Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Foundations, Piles, and Curtain Walls
Foundations, Piles, and Curtain Walls
Uploaded by
Ivy FirmeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Foundations, Piles, and Curtain Walls
Foundations, Piles, and Curtain Walls
Uploaded by
Ivy FirmeCopyright:
Available Formats
SUPER STRUCTURE - VISIBLE building loads down to a suitable bearing
SUB STRUCTURE - HIDDEN stratum.
FOUNDATION SYSTEM - transfers the lateral
loads on the substructure to the ground. END BEARING PILES - depend principally
Foundation systems are classifies into 2 on the bearing resistance of soil or rock
broad categories: beneath their feet for support.
- penetrate through the soft soil
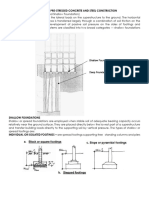
SHALLOW FOUNDATIONS
DEEP FOUNDATIONS FRICTION PILES - depends principally on
the frictional resistance of a surrounding
1. SHALLOW FOUNDATIONS - or spread earth mass for support.
foundations are employed when stable soil of - loose soil extend to a greater depth
adequate bearing capacity occurs relatively near
A. WOOD PILES - the most practicable
the ground surface.
method of obtaining a solid and enduring
1.1 INDIVIDUAL/ISOLATED FOOTINGS foundation for buildings of moderate height
- are spread footings supporting free- is by driving wooden piles.
standing columns and piers. PILE RING - also called a drive
A. Block or square footings band; a steel band which encircles
the head of a timber pile to prevent it
B. Stepped Footings
from splitting when being driven.
C. Slope or pyramidal footings
B. CONCRTE PILES - either plain or
1.2 STRIP FOOTINGS reinforced, possess many advantages over
- continuous spread footings of wooden piles and, in general, can be used
foundation walls. in all places where wooden piles can be
driven. Used where wooden piles would be
STEPPED FOOTINGS - change levels to
subject to decay or deterioration.
accommodate a sloping grade and
maintain depth at all points. 1. PRE-CAST PILES - usually molded
in a yard or at the site allowed to cure
1.3 COMBINED FOOTINGS for 4 weeks before using. Concrete
A. COMBINED FOOTINGS - piles are often sunk by means of water-
supporting two or more columns. Used jet.
where it is not possible to center the size - 30 to 50cm in cross section
footing beneath its supported column length - 20m or more
as in the case of columns located at or
very near the property line. 2. CAST-IN-PLACE PILES -
constructed on the ground in the
B. CANTILIVERED FOOTINGS - used position they are to occupy, and are
in place of a combined footing under often reinforced. All cast in place piles
the same conditions. are covered by patents.
- piles with casing is cased cast in site
C. CONTINUOUS FOOTINGS - concrete pile.
supporting a line of columns & - without casing is uncased cast in site
supporting all of the columns strips at concrete pile.
right angles to each other.
C. STEEL PILES - concrete filled steel
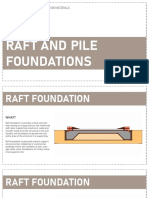
1.4 MAT OR RAFT FOUNDATIONS pipes which are made to bear on rock or
- used on soil of low bearing power where hard pan. Commonly used steel piles:
there is a tendency towards unequal ◌ H - piles - usually of wide flange
settlement due to unequal loading of soil. section. Suitable for frestle type
1. Flat Slabs of plain concrete structure.
2. Beams or girders with a slab ◌ Box piles - rectangular or octagonal in
underneath form filled with concrete.
3. Beams or girders with a slab on ◌ Tube piles - driven into the ground,
top concrete is filled inside the tube piles.
1.5 STEEL GRILLAGE FOUNDATION D. COMPOSITE PILES - combination of
- for steel-grillage foundations the timber and concrete or steel and concrete
foundation bed should first be covered with piles. They may be composed of timber
a layer of concrete not less than 6”in piles with concrete coatings held in position
thickness. by steel reinforcements in the shape pf
expanded metal or wire netting.
2. DEEP FOUNDATIONS - employed when the
E. TIMBER PILES - prepared from trunks
soil underlying a shallow foundation is unstable or
of trees. They may be circular or
of inadequate soil bearing capacity. The type of
square.
deep foundations are pile and caisson
diameter - 30 to 50cm
foundations.
length - not exceeding 20 times its
top width
2.1 PILE FOUNDATIONS
- a system of end bearing or friction piles,
pile caps, and tie beams for transferring b
F. SAND PILES - formed by making hole in ◌ Timber piles
ground and fill with the sand and well ◌ Composite Pile
rammed. The sand should be moist at time ◌ Sand Pile
of placing.
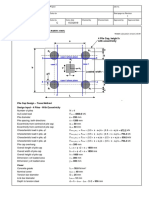
PILE CAP - protect the top of the pile from
G. JACKED PILE - jacked into the ground bow of hammer on top. It is made of steel. Pile
by applying a downward force by a should penetrate into the cap at least 10cm
hydraulic jack. length.
2.2 CAISSON FOUNDATIONS PILE SHOE - it is fitted at bottom end of pile to
- are cast in place, formed by boring with a protect the pile and to facilitate easy pile
large auger or excavation by hand a shaft in driving. It is made of cast iron, steel, or
the earth to a suitable bearing stratum and wrought iron.
filling the shaft with concrete.
PILE DRIVING EQUIPMENT
PILE PILE DRIVING - the operation of inserting
- is a slender structural member made of concrete, pile into ground.
steel, wood or composite materials.
- A pile is driven into the soil or formed in site by PILE DRIVER - equipment used for lifting
excavating a hole and filling it with concrete. hammer and allow to fall on head of pile.
◌ Hammer driving
USES OF PILES ◌ Vibratory pile driver
◌ Watter jetting and hammering
◌ The load of super structure is heavy and its ◌ Partial angering method
distribution is uneven.
◌ The top soil has poor bearing capacity. LEADS - also called leaders. Used to guide
◌ Large fluctuation in subsoil water level. hammer and pile for alignment.
◌ The structure is situated on sea shore or river
WINCHES - used for lift hammer and pile.
bed, where there is danger of scouring action
of water.
PILE HAMMER
◌ Canal or deep drainage line exist near the
foundation. ◌ DROP HAMMER - oldest type of hammer
used. It is rise by a winch and allowed to drop
FACTOR AFFECTING SELECTION OF TYPE OF the top of the pile under gravity from a certain
PILES height.
◌ Nature and type of structure ◌ SINGLE ACTING HAMMER - the ram is
◌ Location raised by air or steam under pressure to the
◌ Material, equipment and fund availability required height.
◌ Type of soil and its properties Weight of hammer - 1000 kg to 10,000 kg
◌ Ground water table
◌ DOUBLE ACTING HAMMER - raise by using
◌ Durability of pile
air or steam pressure and drop the hammer.
◌ Case study of adjacent building
Weight of hammer - 1000 kg to 2500 kg
◌ Facility for pile driving
It can be apply - 90 to 240 blow per min.
◌ Erosion of soil near structure
◌ DIESEL HAMMER
CLASSIFICATION OF PILES
◌ VIBRATORY HAMMER
◌ Based on function
◌ Based on materials PULLING OF PILE
◌ Based on method of installation
◌ to replace the damaged piles
◌ to reuse the existing piles
COMPACTION PILE - pile do not carry any load.
◌ to prepare the data of strata
It is for increase the bearing capacity of soil.
◌ to remove the pile which are driven
TENSION PILE - when structure subjected to temporarily
uplift due to hydro static pressure over turning ◌
moment. Also known as uplift pile. CAUSES OF FAILURE OF PILE
◌ Bad workmanship
ANCHOR PILES - these provided anchorage ◌ Attack by insects on wood
against the horizontal pull from sheet pulling. ◌ Buckling of pile
◌ Breakage due to over driving
FENDER PILE - used to protect water front
◌ Load coming on pile is high than design load
structures against impact from ships or other
◌ Improper type of pile, method of driving,
floating objects.
classification of soil
SHEET PILE - used as bulk heads or as impervious ◌ Damage due to absence of protective cover
cutoff to reduce seepage and uplift under
CAUSES OF FAILURE OF R.C.C. PILE
hydraulic structures.
◌ Improperly design concrete mix
CLASSIFICATION BASED ON PILE ◌ Use of wrong type of cement
MATERIALS ◌ Easy removal of concrete form
◌ Concrete pile ◌ Insufficient concrete cover to the
◌ Steel piles reinforcement
BUILDING - protect the building. Floor, roof, and panel does not transfer vertical loads but simply
wall. encloses the space.
BUILDING ENVELOPE - concrete, wood, glass, SPECIAL PURPOSE CURTAIN WALLS - these are
metal. the same to that of a normal curtain walls.
Additional insulating materials is use in place of
NATURAL LIGHT VENT - doors and windows glazing to restrict sun’s heat.
TYPES OF GLASS
CURTAIN WALL - designed to resist lateral loads ◌ LAMINATED GLASS - made by
due to wind or earthquake and its own self weight. sandwiching a layer of plastic between
TYPES OF CURTAIN WALLS two layers of glass.Commonly used in car
◌ METAL CURTAIN WALLS windshields, building windows, and
◌ WINDOW WALLS other applications where safety and
◌ R.C.C CURTAIN WALLS security are important.
◌ SPECIAL PURPOSE CURTAIN WALLS ◌ FLOAT GLASS - Float glass is a type of
glass that is made by floating molten glass
METAL CURTAIN WALL – an exterior curtain on a bed of molten metal.
wall which may consist entirely or principally of
metal, or may be a combination of metal, glass and ◌ STAIN GLASS - type of glass that is made
other surfacing materials supported by or within a by floating molten glass on a bed of
metal framework. molten metal. Use in windows for churches.
Divide into two categories:
◌ STICK SYSTEM - most common wall ◌ TEMPERED GLASS - shattered when
system especially on low-rise construction break.
and in smaller population centers.
◌ UNITIZE SYSTEM - common to large ◌ TINTED GLASS - reduce the amount of
high-rise buildings although found on heat and glare that enters a building,
buildings as low as four stories. which can lower energy costs for cooling
and improve occupant comfort.
MULLION AND PANEL - another type, only
vertical mullions are installed and fabricated
frames are installed.
SILICON SEALANT & RUBBER
ANCHORS - curtain wall anchors connect the
wall to the building and can be broadly
grouped as both gravity and lateral load
anchors (fixed) or as just lateral load anchors
(slotted).
TWO TYPES OF ANCHORS
◌ CONCRETE EMBEDED
◌ MOUNTING LUG ASSEMBLY
CONCRETE EMBEDED - type in
which anchors are embedded in
concrete.
MOUNTING LUG ASSEMBLY - lug is
provided which the panel is fixed.
PRESSURE PLATE - produced in the
same alloys as the main framing members and
are not usually finished.
SNAP CAPS - or dress caps are firstly a
decorative cover over the pressure plate and
exposed fasteners.
FASTENERS - screws and bolts are used in the
assembly of the curtain wall framing.
WINDOW WALL – installed between floors or
between floor and roof and typically composed of
vertical and horizontal framing members.
R. C.C. OR PRECAST CURTAIN WALL - most
commonly used precast concrete components for
building envelopes. This type of precast concrete
Dubai is home to 17 of the 100 highest
skyscrapers on earth WILLIS TOWER
◌ Height - 442 meters
BURJ KHALIFA - TALLEST BUILDING ON ◌ tallest building until 1996
EARTH ◌ It’s design is called a BUNDLED TUBE
◌ Location - Middle-eastern emirate of
Dubai TAIPEI 101
◌ Height - 828 METERS ◌ Height - 508 meter tall
◌ 6 years in construction ◌ Location - Taiwan
JANUARY 2010 - open the burj khalifa ◌ (SOM plan is 10 meter taller)
in the world
◌ 900 APARTMENTS HANCOCK
◌ 160 ROOM HOTEL ◌ made of steel and glass
◌ 37 FLOORS of OFFICES ◌ Height - 240 meters
◌ constructed in the 1970's
1.5 billion tower opened in 2010 ◌ problem - building swayed and over 5000
glass panels blew out
FEBRUARY 2004 - breaks ground at the burj sit
DAVID BRADFORD - construction manager
PETER IRWIN - wind engineer
JOHN ZERAFA - facade project director
JUMP FORM - fastest way to build a tower like
birch is with reinforced concrete.
- one new floor every week using
this system
12 hours -
Burj Khalifa is the brainchild of Dubai property
developer called EEMAR
EEMAR - property developer, top architecture
firms Skidmore Owings and Merrill (based on
chicago (home of skyscraper))
Chief Engr. - BILL BAKER
Structural system of Burj Khalifa is called the
BUTTRESS CORE - center hexagon middle of
the bldg. Buttresses are the three wings
around the hexagon.
25 separate ingredients to create concrete
that stays liquid but turns solid extremely fast.
◌ new floor every 3 days
192 PILES - depth of a 50 meters to support a
3.7 meter thick raft of solid concrete
- hold building weighs over 500,000 tons
after 3 years of break ground, the construction
reaches 512 METERS & 141 FLOORS
BURJ KHALIFA
◌ 900 apartments
◌ 160 room hotel
◌ 37 floors of offices
PANELS
24, 348 PANELS - must be installed on the
exterior
6.4 meters long and weighs 750 kg
WENDELL ALARMS
PIPE
136 meter tall pipe weighing over 350 tonnes
You might also like
- Pile Vs WellDocument16 pagesPile Vs Wellgvgbabu100% (4)
- Chapter 19: Audit of Owners' Equity: Review QuestionsDocument18 pagesChapter 19: Audit of Owners' Equity: Review QuestionsReznakNo ratings yet
- Materials and Finishes in InteriorDocument10 pagesMaterials and Finishes in InteriorIvy FirmeNo ratings yet
- Mapiful - How To Make Your Home More YouDocument35 pagesMapiful - How To Make Your Home More YouElina100% (1)
- Chapter 1-Pile Foundations-Lecture NoteDocument79 pagesChapter 1-Pile Foundations-Lecture NoteManal EsmaelNo ratings yet
- Presentation On FoundationsDocument14 pagesPresentation On FoundationsShiwangi NagoriNo ratings yet
- Technical Note Guidance On Corrosion Assessment of Ex EquipmentDocument7 pagesTechnical Note Guidance On Corrosion Assessment of Ex EquipmentParthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- 4 Piles Cap With Eccentricity ExampleDocument3 pages4 Piles Cap With Eccentricity ExampleSousei No Keroberos100% (1)
- BT 5 Reviewer (Foundations, Piles, Curtain Walls) - MedenillaIvyDocument4 pagesBT 5 Reviewer (Foundations, Piles, Curtain Walls) - MedenillaIvyIvy FirmeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer BT3Document7 pagesReviewer BT3Ron RamosNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument7 pagesREVIEWERPATRICIA MAE YALUNGNo ratings yet
- 7d Building Technology 1Document45 pages7d Building Technology 1Gilbert DavidNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Foundation in EngineeringDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Foundation in EngineeringCHRISTIAN NATHANIEL PALMANo ratings yet
- Module 18, FounDocument10 pagesModule 18, FounLeo DavifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.PILEFOUND - ModfDocument32 pagesChapter 5.PILEFOUND - ModfnahomdemelashNo ratings yet
- Buildings-Types of FoundationsDocument5 pagesBuildings-Types of FoundationsRonit ChariNo ratings yet
- CHING 3 - Foundation Systems-FarzinDocument5 pagesCHING 3 - Foundation Systems-FarzinAzadeh MohammadiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Building Construction MethodsDocument10 pages1.1 Introduction To Building Construction MethodsAlexNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering ShopworkDocument3 pagesCivil Engineering ShopworkJ O M A RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7.PILEFOUNDDocument42 pagesChapter 7.PILEFOUNDZsoloa adamNo ratings yet
- Junior Design Engineer: Satyavani Projects and Consultants Pvt. LTDDocument59 pagesJunior Design Engineer: Satyavani Projects and Consultants Pvt. LTDyedida viswanadhNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation Tos Assignment - 2 Amey DeshmukhDocument13 pagesPile Foundation Tos Assignment - 2 Amey DeshmukhAmey Deshmukh100% (1)
- Concrete ProportionDocument2 pagesConcrete ProportionJuviya LockserNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Foundations.Document32 pagesPresentation On Foundations.shrikant100% (6)
- Sheet Piles Walls: Name TitleDocument4 pagesSheet Piles Walls: Name TitleKristin ArgosinoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Foundation Systems-Raft Foundation: 1. Definition, Purpose, & General AspectsDocument7 pagesAdvanced Foundation Systems-Raft Foundation: 1. Definition, Purpose, & General Aspects18 FAISAL SHAH100% (1)
- Types of FootingsDocument1 pageTypes of FootingsmarkensteinsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document14 pagesLecture 1Erica Jane TatelNo ratings yet
- 1 FoundationsDocument10 pages1 FoundationsEdriane Jude MalemNo ratings yet
- I. Deep Foundation: A. PileDocument7 pagesI. Deep Foundation: A. PileNikol CapulongNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete FoundationsDocument25 pagesReinforced Concrete FoundationsDiether AguilarNo ratings yet
- BMC Shallow FoundationsDocument6 pagesBMC Shallow Foundationsshenaz AfroseNo ratings yet
- Types of FoundationDocument52 pagesTypes of FoundationMARUFNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14-15 Pile Foundation and Bearing Capacity in Sand and ClayDocument14 pagesLecture 14-15 Pile Foundation and Bearing Capacity in Sand and ClayChauhdary Fazeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter-22 FoundationDocument20 pagesChapter-22 Foundationdesubie bireNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 FoundationDocument53 pagesChapter-3 Foundationkader ArefeNo ratings yet
- Types of FootingDocument3 pagesTypes of FootingRonald DolorNo ratings yet
- Types of FdnsDocument41 pagesTypes of Fdnshiwotnesh girmaNo ratings yet
- Foundation Systems.Document9 pagesFoundation Systems.PRECIOUS AMY TITIWANo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation: P. N. SolankiDocument68 pagesPile Foundation: P. N. Solankilokesh aggarwalNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Types of Shallow FoundationsDocument35 pagesCH-2 Types of Shallow Foundations19CE535 Mandar GawandeNo ratings yet
- Art306 Building and Construction Materials: Assignment IvDocument19 pagesArt306 Building and Construction Materials: Assignment IvAbhishek SoniNo ratings yet
- Builiding FoundationDocument16 pagesBuiliding FoundationSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Shakib Sir URP - FoundationDocument48 pagesShakib Sir URP - FoundationHome Tutor Provider KhulnaNo ratings yet
- Building Construction 5 To 7Document30 pagesBuilding Construction 5 To 7GeraldineNo ratings yet
- Foundation PlanDocument50 pagesFoundation PlanShaina Habib-AgilNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Pile FoundationDocument17 pagesAssignment: Pile Foundationsunil khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Pile FoundationDocument17 pagesAssignment: Pile Foundationsunil khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Foundation or Sub-StructureDocument50 pagesFoundation or Sub-StructuredeepakjoghuNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document149 pagesModule 3Owsu KurianNo ratings yet
- 01 IntroductionDocument26 pages01 IntroductionJoshua OrcalesNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundations NotesDocument11 pagesPile Foundations NotesPutinNo ratings yet
- Ar 373 BT 3 ReviewerDocument11 pagesAr 373 BT 3 ReviewerMelvin AlarillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.1 Foundation (Part 1)Document53 pagesChapter 5.1 Foundation (Part 1)Issack Mattew100% (1)
- Deep Foundation: When Do We Use Deep Foundations?Document7 pagesDeep Foundation: When Do We Use Deep Foundations?Cadfiles aasthaNo ratings yet
- BACLIG, LORNA G. (BSCE 4-2) - CENGR 4220 Assignment No. 4Document14 pagesBACLIG, LORNA G. (BSCE 4-2) - CENGR 4220 Assignment No. 4LORNA BACLIGNo ratings yet
- Deep Foundation DesignDocument31 pagesDeep Foundation Designrose ann claveriaNo ratings yet
- Foundation PDFDocument3 pagesFoundation PDFhamdan linjee SupaiNo ratings yet
- Types of FoundationsDocument30 pagesTypes of FoundationsFahad Areeb100% (1)
- Types of Foundations PDFDocument30 pagesTypes of Foundations PDFHuzaifa Tanzeel0% (1)
- Sub Structure ConstructionDocument56 pagesSub Structure ConstructionamokeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Foundation DEEP FOUNDATIONDocument72 pagesChapter 2-Foundation DEEP FOUNDATIONaakash regmiNo ratings yet
- 1 - Foundation-1Document30 pages1 - Foundation-1Sharjeel AliNo ratings yet
- Foundations: S V Giri Babu Govt. Polytechnic VijayawadaDocument37 pagesFoundations: S V Giri Babu Govt. Polytechnic VijayawadaMeenu ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Phil. History Chap 1 & Chap 2Document42 pagesPhil. History Chap 1 & Chap 2Ivy FirmeNo ratings yet
- Housing Assignment 2Document9 pagesHousing Assignment 2Ivy FirmeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1 Regulatory SignDocument28 pagesLesson 1.1 Regulatory SignIvy FirmeNo ratings yet
- Principles of Surveying 1.2Document10 pagesPrinciples of Surveying 1.2Ivy FirmeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SurveyingDocument31 pagesIntroduction To SurveyingIvy FirmeNo ratings yet
- 5 Different Architectural Interior DesignDocument18 pages5 Different Architectural Interior DesignIvy FirmeNo ratings yet
- Lighting Fixtures (Assignment)Document6 pagesLighting Fixtures (Assignment)Ivy FirmeNo ratings yet
- Level2 013123 PDFDocument12 pagesLevel2 013123 PDFIvy Firme100% (1)
- Philippines Economic Globalization PDFDocument1 pagePhilippines Economic Globalization PDFIvy FirmeNo ratings yet
- Defining GlobalizationDocument1 pageDefining GlobalizationIvy FirmeNo ratings yet
- Shady Othman Nour El Deen: Doha, QatarDocument3 pagesShady Othman Nour El Deen: Doha, QatarHatem HusseinNo ratings yet
- Luxury DIY Sulfate Shampoo - Workbook - VFDocument14 pagesLuxury DIY Sulfate Shampoo - Workbook - VFralucaxjsNo ratings yet
- Brief Hydrogeological Studies of Watershed MR-03 (37) in Context of Groundwater Estimation, Washi, Osmanabad, Maharashtra, IndiaDocument13 pagesBrief Hydrogeological Studies of Watershed MR-03 (37) in Context of Groundwater Estimation, Washi, Osmanabad, Maharashtra, IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Life With MathematicsDocument4 pagesLife With MathematicsHazel CuNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Soft Skills To A Construction ProjectDocument9 pagesThe Importance of Soft Skills To A Construction ProjectJay SayNo ratings yet
- CsToCpp ASomewhatShortGuide PDFDocument56 pagesCsToCpp ASomewhatShortGuide PDFIldar SakhapovNo ratings yet
- Ep English Teachers GuideDocument180 pagesEp English Teachers GuideJessy ChrisNo ratings yet
- Asimakopulos, A. (1975) - A Kaleckian Theory of Income Distribution. Canadian Journal of Economics, 313-333.Document22 pagesAsimakopulos, A. (1975) - A Kaleckian Theory of Income Distribution. Canadian Journal of Economics, 313-333.lcr89No ratings yet
- CDP 22 FinalDocument8 pagesCDP 22 FinalAnonymous GMUQYq8No ratings yet
- The Kinston Waterfront Now!Document46 pagesThe Kinston Waterfront Now!Kofi BooneNo ratings yet
- Steel Material Table PDFDocument1 pageSteel Material Table PDFNathanNo ratings yet
- Security SolutionsDocument3 pagesSecurity SolutionsclubedovarNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet Versamul Ic: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and Company/UndertakingDocument4 pagesSafety Data Sheet Versamul Ic: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and Company/UndertakingJose Rafael Martinez PerezNo ratings yet
- Manual Del Gemcom Surpac - Underground Ring DesignDocument43 pagesManual Del Gemcom Surpac - Underground Ring DesignDavid GarciaNo ratings yet
- Spitfire v2 Semff Combat Plane FullDocument1 pageSpitfire v2 Semff Combat Plane FullFilipe GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Présentation XanLite 2020 ENDocument18 pagesPrésentation XanLite 2020 ENJ.DoeNo ratings yet
- Active Directory GP Programming and Registry ReferenceDocument99 pagesActive Directory GP Programming and Registry ReferenceHarmandeep Singh SagguNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect LINGODADocument31 pagesPresent Perfect LINGODAThayrone NeryNo ratings yet
- HRM1Document13 pagesHRM1Niomi GolraiNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Food Branding On Children's Eating Behaviour and ObesityDocument8 pagesThe Impact of Food Branding On Children's Eating Behaviour and ObesityAlessandraBattagliaNo ratings yet
- Astm A 121 PDFDocument4 pagesAstm A 121 PDFDeepakNo ratings yet
- BHC - Shakib AhmedDocument3 pagesBHC - Shakib AhmedDaniel CrumpNo ratings yet
- Spoken English PPT 1Document147 pagesSpoken English PPT 1Sindhu Manja100% (3)
- Washing MachineDocument6 pagesWashing MachineianNo ratings yet
- Prakash Kadam & Etc. Etc. Vs Ramprasad Vishwanath GuptaDocument18 pagesPrakash Kadam & Etc. Etc. Vs Ramprasad Vishwanath GuptaAshish DavessarNo ratings yet
- Honda CQ Eh8160akDocument37 pagesHonda CQ Eh8160aklondon335No ratings yet