Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5 Asd
5 Asd
Uploaded by
tc casey0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOriginal Title
5 asd
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as txt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 page5 Asd
5 Asd
Uploaded by
tc caseyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as txt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
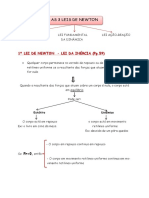
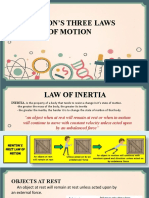
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is
changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is
changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is
changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is
changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is
changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is
changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
You might also like
- How to Achieve Glowing Health and Vitality: The Wisdom of YoganandaFrom EverandHow to Achieve Glowing Health and Vitality: The Wisdom of YoganandaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 4 Ak6566s5 6 DfsDocument2 pages4 Ak6566s5 6 Dfstc caseyNo ratings yet
- 4 Aks5 6 DfsDocument2 pages4 Aks5 6 Dfstc caseyNo ratings yet
- 5 Constant Rate EquationDocument2 pages5 Constant Rate Equationtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 3 Ja sf3 6 DlasdDocument2 pages3 Ja sf3 6 Dlasdtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 1 Asdf Asd GDocument2 pages1 Asdf Asd Gtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 4 Air Life k6sdfgd566s5 6 DfsDocument2 pages4 Air Life k6sdfgd566s5 6 Dfstc caseyNo ratings yet
- 1 ClassificationDocument2 pages1 Classificationtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 3 Ja sf55656 6 DlasdDocument2 pages3 Ja sf55656 6 Dlasdtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 2 Asj KD 5 G AdsDocument3 pages2 Asj KD 5 G Adstc caseyNo ratings yet
- 1 A365sdf Asd GDocument2 pages1 A365sdf Asd Gtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 2 Regulation Asdf566+65 45g65a 45gdssd 555Document3 pages2 Regulation Asdf566+65 45g65a 45gdssd 555tc caseyNo ratings yet
- 5 As 6 54 DDocument2 pages5 As 6 54 Dtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 5 Presentation As7 6 666asd654 DDocument3 pages5 Presentation As7 6 666asd654 Dtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 559 ICSE ClassX Physics Force RN RWDDocument11 pages559 ICSE ClassX Physics Force RN RWDKeerthan Manjunath50% (2)
- As 3 Leis de NewtonDocument9 pagesAs 3 Leis de NewtonAnonymous 6TklKxaQNo ratings yet
- LAWS OF MOTION-Shafee SirDocument23 pagesLAWS OF MOTION-Shafee SirjimmyemandeeNo ratings yet
- Force and Laws of Motion Class9Document29 pagesForce and Laws of Motion Class9Vedika Gore LSGNo ratings yet
- Grade 8Document6 pagesGrade 8Kate BarneyNo ratings yet
- Icse Physics NotesDocument110 pagesIcse Physics Notess9605519No ratings yet
- Newton Laws of MotionDocument1 pageNewton Laws of MotionTom BombadilNo ratings yet
- Newton'S First Law of Motion: (A) de Finition of Ine RtiaDocument1 pageNewton'S First Law of Motion: (A) de Finition of Ine RtiaSadguruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Force and Laws of MotionDocument15 pagesChapter 2 Force and Laws of MotionSuryanshi 018No ratings yet
- Earth Science: 1 Grading Grade 8 "Remediation"Document6 pagesEarth Science: 1 Grading Grade 8 "Remediation"Shane Catherine BesaresNo ratings yet
- What Are The Three Laws of MotionDocument1 pageWhat Are The Three Laws of MotionJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- 18) Laws of Motion - 1551343517Document5 pages18) Laws of Motion - 1551343517ungaranigundla sachivalayamNo ratings yet
- Homework Week 3Document2 pagesHomework Week 3bobNo ratings yet
- Acfrogbqrnchql07zococoo0xp Rwo Wtdyysh7nelbkyfylwwjxdv3g9 2v77id5pwkilb0t Ehq3qr8j7v6hz5vc9hhphddr Qig Ja Iptsvy5dnolva3xxttxwlqh12mm Rxme3 XylqdlwzDocument8 pagesAcfrogbqrnchql07zococoo0xp Rwo Wtdyysh7nelbkyfylwwjxdv3g9 2v77id5pwkilb0t Ehq3qr8j7v6hz5vc9hhphddr Qig Ja Iptsvy5dnolva3xxttxwlqh12mm Rxme3 Xylqdlwzsupersophisticated0132No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument12 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectShaikh ShihabNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document20 pagesWeek 2Abreesha FatimaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Lesson-6Document34 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Lesson-6Anjanette RiparipNo ratings yet
- Emweek1class324 4 21Document13 pagesEmweek1class324 4 21Rakesh ThurpatiNo ratings yet
- Mat Phy CH 1 To 5Document20 pagesMat Phy CH 1 To 5Kamran SaleemNo ratings yet
- Motion & Newton's Laws Lec 6Document20 pagesMotion & Newton's Laws Lec 6doaaeldekkeshiNo ratings yet
- Newton Law of MotionDocument13 pagesNewton Law of Motionsiddhi meenaNo ratings yet
- LEC 5 Principles of StaticsDocument52 pagesLEC 5 Principles of Staticsprajwaleswa2004No ratings yet
- Elementary Statics of 2 & Dimensions R.J.a. Barnard 1921Document272 pagesElementary Statics of 2 & Dimensions R.J.a. Barnard 1921Just BarryNo ratings yet
- NewtonDocument1 pageNewtonKelly LamNo ratings yet
- Sir Issac Newton (1643 - 1727) Galileo Galilei (1564 - 1642)Document38 pagesSir Issac Newton (1643 - 1727) Galileo Galilei (1564 - 1642)jaindevanshNo ratings yet
- CH-5 Laws of MotionDocument12 pagesCH-5 Laws of MotionSaransh KumarNo ratings yet
- Investigating Principles Governing MotionDocument16 pagesInvestigating Principles Governing MotionldrnsolanoNo ratings yet
- Mech 1 NonuDocument20 pagesMech 1 NonuAsnor RandyNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of MotionDocument52 pagesNewtons Laws of MotionOluwaferanmi OgunleyeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PhysicsDocument2 pagesReviewer in PhysicsLei StarosaNo ratings yet
- Affiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education - New DelhiDocument4 pagesAffiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education - New DelhiK.S.SANTHOSH NARAYANANNo ratings yet
- Force and Law of MotionDocument16 pagesForce and Law of MotionDhanya BalasundarrajNo ratings yet
- P e Chapte 2 NotesDocument2 pagesP e Chapte 2 Notesbhavik GuptaNo ratings yet
- General Physics Week 4 5 Q1Document47 pagesGeneral Physics Week 4 5 Q1Park RiRinNo ratings yet
- System of ForcesDocument13 pagesSystem of ForceskanthaNo ratings yet
- Force and Laws of MotionDocument39 pagesForce and Laws of Motiondav borlNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science Force and Law of MotionDocument5 pagesClass 9 Science Force and Law of MotionVishal DeyNo ratings yet
- Physics Key FormulasDocument4 pagesPhysics Key FormulasChidi BenedictNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 5Document13 pagesLaws of Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 5Gracy amutharajNo ratings yet
- Elements of Mechanical EngineeringDocument14 pagesElements of Mechanical EngineeringVivekNo ratings yet
- Law of Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 5Document13 pagesLaw of Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 5pujal dabasNo ratings yet
- Assign Law of MotionDocument2 pagesAssign Law of MotionRodesa Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 2Document24 pagesDynamics 2KNEWTON EducationNo ratings yet
- MS Point RKPSDocument12 pagesMS Point RKPSshivamkumar6203716No ratings yet
- Contact and Non Contact ForcesDocument3 pagesContact and Non Contact ForcesFaizan Ahmed100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Laws of Motion NotesDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Laws of Motion NotesSparkNo ratings yet
- 4 Air Life k6sdfgd566s5 6 DfsDocument2 pages4 Air Life k6sdfgd566s5 6 Dfstc caseyNo ratings yet
- 3 Ja sf55656 6 DlasdDocument2 pages3 Ja sf55656 6 Dlasdtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 5 As 6 54 DDocument2 pages5 As 6 54 Dtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 2 Asj KD 5 G AdsDocument3 pages2 Asj KD 5 G Adstc caseyNo ratings yet