Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsNotes 5.4b
Notes 5.4b
Uploaded by
snezrobloxCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Unit Exam 7Document7 pagesUnit Exam 7Brix Mendoza20% (5)
- Navigation QuestionsDocument237 pagesNavigation QuestionsDIP75% (8)
- 1 Physics1Document16 pages1 Physics1Jason ToddNo ratings yet
- Warm Up: 1. Identify The Pairs of AlternateDocument27 pagesWarm Up: 1. Identify The Pairs of AlternateRavin BoodhanNo ratings yet
- Angles of Elevation and DepressionDocument27 pagesAngles of Elevation and DepressionShivSantosh JhaNo ratings yet
- 11 3 Angles of Elevation and DepressionDocument27 pages11 3 Angles of Elevation and DepressiongiyagirlsNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument7 pagesThis Study Resource WasJamED ALRubioNo ratings yet
- Traverse LectDocument9 pagesTraverse LectratbatcatNo ratings yet
- Geospatial Positioning System - 1Document72 pagesGeospatial Positioning System - 1Jecinta wNo ratings yet
- Application of Spherical TrigonometryDocument17 pagesApplication of Spherical TrigonometryAlfred Cyrus Redulfin100% (1)
- QUIZ #1-A (Introduction, Distance, Correction and Leveling)Document3 pagesQUIZ #1-A (Introduction, Distance, Correction and Leveling)nonononowayNo ratings yet
- Textbook-Right Tri TrigDocument7 pagesTextbook-Right Tri Trigapi-251889735No ratings yet
- Spherical TrigonometryDocument9 pagesSpherical TrigonometryVlaire Janrex LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Ppt-Mathematics 9 (4thQ)Document24 pagesWeek 1 Ppt-Mathematics 9 (4thQ)Rosa Villaluz BanairaNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week2Document24 pagesQ4 Week2khatejazmine.gaudia0414No ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document6 pagesProblem Set 1Danzyl VillatemaNo ratings yet
- Surveying ReviewerDocument7 pagesSurveying ReviewerJin Eve AveNo ratings yet
- Measurement of DistancesDocument6 pagesMeasurement of Distancesvaniedude5No ratings yet
- Triangulation SurveysDocument37 pagesTriangulation Surveysxuseen maxamedNo ratings yet
- 061 - General Navigation - QuestionsDocument47 pages061 - General Navigation - QuestionsEASA ATPL Question Bank100% (5)
- Question Surveying IIDocument7 pagesQuestion Surveying IIahzamshadabNo ratings yet
- Remedial Test (Just The Answers)Document13 pagesRemedial Test (Just The Answers)lornehessNo ratings yet
- Deflection Angle TraverseDocument5 pagesDeflection Angle TraverseJustine BotillaNo ratings yet
- Review Test 1-Questions2018Document4 pagesReview Test 1-Questions2018tanjiayiNo ratings yet
- Deflection, CompoundDocument27 pagesDeflection, CompoundNheilbertNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 - Position On The EarthDocument10 pagesChapter 02 - Position On The EarthIludiran Kola100% (1)
- Math12 - L3 (Solutions of Right Triangles)Document12 pagesMath12 - L3 (Solutions of Right Triangles)Lisa GarciaNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Revision Trigonometry and Non Linear Curve Sketching HW HandoutDocument9 pagesYear 9 Revision Trigonometry and Non Linear Curve Sketching HW HandoutMusab AlbarbariNo ratings yet
- Topic 2. Errors in MeasurementsDocument31 pagesTopic 2. Errors in MeasurementsHans GeronNo ratings yet
- GEng 111g - TutorialDocument25 pagesGEng 111g - TutorialRomnick MalulanNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Lecture One: Bachelor of Software EngineeringDocument16 pagesTrigonometry Lecture One: Bachelor of Software EngineeringSuhleem AhmédNo ratings yet
- Navigation Question Bank: The EarthDocument237 pagesNavigation Question Bank: The Earthreethu reddyNo ratings yet
- Earth Geometry-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-2Document7 pagesEarth Geometry-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-2Daniel GomaNo ratings yet
- Field Work No. 8 Determination of The Height of A Remote PointDocument9 pagesField Work No. 8 Determination of The Height of A Remote PointMikaella TambisNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Traverse SurveyDocument6 pagesWeek 4 Traverse SurveyMike FruelNo ratings yet
- Day 6 - Plane and Spherical Trigonometry L Take Home ProblemsDocument4 pagesDay 6 - Plane and Spherical Trigonometry L Take Home ProblemsJohn LuNo ratings yet
- MTH 202 Course MaterialDocument88 pagesMTH 202 Course MaterialSakote Tobiloba IsaacNo ratings yet
- Earth QuestionsDocument7 pagesEarth QuestionsPrashanti MenonNo ratings yet
- Preboard 2 TNP 2022Document8 pagesPreboard 2 TNP 2022Christorey MontegrandeNo ratings yet
- Earth GeometryDocument9 pagesEarth GeometryMwansa100% (2)
- Law of SinesDocument10 pagesLaw of SinesVeronika SinghNo ratings yet
- Trigo PreboardDocument26 pagesTrigo PreboardMichael Beltran100% (1)
- 8-5 Angle of Elevation DepressionDocument12 pages8-5 Angle of Elevation Depressionrendycap_20No ratings yet
- Bsed Math 3Document2 pagesBsed Math 3Vince Leo Panoncillon GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Trigo AnalyticDocument3 pagesTrigo AnalyticDani LubosNo ratings yet
- Plates PDFDocument13 pagesPlates PDFCRIISSY100% (1)
- Rectangulation - Field Survey ExperimentDocument3 pagesRectangulation - Field Survey ExperimentGowtham AmirNo ratings yet
- DirectionsDocument8 pagesDirectionsJyoti vermaNo ratings yet
- Sines and CosinesDocument24 pagesSines and CosinesJanella Joyce AsinasNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Theodolite, Traversing by Theodolite, Error in TraversingDocument26 pagesIntroduction of Theodolite, Traversing by Theodolite, Error in TraversingRaju Sharma81% (27)
- TrigonometryDocument4 pagesTrigonometrydayatNo ratings yet
- Control Surveying RDocument84 pagesControl Surveying REricka Louis SilisilonNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry ReviewDocument6 pagesTrigonometry Reviewwarlito floresNo ratings yet
- 未命名 3Document6 pages未命名 3madokakamidesuNo ratings yet
- Error CorrectionsDocument36 pagesError Correctionsfrancis baldonado0% (1)
- CE G2 Module No. 2 TrigonometryDocument1 pageCE G2 Module No. 2 TrigonometryDaniela CaguioaNo ratings yet
- Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument4 pagesIdentify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Questionrainel reyesNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersFrom EverandHandbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersNo ratings yet
Notes 5.4b
Notes 5.4b
Uploaded by
snezroblox0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesOriginal Title
notes_5.4b
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesNotes 5.4b
Notes 5.4b
Uploaded by
snezrobloxCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
When a single angle is given, such as 164°, it is understood
that the bearing is measured in a clockwise direction from due
north.
The second method for expressing bearing starts with a north
south line and uses an acute angle to show the direction, either
east or west, from this line.
Example 4 SOLVING A PROBLEM INVOLVING
BEARING (FIRST METHOD)
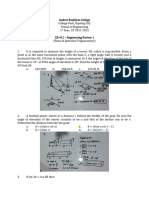
Radar stations A and B are on an eastwest line, 3.7 km apart.
Station A detects a plane at C, on a bearing on 61°. Station B
simultaneously detects the same plane, on a bearing of 331°. Find
the distance from A to C.
Example 5 SOLVING PROBLEM INVOLVING
BEARING (SECOND METHOD)
The bearing from A to C is S 52° E. The bearing from A to B is N
84° E. The bearing from B to C is S 38° W. A plane flying at 250 mph
takes 2.4 hours to go from A to B. Find the distance from A to C.
Example 6 USING TRIGONOMETRY TO MEASURE A
DISTANCE
A method that surveyors use to determine a small distance d
between two points P and Q is called the subtense bar method.
The subtense bar with length b is centered at Q and situated
perpendicular to the line of sight between P and Q. Angle θ is
measured, then the distance d can be determined.
(a) Find d with θ = 1°23′12″ and b = 2.0000 cm.
Example 6 USING TRIGONOMETRY TO MEASURE A
DISTANCE (continued)
(b) Angle θ usually cannot be measured more accurately than to the
nearest 1″. How much change would there be in the value of d if θ
were measured 1″ larger?
Example 4 SOLVING A PROBLEM INVOLVING
ANGLES OF ELEVATION
From a given point on the ground, the angle of elevation to the top
of a tree is 36.7°. From a second point, 50 feet back, the angle of
elevation to the top of the tree is 22.2°. Find the height of the tree
to the nearest foot.
Example 7 SOLVING A PROBLEM INVOLVING
ANGLES OF ELEVATION (continued)
Graphing Calculator Solution
You might also like
- Unit Exam 7Document7 pagesUnit Exam 7Brix Mendoza20% (5)
- Navigation QuestionsDocument237 pagesNavigation QuestionsDIP75% (8)
- 1 Physics1Document16 pages1 Physics1Jason ToddNo ratings yet
- Warm Up: 1. Identify The Pairs of AlternateDocument27 pagesWarm Up: 1. Identify The Pairs of AlternateRavin BoodhanNo ratings yet
- Angles of Elevation and DepressionDocument27 pagesAngles of Elevation and DepressionShivSantosh JhaNo ratings yet
- 11 3 Angles of Elevation and DepressionDocument27 pages11 3 Angles of Elevation and DepressiongiyagirlsNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument7 pagesThis Study Resource WasJamED ALRubioNo ratings yet
- Traverse LectDocument9 pagesTraverse LectratbatcatNo ratings yet
- Geospatial Positioning System - 1Document72 pagesGeospatial Positioning System - 1Jecinta wNo ratings yet
- Application of Spherical TrigonometryDocument17 pagesApplication of Spherical TrigonometryAlfred Cyrus Redulfin100% (1)
- QUIZ #1-A (Introduction, Distance, Correction and Leveling)Document3 pagesQUIZ #1-A (Introduction, Distance, Correction and Leveling)nonononowayNo ratings yet
- Textbook-Right Tri TrigDocument7 pagesTextbook-Right Tri Trigapi-251889735No ratings yet
- Spherical TrigonometryDocument9 pagesSpherical TrigonometryVlaire Janrex LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Ppt-Mathematics 9 (4thQ)Document24 pagesWeek 1 Ppt-Mathematics 9 (4thQ)Rosa Villaluz BanairaNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week2Document24 pagesQ4 Week2khatejazmine.gaudia0414No ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document6 pagesProblem Set 1Danzyl VillatemaNo ratings yet
- Surveying ReviewerDocument7 pagesSurveying ReviewerJin Eve AveNo ratings yet
- Measurement of DistancesDocument6 pagesMeasurement of Distancesvaniedude5No ratings yet
- Triangulation SurveysDocument37 pagesTriangulation Surveysxuseen maxamedNo ratings yet
- 061 - General Navigation - QuestionsDocument47 pages061 - General Navigation - QuestionsEASA ATPL Question Bank100% (5)
- Question Surveying IIDocument7 pagesQuestion Surveying IIahzamshadabNo ratings yet
- Remedial Test (Just The Answers)Document13 pagesRemedial Test (Just The Answers)lornehessNo ratings yet
- Deflection Angle TraverseDocument5 pagesDeflection Angle TraverseJustine BotillaNo ratings yet
- Review Test 1-Questions2018Document4 pagesReview Test 1-Questions2018tanjiayiNo ratings yet
- Deflection, CompoundDocument27 pagesDeflection, CompoundNheilbertNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 - Position On The EarthDocument10 pagesChapter 02 - Position On The EarthIludiran Kola100% (1)
- Math12 - L3 (Solutions of Right Triangles)Document12 pagesMath12 - L3 (Solutions of Right Triangles)Lisa GarciaNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Revision Trigonometry and Non Linear Curve Sketching HW HandoutDocument9 pagesYear 9 Revision Trigonometry and Non Linear Curve Sketching HW HandoutMusab AlbarbariNo ratings yet
- Topic 2. Errors in MeasurementsDocument31 pagesTopic 2. Errors in MeasurementsHans GeronNo ratings yet
- GEng 111g - TutorialDocument25 pagesGEng 111g - TutorialRomnick MalulanNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Lecture One: Bachelor of Software EngineeringDocument16 pagesTrigonometry Lecture One: Bachelor of Software EngineeringSuhleem AhmédNo ratings yet
- Navigation Question Bank: The EarthDocument237 pagesNavigation Question Bank: The Earthreethu reddyNo ratings yet
- Earth Geometry-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-2Document7 pagesEarth Geometry-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-2Daniel GomaNo ratings yet
- Field Work No. 8 Determination of The Height of A Remote PointDocument9 pagesField Work No. 8 Determination of The Height of A Remote PointMikaella TambisNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Traverse SurveyDocument6 pagesWeek 4 Traverse SurveyMike FruelNo ratings yet
- Day 6 - Plane and Spherical Trigonometry L Take Home ProblemsDocument4 pagesDay 6 - Plane and Spherical Trigonometry L Take Home ProblemsJohn LuNo ratings yet
- MTH 202 Course MaterialDocument88 pagesMTH 202 Course MaterialSakote Tobiloba IsaacNo ratings yet
- Earth QuestionsDocument7 pagesEarth QuestionsPrashanti MenonNo ratings yet
- Preboard 2 TNP 2022Document8 pagesPreboard 2 TNP 2022Christorey MontegrandeNo ratings yet
- Earth GeometryDocument9 pagesEarth GeometryMwansa100% (2)
- Law of SinesDocument10 pagesLaw of SinesVeronika SinghNo ratings yet
- Trigo PreboardDocument26 pagesTrigo PreboardMichael Beltran100% (1)
- 8-5 Angle of Elevation DepressionDocument12 pages8-5 Angle of Elevation Depressionrendycap_20No ratings yet
- Bsed Math 3Document2 pagesBsed Math 3Vince Leo Panoncillon GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Trigo AnalyticDocument3 pagesTrigo AnalyticDani LubosNo ratings yet
- Plates PDFDocument13 pagesPlates PDFCRIISSY100% (1)
- Rectangulation - Field Survey ExperimentDocument3 pagesRectangulation - Field Survey ExperimentGowtham AmirNo ratings yet
- DirectionsDocument8 pagesDirectionsJyoti vermaNo ratings yet
- Sines and CosinesDocument24 pagesSines and CosinesJanella Joyce AsinasNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Theodolite, Traversing by Theodolite, Error in TraversingDocument26 pagesIntroduction of Theodolite, Traversing by Theodolite, Error in TraversingRaju Sharma81% (27)
- TrigonometryDocument4 pagesTrigonometrydayatNo ratings yet
- Control Surveying RDocument84 pagesControl Surveying REricka Louis SilisilonNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry ReviewDocument6 pagesTrigonometry Reviewwarlito floresNo ratings yet
- 未命名 3Document6 pages未命名 3madokakamidesuNo ratings yet
- Error CorrectionsDocument36 pagesError Correctionsfrancis baldonado0% (1)
- CE G2 Module No. 2 TrigonometryDocument1 pageCE G2 Module No. 2 TrigonometryDaniela CaguioaNo ratings yet
- Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument4 pagesIdentify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Questionrainel reyesNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersFrom EverandHandbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersNo ratings yet