Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LP Cot2 - 1 2023-2024
LP Cot2 - 1 2023-2024
Uploaded by
Oliver ToquiroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LP Cot2 - 1 2023-2024
LP Cot2 - 1 2023-2024
Uploaded by
Oliver ToquiroCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Plan for Statistics and Probability
AY: 2023-2024 (2nd Semester)
I. Objectives: At the end of the 0ne (1) hour lesson, the Grade 11 shall be able to:
Cognitive Domain Illustrate a random variable (discrete and continuous) M11/12SP-IIIa-1
Affective Domain distinguishes between a discrete and a continuous
random variable. M11/12SP-IIIa-2
Psychomotor finds the possible values of a random variable. M11/12SP-IIIa-3
Domain
Topic/Lesson Exploring Random Variables
A. References Statistics and Probability by: Elisa S. Bacay & Rene R. Belecina, p. 2 - 8
B. Value Focus Fairness and Justice
C. Instructional PowerPoint presentation, LED TV, Laptop
Materials
D. Teaching Creative and Critical Thinking. Engaging students during the lecture times, and facilitating student success as an effort to
Philosophy maintain the field of applied mathematics and statistics as an interesting and applicable discipline.
II. Procedures
Parts of the Lesson Teacher’s Activity Students’ Responses RPMS-PPST Indicators
2.1 Introductory 1. Prayer
Activity 2. Checking of attendance.
3. Ask:
Have tried to order items online? Yes, sir.
How sure are you that your order is ok? Answers vary
Unlocking of Definition of Terms: Objective 2
Difficulties 1. Random variable – is a function that associates a 1.4.2 (Used a range of teaching
real number to each element in the sample space. It is a strategies that enhance learner
variable whose values are determined by chance. achievement in literacy and
2. Discrete random variable - A random variable is numeracy skills.)
a discrete random variable if its set of possible
outcomes is countable. Mostly, discrete random
variables represent count data, such as the
number of defective chairs produced in a factory.
3. Continuous random variable – a random
variable is a continuous random variable if it
takes on values on a continuous scale. Often,
continuous random variables represent
measured data, such as heights, weights, and
temperatures.
II.2 Activity Divide the class into three groups.
(the class perform the Objective 8
Give out activity sheet. One activity per group. activity) 3.5.2 (Adapted and used
(refer to activity sheet) culturally appropriate teaching
strategies to address the needs
of learners from indigenous
groups)
Objective 1
1.1.2 (Applied knowledge of
content within and across
curriculum teaching areas) –
ICT TLE
2.3 Analysis Analyze the activity using the following questions:
a) In Activity 1, what variable is determined? Variable X Objective 3
b) What are the possible values of random variable X 0, 1, 2, 3 1.5.2 (Applied a range of
c) In Activity 2, what variable is determined? Variable Y teaching strategies to develop
d) What are the possible values of random variable Y 0, 1, 2, 3 critical and creative thinking, as
e) In Activity 3, what variable is determined? Variable Z well as other higher-order
f) What are the possible values of random variable Z 0, 1, 2, 3 thinking skills.) –
g) Are activities 1, 2 & 3 are similar? Yes, sir.
h) What kind of random variable is described in the Objective 7
activities? Discrete random variable 3.2.2 (Established a learner-
centered culture by using
Further discussion: teaching strategies that respond
Suppose an experiment is conducted to determine the to their linguistic, cultural,
distance that a certain type of car will travel using 10 liters socioeconomic and religious
of gasoline over a prescribed test course. If the distance is backgrounds.) –
random variable, then we have infinite number of
distances that cannot be equated to the number of whole
numbers. Continuous random variable
What kind of random variable is the experiment?
4.4 Abstraction a) How do you describe a discrete random variable? A random variable is a discrete
random variable if its set of possible
outcomes is countable. Mostly,
discrete random variables represent
count data, such as the number of
defective chairs produced in a
factory.
b) How do you describe a continuous random
variable? A random variable is a continuous
random variable if it takes on values
on a continuous scale. Often,
continuous random variables
represent measured data, such as
heights, weights, and temperatures.
4.5 Application Which of the following experiment is a discrete random Objective 10
variable and a continuous random variable? 5.3.2 (Used strategies for
a. The number of defects in a batch of 100 providing timely, accurate and
constructive feedback to
manufactured products
improve learner performance.)
b. The researcher needs to find participants with a
body fat percentage between 20 and 24 percent.
c. The number of items sold at a store on a certain Objective 7
day 3.2.2 (Established a learner-
d. The sum of the outcomes on rolling two dice centered culture by using
e. The height of an adult male or female. teaching strategies that respond
to their linguistic, cultural,
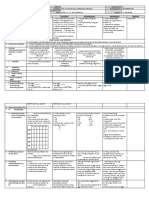
4.6 Assessment Four coins are tossed. Let Z be the random variable
socioeconomic and religious
representing the number of heads that turn up. Find the
values of the random variable Z. backgrounds.)
Possible Outcomes Value of the Random
Variable Z
4.7 Assignment From a box containing 4 black balls and 2 green balls, 3
balls are drawn in succession. Each ball is placed back in
the box before the next draw is made. Let G be a random
variable representing the number of green balls that can be
drawn. Find the values of the random variable G.
Possible Outcomes Value of the Random
Variable G
Prepared by: Checked by:
OLIVER T. ABABA NERELIA L. ALPON, PhD
Teacher III Master Teacher I
You might also like
- DAILY LESSON LOG OF M11GM-Ia-1 & 2 (Week One-Day One) : Facebook Instagram Twitter Social MediaDocument4 pagesDAILY LESSON LOG OF M11GM-Ia-1 & 2 (Week One-Day One) : Facebook Instagram Twitter Social MediaGladzangel Loricabv33% (3)
- Journal 6 2 FinalDocument392 pagesJournal 6 2 FinalFranz ChoqueNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4: I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesDay 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4: I. Objectivesariel a. ortizNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: Statistics AND ProbabilityDocument4 pagesSession 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: Statistics AND ProbabilityEloiza Jane OrdenizaNo ratings yet
- DLL Gen Math Week 6Document6 pagesDLL Gen Math Week 6Ram GazerNo ratings yet
- MATH G11 GM I Day 19Document9 pagesMATH G11 GM I Day 19Marisa NiezNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: Statistics AND ProbabilityDocument4 pagesSession 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: Statistics AND ProbabilityEloiza Jane OrdenizaNo ratings yet
- Stat 1Document4 pagesStat 1demrick100% (1)
- Week 4 Day 1 (Lesson 9)Document4 pagesWeek 4 Day 1 (Lesson 9)PatzAlzateParaguyaNo ratings yet
- DAILY LESSON LOG OF M11GM-Ia-1 & 2 (Week One-Day One) : Facebook Instagram Twitter Social MediaDocument4 pagesDAILY LESSON LOG OF M11GM-Ia-1 & 2 (Week One-Day One) : Facebook Instagram Twitter Social MediaLoreen RoaNo ratings yet
- 2023 2024 Cot 1 Q1 Week 4 Math 6 Detailed Lesson PlanDocument6 pages2023 2024 Cot 1 Q1 Week 4 Math 6 Detailed Lesson PlanMARY ERESA VENZON100% (1)
- G11 Qi Week4Document5 pagesG11 Qi Week4MAYLENE VILLAROSANo ratings yet
- LP For Disabilities, Giftedness, TalentedDocument11 pagesLP For Disabilities, Giftedness, TalentedAlma Mae PutongNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: Statistics AND ProbabilityDocument4 pagesSession 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: Statistics AND ProbabilityEloiza Jane OrdenizaNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : Grade Level:11/12 Learning Competency/IesDocument2 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : Grade Level:11/12 Learning Competency/IesbethNo ratings yet
- DAILY LESSON LOG OF M11GM-Ia-1 & 2 (Week One-Day One) : Facebook Instagram Twitter Social MediaDocument4 pagesDAILY LESSON LOG OF M11GM-Ia-1 & 2 (Week One-Day One) : Facebook Instagram Twitter Social MediaAmanie Usman Amanoddin100% (2)
- Week 4 Day 1 (Lesson 9)Document5 pagesWeek 4 Day 1 (Lesson 9)Lj RafalesNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Learning Planner 1-24 BLANKDocument97 pagesMathematics Learning Planner 1-24 BLANKxgvfqgc7xpNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Average Speed COT 1Document7 pagesLesson Plan in Average Speed COT 1Jhuneanne Mutia Caburnay-LirazanNo ratings yet
- DLP 9Document1 pageDLP 9Erwin B. NavarroNo ratings yet
- I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesI. ObjectivesFRECY MARZANNo ratings yet
- Stat 2Document6 pagesStat 2demrickNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document14 pagesWeek 1Jay Jay h. JantarNo ratings yet
- DLL Gen Math Week 6Document6 pagesDLL Gen Math Week 6Jessa AñanaNo ratings yet
- MATH G11 GM I Day 1Document3 pagesMATH G11 GM I Day 1AJ Diawara CusayNo ratings yet
- DLP CustomformatDocument14 pagesDLP CustomformatJohn Niño BangaNo ratings yet
- SP Iii-8Document3 pagesSP Iii-8Antonio SearesNo ratings yet
- Objectives: School: Grade Level: Teacher: Learning AreaDocument3 pagesObjectives: School: Grade Level: Teacher: Learning AreaRoselyn VecinalNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Day 1 (Lesson 9)Document5 pagesWeek 4 Day 1 (Lesson 9)Vanissa Bianca S. LlanosNo ratings yet
- Detailed Instructional Plan (Iplan) : Grade Level:11/12 Learning Competency/IesDocument3 pagesDetailed Instructional Plan (Iplan) : Grade Level:11/12 Learning Competency/IesbethNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Davao University: Welcome To Statistics and Probability Subject!Document13 pagesAteneo de Davao University: Welcome To Statistics and Probability Subject!Kyle BARRIOSNo ratings yet
- DLL - Gen Math-Week 4Document5 pagesDLL - Gen Math-Week 4Jennelyn JacintoNo ratings yet
- I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesI. ObjectivesFRECY MARZANNo ratings yet
- Teaching PhilosophyDocument11 pagesTeaching PhilosophyAlma Mae PutongNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: Statistics AND ProbabilityDocument4 pagesSession 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: Statistics AND ProbabilityEloiza Jane OrdenizaNo ratings yet
- DLL Gen Math Week 9Document5 pagesDLL Gen Math Week 9Ram GazerNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningLily Anne Ramos Mendoza100% (1)
- LDM Output RoselynDocument59 pagesLDM Output Roselynlbaldomar1969502No ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 5 - Q1 - W3Document9 pagesDLL - Mathematics 5 - Q1 - W3Maria Shimbha MarquezNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 5 q1 w3Document9 pagesDLL Mathematics 5 q1 w3Tony Hernandez0% (1)
- Gen Math - Lesson1&2Document5 pagesGen Math - Lesson1&2Gladzangel LoricabvNo ratings yet
- Elective Maths Syllabus (1) 11 18Document8 pagesElective Maths Syllabus (1) 11 18em81256No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Statistics Week 1Document14 pagesLesson Plan in Statistics Week 1Marvin MacanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Resource Package: Quarter IDocument8 pagesMathematics Resource Package: Quarter IMarie ParkNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3Rishabh MelwankiNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Learning Competency/ies: CodeDocument1 pageDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Learning Competency/ies: CodeDan Albert AbesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For ListeningDocument2 pagesLesson Plan For ListeningJay NamodNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document16 pagesWeek 2Coco LlameraNo ratings yet
- Unit Planner - Fractions - Y15Document6 pagesUnit Planner - Fractions - Y15Deema El MasriNo ratings yet
- LPstat&Prob KoDocument6 pagesLPstat&Prob KoMikael Zohan UngkayNo ratings yet
- SP Iii-2Document10 pagesSP Iii-2DIOMEDIS POLLESCASNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: Let The Students Define The Terms and Count The Sample Space and Determine The ProbabilitiesDocument5 pagesI. Objectives: Let The Students Define The Terms and Count The Sample Space and Determine The ProbabilitiesRichilien Teneso100% (3)
- LP Math7 W1Document3 pagesLP Math7 W1Mary Ann EspendeNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 5 - Q1 - W3Document9 pagesDLL - Mathematics 5 - Q1 - W3michelle milleondagaNo ratings yet
- Smasee Inset Sample Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesSmasee Inset Sample Lesson PlanbezawitwubshetNo ratings yet
- DLP 5Document3 pagesDLP 5Therence UbasNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document17 pagesWeek 2Jay Jay h. JantarNo ratings yet
- Salic-Long Quiz - ED EL 110Document5 pagesSalic-Long Quiz - ED EL 110HafsahNo ratings yet
- Objectives: School: Grade Level: Teacher: Learning Area: Teaching Dates and Time: QuarterDocument3 pagesObjectives: School: Grade Level: Teacher: Learning Area: Teaching Dates and Time: QuarterMaejoy Locagbo PedNo ratings yet
- Values Education Lesson Plan 1Document2 pagesValues Education Lesson Plan 1Oliver ToquiroNo ratings yet
- Research ManualDocument57 pagesResearch ManualOliver ToquiroNo ratings yet
- Stories and Verses About Kindness - English CuF - Jan - 19 24Document10 pagesStories and Verses About Kindness - English CuF - Jan - 19 24Oliver ToquiroNo ratings yet
- OLC - Illustrating Quadrating EquationsDocument3 pagesOLC - Illustrating Quadrating EquationsOliver ToquiroNo ratings yet
- Script For Illustrating Quadratic EquationsDocument1 pageScript For Illustrating Quadratic EquationsOliver ToquiroNo ratings yet
- Don2 ResumeDocument2 pagesDon2 ResumeOliver ToquiroNo ratings yet
- Botany Assignment MUHSIN K P - 872Document9 pagesBotany Assignment MUHSIN K P - 872muhsinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SolutionsDocument134 pagesChapter 2 Solutionsapi-209868636No ratings yet
- Author Literally Writes The Book On Band NerdsDocument3 pagesAuthor Literally Writes The Book On Band NerdsPR.comNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1, Macroeconomics 2016-2017Document3 pagesAssignment 1, Macroeconomics 2016-2017Laurenţiu-Cristian CiobotaruNo ratings yet
- Tans - Aqueous Ammonium Sulfate - 1958Document2 pagesTans - Aqueous Ammonium Sulfate - 1958Yulia Kurniawati100% (1)
- The MelancholicDocument5 pagesThe MelancholicJohn Albert LogoNo ratings yet
- Tesis NeuromarketingDocument124 pagesTesis NeuromarketingAlicia TorresNo ratings yet
- LIFE WITHIN RUINS - Call For Paper - Reviewer - Chiacchiera - ReviewedDocument4 pagesLIFE WITHIN RUINS - Call For Paper - Reviewer - Chiacchiera - ReviewedFrancesco ChiacchieraNo ratings yet
- Peliculas de YouTube Anotadas Dec 2014 VDocument202 pagesPeliculas de YouTube Anotadas Dec 2014 VVladimir IlichNo ratings yet
- Clarinet Scales PracticeDocument3 pagesClarinet Scales Practicefj_pastorNo ratings yet
- Sythesization and Purification of Acetanilide by Acetylation and Re CrystallizationDocument4 pagesSythesization and Purification of Acetanilide by Acetylation and Re CrystallizationToni Sy EncinaresNo ratings yet
- MCS-Transfer Pricing - FinalDocument74 pagesMCS-Transfer Pricing - FinalHarsh N. DhruvaNo ratings yet
- Auto-Reclose On Distribution NetworksDocument57 pagesAuto-Reclose On Distribution NetworksNeelakandan MasilamaniNo ratings yet
- Curacen EssenceDocument21 pagesCuracen Essencerebainaceur1955No ratings yet
- Fashion - PortfolioDocument99 pagesFashion - PortfolioPalak ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document13 pagesLesson 2Hanna CaraigNo ratings yet
- Food Biotechnology Sports NutritionDocument14 pagesFood Biotechnology Sports NutritionAngelo PalmeroNo ratings yet
- Aditing II Q From CH 3,4,5Document2 pagesAditing II Q From CH 3,4,5samuel debebeNo ratings yet
- The New Yorker - 29 06 2020 PDFDocument72 pagesThe New Yorker - 29 06 2020 PDFMilena SlivoskaNo ratings yet
- Paradigm 10 of The New Paradigms of Communication in The Digital WorldDocument16 pagesParadigm 10 of The New Paradigms of Communication in The Digital Worldchimken0812No ratings yet
- ADSArbDocument12 pagesADSArbStephan HardisonNo ratings yet
- The Marketing Management Process: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument37 pagesThe Marketing Management Process: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwinmuhammad yusufNo ratings yet
- Index Construction MethodologyDocument6 pagesIndex Construction MethodologyBadhandasNo ratings yet
- Calcinosis Involving Multiple Paws in A Cat With Chronic Renal Failure and in A Cat With Hyperthyroidism (Pages 74-78)Document5 pagesCalcinosis Involving Multiple Paws in A Cat With Chronic Renal Failure and in A Cat With Hyperthyroidism (Pages 74-78)jenNo ratings yet
- PronunciationDocument54 pagesPronunciationsddadhak90% (20)
- Adriyanmahmoudi 168hourassignmentDocument3 pagesAdriyanmahmoudi 168hourassignmentapi-528485357No ratings yet
- Touchdown PCR PDFDocument6 pagesTouchdown PCR PDFMatheusRsaNo ratings yet
- Land Tenure Information and Land PolicyDocument33 pagesLand Tenure Information and Land PolicyMunirudeen RajiNo ratings yet