Professional Documents
Culture Documents
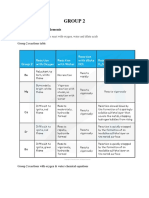
Definitions - Topic 3.1.2 Group 2 - OCR A Chemistry A Level
Definitions - Topic 3.1.2 Group 2 - OCR A Chemistry A Level
Uploaded by
CHRONIKOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Definitions - Topic 3.1.2 Group 2 - OCR A Chemistry A Level
Definitions - Topic 3.1.2 Group 2 - OCR A Chemistry A Level
Uploaded by
CHRONIKCopyright:
Available Formats
Definitions and Concepts for OCR (A) Chemistry A-level
Topic 3.1.2 - Group 2
Base: a substance that can accept H+ ions from another substance. Group 2 compounds can
be used as bases: Ca(OH)2 is used to neutralise acidic soils in agriculture and Mg(OH)2 and
CaCO3 are used as antacids to treat indigestion.
Electron Configuration: the arrangement of electrons into orbitals and energy levels around
the nucleus of an atom/ ion. Group 2 elements have an s2 outer shell electron configuration.
First Ionisation Energy: the removal of one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous
atoms. Factors which affect the first ionisation energy are: the strength of attraction between
the electron and the nucleus, the nuclear charge and the atomic radius.
Group 2 Oxide: a compound with the general formula MO, where M is a group 2 element.
When group 2 oxides react with water, they form an alkaline solution, with alkalinity
increasing down the group.
Oxidation: the loss of electrons / increase in oxidation number.
Redox: a reaction in which oxidation of one element and reduction of another occurs. During
a redox reaction involving group 2 elements, 2 electrons are lost to form 2+ ions. Group 2
elements undergo redox reactions with water, oxygen and dilute acids.
Reduction: the gain of electrons/ decrease in oxidation number.
Second Ionisation Energy: the removal of one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous
1+ ions to form one mole of 2+ ions.
www.pmt.education
You might also like
- Full SorularDocument127 pagesFull Sorularezgigeyik02No ratings yet
- Notes On The Periodic TableDocument6 pagesNotes On The Periodic Tablefletcherberryheath2006No ratings yet
- Group 1 and 2 Elemts: Duaa OmerDocument8 pagesGroup 1 and 2 Elemts: Duaa OmerDuaa OmerdNo ratings yet
- Chemistry STPM Semester 2 Group 2Document12 pagesChemistry STPM Semester 2 Group 2Chong Yin Ping100% (1)
- Redox Chemistry and Groups 1, 2 and 7Document21 pagesRedox Chemistry and Groups 1, 2 and 7Fatema ZannatNo ratings yet
- Redox Chemistry and Groups 1, 2 and 7Document21 pagesRedox Chemistry and Groups 1, 2 and 7Lovely AbishekanNo ratings yet
- Prep2 T1 Mozkra Science enDocument46 pagesPrep2 T1 Mozkra Science ennaglaaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 MetalsDocument19 pagesGroup 2 MetalsSelena JayyNo ratings yet
- IB HL Chemistry Assessment Statements Topics 9 and 19Document4 pagesIB HL Chemistry Assessment Statements Topics 9 and 19AndrewNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument7 pagesDefinitionsLeAndies WongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Group 2A Metals 1. Call The Name of The Elements?Document10 pagesChapter 2: Group 2A Metals 1. Call The Name of The Elements?Phượng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument23 pagesChemistryAbhishek PawarNo ratings yet
- Group WorkDocument7 pagesGroup Workshadaepalmer3No ratings yet
- 3 Electrochemistry 3Document35 pages3 Electrochemistry 3settipallisrilakshminarasimhaNo ratings yet
- 2.7 The Periodic Table - Groups 2 and 7Document84 pages2.7 The Periodic Table - Groups 2 and 7Listiyaning TiasNo ratings yet
- Trends in Group 2 Elements (Alkaline Earth Metals)Document52 pagesTrends in Group 2 Elements (Alkaline Earth Metals)Antonique HeadmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Periodicity (REVISED)Document3 pagesChemical Periodicity (REVISED)Annie Valerie OgedeNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Electrochemical EnergyDocument129 pagesModule 1 - Electrochemical EnergyknightruzelNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: H + F 2HFDocument41 pagesElectrochemistry: H + F 2HFtNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document31 pagesGroup 2Shima SenseiiNo ratings yet
- A Level Notes On Group 1 and 2Document16 pagesA Level Notes On Group 1 and 2kmoiz427No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Physical ChemistryDocument32 pagesElectrochemistry: Physical ChemistryDavidson ChanNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument6 pagesRedox ReactionsManda BaboolalNo ratings yet
- 8B Group 1 2Document14 pages8B Group 1 2pediaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Engineering ChemistryDocument56 pagesLecture Notes - Engineering ChemistryadamjosephNo ratings yet
- Module 018 - ElectrochemistryDocument10 pagesModule 018 - ElectrochemistryLeycoline AlmrenNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document19 pagesGroup 2Muhammad KalimNo ratings yet
- 1.redox IntroDocument20 pages1.redox Introshuhan.yeNo ratings yet
- LP 3 - Inorganic Chemistry 4.25.22Document25 pagesLP 3 - Inorganic Chemistry 4.25.22Ruel AmascualNo ratings yet
- El Ectrochemi Stry: H + F 2HFDocument39 pagesEl Ectrochemi Stry: H + F 2HFtNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Module 1Document35 pagesEngineering Chemistry Module 1Audrey MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document19 pagesLesson 1saidbiala414No ratings yet
- The S-Block ElementsDocument9 pagesThe S-Block ElementsKamal DeshapriyaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Anor Unit 3Document63 pagesLaporan Anor Unit 3Nur hasanah NanaNo ratings yet
- f321 Mod3Document6 pagesf321 Mod3api-275024237No ratings yet
- Redox Reactions (Theory) EditedDocument21 pagesRedox Reactions (Theory) EditedProfSumit LuthraNo ratings yet
- Redox TitrationDocument24 pagesRedox TitrationNamrata patelNo ratings yet
- Cie A2 ElectrochemistryDocument20 pagesCie A2 ElectrochemistrySahanNivanthaNo ratings yet
- Trends in Group IIDocument5 pagesTrends in Group IIEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Earth Metals 1Document59 pagesAlkaline Earth Metals 1mazharpunjabiNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - The Alkaline Earth Metals: AppearanceDocument5 pagesGroup 2 - The Alkaline Earth Metals: AppearanceLourdes Nitro MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry-II 2 MARKSDocument11 pagesEngineering Chemistry-II 2 MARKSViswa NathanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes of 2nd YearDocument8 pagesChemistry Notes of 2nd YearSardar Mehmood AhmedNo ratings yet
- (Week 5) - Module 5-Gen - Chem. 2Document14 pages(Week 5) - Module 5-Gen - Chem. 2Diana Joy Ancheta CldheiNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryFinal Rev 2020 LECDocument104 pagesElectrochemistryFinal Rev 2020 LECsimonjohn spanglerNo ratings yet
- Notes of Chapter 7Document9 pagesNotes of Chapter 7ali asadNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet in General Biology Week 10 Activity 1: Dig Out! ADocument4 pagesAnswer Sheet in General Biology Week 10 Activity 1: Dig Out! AMark Joedel MendezNo ratings yet
- Group I & IIDocument3 pagesGroup I & IINoor Ul AinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 2 04 Notes STPM 2014/2013Document27 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 2 04 Notes STPM 2014/2013Raj Nittiya SugumaranNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Junior College H2 CHEMISTRY (9647) Group II: ReferencesDocument11 pagesPioneer Junior College H2 CHEMISTRY (9647) Group II: ReferencesTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- S5 CHEM (The S-Block Elements)Document30 pagesS5 CHEM (The S-Block Elements)Mwesigwa HannahNo ratings yet
- 2 Electrochemistry (Semester 2)Document49 pages2 Electrochemistry (Semester 2)Esther Ngieng100% (1)
- Corrosion: Chap. 2Document53 pagesCorrosion: Chap. 2Daniel RomeroNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 4Document16 pagesLecture Notes 4Deandra WhitelyNo ratings yet
- General Chemistryt 2 Week 5Document7 pagesGeneral Chemistryt 2 Week 5Charles David NavidadNo ratings yet
- 05 - Group 2 & Redox CORNELLDocument8 pages05 - Group 2 & Redox CORNELLGeorge SolomouNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips Chemistry Unit 1 Edexcel Notes As LevelDocument1 pageQdoc - Tips Chemistry Unit 1 Edexcel Notes As LevelM KNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Definitions Topic 4.2.1 Alcohols OCR A Chemistry A LevelDocument2 pagesDefinitions Topic 4.2.1 Alcohols OCR A Chemistry A LevelCHRONIKNo ratings yet
- Definitions Topic 1Document3 pagesDefinitions Topic 1CHRONIKNo ratings yet
- Definitions Topic 2.2.2 Bonding and Structure OCR A Chemistry A LevelDocument2 pagesDefinitions Topic 2.2.2 Bonding and Structure OCR A Chemistry A LevelCHRONIKNo ratings yet
- Ocr A Chemistry DefinitionDocument44 pagesOcr A Chemistry DefinitionCHRONIKNo ratings yet
- Definitions Module 6Document10 pagesDefinitions Module 6CHRONIKNo ratings yet
- Definitions Module 5Document10 pagesDefinitions Module 5CHRONIKNo ratings yet
- Definitions Module 4Document10 pagesDefinitions Module 4CHRONIKNo ratings yet
- Definitions Module 2Document7 pagesDefinitions Module 2CHRONIKNo ratings yet