Professional Documents
Culture Documents
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
40 viewsOxalic Acid
Oxalic Acid
Uploaded by
Chandan MahakudToxicology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chapter 021 QuestionsDocument29 pagesChapter 021 QuestionsPrecilou Cutanda100% (1)
- Asphyxiant PoisoningDocument47 pagesAsphyxiant PoisoningBenish AfzalNo ratings yet
- Practical English Book 1 Answer KeyDocument29 pagesPractical English Book 1 Answer Keyanna39100% (4)
- Arthritis NCPDocument2 pagesArthritis NCPTri Sha100% (4)
- SBAR HandoutDocument4 pagesSBAR HandoutbrasidinNo ratings yet
- CT BrochureDocument2 pagesCT BrochureDr. Samir M Patel0% (1)
- Clinical Endocrinology of Dogs Cats PDFDocument353 pagesClinical Endocrinology of Dogs Cats PDFsanjagruborovic100% (1)
- Textbook of Orthodontics - Advance CasesDocument719 pagesTextbook of Orthodontics - Advance CasesFersh Jarringtone100% (2)
- ORGANIC POISONS - Doc PPXDocument29 pagesORGANIC POISONS - Doc PPXifrahnadeem393No ratings yet
- Classification of Poisons (According To Mode of Action)Document133 pagesClassification of Poisons (According To Mode of Action)dr rizwanNo ratings yet
- Special ToxicologyDocument127 pagesSpecial ToxicologyNooria ButtNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument14 pagesChemistry Projectparth052006No ratings yet
- Carbolic Acid & Oxalic AcidDocument46 pagesCarbolic Acid & Oxalic AcidImteaz ahamadNo ratings yet
- Carbolic Aci134Document29 pagesCarbolic Aci13404 Sayali KharadeNo ratings yet
- Antacids SYDocument37 pagesAntacids SYRahul LakhaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument12 pagesChemistry Projectparth052006No ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument12 pagesChemistry Projectparth052006No ratings yet
- Corrosive PoisonsDocument29 pagesCorrosive PoisonsfahadqazifreelancerNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and MetalloidsDocument59 pagesAcids, Bases and MetalloidsSubir BiswasNo ratings yet
- Deepak AssignmentDocument5 pagesDeepak AssignmentDEEPAK YadavNo ratings yet
- ClarificationDocument10 pagesClarificationuglysnrNo ratings yet
- Lecture 06 (Corrosive - Organic Acids) 2Document45 pagesLecture 06 (Corrosive - Organic Acids) 2saraNo ratings yet
- Determination of Alkalinity in Given Water Sample: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesDetermination of Alkalinity in Given Water Sample: ObjectivesDani MughalNo ratings yet
- Urinepractical 200121115146Document56 pagesUrinepractical 200121115146Nakul JainNo ratings yet
- Study of Irritant Poisons: Aresenic Album Poisoning (Sankhya, Somalkhar)Document17 pagesStudy of Irritant Poisons: Aresenic Album Poisoning (Sankhya, Somalkhar)Tej PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal AgentsDocument72 pagesGastrointestinal Agentsfarooq shah shabbirNo ratings yet
- 2 ToxicologyDocument18 pages2 Toxicologyنوف الحربي.No ratings yet
- QDocument6 pagesQrenzoNo ratings yet
- GIT Agents 2021Document28 pagesGIT Agents 2021madhanraj7996No ratings yet
- Cathartics 180217081223Document40 pagesCathartics 180217081223Dileep Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- WT Chapter 5Document34 pagesWT Chapter 5Wariyo GalgaloNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment April 2007 Pp2003Document34 pagesWater Treatment April 2007 Pp2003RiyanNo ratings yet
- Practical Notes On Jar TestDocument3 pagesPractical Notes On Jar Testsagar khanalNo ratings yet
- CorrosiveDocument21 pagesCorrosiveTanishq JoshiNo ratings yet
- CatharticsDocument11 pagesCatharticssalwanaseer9999No ratings yet
- Project Presentation Potash AlumDocument9 pagesProject Presentation Potash AlummurkNo ratings yet
- Jawahar Navodaya Vidhyalaya Angul: Analytical Project Chemistr YDocument16 pagesJawahar Navodaya Vidhyalaya Angul: Analytical Project Chemistr YCY CYMONNo ratings yet
- AstringentsDocument18 pagesAstringentsdinesh111180No ratings yet
- Mbbs 2k23 Aim - To Identify The Abnormal Constitutes of UrineDocument22 pagesMbbs 2k23 Aim - To Identify The Abnormal Constitutes of Urine8harshul8No ratings yet
- Physiology of Digestion HandoutDocument3 pagesPhysiology of Digestion Handoutrolandroly93No ratings yet
- Post Lab Experiment 11 13 PDFDocument4 pagesPost Lab Experiment 11 13 PDFDekdek MendozaNo ratings yet
- Final Course Beverages (09-02-2021)Document20 pagesFinal Course Beverages (09-02-2021)Asia AmirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument17 pagesChemistry Projectpooja shreeNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Constituents of Urine - 1Document5 pagesAbnormal Constituents of Urine - 1kalpithareddynomulaNo ratings yet
- Urine AnalysisDocument98 pagesUrine AnalysisLucia SurduNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory AntacidsDocument25 pagesChemistry Investigatory AntacidsJayasree MNo ratings yet
- ID - 23150501 Presentation (Food Engineering)Document18 pagesID - 23150501 Presentation (Food Engineering)ug1707026No ratings yet
- Analysis of Abnormal Constituents of Urine - 16th December 2019Document28 pagesAnalysis of Abnormal Constituents of Urine - 16th December 2019mubashirNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Constituents of UrineDocument7 pagesAbnormal Constituents of UrineAnjuNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 08 - Elements of Civil EngineeringDocument22 pagesLecture - 08 - Elements of Civil EngineeringSanthoshMBSanthuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project ANTACIDDocument17 pagesChemistry Project ANTACIDMAX MusicNo ratings yet
- Env Sci4Document17 pagesEnv Sci4Mosaab AlhbaneNo ratings yet
- Topic 3.2 Biochemical TestsDocument46 pagesTopic 3.2 Biochemical TestsSerena SakaNo ratings yet
- Special StainsDocument18 pagesSpecial StainsJil BellaNo ratings yet
- Renal Drugs Diuretics Agents: by Desalegn Chilo (B.Pharm, MSC)Document54 pagesRenal Drugs Diuretics Agents: by Desalegn Chilo (B.Pharm, MSC)Remedan TahaNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases, and Salts 1Document13 pagesAcids, Bases, and Salts 1Ramadas BhiseNo ratings yet
- HYP E R ACI D I T Y Cause FOR Intake OF AntacidsDocument14 pagesHYP E R ACI D I T Y Cause FOR Intake OF AntacidsamuNo ratings yet
- Lab Expercise # 10: Determination of Residual ChlorineDocument3 pagesLab Expercise # 10: Determination of Residual ChlorineNaeem Akhtar SamoonNo ratings yet
- AcidsDocument23 pagesAcidszuriellgotoraNo ratings yet
- LEC 11 Official Inorganic CompoundsDocument28 pagesLEC 11 Official Inorganic CompoundsishafatimapakistaniNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument17 pagesBiologyVictor OkosunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document59 pagesChapter 4Solomon DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Characteristics of EthanolDocument8 pagesBiochemical Characteristics of EthanolRida ArifNo ratings yet
- B-4Document20 pagesB-4MD. Humayun KobirNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 27: Constituents of UrineDocument50 pagesActivity No. 27: Constituents of Urinemhai requilmanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastFrom EverandChemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterFrom EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterNo ratings yet
- Bathes MethodDocument7 pagesBathes MethodluisazcarateNo ratings yet
- PFL Biotech Services: Bilingual German/English Medical Interviewers - 100% Work From HomeDocument1 pagePFL Biotech Services: Bilingual German/English Medical Interviewers - 100% Work From HomeAshok VannanNo ratings yet
- Modes of Mechanical VentilationDocument34 pagesModes of Mechanical Ventilationsbraj86100% (1)
- Tegaderm FAMILY 2013Document20 pagesTegaderm FAMILY 2013andreirazorNo ratings yet
- 10 Unsolved Mysteries of The WorldDocument11 pages10 Unsolved Mysteries of The WorldjackiscleverNo ratings yet
- Paranoid Schizophrenia: A Case Study OnDocument32 pagesParanoid Schizophrenia: A Case Study OnMark ElbenNo ratings yet
- Dr. Reckeweg - R5Document2 pagesDr. Reckeweg - R5ManpreetSinghGrewalNo ratings yet
- TADs InformedConsentDocument1 pageTADs InformedConsentElmer ZapataNo ratings yet
- Basic Medical Arabic EnglishDocument10 pagesBasic Medical Arabic EnglishLuisMunozD'Santos100% (3)
- Handout GuidanceDocument2 pagesHandout GuidanceKhrycys Olairez RNNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Aneurysm FINALDocument33 pagesCerebral Aneurysm FINALkanejasper0% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Teeth and Oral CavityDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Teeth and Oral CavityVillanz Vimal ChanderNo ratings yet
- Conjoined TwinsDocument22 pagesConjoined TwinsOshii Precious ImamNo ratings yet
- Possibility of The Use Polish Soda Lime As The Absorbent in The Canisters of The Oxygen Breathing Apparatus Type Oxy-NGDocument11 pagesPossibility of The Use Polish Soda Lime As The Absorbent in The Canisters of The Oxygen Breathing Apparatus Type Oxy-NGindiomajaderoNo ratings yet
- Cross Contamination Control Facility DesignDocument22 pagesCross Contamination Control Facility DesignAlok Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Amoxillin Glimepirid Amoxillin Metronidazol Metformin: Ambroxol Tablet Ambroxol TabletDocument10 pagesAmoxillin Glimepirid Amoxillin Metronidazol Metformin: Ambroxol Tablet Ambroxol TabletSeptia MonalisaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Fitness Levels Among Undergraduate Students of A Nigerian University Using Coopers 12 Minute Walk TestDocument3 pagesAerobic Fitness Levels Among Undergraduate Students of A Nigerian University Using Coopers 12 Minute Walk TestIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Radioimmunoassay (2002b)Document48 pagesRadioimmunoassay (2002b)api-19916399No ratings yet
- Argumentative Essay SampleDocument10 pagesArgumentative Essay SampleWin Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- A Simple and Reliable Submental Intubation.68Document4 pagesA Simple and Reliable Submental Intubation.68Tîrban Pantelimon FlorinNo ratings yet
- Ihc Guidebook Introduction To Immunohistochemistry Chapter1Document10 pagesIhc Guidebook Introduction To Immunohistochemistry Chapter1KharismaUtariNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakaDeborah Cindy KaramoyNo ratings yet
- Final DengueDocument32 pagesFinal Dengueprincesshanty100% (2)
Oxalic Acid
Oxalic Acid
Uploaded by
Chandan Mahakud100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
40 views12 pagesToxicology
Original Title
Oxalic acid ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentToxicology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
40 views12 pagesOxalic Acid
Oxalic Acid
Uploaded by
Chandan MahakudToxicology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 12
OXALIC ACID
Manoj Kumar Nayak.
3rd prof. BAMS.
Roll No-24
KATS Ayurvedic college
Introduction
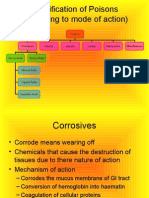
• Oxalic acid is a corrosive acid .
• Also called acid of sugar,salt of sorel.
• Chemical formula is C2H2O4.
• Found in several green leafy vegetables
like carrots,
Cabbage ,Brocoli in form of oxalate.
• Excreted approximately 20mg daily via
urine .
Characteristics
• It is available as colorless, transparent, prismatic
crystalline form
• Causes bleaching of ink and iron stain.
• Sour and slightly bitter in taste .
• Sparingly soluble in water.
• Resembling like magnesium sulphate and
zinc sulphate.
uses
• Bleaching and cleansing agent in household
products.
• Stain remover .
• Metal cleaner .
• In dye and leather industry.
• Fatal dose -15 to 20 gm . However smallest recorded dose is 5gm.
• Fatal period- 1to 2 hrs , and it may be upto 5days
• Action
• The characteristic and severity of symptoms depends upon the amount and
concentration of acid taken.
• 2 distinctive effects are seen .
1. Local effects.
2. Systemic/Remote effects.
• Rarely damages the skin but readily corroded the mucous membrane of
elementary canal .
a. Shock – Large concentration dose would kill with couple of hours by shock, I.e
narcotic effects on body .
b. Hypocalcemia – Combines with serum calcium and causes death within 12 hrs .
• Because when oxalic acid combines with serum calcium it
produces ca-oxalates crystals which decrease the free ca++ level.
• Cause numbness and tingling sensations, seen in face ,extremities
and convulsions may appear .
c. Renal damage/kidney failure- the oxalates previously formed
cause tubular necrosis, congestion in kidney as crystal are insoluble
which cause renal oedema, elctrolyte imbalance, local necrosis of
tubular epithelium and may cause death in 2 to 14 days .
• Present of blood, albumin and ca-oxalates crystalsin urine .
Sign And Symptoms
• In concentrated form it acts as corrosive
• In dilute form it acts as an irritant
• Bitterness & burning sensation in mouth.
• Nausea & Vomiting, sometimes vomitus is
mixed with blood.
• In Severe cases the dark colour vomit is present known as ground
coffee appearance & purging is mixed with blood.
• Other symptoms of dehydration are present such as tingling &
numbness sensation in the fingers & toes.
Treatment :
• Gastric lavage : stomach wash using lime water .
but not warm water as dissolution is more .
• Antidote: any ca++ preparation which cause the poison
into Insoluble Ca-Oxalates.
E.g. Chalk water; suspension of 30 gm of water/milk will
neutralize Approx. 20gm of oxalic acid .
• Ca-Gluconate mainly used I.e 10ml/10% (oral/iv).
• In severity parathhrmone Extract given .
• Demulcents are given to protect the mucous membrane
from corrosive action of poison.
• Rest of the treatment is symptomatic.
Post-Morterm Appearance :
• Externally: No specific findings, but sign of dehydration are present.
• Internal:The tongue and oesophagus is found bleached.
• Gastric mucosa is found severely inflammed.
• Kidney shows oedema & congestion.
• Stomach contains dark brown gelatin liquid due to formation of acid
• Hematin.
• Blood vessels of submucosa layer shows dark lines due to acid
Hematin.
• If the effects are narcotics then congestion of lungs,liver,kidney,and
brain .
Medico-legal Importance:
• Accidental poisoning is due to Being taken for Mg-sulphate or
Na-bicarbonate .
• Suicidal and homicidal are rare due to sour taste and corrosiveness.
• It’s solution can cause hairfall.
• Oxalic acid is sometimes used to erase writing in attempts
at forgery.
You might also like
- Chapter 021 QuestionsDocument29 pagesChapter 021 QuestionsPrecilou Cutanda100% (1)
- Asphyxiant PoisoningDocument47 pagesAsphyxiant PoisoningBenish AfzalNo ratings yet
- Practical English Book 1 Answer KeyDocument29 pagesPractical English Book 1 Answer Keyanna39100% (4)
- Arthritis NCPDocument2 pagesArthritis NCPTri Sha100% (4)
- SBAR HandoutDocument4 pagesSBAR HandoutbrasidinNo ratings yet
- CT BrochureDocument2 pagesCT BrochureDr. Samir M Patel0% (1)
- Clinical Endocrinology of Dogs Cats PDFDocument353 pagesClinical Endocrinology of Dogs Cats PDFsanjagruborovic100% (1)
- Textbook of Orthodontics - Advance CasesDocument719 pagesTextbook of Orthodontics - Advance CasesFersh Jarringtone100% (2)
- ORGANIC POISONS - Doc PPXDocument29 pagesORGANIC POISONS - Doc PPXifrahnadeem393No ratings yet
- Classification of Poisons (According To Mode of Action)Document133 pagesClassification of Poisons (According To Mode of Action)dr rizwanNo ratings yet
- Special ToxicologyDocument127 pagesSpecial ToxicologyNooria ButtNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument14 pagesChemistry Projectparth052006No ratings yet
- Carbolic Acid & Oxalic AcidDocument46 pagesCarbolic Acid & Oxalic AcidImteaz ahamadNo ratings yet
- Carbolic Aci134Document29 pagesCarbolic Aci13404 Sayali KharadeNo ratings yet
- Antacids SYDocument37 pagesAntacids SYRahul LakhaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument12 pagesChemistry Projectparth052006No ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument12 pagesChemistry Projectparth052006No ratings yet
- Corrosive PoisonsDocument29 pagesCorrosive PoisonsfahadqazifreelancerNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and MetalloidsDocument59 pagesAcids, Bases and MetalloidsSubir BiswasNo ratings yet
- Deepak AssignmentDocument5 pagesDeepak AssignmentDEEPAK YadavNo ratings yet
- ClarificationDocument10 pagesClarificationuglysnrNo ratings yet
- Lecture 06 (Corrosive - Organic Acids) 2Document45 pagesLecture 06 (Corrosive - Organic Acids) 2saraNo ratings yet
- Determination of Alkalinity in Given Water Sample: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesDetermination of Alkalinity in Given Water Sample: ObjectivesDani MughalNo ratings yet
- Urinepractical 200121115146Document56 pagesUrinepractical 200121115146Nakul JainNo ratings yet
- Study of Irritant Poisons: Aresenic Album Poisoning (Sankhya, Somalkhar)Document17 pagesStudy of Irritant Poisons: Aresenic Album Poisoning (Sankhya, Somalkhar)Tej PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal AgentsDocument72 pagesGastrointestinal Agentsfarooq shah shabbirNo ratings yet
- 2 ToxicologyDocument18 pages2 Toxicologyنوف الحربي.No ratings yet
- QDocument6 pagesQrenzoNo ratings yet
- GIT Agents 2021Document28 pagesGIT Agents 2021madhanraj7996No ratings yet
- Cathartics 180217081223Document40 pagesCathartics 180217081223Dileep Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- WT Chapter 5Document34 pagesWT Chapter 5Wariyo GalgaloNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment April 2007 Pp2003Document34 pagesWater Treatment April 2007 Pp2003RiyanNo ratings yet
- Practical Notes On Jar TestDocument3 pagesPractical Notes On Jar Testsagar khanalNo ratings yet
- CorrosiveDocument21 pagesCorrosiveTanishq JoshiNo ratings yet
- CatharticsDocument11 pagesCatharticssalwanaseer9999No ratings yet
- Project Presentation Potash AlumDocument9 pagesProject Presentation Potash AlummurkNo ratings yet
- Jawahar Navodaya Vidhyalaya Angul: Analytical Project Chemistr YDocument16 pagesJawahar Navodaya Vidhyalaya Angul: Analytical Project Chemistr YCY CYMONNo ratings yet
- AstringentsDocument18 pagesAstringentsdinesh111180No ratings yet
- Mbbs 2k23 Aim - To Identify The Abnormal Constitutes of UrineDocument22 pagesMbbs 2k23 Aim - To Identify The Abnormal Constitutes of Urine8harshul8No ratings yet
- Physiology of Digestion HandoutDocument3 pagesPhysiology of Digestion Handoutrolandroly93No ratings yet
- Post Lab Experiment 11 13 PDFDocument4 pagesPost Lab Experiment 11 13 PDFDekdek MendozaNo ratings yet
- Final Course Beverages (09-02-2021)Document20 pagesFinal Course Beverages (09-02-2021)Asia AmirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument17 pagesChemistry Projectpooja shreeNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Constituents of Urine - 1Document5 pagesAbnormal Constituents of Urine - 1kalpithareddynomulaNo ratings yet
- Urine AnalysisDocument98 pagesUrine AnalysisLucia SurduNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory AntacidsDocument25 pagesChemistry Investigatory AntacidsJayasree MNo ratings yet
- ID - 23150501 Presentation (Food Engineering)Document18 pagesID - 23150501 Presentation (Food Engineering)ug1707026No ratings yet
- Analysis of Abnormal Constituents of Urine - 16th December 2019Document28 pagesAnalysis of Abnormal Constituents of Urine - 16th December 2019mubashirNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Constituents of UrineDocument7 pagesAbnormal Constituents of UrineAnjuNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 08 - Elements of Civil EngineeringDocument22 pagesLecture - 08 - Elements of Civil EngineeringSanthoshMBSanthuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project ANTACIDDocument17 pagesChemistry Project ANTACIDMAX MusicNo ratings yet
- Env Sci4Document17 pagesEnv Sci4Mosaab AlhbaneNo ratings yet
- Topic 3.2 Biochemical TestsDocument46 pagesTopic 3.2 Biochemical TestsSerena SakaNo ratings yet
- Special StainsDocument18 pagesSpecial StainsJil BellaNo ratings yet
- Renal Drugs Diuretics Agents: by Desalegn Chilo (B.Pharm, MSC)Document54 pagesRenal Drugs Diuretics Agents: by Desalegn Chilo (B.Pharm, MSC)Remedan TahaNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases, and Salts 1Document13 pagesAcids, Bases, and Salts 1Ramadas BhiseNo ratings yet
- HYP E R ACI D I T Y Cause FOR Intake OF AntacidsDocument14 pagesHYP E R ACI D I T Y Cause FOR Intake OF AntacidsamuNo ratings yet
- Lab Expercise # 10: Determination of Residual ChlorineDocument3 pagesLab Expercise # 10: Determination of Residual ChlorineNaeem Akhtar SamoonNo ratings yet
- AcidsDocument23 pagesAcidszuriellgotoraNo ratings yet
- LEC 11 Official Inorganic CompoundsDocument28 pagesLEC 11 Official Inorganic CompoundsishafatimapakistaniNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument17 pagesBiologyVictor OkosunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document59 pagesChapter 4Solomon DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Characteristics of EthanolDocument8 pagesBiochemical Characteristics of EthanolRida ArifNo ratings yet
- B-4Document20 pagesB-4MD. Humayun KobirNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 27: Constituents of UrineDocument50 pagesActivity No. 27: Constituents of Urinemhai requilmanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastFrom EverandChemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterFrom EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterNo ratings yet
- Bathes MethodDocument7 pagesBathes MethodluisazcarateNo ratings yet
- PFL Biotech Services: Bilingual German/English Medical Interviewers - 100% Work From HomeDocument1 pagePFL Biotech Services: Bilingual German/English Medical Interviewers - 100% Work From HomeAshok VannanNo ratings yet
- Modes of Mechanical VentilationDocument34 pagesModes of Mechanical Ventilationsbraj86100% (1)
- Tegaderm FAMILY 2013Document20 pagesTegaderm FAMILY 2013andreirazorNo ratings yet
- 10 Unsolved Mysteries of The WorldDocument11 pages10 Unsolved Mysteries of The WorldjackiscleverNo ratings yet
- Paranoid Schizophrenia: A Case Study OnDocument32 pagesParanoid Schizophrenia: A Case Study OnMark ElbenNo ratings yet
- Dr. Reckeweg - R5Document2 pagesDr. Reckeweg - R5ManpreetSinghGrewalNo ratings yet
- TADs InformedConsentDocument1 pageTADs InformedConsentElmer ZapataNo ratings yet
- Basic Medical Arabic EnglishDocument10 pagesBasic Medical Arabic EnglishLuisMunozD'Santos100% (3)
- Handout GuidanceDocument2 pagesHandout GuidanceKhrycys Olairez RNNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Aneurysm FINALDocument33 pagesCerebral Aneurysm FINALkanejasper0% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Teeth and Oral CavityDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Teeth and Oral CavityVillanz Vimal ChanderNo ratings yet
- Conjoined TwinsDocument22 pagesConjoined TwinsOshii Precious ImamNo ratings yet
- Possibility of The Use Polish Soda Lime As The Absorbent in The Canisters of The Oxygen Breathing Apparatus Type Oxy-NGDocument11 pagesPossibility of The Use Polish Soda Lime As The Absorbent in The Canisters of The Oxygen Breathing Apparatus Type Oxy-NGindiomajaderoNo ratings yet
- Cross Contamination Control Facility DesignDocument22 pagesCross Contamination Control Facility DesignAlok Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Amoxillin Glimepirid Amoxillin Metronidazol Metformin: Ambroxol Tablet Ambroxol TabletDocument10 pagesAmoxillin Glimepirid Amoxillin Metronidazol Metformin: Ambroxol Tablet Ambroxol TabletSeptia MonalisaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Fitness Levels Among Undergraduate Students of A Nigerian University Using Coopers 12 Minute Walk TestDocument3 pagesAerobic Fitness Levels Among Undergraduate Students of A Nigerian University Using Coopers 12 Minute Walk TestIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Radioimmunoassay (2002b)Document48 pagesRadioimmunoassay (2002b)api-19916399No ratings yet
- Argumentative Essay SampleDocument10 pagesArgumentative Essay SampleWin Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- A Simple and Reliable Submental Intubation.68Document4 pagesA Simple and Reliable Submental Intubation.68Tîrban Pantelimon FlorinNo ratings yet
- Ihc Guidebook Introduction To Immunohistochemistry Chapter1Document10 pagesIhc Guidebook Introduction To Immunohistochemistry Chapter1KharismaUtariNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakaDeborah Cindy KaramoyNo ratings yet
- Final DengueDocument32 pagesFinal Dengueprincesshanty100% (2)