Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views320N KRE Chart
320N KRE Chart
Uploaded by
rmerchant789Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Ncstudio V9 Programming Manual-R5.1Document102 pagesNcstudio V9 Programming Manual-R5.1beanib83No ratings yet
- Nomenclature Super Notes by AKansha KarnwalDocument8 pagesNomenclature Super Notes by AKansha KarnwalVALOARDNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Mechanisms & Hydrocarbons 2022Document6 pagesComparison of Mechanisms & Hydrocarbons 2022PriyaNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument18 pagesAldehyde, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidSimi Sunil100% (2)
- K - Enols and Enolates 11 - F14Document1 pageK - Enols and Enolates 11 - F14shinexblazerNo ratings yet
- Alkene PreparationDocument1 pageAlkene Preparationtemp accNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 10062021Document1 pageIncidence Map 10062021Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- V. List of Abbreviations: Abbreviation Chemical Name Chemical StructureDocument14 pagesV. List of Abbreviations: Abbreviation Chemical Name Chemical StructureduongnguyenNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 1111Document1 pageIncidence Map 1111WBKONo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 10122021Document1 pageIncidence Map 10122021Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- RamachandranPlot AsimplifiedapproachDocument7 pagesRamachandranPlot Asimplifiedapproachuniversal tradersNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 09272021Document1 pageIncidence Map 09272021Debbie Bunton HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanisms of Enzyme Action: (WEEK 7)Document44 pagesMolecular Mechanisms of Enzyme Action: (WEEK 7)oczhinviaNo ratings yet
- Red Zone Map: 12/16/21Document1 pageRed Zone Map: 12/16/21Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 101121Document1 pageIncidence Map 101121Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chm301 Chapter 3 & 4Document2 pagesTutorial Chm301 Chapter 3 & 4fatinNo ratings yet
- Dec. 21, 2021 Incident MapDocument1 pageDec. 21, 2021 Incident MapDebbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- ProtienDocument3 pagesProtienkkkNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument18 pagesAldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidInfinite SinghNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 10252021Document1 pageIncidence Map 10252021Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Chy-Ch-H: HehehehehehahohDocument2 pagesChy-Ch-H: HehehehehehahohcebrowningNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test-1 SolutionDocument3 pagesCbse Test-1 SolutionAbirami SNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Dec 16, 2022Document4 pagesAdobe Scan Dec 16, 2022Pankaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and Ketone HandwrittenDocument2 pagesAldehyde and Ketone HandwrittenHarshvardhan KhatodNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 102221Document1 pageIncidence Map 102221Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- OCOC-1 Live Class-3 Teacher NotesDocument41 pagesOCOC-1 Live Class-3 Teacher Notesmardarchod 123No ratings yet
- Incidence Map 09282021Document1 pageIncidence Map 09282021haeli spearsNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 09242021Document1 pageIncidence Map 09242021Debbie Bunton HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Short Notes Nitesh DevnaniDocument4 pagesIUPAC Short Notes Nitesh Devnaniunderprocess786No ratings yet
- Incidence Map 08112021Document1 pageIncidence Map 08112021haeli spearsNo ratings yet
- King Abdulaziz University: H Relative Atomic Mass To Nearest Whole Number Key SymbolDocument10 pagesKing Abdulaziz University: H Relative Atomic Mass To Nearest Whole Number Key SymbolSereen MohammedNo ratings yet
- Ky Red Zone MapDocument1 pageKy Red Zone MapBryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 09072021Document1 pageIncidence Map 09072021Debbie Bunton HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Modul 3Document9 pagesModul 3yuri.angell1234No ratings yet
- Red Zone Map 10/19/21Document1 pageRed Zone Map 10/19/21Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Elements W Atomic Mass PubChemDocument1 pagePeriodic Table of Elements W Atomic Mass PubChemImmaculada AcantoNo ratings yet
- Roadmap Problem - 5Document1 pageRoadmap Problem - 5abhyudaipathwayNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 08182021Document1 pageIncidence Map 08182021Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument1 pagePeriodic TableSYED ALINo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument1 pageCarboxylic AcidsMd AmanNo ratings yet
- 20 - Metabolismo de PirimidinasDocument1 page20 - Metabolismo de PirimidinasgustasconNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 09022021Document1 pageIncidence Map 09022021Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- 13C and 1H NMR (RMN 1H y 13C)Document1 page13C and 1H NMR (RMN 1H y 13C)veromendoNo ratings yet
- KY Red Zone Map: 10/27Document1 pageKY Red Zone Map: 10/27Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- KY Red Zone Map: 11/30/21Document1 pageKY Red Zone Map: 11/30/21Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation of Proteins: Primary StructureDocument41 pagesStructural Organisation of Proteins: Primary StructureanaNo ratings yet
- KY Red Zone MapDocument1 pageKY Red Zone MapBryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- RXN Shirt NotesDocument3 pagesRXN Shirt NotesnismabdlazeezNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Elements W Oxidation States PubChemDocument1 pagePeriodic Table of Elements W Oxidation States PubChemHuey KaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry (2) 1 26Document26 pagesOrganic Chemistry (2) 1 26Mr valorant ipadNo ratings yet
- KY Red Zone Map: 11/23/21Document1 pageKY Red Zone Map: 11/23/21Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 09222021Document1 pageIncidence Map 09222021haeli spearsNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 08232021Document1 pageIncidence Map 08232021haeli spearsNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument29 pagesHydrocarbongoswamiaddNo ratings yet
- PeriodictableDocument1 pagePeriodictableapi-3820360No ratings yet
- Polymerization of Methyl MethacrylateDocument10 pagesPolymerization of Methyl MethacrylateMohamed Abdel AzizNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 111521Document1 pageIncidence Map 111521Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 08032021Document1 pageIncidence Map 08032021Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Pedoman Obat EmergencyDocument10 pagesPedoman Obat EmergencyPOKJA PKPONo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 08192021Document1 pageIncidence Map 08192021Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- Ba SyllabusDocument5 pagesBa SyllabusKamlesh Kumar MandalNo ratings yet
- Tvonics DTR Fp1600 User GuideDocument32 pagesTvonics DTR Fp1600 User Guidevince_thomas7654No ratings yet
- Grade 12 Second Semester ScheduleDocument2 pagesGrade 12 Second Semester ScheduleLeeyan DerNo ratings yet
- Astm A184Document3 pagesAstm A184racingspirit800% (1)
- Training-Coating Machine OperationDocument12 pagesTraining-Coating Machine Operationraju1559405No ratings yet
- Initial Environmental Examination (Iee) Checklist For Plastic Recycling 1.0 General InformationDocument23 pagesInitial Environmental Examination (Iee) Checklist For Plastic Recycling 1.0 General Informationavie100% (1)
- Eat Lots of Chocolates When Time Gets Tough, and Eat Even More When Times Are Great.Document2 pagesEat Lots of Chocolates When Time Gets Tough, and Eat Even More When Times Are Great.Miruna MocleașăNo ratings yet
- Updated Term Paper (5310) PDFDocument21 pagesUpdated Term Paper (5310) PDFSourae MridhaNo ratings yet
- DermatomycosesDocument2 pagesDermatomycosesRay CullenNo ratings yet
- Asco Solenoid ValveDocument4 pagesAsco Solenoid ValveSayak GhoshNo ratings yet
- IAAC Final Round 2020Document9 pagesIAAC Final Round 2020Dennil JobyNo ratings yet
- Gothra PattikaDocument172 pagesGothra PattikaParimi VeeraVenkata Krishna SarveswarraoNo ratings yet
- List of Map Items Class X 2017-18Document3 pagesList of Map Items Class X 2017-18Mayank GhatpandeNo ratings yet
- LEAP Brochure 2013Document15 pagesLEAP Brochure 2013Reparto100% (1)
- Method Statement For Anti Termite TreatmentDocument7 pagesMethod Statement For Anti Termite TreatmentSagar Aliasjackey100% (2)
- Expanded Immunization Program EpiDocument22 pagesExpanded Immunization Program EpiGirome BairaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6-10 Level 1Document10 pagesCHAPTER 6-10 Level 1Liana SimionNo ratings yet
- OSHA 1926 Subpart M App C - Personal Fall Arrest Systems - Non-Mandatory Guidelines For Complying With 1926.502 (D)Document8 pagesOSHA 1926 Subpart M App C - Personal Fall Arrest Systems - Non-Mandatory Guidelines For Complying With 1926.502 (D)Gunnie PandherNo ratings yet
- Merlin Installer ManualDocument19 pagesMerlin Installer Manualguywk100% (1)
- Practice 2Document2 pagesPractice 2beebrwNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment TemplateDocument7 pagesRisk Assessment TemplateMihiretu MelkamuNo ratings yet
- ABB Analog Signal Converter and Serial Data ConverterDocument42 pagesABB Analog Signal Converter and Serial Data ConverterKmj KmjNo ratings yet
- G6 Earth Science Revision Guide - 8Document16 pagesG6 Earth Science Revision Guide - 8Maria JiaNo ratings yet
- Proyek PT Asiana Technologies PDFDocument49 pagesProyek PT Asiana Technologies PDFAlexandro AndooNo ratings yet
- P 75-92 QTR 2 TG Module 2 Plant and Animal CellsDocument18 pagesP 75-92 QTR 2 TG Module 2 Plant and Animal CellsJane Limsan PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- F 263544Document11 pagesF 263544Mkhululi KhumaloNo ratings yet
- Tech Bulletin 718 PDFDocument28 pagesTech Bulletin 718 PDFJ. BangjakNo ratings yet
- © Iessg: The Global Positioning SystemDocument23 pages© Iessg: The Global Positioning SystemMiDa AlaribyNo ratings yet
320N KRE Chart
320N KRE Chart
Uploaded by
rmerchant7890 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOriginal Title
320N KRE chart
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 page320N KRE Chart
320N KRE Chart
Uploaded by
rmerchant789Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
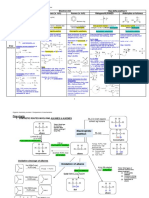
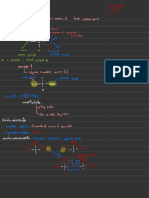
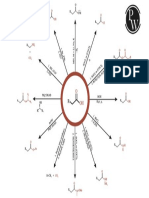
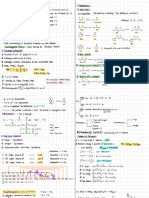
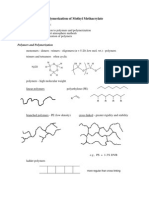
Iverson CH 320N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then
identify location(s) of new bonds,
especially C-C or C=C bonds. With that information, use the following KREs to determine which reactions are appropriate.
O
KRE: An imine indicates an New bond H 2N New C-C bond
N
New C-C bond MgBr aldehyde or ketone reacting H O O O
O with a primary amine or
KRE: A new C-C bond two 1) ph 4.0
or ammonia KRE: This is a cyclic β-ketoester β 1) 1.0 eq. NaOEt
carbons away from an -OH H α O
group indicates an OH CuLi that indicates a Dieckmann reaction 6 1 (or LDA) 6 5 4
3
2 1
5 2 O O
organometallic reacting starting with a 6-carbon diester. *
2) H3O (mild) 2 Notice that Dieckman reactions 4 3
with an epoxide. or
Fischer O require 1.0 equivalent of base. Racemic 2) H3O (mild) O
Li HO
esterification
O H2SO4 (catalytic)
New bond OH
O KRE: Ester group O 1) 1.0 eq. NaOEt
New C-C bond New C-C (or LDA)
O KRE: This is a nucleophile O O
HO O bond O
KRE: A new C-C bond on 1) linked to the β-carbon of β
O
the same carbon as a H MgBr the amide. This is also a β α
Cl 2)
secondary -OH group methyl ketone. Putting α NH2
* O
indicates a Grignard Racemic these together indicates a NH2
2) H3O (mild) New bond
reacting with an aldehyde. OH Michael reaction starting 3) H3O (strong) and heat
KRE: This is a lactone (cyclic O O O with acetoester
O ester). The six-membered ring H2SO4 (catalytic)
New C-C bond 5 1
New C-C
indicates a 5-carbon hydroxy acid 4 2
5 3 O O
KRE: A new C-C bond on 1) starting material that undergoes 4 2 HO 1 OH bond
MgBr 3 O
the same carbon as a Fischer esterification. 1) 1.0 eq. NaOEt
tertiary -OH group indicates KRE: Reaction of a β (or LDA)
a Grignard reacting with a O nucleophile (β-diketone) O
2) H3O (mild) α O
ketone. OH connected to the β-carbon β
of a carbonyl (the ester) 2) α
O
New C-C bond Cl O
2 H 2N 3) H3O (mild) O
KRE: A new C-C bond on 1) CO2 or O O
MgBr O
on a carboxylic acid in O New bond
which one carbon atom was KRE: Amide group
added indicates a Grignard 2) H3O (mild) O O
N 1) 1.0 eq. LDA
reacting with CO2. OH H O
O New C-C bond 2) Br α
H 2N
New C-C bond
O KRE: alkylated ketone deriving Or
from either an enolate made with α *
N
O LDA or using an enamine
KRE: A new C-C bond Racemic
from a CN on the same C OH HCN O 1) Br N
carbon as an -OH group Racemic New C-C α
* KRE: Two identical new C- OH 2) H3O (mild)
indicates HCN reacting bond 1)
with a ketone or aldehyde. C bonds on the same carbon O
as a tertiary -OH group 2 MgBr
indicates two equivalents of
a Grignard reacting with an 2) H3O (mild)
New C-C bond New C-C bond
ester. New C-C 1) 1.0 eq. LDA O
bond O O O 2) O
O New C-C Cl α
KRE: A new C-C bond 1) KRE: A ketone with an new O bond KRE: A β-diketone α
from an alkyne on the same OH 1) β
C-C adjacent to the Cl CuLi indicates reaction of an acid
carbon as an -OH group Racemic * Or
* carbonyl indicates an acid chloride with either an
O
indicates an alkyne anion chloride reacting with a 2 enolate made with LDA or
2) H3O (mild) 2) H3O (mild)
reacting with a ketone or Gilman reagent. using an enamine 1) Cl
N
aldehyde. Racemic
α
2) H3O (mild)
New C-C bond
New C=C bond O α
KRE: An β-hydroxy aldehyde with H
an indicates an aldol reaction with NaOH (catalytic)
P(Ph)3 α 1) 1.0 eq. NaOEt
KRE: A new Z C=C bond H no dehydration. H
O
* * (or LDA) O O
indicates an alkyl Wittig β O New C-C bond
reagent was used. Z alkene 2)
Br
Racemic OH O KRE: A methyl ketone with α α
substitution at the α-carbon * O
indicates an acetoester synthesis. 3) 1.0 eq. NaOEt
O New C-C
The second new C-C bond (or LDA)
bond
New C-C bond O O indicates a second alkylation with 4) CH3Br
Racemic
KRE: A new E C=C bond CH3Br
indicates a Wittig reagent H New C=C bond 5) H3O (strong) and heat
P(Ph)3 α
with a carbonyl adjacent to H
the negative charge (enolate α
Wittig) was used. E alkene KRE: An α,β-unsaturated E,Z Mixture 1) NaOH (catalytic) H
aldehyde with an E.Z mixture O New C-C bond
O
New bond New bond indicates an aldol reaction 1) 1.0 eq. NaOEt O O
O KRE: A carboxylic acid with
followed by dehydration in 2) H3O (mild) and heat O (or LDA)
α substitution at the α-carbon α
H3CO OCH3 CH3OH acid. H indicates a malonic ester
KRE: An acetal where a HO O O
synthesis. α 2) Br
carbonyl used to be H
indicates acetal formation H H2SO4 (catalytic) 3) H3O (strong) and heat
New C=C
with an alcohol. O
bond
O
O New C-C bond 1) 0.5 eq. NaOEt
OH New C-C bond O
KRE: This is a very tricky one. A (or LDA) α
KRE: A five or six- New bond HO β O α O
O New bond KRE: This is an α,β-unsaturated 1) NaOH (catalytic) symmetric ketone indicates a Claisen
membered ring cyclic acetal O H 6 α reaction followed by ester hydrolysis
aldehyde that indicates an aldol 1 H 2) H3O (strong)
where a carbonyl used to be H2SO4 (catalytic) 5 2 H
reaction followed by dehydration. In 5 3 1 and decarboxylation of the resulting β- O and heat
indicates acetal formation H 4 3 2) H3O (mild) H 6 4 2
keto ester.
this case the ring is formed because a
with a two or three carbon and heat
6-carbon dialdehyde is used.
diol. O
New bond O
O
New C-C bond
O OH O CH3 O
KRE: A five or six-membered New C-C bond 7 9 CH3
H2SO4 (catalytic) O KRE: A new six- 8
ring cyclic hemiacetal indicates 4 5 1 * 3 7 3
4 * 1) 0.5 eq. NaOEt membered ring with 2 *
10
2
3 2 β O 4 8 4
or 5-carbon hydroxyaldehyde 4 2 HO 5 1 H KRE: A β-ketoester indicates a α (or LDA) two new C-C bonds
starting material. 3 Racemic α 5 1 5 1
Claisen reaction. and an α,β-unsaturated 10 9
O 6 Catalytic NaOH 6
Racemic 2) H3O (mild) ketone indicates a O O
O O Racemic and heat
Robinson Annulation
reaction. New C-C bond
You might also like
- Ncstudio V9 Programming Manual-R5.1Document102 pagesNcstudio V9 Programming Manual-R5.1beanib83No ratings yet
- Nomenclature Super Notes by AKansha KarnwalDocument8 pagesNomenclature Super Notes by AKansha KarnwalVALOARDNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Mechanisms & Hydrocarbons 2022Document6 pagesComparison of Mechanisms & Hydrocarbons 2022PriyaNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument18 pagesAldehyde, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidSimi Sunil100% (2)
- K - Enols and Enolates 11 - F14Document1 pageK - Enols and Enolates 11 - F14shinexblazerNo ratings yet
- Alkene PreparationDocument1 pageAlkene Preparationtemp accNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 10062021Document1 pageIncidence Map 10062021Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- V. List of Abbreviations: Abbreviation Chemical Name Chemical StructureDocument14 pagesV. List of Abbreviations: Abbreviation Chemical Name Chemical StructureduongnguyenNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 1111Document1 pageIncidence Map 1111WBKONo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 10122021Document1 pageIncidence Map 10122021Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- RamachandranPlot AsimplifiedapproachDocument7 pagesRamachandranPlot Asimplifiedapproachuniversal tradersNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 09272021Document1 pageIncidence Map 09272021Debbie Bunton HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanisms of Enzyme Action: (WEEK 7)Document44 pagesMolecular Mechanisms of Enzyme Action: (WEEK 7)oczhinviaNo ratings yet
- Red Zone Map: 12/16/21Document1 pageRed Zone Map: 12/16/21Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 101121Document1 pageIncidence Map 101121Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chm301 Chapter 3 & 4Document2 pagesTutorial Chm301 Chapter 3 & 4fatinNo ratings yet
- Dec. 21, 2021 Incident MapDocument1 pageDec. 21, 2021 Incident MapDebbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- ProtienDocument3 pagesProtienkkkNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument18 pagesAldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidInfinite SinghNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 10252021Document1 pageIncidence Map 10252021Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Chy-Ch-H: HehehehehehahohDocument2 pagesChy-Ch-H: HehehehehehahohcebrowningNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test-1 SolutionDocument3 pagesCbse Test-1 SolutionAbirami SNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Dec 16, 2022Document4 pagesAdobe Scan Dec 16, 2022Pankaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and Ketone HandwrittenDocument2 pagesAldehyde and Ketone HandwrittenHarshvardhan KhatodNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 102221Document1 pageIncidence Map 102221Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- OCOC-1 Live Class-3 Teacher NotesDocument41 pagesOCOC-1 Live Class-3 Teacher Notesmardarchod 123No ratings yet
- Incidence Map 09282021Document1 pageIncidence Map 09282021haeli spearsNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 09242021Document1 pageIncidence Map 09242021Debbie Bunton HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Short Notes Nitesh DevnaniDocument4 pagesIUPAC Short Notes Nitesh Devnaniunderprocess786No ratings yet
- Incidence Map 08112021Document1 pageIncidence Map 08112021haeli spearsNo ratings yet
- King Abdulaziz University: H Relative Atomic Mass To Nearest Whole Number Key SymbolDocument10 pagesKing Abdulaziz University: H Relative Atomic Mass To Nearest Whole Number Key SymbolSereen MohammedNo ratings yet
- Ky Red Zone MapDocument1 pageKy Red Zone MapBryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 09072021Document1 pageIncidence Map 09072021Debbie Bunton HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Modul 3Document9 pagesModul 3yuri.angell1234No ratings yet
- Red Zone Map 10/19/21Document1 pageRed Zone Map 10/19/21Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Elements W Atomic Mass PubChemDocument1 pagePeriodic Table of Elements W Atomic Mass PubChemImmaculada AcantoNo ratings yet
- Roadmap Problem - 5Document1 pageRoadmap Problem - 5abhyudaipathwayNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 08182021Document1 pageIncidence Map 08182021Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument1 pagePeriodic TableSYED ALINo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument1 pageCarboxylic AcidsMd AmanNo ratings yet
- 20 - Metabolismo de PirimidinasDocument1 page20 - Metabolismo de PirimidinasgustasconNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 09022021Document1 pageIncidence Map 09022021Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- 13C and 1H NMR (RMN 1H y 13C)Document1 page13C and 1H NMR (RMN 1H y 13C)veromendoNo ratings yet
- KY Red Zone Map: 10/27Document1 pageKY Red Zone Map: 10/27Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- KY Red Zone Map: 11/30/21Document1 pageKY Red Zone Map: 11/30/21Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation of Proteins: Primary StructureDocument41 pagesStructural Organisation of Proteins: Primary StructureanaNo ratings yet
- KY Red Zone MapDocument1 pageKY Red Zone MapBryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- RXN Shirt NotesDocument3 pagesRXN Shirt NotesnismabdlazeezNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Elements W Oxidation States PubChemDocument1 pagePeriodic Table of Elements W Oxidation States PubChemHuey KaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry (2) 1 26Document26 pagesOrganic Chemistry (2) 1 26Mr valorant ipadNo ratings yet
- KY Red Zone Map: 11/23/21Document1 pageKY Red Zone Map: 11/23/21Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 09222021Document1 pageIncidence Map 09222021haeli spearsNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 08232021Document1 pageIncidence Map 08232021haeli spearsNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument29 pagesHydrocarbongoswamiaddNo ratings yet
- PeriodictableDocument1 pagePeriodictableapi-3820360No ratings yet
- Polymerization of Methyl MethacrylateDocument10 pagesPolymerization of Methyl MethacrylateMohamed Abdel AzizNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 111521Document1 pageIncidence Map 111521Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 08032021Document1 pageIncidence Map 08032021Debbie HarbsmeierNo ratings yet
- Pedoman Obat EmergencyDocument10 pagesPedoman Obat EmergencyPOKJA PKPONo ratings yet
- Incidence Map 08192021Document1 pageIncidence Map 08192021Bryce ShreveNo ratings yet
- Ba SyllabusDocument5 pagesBa SyllabusKamlesh Kumar MandalNo ratings yet
- Tvonics DTR Fp1600 User GuideDocument32 pagesTvonics DTR Fp1600 User Guidevince_thomas7654No ratings yet
- Grade 12 Second Semester ScheduleDocument2 pagesGrade 12 Second Semester ScheduleLeeyan DerNo ratings yet
- Astm A184Document3 pagesAstm A184racingspirit800% (1)
- Training-Coating Machine OperationDocument12 pagesTraining-Coating Machine Operationraju1559405No ratings yet
- Initial Environmental Examination (Iee) Checklist For Plastic Recycling 1.0 General InformationDocument23 pagesInitial Environmental Examination (Iee) Checklist For Plastic Recycling 1.0 General Informationavie100% (1)
- Eat Lots of Chocolates When Time Gets Tough, and Eat Even More When Times Are Great.Document2 pagesEat Lots of Chocolates When Time Gets Tough, and Eat Even More When Times Are Great.Miruna MocleașăNo ratings yet
- Updated Term Paper (5310) PDFDocument21 pagesUpdated Term Paper (5310) PDFSourae MridhaNo ratings yet
- DermatomycosesDocument2 pagesDermatomycosesRay CullenNo ratings yet
- Asco Solenoid ValveDocument4 pagesAsco Solenoid ValveSayak GhoshNo ratings yet
- IAAC Final Round 2020Document9 pagesIAAC Final Round 2020Dennil JobyNo ratings yet
- Gothra PattikaDocument172 pagesGothra PattikaParimi VeeraVenkata Krishna SarveswarraoNo ratings yet
- List of Map Items Class X 2017-18Document3 pagesList of Map Items Class X 2017-18Mayank GhatpandeNo ratings yet
- LEAP Brochure 2013Document15 pagesLEAP Brochure 2013Reparto100% (1)
- Method Statement For Anti Termite TreatmentDocument7 pagesMethod Statement For Anti Termite TreatmentSagar Aliasjackey100% (2)
- Expanded Immunization Program EpiDocument22 pagesExpanded Immunization Program EpiGirome BairaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6-10 Level 1Document10 pagesCHAPTER 6-10 Level 1Liana SimionNo ratings yet
- OSHA 1926 Subpart M App C - Personal Fall Arrest Systems - Non-Mandatory Guidelines For Complying With 1926.502 (D)Document8 pagesOSHA 1926 Subpart M App C - Personal Fall Arrest Systems - Non-Mandatory Guidelines For Complying With 1926.502 (D)Gunnie PandherNo ratings yet
- Merlin Installer ManualDocument19 pagesMerlin Installer Manualguywk100% (1)
- Practice 2Document2 pagesPractice 2beebrwNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment TemplateDocument7 pagesRisk Assessment TemplateMihiretu MelkamuNo ratings yet
- ABB Analog Signal Converter and Serial Data ConverterDocument42 pagesABB Analog Signal Converter and Serial Data ConverterKmj KmjNo ratings yet
- G6 Earth Science Revision Guide - 8Document16 pagesG6 Earth Science Revision Guide - 8Maria JiaNo ratings yet
- Proyek PT Asiana Technologies PDFDocument49 pagesProyek PT Asiana Technologies PDFAlexandro AndooNo ratings yet
- P 75-92 QTR 2 TG Module 2 Plant and Animal CellsDocument18 pagesP 75-92 QTR 2 TG Module 2 Plant and Animal CellsJane Limsan PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- F 263544Document11 pagesF 263544Mkhululi KhumaloNo ratings yet
- Tech Bulletin 718 PDFDocument28 pagesTech Bulletin 718 PDFJ. BangjakNo ratings yet
- © Iessg: The Global Positioning SystemDocument23 pages© Iessg: The Global Positioning SystemMiDa AlaribyNo ratings yet