet
- Tauck Australia Expands: WeeklyDocument3 pagesTauck Australia Expands: WeeklycruiseweeklyNo ratings yet
- (1899) (Vol. 2) A Sailor's Life Under Four SovereignsDocument364 pages(1899) (Vol. 2) A Sailor's Life Under Four SovereignsHerbert Hillary Booker 2ndNo ratings yet
- Document Analysis Worksheet: Analyze A PaintingDocument4 pagesDocument Analysis Worksheet: Analyze A PaintingPatrick SanchezNo ratings yet
- Integrated NLP Train The Trainer BootcampDocument8 pagesIntegrated NLP Train The Trainer BootcampHitesh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Catheterisation Standard Operating ProcedureDocument27 pagesCatheterisation Standard Operating ProcedureSherly RositaNo ratings yet
- CHEMFISH Fluorinated CompoundsDocument11 pagesCHEMFISH Fluorinated Compoundssunny StevenNo ratings yet
- Module 2 TheoDocument6 pagesModule 2 TheoMichlee Joy Paguila LagocNo ratings yet
- Sambo Catalog Torque LimiterDocument2 pagesSambo Catalog Torque LimiterRicNo ratings yet
- 78-2017ernakulam, KannurDocument13 pages78-2017ernakulam, KannurBingo MeNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Research Methods For ManagementDocument19 pagesAssignment - Research Methods For Managementnatashashaikh93No ratings yet
- 7 VideoDocument17 pages7 VideoKARTIKNo ratings yet
- BodhisattvacaryāvatāraDocument10 pagesBodhisattvacaryāvatāraLiu Fengshui100% (1)
- Reading Cases and Interpreting Statutes Workshop - Answers: Ommon AW Easoning and NstitutionsDocument9 pagesReading Cases and Interpreting Statutes Workshop - Answers: Ommon AW Easoning and NstitutionsshaunNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Ecumenical ChurchDocument13 pagesGroup 1 - Ecumenical ChurchLesther RobloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - REVIEW QUESTION - PROBLEM - Instruction Sets - Addresing Modes and Formats - OkDocument5 pagesChapter 13 - REVIEW QUESTION - PROBLEM - Instruction Sets - Addresing Modes and Formats - OkHo Trong Nghia (K17 QN)No ratings yet
- Ship49417 - en - Economic Impact of Cruise Ports - Case of MiamiDocument33 pagesShip49417 - en - Economic Impact of Cruise Ports - Case of MiamiRebeca Paz Aguilar MundacaNo ratings yet
Els Plan
Els Plan
Uploaded by
jullienne0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views7 pagesPLAN
Original Title
ELS PLAN
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPLAN
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views7 pagesEls Plan
Els Plan
Uploaded by
julliennePLAN
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
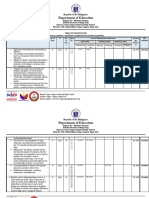
FIRST QUARTER
LP NO. LESSON OBJECTIVES MIN % # OF DATE
DAYS
LP 1 Lesson 1: Universe 1. Describe the structure and composition of the Universe; 60 3. 28 2
and the Solar 2. State the different hypothesis that preceded the Big Bang
System Theory of the Origin of the Universe.
3. Explain the red-shift and how it used as proof of an
expanding universe; and
4. Explain the Big Bang Theory and evidences supporting the
theory.
LP 2 Lesson 2: Universe 1. Identify the large scale and small scale properties of the Solar 60 3.28 2
and System;
the Solar System 2. Discuss the different hypotheses explaining the origin of the
solar system; and
3. Become familiar with the most recent
advancements/information on the solar system.
LP 3 Lesson 3: Universe 1. Recognize the difference in the physical and chemical 60 3.28 2
and properties between the Earth and its neighboring planes; and
the Solar System 2. Identify the factors that allow a planet to support life.
LP 4 Lesson 4: Earth 1. Define the concept of a system; 90 4.92 4
Subsystems 2. Recognize the Earth as a system composed of subsystems;
and
3. Discuss the historical development of the concept of Earth
System.
LP 5 Lesson 5: The 1. Describe the Earth’s interior (in terms of crust, mantle, core); 105 5.74 5
Internal Structure of and
the 2. Compare the Earth’s layers
Earth
LP 6 Lesson 6: Minerals 1. Demonstrate understanding about physical and chemical 45 2.46 2
and Rocks properties of minerals
2. Identify some common rock-forming minerals
3. Classify minerals based on chemical affinity
LP 7 Lesson 7: Minerals 1. Classify and describe the three basic rock types; 60 3.28 32
and 2. Establish relationships between rock types and the origin and
Rocks environment
of deposition/formation;
3. Understand the different geologic processes involved in rock
formation
LP 8 Lesson 8: Exogenic 1. Define weathering and distinguish between the two main 60 3.28 2
Processes types of weathering
2. Identify the factors that affect the rate of weathering
LP 9 Lesson 9: Exogenic 1. Identify the different agents of erosion and deposition 75 4.10 3
Processes (Erosion 2. Describe characteristic surface features and landforms
and created and the processes that contributed to their formation
Deposition)
LP 10 Lesson 10: Exogenic 1. Identify the controls and triggers of mass wasting 65 3.55 3
Processes (Mass 2. Distinguish between different mass wasting processes
Wasting)
LP 11 Lesson 11: 1. Know the sources and significance of the Earth's internal heat 45 2.46 2
Endogenic 2. Understand and explain the requirements for magma MIN
Processes generation
LP 12 Lesson 12: 1. Explain how and why magma rises up, 60 3.28 2
Endogenic 2. Understand the concept of Bowen’s reaction series, and MIN
Processes 3. Identify, understand, and explain magmatic differentiation
mechanisms operating beneath the surface of the Earth
LP 13 Lesson 13: 1. Understand the different index minerals used for 45 2.46 2
Endogenic metamorphic rocks.
Processes 2. Understand what causes the metamorphic texture
LP 14 Lesson 14: 1. Discuss the history behind the Theory of Continental Drift; 90 4.92 4
Endogenic 2. Describe the Continental Drift Theory; and
Processes 3. Enumerate and explain the evidence used to support the idea
of drifting
continents
LP 15 Lesson 15: 1. Discuss the history behind the Theory of Continental Drift; 75 4.10 3
Deformation of the 2. Describe the Continental Drift Theory;
Crust 3. Enumerate and explain the evidence used to support the idea
of drifting
continents;
4. Identify major physiographic features of ocean basins
5. Describe the process of seafloor spreading; and
6. Demonstrate understanding of the theory of plate tectonics
and how plate
tectonic processes lead to changes in Earth’s surface features
LP 16 Lesson 16: History 1. Acquire familiarity with the Geologic Time Scale; 60 3.28 2
of the Earth 2. Show the contributions of different personalities in the
establishment of the
Geologic Time Scale;
3. Describe how relative and absolute dating were used to
subdivide geologic
time;and
4. Explain how fossils have been used to define and identify
subdivision of the
geologic time scale
LP 17 Lesson 17: History 1. Appreciate the immensity of geologic time and recognize that 60 3.28 2
of the Earth the Earth
has a very long history;
2. Identify the timing and duration of the major events in
Earth’s History;
3. Recognize how short human history is in relation to the
history of the Earth
LP 18 Lesson 18: Natural 1. Describe and explain the hazards associated with 120 6.55 5
Hazards, Mitigation earthquakes;
and Adaptation: 2. Identify areas from the Philippine map where earthquakes are
Geologic Processes most likely
and to happen;
Hazards 3. Identify and give examples of possible geologic hazards
associated with
earthquakes;
4. Demonstrate their understanding of the scope of the effects
and damage
of earthquakes by determining the possibility of such effects
occurring in
their area and vicinity and where it will most likely happen; and
5. Manifest awareness by participating in earthquake-related
hazard prevention activities and drills.
LP 19 Lesson 19: Natural 1. Identify and understand how certain human activities can 60 3.28 2
Hazards, Mitigation hasten the occurrence of landslides.
and Adaptation: 2. Find possible and practical solutions on how to lessen these
Geologic Processes identified human activities so as to lessen or prevent the
and occurrence of landslides.
Hazards 3. Design an information campaign to inform locals how they
contribute to the occurrence of landslides in their area.
LP 20 Lesson 20: Natural 1. Identify and classify the different types of 60 3.28 2
Hazards, Mitigation hydrometeorological hazards.
and 2. Evaluate their community for potential hazards induced by
Adaptation: extreme atmospheric and hydrologic conditions.
Hydrometeorological
Phenomena and
Hazards
LP 21 Lesson 21: Natural 1. Become familiar with the guidelines (government and private 60 3.28 2
Hazards, Mitigation institutions) designed to help people prepare for and respond to
and the risks associated with flooding and other hazards.
Adaptation: 2. Adapt and apply these guidelines to their school or to their
Hydrometeorological community
Phenomena
LP 22 Lesson 22: Natural (1) Recognize the coastal processes that influence the coastal 60 3.28 2
Hazards, Mitigation landforms and associated hazards.
and (2) Illustrate and describe how the coastal processes determine
Adaptation: Marine the present coastal hazards whether coastal erosion,
and submersion or saltwater intrusion.
Coastal Processes
and
their Effects
LP 23 Lesson 23: Natural 1. Identify and appraise their chosen area within the community 360 19.67 16
Hazards, Mitigation for possible coastal hazards.
and 2. Design a field activity of a chosen coastal area to assess or
Adaptation: Marine monitor the present condition of the area.
and
Coastal Processes
and
their Effects
LP 24 Lesson 24: Natural 1. Explain the different ways to cope with coastal hazards, 60 3.28 2
Hazards, Mitigation particularly on coastal erosion, submersion and saltwater
and intrusion.
Adaptation: Marine 2. Evaluate the appropriateness and effectivity of the different
and mitigation measures to minimize or prevent various coastal
Coastal Processes hazards.
and
their Effects
TOTAL 1830 100 % 75
SECOND QUARTER
LP 25 Lesson 25: 1. Discuss the historical development of the concept of life 120
Introduction including theories,
to Life Science experiments and evidences;
2. Describe the conditions on early Earth that made the origin of
life possible
and the first life forms; and
3. Discuss the unifying themes of life and how they are
interconnected
LP 26 Lesson 26: 1. Describe the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic 200
Bioenergetics cells
Structures and 2. Explain the functions of various cell structures/organelles
Functions 3. Enumerate structures unique to plant cells/animal
of Cells cells/bacteria
4. Discuss the functions of cytoskeleton and extracellular
components
LP 27 Lesson 27: 1. Review the forms of energy 200
Bioenergetics 2. Describe the first two laws of thermodynamics
Photosynthesis and 3. Differentiate the nature of enzyme activity
Energy Flow 4. Explain photosynthesis as a re-dox process
5. Diagram the events in light reactions
6. Illustrate the Calvin cycle
LP 28 Lesson 28: 1. Enumerate the stages of cellular respiration 250
Bioenergetics 2. Identify the requirements and products of each stage in the
Utilization of Energy process of
breakdown of molecules from glucose to carbon dioxide and
water
3. Explain the major stages of cellular respiration
4. Discuss how ATP is used by cells
5. Describe the relationship of photosynthesis and cellular
respiration
LP 29 Lesson 29: 1. Identify the different ways how plants reproduce. 90
Perpetuation of Life 2. Differentiate asexual reproduction from asexual reproduction.
3. Learn the advantage and disadvantage of both types of
reproduction.
4. Relate how the different types of reproduction are being used
in farming
practices in the Philippines
LP 30 Lesson 30: 1. Recall the function of plant organs in sexual reproduction 75
Perpetuation of Life 2. Learn the structure to function relationship in biological
system
3. Relate structure function relationship among flowers, fruits
and seeds
4. Identify local plants and how the structure of their flower,
fruit and/or seeds
are aided in dispersal
LP 31 Lesson 31: 1. Identify the different ways how plants reproduce. 75
Perpetuation of Life 2. Differentiate asexual reproduction from asexual reproduction.
3. Learn the advantage and disadvantage of both types of
reproduction.
4. Relate how animal reproduction impacts ecosystem imbalance
LP 32 Lesson 32: 1. Describe the central dogma. 60
Perpetuation of Life 2. Explain the process of replication.
3. Explain the process of transcription.
4. Explain the process of translation.
5. Synthesize the implication of the central dogma
LP 33 Lesson 33: 1. Relate their knowledge of the central dogma on genetic 60
Perpetuation of Life engineering
2. Know the process of genetic engineering
3. Describe the definition of genetically modified organism
LP 34 Lesson 34: 1. Relate their knowledge of the central dogma on genetic 60
Perpetuation of Life engineering
2. Know the process of genetic engineering
3. Describe the definition of genetically modified organism
LP 35 Lesson 35: How 1. Know the structure function relationship in the various organ 90
Animals systems
Survive (Nutrition) 2. Able to synthesize the various functions of the organ systems
in the day-today activity of an individual
3. Used their knowledge of physiological processes to
understand the
different diseases associated with the organ systems
LP 36 Lesson 36: How 1. Know the structure function relationship in the various organ 90
Animals systems
Survive (Circulation 2. Able to synthesize the various functions of the organ systems
and in the day-today activity of an individual
Gas Exchange) 3. Used their knowledge of physiological processes to
understand the
different diseases associated with the organ systems
LP 37 Lesson 37: How 1. Know the structure function relationship in the various organ 90
Animals systems
Survive 2. Able to synthesize the various functions of the organ systems
(Homeostasis in the day-today
and Waste activity of an individual
Removal) 3. Used their knowledge of physiological processes to
understand the
different diseases associated with the organ systems
LP 38 Lesson 38: How 1. Know the structure function relationship in the various organ 90
Animals systems
Survive (Immune 2. Able to synthesize the various functions of the organ systems
System) in the day-today
activity of an individual
3. Used their knowledge of physiological processes to
understand the
different diseases associated with the organ systems
LP 39 Lesson 39: How 1. Know the structure function relationship in the various organ 90
Animals Survive systems
(Hormones) 2. Able to synthesize the various functions of the organ systems
in the day-today activity of an individual
3. Used their knowledge of physiological processes to
understand the different diseases associated with the organ
systems
LP 40 Lesson 40: How 1. Know the structure function relationship in the various organ 90
Animals Survive systems
(Nervous System) 2. Able to synthesize the various functions of the organ systems
in the day-today
activity of an individual
3. Used their knowledge of physiological processes to
understand the
different diseases associated with the organ systems
LP 41 Lesson 41: How 1. Know the structure function relationship in the various organ 90
Animals Survive systems
(Locomotion) 2. Able to synthesize the various functions of the organ systems
in the day-today
activity of an individual
3. Used their knowledge of physiological processes to
understand the
different diseases associated with the organ systems
Lesson 42: Plant 1. Know the structure function relationship in the various organ 90
Form and Function systems
and 2. Able to synthesize the various functions of the organ systems
Plant Growth and in the day-today
Development activity of an individual
3. Used their knowledge of physiological processes to
understand the
different diseases associated with the organ systems
LP 43 Lesson 43: The 1. Present evidence in support of evolution 180
Process of 2. Design a poster tracing the evolutionary changes in a crop
Evolution, plant (e.g. rice
Evidence for or corn) that occurred through domestication
Evolution, and 3. Explain how organisms are classified based on evolutionary
Classifying relationships
Organisms Based on
Evolutionary
Relationships
LP 44 Lesson 44: 1. Create a concept map of the historical developments of the 300
Evolution Theory of
Evolution
2. Differentiate Lamarckian Evolution and Darwinian Evolution
through
illustrations or models
3. Understand Darwin’s Theory of Evolution
4. Clarify Misconceptions about the Theory of Evolution
LP 45 Lesson 45: 1. Understand the basic concepts of ecology (Trophic Levels and 175
Interaction Energy Flow)
and 2. Illustrate the following cycles: water, carbon, nutrient
Interdependence (nitrates, phosphates) and relate these to water conservation,
global warming and climate change, and nutrient/organic
pollution.
LP 46 Lesson 46: 1. Define and differentiate biotic potential and environmental 175
Interaction resistance
and 2. Illustrate and explain the different population distribution
Interdependence patterns
3. Differentiate population size and density
4. Understand the different mechanisms that regulated
population density.
LP 47 Lesson 47: 1. Characterize the different biomes of the world; 270
Interaction 2. Characterize the different terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
and 3. Discuss the connectivity of terrestrial and aquatic
Interdependence ecosystems.
4. Discuss how the human populations affect ecosystems.
You might also like
- TBDY 2018 EnglishDocument608 pagesTBDY 2018 EnglishaygunbayramNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument4 pagesEarth and Life ScienceArmelin AlipayoNo ratings yet
- PE11 - MELC 4 Module 4 - Week7 For Teacher PDFDocument24 pagesPE11 - MELC 4 Module 4 - Week7 For Teacher PDFRommel Cando80% (5)
- MELCS UnpackingDocument2 pagesMELCS UnpackingTawagin Mo Akong Merts100% (5)
- MELCs in Earth and Life ScienceDocument5 pagesMELCs in Earth and Life ScienceAdonis Besa100% (14)
- AGoT2 Illustrated Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAGoT2 Illustrated Cheat SheetIgor Silva100% (1)
- M. Ashraf Adeel - Epistemology of The Quran - Elements of A Virtue Approach To Knowledge and Understanding-Springer Internati PDFDocument141 pagesM. Ashraf Adeel - Epistemology of The Quran - Elements of A Virtue Approach To Knowledge and Understanding-Springer Internati PDFimreadingNo ratings yet
- Bow ElsDocument15 pagesBow ElsMarilyn TabuenaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science 11 Module (Week 1-5)Document38 pagesEarth Science 11 Module (Week 1-5)Hilary Grace Sumbi GargarNo ratings yet
- 3rd Grade Science SyllabusDocument6 pages3rd Grade Science Syllabusepetadavid41No ratings yet
- First Semester Syllabus in Earth Science 11 First QuarterDocument11 pagesFirst Semester Syllabus in Earth Science 11 First QuarterElvie CalinisanNo ratings yet
- ELS and G10 ScienceDocument8 pagesELS and G10 ScienceJadeNo ratings yet
- WEEK5Document5 pagesWEEK5Marianne Joy Flormata AlulodNo ratings yet
- SHS Core Subjects MELC Earth and LIfe ScienceDocument6 pagesSHS Core Subjects MELC Earth and LIfe ScienceBaby Yanyan100% (3)
- Ahs13 Filipino Sa Piling Larangan Akademik Week 2 PDFDocument6 pagesAhs13 Filipino Sa Piling Larangan Akademik Week 2 PDFJoy RamosNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science 11Document4 pagesEarth and Life Science 11deborah dumapeNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science 11Document4 pagesEarth and Life Science 11DEBORAH DUMAPENo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Slem q1Document69 pagesEarth and Life Slem q1Kenji YamaguchiNo ratings yet
- DLL 5Document5 pagesDLL 5jullienneNo ratings yet
- Science 10 BowDocument10 pagesScience 10 BowGERRY CHEL LAURENTENo ratings yet
- Learning Continuity Plan SY 2020 - 2021Document5 pagesLearning Continuity Plan SY 2020 - 2021allanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Modular 2Document1 pageEarth Science Modular 2Prasann KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science - BCO - MELCDocument12 pagesGrade 10 Science - BCO - MELCMarfe Montelibano0% (1)
- DLL 1Document2 pagesDLL 1jullienneNo ratings yet
- DLL 2Document2 pagesDLL 2jullienneNo ratings yet
- Proposed Budget of WorkDocument3 pagesProposed Budget of WorkMarilou DuqueNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Water Worlds in The Solar System PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Water Worlds in The Solar System PDFmatthew.robertson769100% (27)
- SHS Core Subjects MELC Earth CienceDocument6 pagesSHS Core Subjects MELC Earth CienceBaby Yanyan67% (3)
- Water Worlds in The Solar System Antony Joseph All ChapterDocument67 pagesWater Worlds in The Solar System Antony Joseph All Chapterjamie.mcneal448100% (6)
- CH 23-6 Earth History FoldableDocument1 pageCH 23-6 Earth History Foldabletownsenr94No ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument5 pagesEarth ScienceVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- TOS sCIENCE 1ST Quarter 1st Sem 20 21Document13 pagesTOS sCIENCE 1ST Quarter 1st Sem 20 21Arjune PantallanoNo ratings yet
- ESCIDocument5 pagesESCIGenesis AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- DLL 1Document4 pagesDLL 1jullienneNo ratings yet
- MELCS Unpacking2Document2 pagesMELCS Unpacking2Tawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- MELCS UnpackingDocument2 pagesMELCS UnpackingTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Budget-of-Work-Earth and Life ScienceDocument5 pagesBudget-of-Work-Earth and Life Sciencejoei Arquero100% (1)
- Quarter 1 Lesson 1Document3 pagesQuarter 1 Lesson 1Lester EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Flexible Assessment Activities and Flexible Learning StrategiesDocument5 pagesFlexible Assessment Activities and Flexible Learning StrategiesAisa EdzaNo ratings yet
- DLL 2Document5 pagesDLL 2jullienneNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesAndrie Vonn Perocho NerpiolNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity in Science 10 Group 1Document2 pagesLearning Activity in Science 10 Group 1NikkoOdejarNo ratings yet
- Earth Science IntroDocument25 pagesEarth Science IntroMiku BinondoNo ratings yet
- 1module 2 - Lesson 2 - Activity 2Document3 pages1module 2 - Lesson 2 - Activity 2JESSA SUMAYANGNo ratings yet
- 1module 2 - Lesson 2 - Activity 2Document3 pages1module 2 - Lesson 2 - Activity 2JESSA SUMAYANGNo ratings yet
- Week One DLLDocument4 pagesWeek One DLLKlarissa LomibaoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument113 pagesEarth and Life ScienceDo Lai NabNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide SampleDocument11 pagesLearning Guide Samplelj BoniolNo ratings yet
- Els W6Document11 pagesEls W6renliejanepNo ratings yet
- Distance Learning Activity Plan: Subject: Earth & Life ScienceDocument6 pagesDistance Learning Activity Plan: Subject: Earth & Life ScienceCatherine De LunaNo ratings yet
- Ii. Content Iii. Learning ResourcesDocument3 pagesIi. Content Iii. Learning ResourcesAq Nga ToNo ratings yet
- Science10 q1 WLP Week1Document2 pagesScience10 q1 WLP Week1Kristine Mae TaboyNo ratings yet
- Earth Science TMDocument64 pagesEarth Science TMMary Vi D. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Ciencias 5 3 Per ModDocument6 pagesCiencias 5 3 Per ModWill ChoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science ModuleDocument112 pagesEarth and Life Science ModuleLeidi Mae S. TugayNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science ModuleDocument117 pagesEarth and Life Science ModuleGlenda AstodilloNo ratings yet
- Earth As The Habitable Planet DAY 1Document47 pagesEarth As The Habitable Planet DAY 1ehlie canlasNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Syllabus SY 11 12 PDFDocument5 pagesEarth Science Syllabus SY 11 12 PDFGeneris SuiNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusJaquilin JosephNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science ModuleDocument114 pagesEarth and Life Science ModuleMax LiaraNo ratings yet
- DLL June 3-7-19-ElsDocument4 pagesDLL June 3-7-19-ElsCristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Atmospheric Science: Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandHandbook of Atmospheric Science: Principles and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- The Stromboli Volcano: An Integrated Study of the 2002 - 2003 EruptionFrom EverandThe Stromboli Volcano: An Integrated Study of the 2002 - 2003 EruptionSonia CalvariNo ratings yet
- Extreme Events and Natural Hazards: The Complexity PerspectiveFrom EverandExtreme Events and Natural Hazards: The Complexity PerspectiveA. Surjalal SharmaNo ratings yet
- School-Summary_JHS_v2.0Document34 pagesSchool-Summary_JHS_v2.0jullienneNo ratings yet
- School-Summary_SHS_v2.0 GRADE 12 V1Document10 pagesSchool-Summary_SHS_v2.0 GRADE 12 V1jullienneNo ratings yet
- TVL 11 FAIRMONT RAM SCORESHEETSDocument22 pagesTVL 11 FAIRMONT RAM SCORESHEETSjullienneNo ratings yet
- Class-Scoresheet_SHS_v2.0-1NEON-RAMDocument28 pagesClass-Scoresheet_SHS_v2.0-1NEON-RAMjullienneNo ratings yet
- School-Form-1-SF-1-35Document6 pagesSchool-Form-1-SF-1-35jullienneNo ratings yet
- School-Summary_SHS_v2.0 GRADE 12Document30 pagesSchool-Summary_SHS_v2.0 GRADE 12jullienneNo ratings yet
- 2ND 23-24 LLS NewDocument1 page2ND 23-24 LLS NewjullienneNo ratings yet
- Pe Exam Ist Sem 2024 - 024007Document2 pagesPe Exam Ist Sem 2024 - 024007jullienneNo ratings yet
- 1ST 23-24 LLS NewDocument1 page1ST 23-24 LLS NewjullienneNo ratings yet
- LR Action Plan 23-24Document2 pagesLR Action Plan 23-24jullienneNo ratings yet
- LR Action Plan 23-24 FinalDocument2 pagesLR Action Plan 23-24 FinaljullienneNo ratings yet
- MID-MRF-JGADocument13 pagesMID-MRF-JGAjullienneNo ratings yet
- PD 3RD 23-24 LLS NewDocument1 pagePD 3RD 23-24 LLS NewjullienneNo ratings yet
- M and e Tool LRMSDocument6 pagesM and e Tool LRMSjullienneNo ratings yet
- Ram MPSDocument3 pagesRam MPSjullienneNo ratings yet
- Mid Year AccomplishmentDocument2 pagesMid Year AccomplishmentjullienneNo ratings yet
- 4TH 23-24 LLS NewDocument1 page4TH 23-24 LLS NewjullienneNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report SHS ClinicDocument4 pagesAccomplishment Report SHS ClinicjullienneNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report For Grade Level Chairmanship & Shs Math Coor Sy 2023-2024.Document9 pagesAccomplishment Report For Grade Level Chairmanship & Shs Math Coor Sy 2023-2024.jullienneNo ratings yet
- Yes-O Ar 24Document1 pageYes-O Ar 24jullienneNo ratings yet
- Molecular PolarityDocument13 pagesMolecular PolarityjullienneNo ratings yet
- Cot 1-Taleon 2023Document6 pagesCot 1-Taleon 2023jullienneNo ratings yet
- Cot 2 - Nedy 2023Document5 pagesCot 2 - Nedy 2023jullienneNo ratings yet
- PPG 18-Mar 4 EMPTYDocument4 pagesPPG 18-Mar 4 EMPTYjullienneNo ratings yet
- PS Q2 Tos-23-24Document4 pagesPS Q2 Tos-23-24jullienneNo ratings yet
- PPG 17-Mar 4Document5 pagesPPG 17-Mar 4jullienneNo ratings yet
- PPG 17Document4 pagesPPG 17jullienneNo ratings yet
- PPG 18-Mar 4Document5 pagesPPG 18-Mar 4jullienneNo ratings yet
- Sci 10 4TH ExamDocument6 pagesSci 10 4TH ExamjullienneNo ratings yet
- Subsystem of EarthDocument2 pagesSubsystem of EarthjullienneNo ratings yet
- Love Song For A VampireDocument1 pageLove Song For A VampireVivianamorteccinaNo ratings yet
- PKM Full C.V. Sept 2021Document11 pagesPKM Full C.V. Sept 2021aopera87No ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Stroke-Associated PneumoniaDocument16 pagesDiagnosis of Stroke-Associated PneumoniaCecilia Casandra UneputtyNo ratings yet
- Malunggay Oleifera As Cleaning AgentDocument2 pagesMalunggay Oleifera As Cleaning AgentMackieNo ratings yet
- Subcontract Agreement (Jenesis) V.1.1Document4 pagesSubcontract Agreement (Jenesis) V.1.1sigit l.prabowoNo ratings yet
- Driscoll WordsDocument55 pagesDriscoll WordsMatthew James DriscollNo ratings yet
- 20120-Article Text-29342-1-10-20200625Document5 pages20120-Article Text-29342-1-10-20200625Min PuNo ratings yet
- 080930-Antarctica TourismDocument15 pages080930-Antarctica TourismVân PhươngNo ratings yet
- Linda Hutcheon - Historiographic MetafictionDocument30 pagesLinda Hutcheon - Historiographic Metafictiongrebucko100% (2)
- Karachi: List of Valid Licence Holder of Banaspati (Ps:221-2003®) July 2014Document76 pagesKarachi: List of Valid Licence Holder of Banaspati (Ps:221-2003®) July 2014Okita MiraningrumNo ratings yet
- Tauck Australia Expands: WeeklyDocument3 pagesTauck Australia Expands: WeeklycruiseweeklyNo ratings yet
- (1899) (Vol. 2) A Sailor's Life Under Four SovereignsDocument364 pages(1899) (Vol. 2) A Sailor's Life Under Four SovereignsHerbert Hillary Booker 2ndNo ratings yet
- Document Analysis Worksheet: Analyze A PaintingDocument4 pagesDocument Analysis Worksheet: Analyze A PaintingPatrick SanchezNo ratings yet
- Integrated NLP Train The Trainer BootcampDocument8 pagesIntegrated NLP Train The Trainer BootcampHitesh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Catheterisation Standard Operating ProcedureDocument27 pagesCatheterisation Standard Operating ProcedureSherly RositaNo ratings yet
- CHEMFISH Fluorinated CompoundsDocument11 pagesCHEMFISH Fluorinated Compoundssunny StevenNo ratings yet
- Module 2 TheoDocument6 pagesModule 2 TheoMichlee Joy Paguila LagocNo ratings yet
- Sambo Catalog Torque LimiterDocument2 pagesSambo Catalog Torque LimiterRicNo ratings yet
- 78-2017ernakulam, KannurDocument13 pages78-2017ernakulam, KannurBingo MeNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Research Methods For ManagementDocument19 pagesAssignment - Research Methods For Managementnatashashaikh93No ratings yet
- 7 VideoDocument17 pages7 VideoKARTIKNo ratings yet
- BodhisattvacaryāvatāraDocument10 pagesBodhisattvacaryāvatāraLiu Fengshui100% (1)
- Reading Cases and Interpreting Statutes Workshop - Answers: Ommon AW Easoning and NstitutionsDocument9 pagesReading Cases and Interpreting Statutes Workshop - Answers: Ommon AW Easoning and NstitutionsshaunNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Ecumenical ChurchDocument13 pagesGroup 1 - Ecumenical ChurchLesther RobloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - REVIEW QUESTION - PROBLEM - Instruction Sets - Addresing Modes and Formats - OkDocument5 pagesChapter 13 - REVIEW QUESTION - PROBLEM - Instruction Sets - Addresing Modes and Formats - OkHo Trong Nghia (K17 QN)No ratings yet
- Ship49417 - en - Economic Impact of Cruise Ports - Case of MiamiDocument33 pagesShip49417 - en - Economic Impact of Cruise Ports - Case of MiamiRebeca Paz Aguilar MundacaNo ratings yet