Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity
Activity
Uploaded by
DINSEFA KAMILCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Steven Weinberg - Foundations of Modern Physics-Cambridge University Press (2021)Document325 pagesSteven Weinberg - Foundations of Modern Physics-Cambridge University Press (2021)puceiroale100% (13)
- Test Bank For Physics For Scientists and Engineers 4th by KnightDocument27 pagesTest Bank For Physics For Scientists and Engineers 4th by Knightguyzunigaiadzrbpfes100% (27)
- DynamicsDocument8 pagesDynamicsSurafel BehailuNo ratings yet
- Kinematics PDFDocument7 pagesKinematics PDFBetseha MerawiNo ratings yet
- Cuestiones - T5Document4 pagesCuestiones - T5Ian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 11 Unit 4 WorksheetDocument14 pagesPhysics Grade 11 Unit 4 Worksheetsample nameNo ratings yet
- Dej/Wondirad Preparatory School: Physics UEE Compiled On Rotational Motion (2003-2011)Document5 pagesDej/Wondirad Preparatory School: Physics UEE Compiled On Rotational Motion (2003-2011)Eyuel EnitoNo ratings yet
- Dej/Wondirad Preparatory School: Physics UEE Compiled On Work, Energy and Power (2003-2011)Document4 pagesDej/Wondirad Preparatory School: Physics UEE Compiled On Work, Energy and Power (2003-2011)Eyuel Enito0% (1)
- MotionDocument17 pagesMotionJohnNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Physics Class XiDocument6 pagesSample Paper Physics Class XiBhaskar JhaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Chapter 9 Review SheetDocument9 pagesAP Physics Chapter 9 Review SheetEAGLEFORCE06No ratings yet
- Midterm Exam 2016 2017 01Document4 pagesMidterm Exam 2016 2017 01Bá Phong LêNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 2016-17 Quiz3Document6 pagesPhysics 1 2016-17 Quiz3Khoa TrầnNo ratings yet
- DP2 HL QPDocument26 pagesDP2 HL QPChinmay BhaveNo ratings yet
- Physics SolvedDocument16 pagesPhysics SolvedAbhijeet Singh PanwarNo ratings yet
- Lows of MotionDocument20 pagesLows of MotionSaswata Sundar LagaNo ratings yet
- DP2 SL QPDocument19 pagesDP2 SL QPChinmay BhaveNo ratings yet
- Physics Equilibrium QueDocument3 pagesPhysics Equilibrium QueLemi NegesoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 03 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 03 PDFVijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- Midterm Exam 2016-2017-01Document4 pagesMidterm Exam 2016-2017-01Gia Hân EmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions Uniform Circular Motion Newton S Law PF Gravitation and Rotational MotionDocument9 pagesChapter Questions Uniform Circular Motion Newton S Law PF Gravitation and Rotational MotionJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Practice Physics TestDocument7 pagesPractice Physics Testthey12No ratings yet
- Jee 2014 Booklet3 HWT Energy & MomentumDocument19 pagesJee 2014 Booklet3 HWT Energy & MomentumvarunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Practica IiDocument9 pagesPractica IiEduardo FernandezNo ratings yet
- NL CQ 6 SSPDocument4 pagesNL CQ 6 SSPGokul NathNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers 3rd Edition Knight Test BankDocument26 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers 3rd Edition Knight Test Bankdiemdac39kgkw100% (27)
- University of The Philippines College of Science: Name Section Student Number Set ADocument10 pagesUniversity of The Philippines College of Science: Name Section Student Number Set ASherylleen RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ForumDocument10 pagesForumfestus wikannandaNo ratings yet
- Exam 3a Rev QuesDocument35 pagesExam 3a Rev QuesUmesh Reddy100% (1)
- AP Physics C 2004 With AnswersDocument18 pagesAP Physics C 2004 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- End of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CDocument4 pagesEnd of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CChristina ZhangNo ratings yet
- Phy1121 Discussion Group September 24, 2014Document3 pagesPhy1121 Discussion Group September 24, 2014throwaway1609No ratings yet
- Part A - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesPart A - Multiple Choice QuestionsBryan SutantoNo ratings yet
- Physics 712 ND LE1 Stsem 20112012Document12 pagesPhysics 712 ND LE1 Stsem 20112012Alexis Julia CanariaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C MomentumDocument34 pagesAP Physics C MomentumShamanthakNo ratings yet
- NUS Physics PaperDocument6 pagesNUS Physics PaperBilin ZhuangNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument10 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionAlejandro Torrico MorenoNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1-HW1204Document4 pagesAP Physics 1-HW1204張晉嘉No ratings yet
- POW SAT-2 CoMDocument7 pagesPOW SAT-2 CoMLonely PotatoNo ratings yet
- Momentum and ImpulseDocument28 pagesMomentum and ImpulseAli AtwiNo ratings yet
- BB 2.0 - NLMDocument142 pagesBB 2.0 - NLMParthMaluNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Semester One MC Exam ReviewDocument6 pagesAP Physics Semester One MC Exam ReviewJordana BrenesNo ratings yet
- Soal Pembinaan Olimpiade Hari Ke-2Document5 pagesSoal Pembinaan Olimpiade Hari Ke-2IslahwaniLokaVitaRestiNo ratings yet
- SpringerDocument10 pagesSpringerMonico AlejoNo ratings yet
- 4 SJPO-2013-GenDocument19 pages4 SJPO-2013-Genronghui009No ratings yet
- MECH Multiple Choice 2004Document7 pagesMECH Multiple Choice 2004clarencetan95No ratings yet
- Practice Test 2Document7 pagesPractice Test 2Maria YurlovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Dynamic RevisionDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Dynamic Revision陈伟明No ratings yet
- Practice Momentum TestDocument5 pagesPractice Momentum TestKinalPatelNo ratings yet
- 2nd LE Sample ExamDocument13 pages2nd LE Sample ExamElla CardenasNo ratings yet
- Momentum and Impulse MC Practice ProblemsDocument10 pagesMomentum and Impulse MC Practice ProblemsJayNo ratings yet
- Trialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionDocument6 pagesTrialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionMathew Cheng Yu HaoNo ratings yet
- Physics 6Document20 pagesPhysics 6Kazuto ShibaNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Newtons Laws ReviewDocument6 pagesDay 2 Newtons Laws Reviewnoel castilloNo ratings yet
- Application of Newton's Second Law: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Painter On A PlatformDocument9 pagesApplication of Newton's Second Law: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Painter On A PlatformBoldie LutwigNo ratings yet
- (A) 2 KG, (6 M/S) IDocument10 pages(A) 2 KG, (6 M/S) Ikush jindalNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam A1Document3 pagesMidterm Exam A1Bá Phong LêNo ratings yet
- Unit I and Unit II Multiple Choice Practice TestDocument11 pagesUnit I and Unit II Multiple Choice Practice TestChristian Firsching0% (1)
- Aits 2223 FT Vi Jeem OfflineDocument15 pagesAits 2223 FT Vi Jeem OfflineSuvrajyoti TaraphdarNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena Introduction and First Law of Thermodynamics: Unit-I Philosophy and Fundamentals of Transport PhenomenaDocument11 pagesTransport Phenomena Introduction and First Law of Thermodynamics: Unit-I Philosophy and Fundamentals of Transport PhenomenaSivakumarNo ratings yet
- Mock Ext. P2 For S4 2017.Document6 pagesMock Ext. P2 For S4 2017.cyber secNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms (Magnetism)Document4 pagesDefinition of Terms (Magnetism)Teresa PulgaNo ratings yet
- AEP 3330 Final - Some EquationsDocument1 pageAEP 3330 Final - Some EquationsJesse ZhangNo ratings yet
- APPENDIX-5.2 ISO 5802 - Circular Traverse Measure PointDocument3 pagesAPPENDIX-5.2 ISO 5802 - Circular Traverse Measure PointLâm trầnNo ratings yet
- CHEM 474 - Lecture 1 NotesDocument11 pagesCHEM 474 - Lecture 1 NotesjeannietranNo ratings yet
- IAL Unit 5 Edexcel NotesDocument27 pagesIAL Unit 5 Edexcel NotesThangavel SarujanNo ratings yet
- Spintronics Device 22053502 b26Document2 pagesSpintronics Device 22053502 b26AYUSHKA NANDANo ratings yet
- 17 LectureslidesDocument154 pages17 LectureslidesAlinaBogoiNo ratings yet
- 03 Translation MatricesDocument8 pages03 Translation MatricessolteanNo ratings yet
- Simulating Chemistry On A Quantum ComputerDocument52 pagesSimulating Chemistry On A Quantum ComputerShilpi JainNo ratings yet
- TS - SR - Physics - Imp - Questions 2022-23Document5 pagesTS - SR - Physics - Imp - Questions 2022-23Kota ๖ۣۜRαkͥesͣhͫ0% (1)
- Introduction Phy370Document2 pagesIntroduction Phy370Taehyung KimNo ratings yet
- 7.2 The Particle Theory of Matter AnswerDocument6 pages7.2 The Particle Theory of Matter AnswerMatthew ScherbatyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - FluidDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - Fluidfieyza adnNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School (Joka) South Kolkata SYLLABUS - 2020-2021 Class Xi PhysicsDocument3 pagesDelhi Public School (Joka) South Kolkata SYLLABUS - 2020-2021 Class Xi PhysicsMalNo ratings yet
- Department of Physics: Lab Report of GM Counter ExperimentDocument10 pagesDepartment of Physics: Lab Report of GM Counter ExperimentHaidar AliNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Quiz 1: Energy Bands ECE 606: Solid State DevicesDocument2 pagesWeek 3 Quiz 1: Energy Bands ECE 606: Solid State DevicesASHISH KUSHWAHANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11-1Document20 pagesChapter 11-1Tsiye TekleyohanisNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Formula Sheet (Coaching)Document42 pagesClass 12 Physics Formula Sheet (Coaching)Atharva Maheshwari100% (1)
- Betatron 1Document3 pagesBetatron 1dileepNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Phy 281-1Document22 pagesLecture Notes - Phy 281-1Muhammed AbdulsalamNo ratings yet
- 7 Marking Scheme: Worksheet: P V NRT P 1.22 × 10 PV NRT y PVDocument3 pages7 Marking Scheme: Worksheet: P V NRT P 1.22 × 10 PV NRT y PVН. НаранцацралтNo ratings yet
- Baao 2018Document11 pagesBaao 2018physicsolympiad19No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Differential Equations PDFDocument15 pagesChapter 7 Differential Equations PDFfahmi100% (1)
- Robitaille, P.-M., Blackbody Radiation and The Loss of Universality - Implications For Planck's Formulation and Boltzman's ConstantDocument3 pagesRobitaille, P.-M., Blackbody Radiation and The Loss of Universality - Implications For Planck's Formulation and Boltzman's ConstantDrenko MarićNo ratings yet
- PNP Handout3Document62 pagesPNP Handout3Anil HirparaNo ratings yet
- Notes - Matter in Our Surroundings - ExpDocument6 pagesNotes - Matter in Our Surroundings - Expdeborah hildaNo ratings yet
Activity
Activity
Uploaded by
DINSEFA KAMILOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity
Activity
Uploaded by
DINSEFA KAMILCopyright:
Available Formats
School of Indiana Alem Bank Branch Department of Natural Science Physics Division
Collection of UEE [2003-2015] E.C. regarding impulse, linear momentum, and center of mass.
1. A cart moving at a speed V collides with an identical stationary cart on an air track and the two stick
together after collision. What is their velocity after collision? [UEE: 2003]
A. -0.5 V B. Zero C. 0.5 V D. V
2. A car (mass m1) is driving at velocity v, when it smashes into an unmoving car (mass m2), locking bumpers.
Both cars move together at the same velocity. The common velocity will be given by :[UEE: 2004]
m1 v m2 v m1 v (m1 +m2 )v
A. B. C. D.
m2 m1 (m1 +m2 ) m1
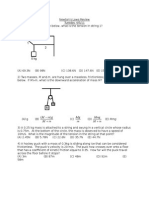
3. A bullet of mass 10 gm, moving horizontally, strikes and embeds itself in a box of mass 1 kg suspended from
a light string as shown in the figure below. If the composite mass rises to a height H = 0.45 m, then what is
the speed of the bullet before collision? [UEE: 2005]
A. 303 m/s
B. 300 m/s
C. 90.9 m/s
D. 90 m/s
4. A rocket moving in free space has speed of 3 × 103 𝑚/𝑠 relative to the earth. Its engines are turned on, and
fuel is ejected in a direction opposite the rocket’s motion at a speed of 5 × 103 𝑚/𝑠 relative to the rocket.
What is the speed of the rocket relative to the earth once the rocket’s mass is reduced to half its mass before
ignition? [UEE: 2005] [old curriculum]
A. 7 × 103 𝑚/𝑠 B. 5 × 103 𝑚/𝑠 C. 4 × 103 𝑚/𝑠 D.2 × 103 𝑚/𝑠
5. Two particles with masses 2m and 3m are moving toward each other along the x axis with the same initial
speeds v. Particle 2m is traveling to the left, and particle 3m is traveling to the right. They undergo an
elastic glancing collision such that particle 2m is moving in the negative y direction after the collision. What
are the x component of the final velocity of particle 3m and the kinetic energy of the particle 2m,
respectively? [UEE: 2006] [old curriculum]
A. 0.33 v and 0.7 mv2 B. 0.33 v and 1.4 mv2 C. 0.67 v and 0.7 mv2 D. 0.67 v and 1.4 mv2
6. A hard ball moving on a horizontal frictionless surface with a speed of 5 m/s in the positive x direction
strikes a stationary hard ball of the same mass. After the collision, the first ball moves with a speed of 4 m/s
along a direction that makes an angle of 370 with its initial direction of motion. What is the struck ball’s
speed and the smallest angle between its direction of motion and the positive x axis after the collision?
[UEE: 2007]. [old curriculum]
A. 3 m/s and 530 B. 3 m/s and 370 C. 4 m/s and 530 D. 4 m/s and 370
7. A man standing on a frictionless surface continuously fired 120 bullets horizontally in 1 minute using a
machine gun. If each bullet has a mass of 10 g and leaves the muzzle of the gun with a speed of 800 m/s,
what is the average force exerted by the gun on the man? [UEE:2007]
A. 8 N B.16 N C. 960 N D. 16000 N
8. What is the necessary and sufficient condition for conservation of linear momentum? [UEE:2008]
A. The presence of more linear than nonlinear forces in the system.
B. Net force on the system is zero.
C. The presence of only non-linear forces.
D. Internal forces exceed external forces.
9. A large mass (A) and a small mass (B) are pushing one another apart, as shown in the figure below. The
small mass moves away at a velocity of 20 m/s to the right. What is the recoil velocity of the large mass?
(UEE:2008)
A. -20 m/s
B. 8 m/s
C. 20 m/s
D. -8 m/s
2016 E.C Page 1
10. Find the distance of the center of mass of the system shown in the diagram from point A. The rod is
massless. [uee:2008]
A. 3.73 m 3 kg 3 kg 3 kg 2 kg
B. 2.09 m A
C. 2.45 m
D. 5.86 m 3m 3m 1m
11. A 1kg object explodes and breaks up in three pieces. One piece has a mass of 400 g and has a velocity of (15
î+ 10 ĵ)m/s. A second piece has a mass of 250 g and has a velocity of (25 𝑖̂+ 10 𝑗̂) m/s. What is the velocity of
the third piece? [UEE: 2009] [old curriculum]
A. (-4.3 î +35 ĵ) m/s B. (-35î – 4.3 ĵ) m/s C. (45î – 4.3 ĵ) m/s D. (-35î – 4.3 ĵ) m/s
12. A Uranium atom initially at rest has amass of 2 units and spontaneously disintegrated in to two fragments.
One of the fragments has a mass of 0.8 units and moves at a speed of 24 m/s as shown in figure below. What
is the speed of the second fragments? [UEE: 2009] [old curriculum]
A. 25.6 m/s
B. 21.3 m/s
C. 16 m/s
D. 14.8 m/s
13. For a constant force F, if the impulse imparted to the system is large, then what can you conclude about the
collision? [UEE:2010]
A. Linear momentum is conserved. C. The contact or impact time is large.
B. Kinetic energy is conserved. D. The change in velocity is small.
14. An open trolley is rolling on a level surface without friction loss through a vertical downpour of rain, as
shown in the figure below.
As the trolley rolls, an appreciable amount of rainwater accumulates in the cart. What will be the speed of
the cart? [UEE: 2010][old curriculum]
A. It increases because of conservation of mechanical energy.
B. It decreases because of conservation of momentum.
C. It decreases because of conservation of mechanical energy.
D. It remains the same because the raindrops are falling perpendicular to the direction of the cart’s motion.
15. A ball of mass M moves with speed V in the + x-direction. It explodes into two pieces that go off at angles ѳ1
and ѳ2, as shown below. What are the magnitudes of the momenta of the two pieces? (UEE: 2011).
𝑀𝑉𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃2 𝑀𝑉𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃1
A. 𝑃1 = and 𝑃2 =
sin(𝜃1 +𝜃2 ) sin(𝜃1 +𝜃2 )
𝑀𝑉𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃2 𝑀𝑉𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃1
B. 𝑃1 = sin(𝜃1 +𝜃2 )
and 𝑃2 = sin(𝜃1 +𝜃2 )
C. 𝑃1 = 𝑀𝑉𝑡𝑎𝑛𝜃2 and 𝑃2 = 𝑀𝑉𝑡𝑎𝑛𝜃1
𝑀𝑉𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃2 𝑀𝑉𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃1
D. 𝑃1 = and 𝑃2 =
cos(𝜃1 +𝜃2 ) cos(𝜃1 +𝜃2 )
∆m
16. The rate of change of momentum of the raindrop can be given by F = ma +u ∆t
. In this expression what
does u represent? [UEE: 2011]. [old curriculum]
A. The velocity of the extra mass added to the raindrop.
B. The velocity of the raindrop.
C. The velocity of the loss in mass of raindrop.
2016 E.C Page 2
D. The rate of change of the velocity for combined system.
17. Which one of the following statements is correct about the impulse on an object? (UEE: 2013/14)
A. The impulse on an object is changed when the net force acting on the object is zero.
B. The area under the curve of momentum versus time graph is the impulse on an object.
C. Impulse is the change in momentum when a force is exerted on an object for a very short period of time.
D. Impulse is the rate of change in momentum due to external force exerted on an object for a very short
period of time.
18. Consider two collisions, that occurred between two trollies having the same mass; moving with the same
speed, and in opposite directions,
Collision 1:- after collision the two trollies bounce back with the same speed.
Collision 2:- after collision the two trollies stick together due to magnetic coupler.
Which of the following statement is correct about the two collisions? (UEE: 2013/14)
A. Both collisions are elastic.
B. Collision 1 is elastic and collision 2 is inelastic
C. Both collisions are inelastic.
D. Collision 1 is inelastic and collision 2 is elastic.
19. A ball of mass m moving witth a speed v strikes a hard wall at an angle 𝜃 with the wall. It is refelected with
the same speed at the same angle as shown in the figure below.
If the ball is incontact with the wall for time t, then the average force acting on the wall is given by
[uee:2014/15] [old curriculum]
𝑚𝑣 𝑚𝑣 2𝑚𝑣 2𝑚𝑣
A. t
𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃 B. t
𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃 C. t
𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃 D. t
𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
20. Two masses of m1 and m2 are balanced on horizontal stick of negligible mass pivoted at the center of mass of
the sysytem. If the distance from m1 to the center of mass is 3.0m and the distance from the m2 to the center
of mass is 1.0m, the ratio of m1 to m2(m1/m2)is______.[uee:2012/13]
A. 1/3 B. 3 C. ¾ D. 4/3
21. Consider a system of two point masses M1 and M2, with M1=0.5M2. The two masses are located on the x-y
plane as shown in the figure below.
Which one of the following alternatives indicates the position of center of mass of the system? [uee:2015]
5 7 16 11 11 16
A. (5,4)𝑐𝑚 B. (3 , 3) 𝑐𝑚 C. ( 3 ,3
) 𝑐𝑚 D. ( 3 , 3
) 𝑐𝑚
22. A stationary mass explodes into two parts of masses 0.4kg and 4kg. If the larger mass has a kinetic energy
of 100J, what is the kinetic energy of the smaller mass? [uee:2004]
A. 4√50J B. 100J C. 1000 J D. The change in kinetic energy is the same for both particles
Additional exercise
23. Body A of mass 4m moving with speed u collides with another body B of mass 2m, at rest. The collision is
head on and elastic in nature. After the collision the fraction of energy lost by the colliding body A is
(a) 5/9 (b) 1/9 (c) 8/9 (d) 4/9
2016 E.C Page 3
24. A bullet of mass 10 g moving horizontally with a velocity of 400 m s–1 strikes a wooden block of mass 2 kg
which is suspended by light inextensible string of length 5 m. As a result, the centre of gravity of the block is
found to rise a vertical distance of 10 cm. The speed of the bullet after it emerges out horizontally from the
block will be
(a) 100 m s–1 (b) 80 m s–1 (c) 120 m s–1 (d) 160 m s–1
25. Two identical balls A and B having velocities of 0.5 m s–1 and –0.3 m s–1 respectively collide elastically in one
dimension. The velocities of B and A after the collision respectively will be
(a) –0.5 m s–1 and 0.3 m s–1 (c) –0.3 m s–1 and 0.5 m s–1
(b) 0.5 m s and –0.3 m s
–1 –1 (d) 0.3 m s–1 and 0.5 m s–1
26. A ball is thrown vertically downwards from a height of 20 m with an initial velocity v0. It collides with the
ground, loses 50 percent of its energy in collision and rebounds to the same height. The initial velocity v0 is
(Take g = 10 m s–2)
(a) 28 m s–1 (b) 10 m s–1 (c) 14 m s–1 (d) 20 m s–1
27. A ball moving with velocity 2 m/s collides head on with another stationary ball of double the mass. If the
coefficient of restitution is 0.5, then their velocities (in m/s) after collision will be
(a) 0, 1 (b) 1, 1 (c) 1, 0.5 (d) 0, 2
28. Two equal masses m1 and m2 moving along the same straight line with velocities + 3 m/s and –5 m/s
respectively collide elastically. Their velocities after the collision will be respectively
(a) – 4 m/s and +4 m/s (b) +4 m/s for both (c) – 3 m/s and +5 m/s (d) – 5 m/s and + 3 m/s.
29. A rubber ball is dropped from a height of 5 m on a plane. On bouncing it rises to 1.8 m. The ball loses its
velocity on bouncing by a factor of
3 2 16 9
(a) (b) (c) (d)
5 5 25 25
30. A metal ball of mass 2 kg moving with speed of 36 km/h has a head on collision with a stationary ball of
mass 3 kg. If after collision, both the balls move as a single mass, then the loss in K.E. due to collision is
(a) 100 J (b) 140 J (c) 40 J (d) 60 J.
31. A moving body of mass m and velocity 3 km/hour collides with a body at rest of mass 2m and sticks to it.
Now the combined mass starts to move. What will be the combined velocity?
(a) 3 km/hour (b) 4 km/hour (c) 1 km/hour (d) 2 km/hour
32. A bullet of mass m travelling with a speed v hits a block of mass M initially at rest and gets embedded in it.
The combined system is free to move and there is no other force acting on the system. The heat generated in
the process is
𝑚𝑣 2 𝑀𝑚𝑣 2 𝑀𝑚𝑣 2
(a) zero (b) 2
(c) 2(𝑀−𝑚) (d) 2(𝑀+𝑚)
33. A person holding a rifle (mass of person and rifle together is 100 kg) stands on a smooth surface and fires 10
shots horizontally, in 5 s. Each bullet has a mass of 10 g with a muzzle velocity of 800 m s–1. The final
velocity acquired by the person and the average force exerted on the person are
(a) – 0.08 m s–1, 16 N (b) – 0.8 ms–1, 8 N (c) – 1.6 m s–1, 16 N (d) – 1.6 m s–1, 8 N
34. A mass of 1 kg is thrown up with a velocity of 100 m/s. After 5 seconds, it explodes into two parts. One part
of mass 400 g comes down with a velocity 25 m/s. The velocity of other part is (Take g = 10 m s–2)
(a) 40 m/s (b) 80 m/s (c) 100 m/s (d) 60 m/s
35. Which one of the following statements is incorrect about an elastic collision between two particles?
(A) The total kinetic energy of the system is always conserved.
(B) The kinetic energy of the system before collision is equal to the kinetic energy of the system after
collision.
(C) The linear momentum of the system is conserved.
(D) The mechanical energy of the system before collision is equal to the mechanical energy of system after
collision. But the kinetic energy of the system is not always conserved. It is conserved only before and
after the collision.
36. A bullet is fired from a gun. The force on the bullet is given by F = 600 − 2 × 105 t where, F is in newton and t
in seconds. The force on the bullet becomes zero as soon as it leaves the barrel. What is the average impulse
imparted to the bullet?
(a) 9 N-s (b) zero (c) 1.8 N-s (d) 0.9 N-s
2016 E.C Page 4
37. A bomb of mass 9 kg explodes into two pieces of masses 3 kg and 6 kg. The velocity of mass 3 kg is 16 m/s.
The kinetic energy of mass 6 kg is
(A) 96 J (B) 384 J (C) 192 J (D) 768 J
38. Two balls of same mass are dropped from the same height h, on to the floor. The first ball bounces to a
ℎ ℎ
height 4 , after the collision & the second ball to a height 16. The impulses applied by the first & second ball
on the floor are J1 and J2 respectively. Then
(A) 5 J1 = 6 J2 (B) 6 J1= 5 J2 (C) J1= 2 J2 (D) 2 J1= J2
39. A particle of mass m moving with velocity u makes an elastic onedimensional collision with a stationary
particle of mass m. They are in contact for a very brief time T. Their force of interaction increases from
zero to F0 linearly in time 𝑇⁄2, and decreases linearly to zero in a further time 𝑇⁄2. The magnitude of F0 is
mu 2mu mu
(A) (B) (C) (D) none of these
T T 2T
40. A boy hits a baseball with a bat and imparts an impulse J to the ball. The boy hits the ball again with
the same force, except that the ball and the bat are in contact for twice the amount of time as in the first
hit. The new impulse equals:
(A) half the original impulse (C) the original impulse
(B) twice the original impulse (D) four times the original impulse
41. A body of mass 3 kg collides elastically with another body at rest and then continues to move in the original
direction with one half of its original speed. What is the mass of the target body?
(A) 1 kg (B) 1.5 kg (C) 2 kg (D) 5 kg
42. Three blocks are initially placed as shown in the figure. Block 4 has mass and initial velocity v to the right.
Block B with mass m and block C with mass 4m are both initially at rest. Neglect friction. All collisions are
elastic. The final velocity of blocks 4 is
(A) 0.6v to the left
(B) 1.4v to the left
(C) v to the left
(D) 0.4v to the right
43. During collision between a closed system of particles, in the absence of external forces:
(A) The total kinetic energy of the system remains constant
(B) The momentum of each particle remains constant
(C) Momentum is exchanged between different particles
(D) Momentum and kinetic energy, both are exchanged between different particles.
44. Three particles of masses 1 kg, 2 kg and 3 kg are situated the corners of an equilateral triangle move at
speed 6 ms–1, 3 ms–1 and 2 ms–1 respectively. Each particle maintains a direction towards the particle at the
next corner symmetrically. Find velocity of CM of the system at this instant.
(A) 3 ms–1
(B) 6 ms–1
(C) 5 ms–1
(D) zero
45. Masses 8, 2, 4, 2 kg are placed at the corners A, B, C, D respectively of a square ABCD of diagonal 80 cm .
The distance of centre of mass from A will be
(A) 20 cm (B) 30 cm (C) 40 cm (D) 60 cm
Compiled by: Wesen G.
2016 E.C Page 5
You might also like
- Steven Weinberg - Foundations of Modern Physics-Cambridge University Press (2021)Document325 pagesSteven Weinberg - Foundations of Modern Physics-Cambridge University Press (2021)puceiroale100% (13)
- Test Bank For Physics For Scientists and Engineers 4th by KnightDocument27 pagesTest Bank For Physics For Scientists and Engineers 4th by Knightguyzunigaiadzrbpfes100% (27)
- DynamicsDocument8 pagesDynamicsSurafel BehailuNo ratings yet
- Kinematics PDFDocument7 pagesKinematics PDFBetseha MerawiNo ratings yet
- Cuestiones - T5Document4 pagesCuestiones - T5Ian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 11 Unit 4 WorksheetDocument14 pagesPhysics Grade 11 Unit 4 Worksheetsample nameNo ratings yet
- Dej/Wondirad Preparatory School: Physics UEE Compiled On Rotational Motion (2003-2011)Document5 pagesDej/Wondirad Preparatory School: Physics UEE Compiled On Rotational Motion (2003-2011)Eyuel EnitoNo ratings yet
- Dej/Wondirad Preparatory School: Physics UEE Compiled On Work, Energy and Power (2003-2011)Document4 pagesDej/Wondirad Preparatory School: Physics UEE Compiled On Work, Energy and Power (2003-2011)Eyuel Enito0% (1)
- MotionDocument17 pagesMotionJohnNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Physics Class XiDocument6 pagesSample Paper Physics Class XiBhaskar JhaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Chapter 9 Review SheetDocument9 pagesAP Physics Chapter 9 Review SheetEAGLEFORCE06No ratings yet
- Midterm Exam 2016 2017 01Document4 pagesMidterm Exam 2016 2017 01Bá Phong LêNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 2016-17 Quiz3Document6 pagesPhysics 1 2016-17 Quiz3Khoa TrầnNo ratings yet
- DP2 HL QPDocument26 pagesDP2 HL QPChinmay BhaveNo ratings yet
- Physics SolvedDocument16 pagesPhysics SolvedAbhijeet Singh PanwarNo ratings yet
- Lows of MotionDocument20 pagesLows of MotionSaswata Sundar LagaNo ratings yet
- DP2 SL QPDocument19 pagesDP2 SL QPChinmay BhaveNo ratings yet
- Physics Equilibrium QueDocument3 pagesPhysics Equilibrium QueLemi NegesoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 03 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 03 PDFVijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- Midterm Exam 2016-2017-01Document4 pagesMidterm Exam 2016-2017-01Gia Hân EmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions Uniform Circular Motion Newton S Law PF Gravitation and Rotational MotionDocument9 pagesChapter Questions Uniform Circular Motion Newton S Law PF Gravitation and Rotational MotionJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Practice Physics TestDocument7 pagesPractice Physics Testthey12No ratings yet
- Jee 2014 Booklet3 HWT Energy & MomentumDocument19 pagesJee 2014 Booklet3 HWT Energy & MomentumvarunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Practica IiDocument9 pagesPractica IiEduardo FernandezNo ratings yet
- NL CQ 6 SSPDocument4 pagesNL CQ 6 SSPGokul NathNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers 3rd Edition Knight Test BankDocument26 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers 3rd Edition Knight Test Bankdiemdac39kgkw100% (27)
- University of The Philippines College of Science: Name Section Student Number Set ADocument10 pagesUniversity of The Philippines College of Science: Name Section Student Number Set ASherylleen RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ForumDocument10 pagesForumfestus wikannandaNo ratings yet
- Exam 3a Rev QuesDocument35 pagesExam 3a Rev QuesUmesh Reddy100% (1)
- AP Physics C 2004 With AnswersDocument18 pagesAP Physics C 2004 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- End of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CDocument4 pagesEnd of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CChristina ZhangNo ratings yet
- Phy1121 Discussion Group September 24, 2014Document3 pagesPhy1121 Discussion Group September 24, 2014throwaway1609No ratings yet
- Part A - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesPart A - Multiple Choice QuestionsBryan SutantoNo ratings yet
- Physics 712 ND LE1 Stsem 20112012Document12 pagesPhysics 712 ND LE1 Stsem 20112012Alexis Julia CanariaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C MomentumDocument34 pagesAP Physics C MomentumShamanthakNo ratings yet
- NUS Physics PaperDocument6 pagesNUS Physics PaperBilin ZhuangNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument10 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionAlejandro Torrico MorenoNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1-HW1204Document4 pagesAP Physics 1-HW1204張晉嘉No ratings yet
- POW SAT-2 CoMDocument7 pagesPOW SAT-2 CoMLonely PotatoNo ratings yet
- Momentum and ImpulseDocument28 pagesMomentum and ImpulseAli AtwiNo ratings yet
- BB 2.0 - NLMDocument142 pagesBB 2.0 - NLMParthMaluNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Semester One MC Exam ReviewDocument6 pagesAP Physics Semester One MC Exam ReviewJordana BrenesNo ratings yet
- Soal Pembinaan Olimpiade Hari Ke-2Document5 pagesSoal Pembinaan Olimpiade Hari Ke-2IslahwaniLokaVitaRestiNo ratings yet
- SpringerDocument10 pagesSpringerMonico AlejoNo ratings yet
- 4 SJPO-2013-GenDocument19 pages4 SJPO-2013-Genronghui009No ratings yet
- MECH Multiple Choice 2004Document7 pagesMECH Multiple Choice 2004clarencetan95No ratings yet
- Practice Test 2Document7 pagesPractice Test 2Maria YurlovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Dynamic RevisionDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Dynamic Revision陈伟明No ratings yet
- Practice Momentum TestDocument5 pagesPractice Momentum TestKinalPatelNo ratings yet
- 2nd LE Sample ExamDocument13 pages2nd LE Sample ExamElla CardenasNo ratings yet
- Momentum and Impulse MC Practice ProblemsDocument10 pagesMomentum and Impulse MC Practice ProblemsJayNo ratings yet
- Trialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionDocument6 pagesTrialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionMathew Cheng Yu HaoNo ratings yet
- Physics 6Document20 pagesPhysics 6Kazuto ShibaNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Newtons Laws ReviewDocument6 pagesDay 2 Newtons Laws Reviewnoel castilloNo ratings yet
- Application of Newton's Second Law: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Painter On A PlatformDocument9 pagesApplication of Newton's Second Law: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Painter On A PlatformBoldie LutwigNo ratings yet
- (A) 2 KG, (6 M/S) IDocument10 pages(A) 2 KG, (6 M/S) Ikush jindalNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam A1Document3 pagesMidterm Exam A1Bá Phong LêNo ratings yet
- Unit I and Unit II Multiple Choice Practice TestDocument11 pagesUnit I and Unit II Multiple Choice Practice TestChristian Firsching0% (1)
- Aits 2223 FT Vi Jeem OfflineDocument15 pagesAits 2223 FT Vi Jeem OfflineSuvrajyoti TaraphdarNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena Introduction and First Law of Thermodynamics: Unit-I Philosophy and Fundamentals of Transport PhenomenaDocument11 pagesTransport Phenomena Introduction and First Law of Thermodynamics: Unit-I Philosophy and Fundamentals of Transport PhenomenaSivakumarNo ratings yet
- Mock Ext. P2 For S4 2017.Document6 pagesMock Ext. P2 For S4 2017.cyber secNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms (Magnetism)Document4 pagesDefinition of Terms (Magnetism)Teresa PulgaNo ratings yet
- AEP 3330 Final - Some EquationsDocument1 pageAEP 3330 Final - Some EquationsJesse ZhangNo ratings yet
- APPENDIX-5.2 ISO 5802 - Circular Traverse Measure PointDocument3 pagesAPPENDIX-5.2 ISO 5802 - Circular Traverse Measure PointLâm trầnNo ratings yet
- CHEM 474 - Lecture 1 NotesDocument11 pagesCHEM 474 - Lecture 1 NotesjeannietranNo ratings yet
- IAL Unit 5 Edexcel NotesDocument27 pagesIAL Unit 5 Edexcel NotesThangavel SarujanNo ratings yet
- Spintronics Device 22053502 b26Document2 pagesSpintronics Device 22053502 b26AYUSHKA NANDANo ratings yet
- 17 LectureslidesDocument154 pages17 LectureslidesAlinaBogoiNo ratings yet
- 03 Translation MatricesDocument8 pages03 Translation MatricessolteanNo ratings yet
- Simulating Chemistry On A Quantum ComputerDocument52 pagesSimulating Chemistry On A Quantum ComputerShilpi JainNo ratings yet
- TS - SR - Physics - Imp - Questions 2022-23Document5 pagesTS - SR - Physics - Imp - Questions 2022-23Kota ๖ۣۜRαkͥesͣhͫ0% (1)
- Introduction Phy370Document2 pagesIntroduction Phy370Taehyung KimNo ratings yet
- 7.2 The Particle Theory of Matter AnswerDocument6 pages7.2 The Particle Theory of Matter AnswerMatthew ScherbatyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - FluidDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - Fluidfieyza adnNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School (Joka) South Kolkata SYLLABUS - 2020-2021 Class Xi PhysicsDocument3 pagesDelhi Public School (Joka) South Kolkata SYLLABUS - 2020-2021 Class Xi PhysicsMalNo ratings yet
- Department of Physics: Lab Report of GM Counter ExperimentDocument10 pagesDepartment of Physics: Lab Report of GM Counter ExperimentHaidar AliNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Quiz 1: Energy Bands ECE 606: Solid State DevicesDocument2 pagesWeek 3 Quiz 1: Energy Bands ECE 606: Solid State DevicesASHISH KUSHWAHANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11-1Document20 pagesChapter 11-1Tsiye TekleyohanisNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Formula Sheet (Coaching)Document42 pagesClass 12 Physics Formula Sheet (Coaching)Atharva Maheshwari100% (1)
- Betatron 1Document3 pagesBetatron 1dileepNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Phy 281-1Document22 pagesLecture Notes - Phy 281-1Muhammed AbdulsalamNo ratings yet
- 7 Marking Scheme: Worksheet: P V NRT P 1.22 × 10 PV NRT y PVDocument3 pages7 Marking Scheme: Worksheet: P V NRT P 1.22 × 10 PV NRT y PVН. НаранцацралтNo ratings yet
- Baao 2018Document11 pagesBaao 2018physicsolympiad19No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Differential Equations PDFDocument15 pagesChapter 7 Differential Equations PDFfahmi100% (1)
- Robitaille, P.-M., Blackbody Radiation and The Loss of Universality - Implications For Planck's Formulation and Boltzman's ConstantDocument3 pagesRobitaille, P.-M., Blackbody Radiation and The Loss of Universality - Implications For Planck's Formulation and Boltzman's ConstantDrenko MarićNo ratings yet
- PNP Handout3Document62 pagesPNP Handout3Anil HirparaNo ratings yet
- Notes - Matter in Our Surroundings - ExpDocument6 pagesNotes - Matter in Our Surroundings - Expdeborah hildaNo ratings yet