Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Leukemia 1 1
Leukemia 1 1
Uploaded by
simoo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesType of leukemia
Original Title
leukemia-1-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentType of leukemia
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesLeukemia 1 1
Leukemia 1 1
Uploaded by
simooType of leukemia
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
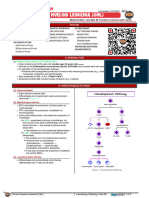
Diagnosis of leukemia
Acute lymphoblast Acute myeloid Chronic Chronic myeloid
leukemia(ALL) leukemia(AML) lymphoid leukemia(CML)
leukemia(CLL)
RBC: decrease (anemia) RBC: decrease RBC: decrease RBC: decrease
CBC PLTs: decrease (anemia) (anemia) (anemia)
(thrombocytopenia) PLTs: decrease PLTs: decrease PLTs: decrease
WBC: increase with (thrombocytopenia) (thrombocytope (thrombocytopenia)
neutropenia WBC: variable nia) WBC: increase
WBC: markedly granulocytes (N, E,
increase B)
RBC: normocytic, RBC: normocytic, RBC:
Blood normochromic normochromic normocytic, WBC:70%
film WBC:90% WBC: 90% normochromic granulocyte with
lymphoblasts, are seen Myoblasts are seen. WBC:70% myeloid series
10% prolymphocyte, 10% mature cell (N, abnormal 30% myeloblast.
lymphocyte. B, E) and band form lymphocytes
with smudge
cell (rupture of
lymphocyte)
30%
prolymphocyte,
lymphoblast.
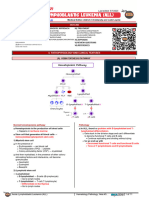
Acute lymphoblast Acute myeloid Chronic Chronic
leukemia(ALL) leukemia(AML) lymphoid myeloid
leukemia(CLL) leukemia(CML
)
Normal bone marrow Having at least 20% In people with
Bone contains 5% or less ALL
blasts in the marrow CML
In leukemia, abnormal blasts
marrow constitute between 30%- or blood is generally The bone
90% or 100% of bone required for a marrow is often
marrow. diagnosis of AML hypercellular
Spinal tap
If bone marrow examination normal range of blast because it is full
confirms ALL, a spinal tap count is 5% or less. pf leukemia cells
(lumber puncture) may be (specially
performed. a sample of CSF myelocyte)
fluid with leukemia cell is a
sign that the disease has
spread to the nerves system.
In most case of childhood
ALL.
Leukemia cells are not found
in the CSF (cerebrospinal
fluid).
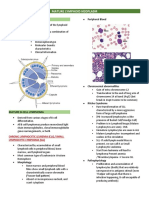
Cytochemistry Cytochemistry Cytochemistry Cytochemistry
Special 1)Acid Phosphatase and
cytochemical stain:
1) Sudan black stain: stains
2)Immunophenotyping cytochemical
tests:
test PAS (periodic acid
Schiff)) cytochemical
phospholipids and
lipoproteins present in (CD marker) to
stain:
Neutrophile
stain monocytes and granulocytes differentiate between:
(SBB)POSITIVE. B lymphocyte (CD ,19, alkaline
2)Immunophenotyping 2) Myeloperoxidase stain: phosphates
20, 21, 22)
tests (CD marker stain peroxidase present in
T lymphocyte (CD 3, 7) (NAP)
(cluster of primary granules of myeloid
cells, demonstrate presence cytogenetic:
differentiation) to of Auer rods (MPO) POSITIVE. in some cases of CLL, cytogenetic:
differentiate between cytogenetic: part of a chromosome Philadelphia
B lymphocyte (CD ,19, are used for genetic analysis. may be missing. this is
cytogenetic testing can detect
chromosome and
20, 21, 22) translocations
called a deletion. BCR-ABL gene
T lymphocyte (CD 3, 7) of chromosomes and genetic the most common This type of test is
abnormalities. deletions occur in parts used to confirm the
-A translocation (8,21) of chromosomes 13,11 diagnosis of CML
For ex, means a part of or 17
chromosome 8 is located on
chromosome 21 and vice
versa (seen most often in
patients with M2
-translocation between
chromosome 15 and 17 (seen
most often in patients with
M3)
You might also like
- CONCEPT MAP (Central Dogma of Molecular Biology)Document1 pageCONCEPT MAP (Central Dogma of Molecular Biology)ShekinahNo ratings yet
- Leukaemia: Definition: Leukemia Is A Malignant Disease of The Hematopoietic System (Blood Forming Cells)Document16 pagesLeukaemia: Definition: Leukemia Is A Malignant Disease of The Hematopoietic System (Blood Forming Cells)Arnab Ghosh100% (1)
- 1 Acute LeukemiaDocument14 pages1 Acute Leukemiaسمير هزاعNo ratings yet
- Hematology Pathology - 006) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) (Notes)Document8 pagesHematology Pathology - 006) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) (Notes)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- IT 9 - Hematology Malignancy - NDDocument93 pagesIT 9 - Hematology Malignancy - NDDesi MawarniNo ratings yet
- Haematologic MalignanciesDocument18 pagesHaematologic MalignanciesMukesh SahooNo ratings yet
- Leukemia AcuteDocument7 pagesLeukemia AcutefallstarrNo ratings yet
- Leukocyte Total and Differential CountDocument37 pagesLeukocyte Total and Differential CountHend HamedNo ratings yet
- Answers - Haematological Malignancies Digital Images QuizDocument4 pagesAnswers - Haematological Malignancies Digital Images Quizcande casanasNo ratings yet
- 3 Bone Marrow ExaminationDocument105 pages3 Bone Marrow ExaminationShourav SarkarNo ratings yet
- ALL Ferri 2019 PDFDocument5 pagesALL Ferri 2019 PDFMia FernandezNo ratings yet
- ' / 5 Introduction of LeukemiasaDocument37 pages' / 5 Introduction of LeukemiasashaikhaboausaibaNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument40 pagesLeukemiaYeni Jesika SilitongaNo ratings yet
- The LeukemiasDocument52 pagesThe Leukemiasمصطفي خندقاوي100% (1)
- Leukemia: Dr. Suhaemi, SPPD, FinasimDocument96 pagesLeukemia: Dr. Suhaemi, SPPD, Finasimwie_wie_wieNo ratings yet
- Wa0125Document2 pagesWa0125Ahmed shabanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Lymphocytic LeukaemiaDocument14 pagesChronic Lymphocytic LeukaemiadrshekarforyouNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic LeukemiasDocument3 pagesAcute and Chronic Leukemiaskaku100% (2)
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia 2222Document19 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemia 2222نواف الزهرانيNo ratings yet
- Case 2 (Mantle Cell Lymphoma)Document3 pagesCase 2 (Mantle Cell Lymphoma)gaber 230No ratings yet
- Acute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaDocument27 pagesAcute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaMahalakshmi PalanisamiNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Hematology MalignanciesDocument5 pagesBasic Concepts of Hematology MalignanciesViolet MillerNo ratings yet
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) : Curs An IV - Limba Engleza 2012-2013Document49 pagesChronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) : Curs An IV - Limba Engleza 2012-2013Tresor MbuyiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Leukaemia 111Document15 pagesChronic Leukaemia 111Razib HasanNo ratings yet
- Acute Leukemia HandoutDocument10 pagesAcute Leukemia Handoutnonie jacobNo ratings yet
- Leukemia 16-12-2019vDocument38 pagesLeukemia 16-12-2019vChrisandiNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloproliferative Acute Lymphoproliferative Chronic Myeloproliferative Chronic Lymphoproliferative Plasma Cell NeoplasmDocument1 pageAcute Myeloproliferative Acute Lymphoproliferative Chronic Myeloproliferative Chronic Lymphoproliferative Plasma Cell NeoplasmAudreySlitNo ratings yet
- Hematology 1 LeukemiaDocument140 pagesHematology 1 LeukemiamaryantoinetteriveraNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument38 pagesHematologysultana alturkiNo ratings yet
- AML ALL CML/CGL CLL: TraitsDocument2 pagesAML ALL CML/CGL CLL: TraitsNischal ShahNo ratings yet
- Kuliah LeukimiaDocument31 pagesKuliah LeukimiaMohammad SutamiNo ratings yet
- Molecular Detection of BCR-ABL Fusion GeneDocument14 pagesMolecular Detection of BCR-ABL Fusion GeneNimra ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- 6.7 Acute and Chronic Leukemias - Feb 11 - Dra. CaliwaganDocument14 pages6.7 Acute and Chronic Leukemias - Feb 11 - Dra. CaliwaganJCAsssssiloNo ratings yet
- Acute Leukaemia-Update: DR Niranjan N. RathodDocument89 pagesAcute Leukaemia-Update: DR Niranjan N. RathodratanNo ratings yet
- Mature B Cell Lymphoma CLL PLL HCLDocument4 pagesMature B Cell Lymphoma CLL PLL HCLlai cruzNo ratings yet
- Chart - WBC DisordersDocument1 pageChart - WBC DisordersSamuel RothschildNo ratings yet
- Patho - 4th Asessment - Chronic Leukemias - 27 Jan 2007Document28 pagesPatho - 4th Asessment - Chronic Leukemias - 27 Jan 2007api-3703352No ratings yet
- Anurbf 132 135Document4 pagesAnurbf 132 135Victor GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Hematologic Pathology p24-35Document12 pagesHematologic Pathology p24-35zeroun24100% (6)
- Molecular Basis of Acute LeukemiaDocument31 pagesMolecular Basis of Acute LeukemiaVivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- P2 KompleteDocument221 pagesP2 KompleteNikola SiladiNo ratings yet
- Week 05. Acute LeukemiasDocument26 pagesWeek 05. Acute LeukemiasAshley ArnoldNo ratings yet
- Flow Cytometry Immunophenotypic Characteristics of Monocytic Population in Acute Monocytic LeukemiaDocument13 pagesFlow Cytometry Immunophenotypic Characteristics of Monocytic Population in Acute Monocytic Leukemiadrafq2000100% (1)
- 25 Yo Male With Fever of 1month Duration HB 5.0gm/dl TLC: 70,000 Cells/cumm Platelets: 40,000/cummDocument47 pages25 Yo Male With Fever of 1month Duration HB 5.0gm/dl TLC: 70,000 Cells/cumm Platelets: 40,000/cummMahalakshmi PalanisamiNo ratings yet
- Hematology Pathology - 003) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) (Notes)Document11 pagesHematology Pathology - 003) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) (Notes)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- BoardReviewPart2B MalignantHemePathDocument207 pagesBoardReviewPart2B MalignantHemePathMaria Cristina Alarcon NietoNo ratings yet
- Acute Leukemias of Ambiguous LineageDocument8 pagesAcute Leukemias of Ambiguous Lineageanon_62668703No ratings yet
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) : Gulzar A. BhatDocument15 pagesChronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) : Gulzar A. Bhatmettu_555No ratings yet
- Intro To Bone MarrowDocument10 pagesIntro To Bone MarrowMinh ChâuNo ratings yet
- Apl What A Blast3884Document60 pagesApl What A Blast3884MUDASIR REHMANNo ratings yet
- Lecture 33-LeukemiaDocument21 pagesLecture 33-LeukemiaYasir KareemNo ratings yet
- (Romanian Journal of Internal Medicine) Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia in Adults. Pathologic Features and PrognosisDocument6 pages(Romanian Journal of Internal Medicine) Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia in Adults. Pathologic Features and PrognosisPepeeNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Leukemia: Tri RatnaningsihDocument49 pagesDiagnosis of Leukemia: Tri RatnaningsihPorisNo ratings yet
- Hematology - PathophysiologyDocument28 pagesHematology - Pathophysiologyjmosser100% (2)
- Prof. Dr. Gamal Abdul Hamid University of AdenDocument95 pagesProf. Dr. Gamal Abdul Hamid University of AdenAarpit PatwaNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Leukemia FinalDocument68 pagesAcute and Chronic Leukemia FinalHannah LeiNo ratings yet
- Acute Monocytic Leukemia and Acute Lmphocytic Leukemia: OccurrenceDocument12 pagesAcute Monocytic Leukemia and Acute Lmphocytic Leukemia: OccurrenceAngelo Jude CobachaNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics: Laboratory HematologyDocument35 pagesCytogenetics: Laboratory HematologyBai GraceNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Leukemia: From initial gene mutation to survivorship supportFrom EverandFast Facts: Leukemia: From initial gene mutation to survivorship supportNo ratings yet
- Haemophilus InfluenzaeDocument20 pagesHaemophilus Influenzaevignesh9489No ratings yet
- Meiosis-FoldableDocument7 pagesMeiosis-Foldableapi-267309851No ratings yet
- Antigen-Stimulated PBMC Transcriptional Protective Signatures For Malaria ImmunizationDocument18 pagesAntigen-Stimulated PBMC Transcriptional Protective Signatures For Malaria Immunizationyowan wandikboNo ratings yet
- Jamiel James Arceno Biochemisty Bsn1BDocument2 pagesJamiel James Arceno Biochemisty Bsn1BjamielNo ratings yet
- Urea CycleDocument3 pagesUrea CycleHshshdhdNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/13Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/13lllllisaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document6 pagesModule 1Yen BuYenNo ratings yet
- Targeting The Untargetable KRAS in Cancer Therapy: Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica BDocument9 pagesTargeting The Untargetable KRAS in Cancer Therapy: Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica Bmothi lalNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (Light and Dark Reaction) :: Concept Notes With Formative ActivitiesDocument12 pagesPhotosynthesis (Light and Dark Reaction) :: Concept Notes With Formative ActivitiesMonica SolomonNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument3 pagesMuscle Tissuekugmo89No ratings yet
- 06 - Cell Specialization and Organization (Solutions2)Document2 pages06 - Cell Specialization and Organization (Solutions2)vincentxia0413No ratings yet
- FAB Classification of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML)Document2 pagesFAB Classification of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML)Christine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- 2016 Genes and Athletic Performance An UpdateDocument15 pages2016 Genes and Athletic Performance An UpdateFrancisco Antonó Castro WeithNo ratings yet
- Uji Toksisitas Daun Kelor (Moringa Oleifera) Terhadap Sel Fibroblas Gingiva Menggunakan Uji MTT AssayDocument8 pagesUji Toksisitas Daun Kelor (Moringa Oleifera) Terhadap Sel Fibroblas Gingiva Menggunakan Uji MTT AssayPratidina Fitri RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- 4 Gi Hormones I: Endocrine HormonesDocument4 pages4 Gi Hormones I: Endocrine HormonesLinh PhanNo ratings yet
- 13-High-Level Production of Human Type I Collagen in The Yeast P.pastoris PDFDocument10 pages13-High-Level Production of Human Type I Collagen in The Yeast P.pastoris PDFytngllc_197006458No ratings yet
- Breast Cancer ExtendedDocument260 pagesBreast Cancer ExtendedCarleta StanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document10 pagesUnit 1evanjalinNo ratings yet
- Quaternary Structure of ProteinDocument18 pagesQuaternary Structure of ProteinRoopa RanganathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 BloodDocument6 pagesChapter 10 BloodSymonette OcturaNo ratings yet
- Learning Unit 7 - Benign Reactive ChangesDocument28 pagesLearning Unit 7 - Benign Reactive ChangesMarelize ErasmusNo ratings yet
- Reactive Oxygen Species and Seed Germination: Marcelo Pedrosa Gomes & Queila Souza GarciaDocument7 pagesReactive Oxygen Species and Seed Germination: Marcelo Pedrosa Gomes & Queila Souza GarciaBetina PNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 WorksheetDocument2 pagesLesson 1 WorksheetJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- MIT20 441JF09 Quiz3 SampleDocument4 pagesMIT20 441JF09 Quiz3 SampleGuilherme HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles QuizDocument16 pagesCell Organelles Quizعبدالله عفيف الشخصNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Webquest Day 2 With Notes Filled inDocument3 pagesCell Organelles Webquest Day 2 With Notes Filled inJustin TisNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration 9-12Document56 pagesCellular Respiration 9-12David BayaniNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument6 pagesProteinsAlliyah Gail LoraniaNo ratings yet