Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Ja sf55656 6 Dlasd
3 Ja sf55656 6 Dlasd
Uploaded by
tc casey0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesasdg The Treate of test antonipie is kjanitfciepate dot be reaelased on the dcude tdate.
Original Title
3 ja sf55656 6 dlasd
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentasdg The Treate of test antonipie is kjanitfciepate dot be reaelased on the dcude tdate.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as txt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pages3 Ja sf55656 6 Dlasd
3 Ja sf55656 6 Dlasd
Uploaded by
tc caseyasdg The Treate of test antonipie is kjanitfciepate dot be reaelased on the dcude tdate.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as txt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
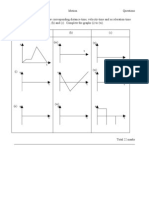
A body remains aAt any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the
body's acceleration mult motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is
changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directionst rest, or in motion at a consta body is equal to the body's
acceleration multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's
momentum is changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is bAt any instant of time, the
net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration mult motion at a constant
speed in a straight line, except insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is
changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directionsody is equal to the body's acceleration multiplied by its mass
or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multequal to the body's acceleration multnt speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is
changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
body is equal to the body's acceleration multiplied by its mass or, equivalently,
the rate at which the body's momentum is changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
mult
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constan body is equal to the body's
acceleration multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's
momentum is changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
mult speed in a straight line, except insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is
changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these for body is equal to the body's
acceleration multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's
momentum is changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multces have the same magnitude but opposite directions
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is
changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is
changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in body is equal to the
body's acceleration multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the
body's momentum is changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multa straight line, except insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is
changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except
insofar as it is acted upon by a force.
At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration
multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is
changing with time.
If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but
opposite directions
You might also like
- Gravity Gradient Torque PDFDocument12 pagesGravity Gradient Torque PDFHimanshuPrabhatNo ratings yet
- NEET MATERIAL Circular MotionDocument27 pagesNEET MATERIAL Circular MotionApex Institute100% (6)
- Learning Plan in Grade 8 and Grade 7Document14 pagesLearning Plan in Grade 8 and Grade 7marilyncomia73100% (3)
- 2 Asj KD 5 G AdsDocument3 pages2 Asj KD 5 G Adstc caseyNo ratings yet
- 2 Regulation Asdf566+65 45g65a 45gdssd 555Document3 pages2 Regulation Asdf566+65 45g65a 45gdssd 555tc caseyNo ratings yet
- 3 Ja sf3 6 DlasdDocument2 pages3 Ja sf3 6 Dlasdtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 1 Asdf Asd GDocument2 pages1 Asdf Asd Gtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 5 As 6 54 DDocument2 pages5 As 6 54 Dtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 1 A365sdf Asd GDocument2 pages1 A365sdf Asd Gtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 1 ClassificationDocument2 pages1 Classificationtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 5 Constant Rate EquationDocument2 pages5 Constant Rate Equationtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 4 Air Life k6sdfgd566s5 6 DfsDocument2 pages4 Air Life k6sdfgd566s5 6 Dfstc caseyNo ratings yet
- 5 Presentation As7 6 666asd654 DDocument3 pages5 Presentation As7 6 666asd654 Dtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 4 Aks5 6 DfsDocument2 pages4 Aks5 6 Dfstc caseyNo ratings yet
- 4 Ak6566s5 6 DfsDocument2 pages4 Ak6566s5 6 Dfstc caseyNo ratings yet
- 5 AsdDocument1 page5 Asdtc caseyNo ratings yet
- As 3 Leis de NewtonDocument9 pagesAs 3 Leis de NewtonAnonymous 6TklKxaQNo ratings yet
- 559 ICSE ClassX Physics Force RN RWDDocument11 pages559 ICSE ClassX Physics Force RN RWDKeerthan Manjunath50% (2)
- LAWS OF MOTION-Shafee SirDocument23 pagesLAWS OF MOTION-Shafee SirjimmyemandeeNo ratings yet
- Force and Laws of Motion Class9Document29 pagesForce and Laws of Motion Class9Vedika Gore LSGNo ratings yet
- Grade 8Document6 pagesGrade 8Kate BarneyNo ratings yet
- Icse Physics NotesDocument110 pagesIcse Physics Notess9605519No ratings yet
- Newton'S First Law of Motion: (A) de Finition of Ine RtiaDocument1 pageNewton'S First Law of Motion: (A) de Finition of Ine RtiaSadguruNo ratings yet
- Emweek1class324 4 21Document13 pagesEmweek1class324 4 21Rakesh ThurpatiNo ratings yet
- Elementary Statics of 2 & Dimensions R.J.a. Barnard 1921Document272 pagesElementary Statics of 2 & Dimensions R.J.a. Barnard 1921Just BarryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Force and Laws of MotionDocument15 pagesChapter 2 Force and Laws of MotionSuryanshi 018No ratings yet
- Week 2Document20 pagesWeek 2Abreesha FatimaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: 1 Grading Grade 8 "Remediation"Document6 pagesEarth Science: 1 Grading Grade 8 "Remediation"Shane Catherine BesaresNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument12 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectShaikh ShihabNo ratings yet
- 18) Laws of Motion - 1551343517Document5 pages18) Laws of Motion - 1551343517ungaranigundla sachivalayamNo ratings yet
- Acfrogbqrnchql07zococoo0xp Rwo Wtdyysh7nelbkyfylwwjxdv3g9 2v77id5pwkilb0t Ehq3qr8j7v6hz5vc9hhphddr Qig Ja Iptsvy5dnolva3xxttxwlqh12mm Rxme3 XylqdlwzDocument8 pagesAcfrogbqrnchql07zococoo0xp Rwo Wtdyysh7nelbkyfylwwjxdv3g9 2v77id5pwkilb0t Ehq3qr8j7v6hz5vc9hhphddr Qig Ja Iptsvy5dnolva3xxttxwlqh12mm Rxme3 Xylqdlwzsupersophisticated0132No ratings yet
- What Are The Three Laws of MotionDocument1 pageWhat Are The Three Laws of MotionJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- Newton Laws of MotionDocument1 pageNewton Laws of MotionTom BombadilNo ratings yet
- Motion & Newton's Laws Lec 6Document20 pagesMotion & Newton's Laws Lec 6doaaeldekkeshiNo ratings yet
- Homework Week 3Document2 pagesHomework Week 3bobNo ratings yet
- System of ForcesDocument13 pagesSystem of ForceskanthaNo ratings yet
- LEC 5 Principles of StaticsDocument52 pagesLEC 5 Principles of Staticsprajwaleswa2004No ratings yet
- Mat Phy CH 1 To 5Document20 pagesMat Phy CH 1 To 5Kamran SaleemNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Lesson-6Document34 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Lesson-6Anjanette RiparipNo ratings yet
- Sir Issac Newton (1643 - 1727) Galileo Galilei (1564 - 1642)Document38 pagesSir Issac Newton (1643 - 1727) Galileo Galilei (1564 - 1642)jaindevanshNo ratings yet
- Mech 1 NonuDocument20 pagesMech 1 NonuAsnor RandyNo ratings yet
- Force and Law of MotionDocument16 pagesForce and Law of MotionDhanya BalasundarrajNo ratings yet
- CH-5 Laws of MotionDocument12 pagesCH-5 Laws of MotionSaransh KumarNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of MotionDocument52 pagesNewtons Laws of MotionOluwaferanmi OgunleyeNo ratings yet
- Investigating Principles Governing MotionDocument16 pagesInvestigating Principles Governing MotionldrnsolanoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PhysicsDocument2 pagesReviewer in PhysicsLei StarosaNo ratings yet
- Newton Law of MotionDocument13 pagesNewton Law of Motionsiddhi meenaNo ratings yet
- P e Chapte 2 NotesDocument2 pagesP e Chapte 2 Notesbhavik GuptaNo ratings yet
- General Physics Week 4 5 Q1Document47 pagesGeneral Physics Week 4 5 Q1Park RiRinNo ratings yet
- Force and Laws of MotionDocument39 pagesForce and Laws of Motiondav borlNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science Force and Law of MotionDocument5 pagesClass 9 Science Force and Law of MotionVishal DeyNo ratings yet
- Laws of - MottionDocument26 pagesLaws of - MottionnitikanehiNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 5Document13 pagesLaws of Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 5Gracy amutharajNo ratings yet
- Affiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education - New DelhiDocument4 pagesAffiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education - New DelhiK.S.SANTHOSH NARAYANANNo ratings yet
- Law of Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 5Document13 pagesLaw of Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 5pujal dabasNo ratings yet
- PMR4GP19 Basic of Biomechanics - Mechanical LoadingDocument25 pagesPMR4GP19 Basic of Biomechanics - Mechanical LoadingditaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Laws of Motion NotesDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Laws of Motion NotesSparkNo ratings yet
- Law of Motion Need To ReviseDocument1 pageLaw of Motion Need To RevisephilfrancoNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument100 pagesDynamicsRAMAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- MS Point RKPSDocument12 pagesMS Point RKPSshivamkumar6203716No ratings yet
- Mechanics and MotionDocument5 pagesMechanics and Motionjoel paderesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 TheoryDocument25 pagesUnit 1 TheoryparthibankNo ratings yet
- Human Movement: How the Body Walks, Runs, Jumps, and KicksFrom EverandHuman Movement: How the Body Walks, Runs, Jumps, and KicksRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- 4 Air Life k6sdfgd566s5 6 DfsDocument2 pages4 Air Life k6sdfgd566s5 6 Dfstc caseyNo ratings yet
- 5 As 6 54 DDocument2 pages5 As 6 54 Dtc caseyNo ratings yet
- 2 Asj KD 5 G AdsDocument3 pages2 Asj KD 5 G Adstc caseyNo ratings yet
- 5 AsdDocument1 page5 Asdtc caseyNo ratings yet
- CGDocument9 pagesCGAngelica Estoce SalonnNo ratings yet
- Plus One Physics Previous Question PaperDocument44 pagesPlus One Physics Previous Question Papersidharth7manoj75% (4)
- Angle Inclination & Acceleration (2.1 Linear Motion)Document1 pageAngle Inclination & Acceleration (2.1 Linear Motion)wengsungNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Test 1Document2 pagesCH 12 Test 1Aman Bhutta0% (1)
- Physics Question BanksDocument32 pagesPhysics Question Banksthuthao2007No ratings yet
- EPI Circular MotionDocument10 pagesEPI Circular MotionDavid BladesNo ratings yet
- The Control of Flight Force by A Flapping Wing: Lift and Drag ProductionDocument21 pagesThe Control of Flight Force by A Flapping Wing: Lift and Drag ProductionRAJARATNANo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of PhysicsDocument4 pagesBasic Principles of PhysicsDarry BlanciaNo ratings yet
- Classical Mechanics-I FINALDocument6 pagesClassical Mechanics-I FINALDr. P. K. SamantaNo ratings yet
- Centripetal Acceleration and ForceDocument2 pagesCentripetal Acceleration and ForceRenor SagunNo ratings yet
- Motion in 1dDocument12 pagesMotion in 1dkhushi23277No ratings yet
- Laboratory 2bDocument11 pagesLaboratory 2bH2 MgZNo ratings yet
- IB Questionbank Physics 1: (Total 1 Mark)Document9 pagesIB Questionbank Physics 1: (Total 1 Mark)Akshaj RajbhandariNo ratings yet
- Principles of DynamicsDocument61 pagesPrinciples of DynamicsLeah Rivera100% (2)
- Track-Ben Blackmer-TF Techniques - Developing Warm-Ups Cool-DownsDocument5 pagesTrack-Ben Blackmer-TF Techniques - Developing Warm-Ups Cool-Downscorrado de simoneNo ratings yet
- A=iαt + jβ t kγ t α, β γ dA/dt d A/dt - A=iαt + jβ t kγ t dA/dt d A/dtDocument5 pagesA=iαt + jβ t kγ t α, β γ dA/dt d A/dt - A=iαt + jβ t kγ t dA/dt d A/dtFahmi MadaniNo ratings yet
- Class: XI Topic: Moment of Inertia & Torque Sub: PhysicsDocument8 pagesClass: XI Topic: Moment of Inertia & Torque Sub: PhysicsSudharsan Gupta SudhirNo ratings yet
- ApplicationsDocument10 pagesApplicationsCatherine GuzmanNo ratings yet
- SCI8 - Q1 - M1 - Newton's Laws of MotioDocument22 pagesSCI8 - Q1 - M1 - Newton's Laws of MotioColourBlueNo ratings yet
- Manual Robot GR-C PDFDocument225 pagesManual Robot GR-C PDFbuggynotNo ratings yet
- The Assimilation of Newtonian Mechanics PDFDocument273 pagesThe Assimilation of Newtonian Mechanics PDFAdilene PalmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Study GuideDocument9 pagesPhysics Study GuideAlexandra SolanoNo ratings yet
- Holger Babinsky 2003 Phys. Educ. 38 001Document8 pagesHolger Babinsky 2003 Phys. Educ. 38 001batanejaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Crossword Puzzle On MOTIONDocument3 pagesActivity 3 Crossword Puzzle On MOTIONDonna Catbagan AgbunagNo ratings yet
- Physics Textbook 10-12Document68 pagesPhysics Textbook 10-12Joseph MayelanoNo ratings yet
- Lecture SP 015 Lesson 2 PDFDocument23 pagesLecture SP 015 Lesson 2 PDFAnonymous hKDpglNo ratings yet
- What Is Force (Forces Concept Map) L v1 Xz0 s1Document7 pagesWhat Is Force (Forces Concept Map) L v1 Xz0 s1Inform7105No ratings yet