Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GROUP 4 - Maxillofacial Prosthodontics
GROUP 4 - Maxillofacial Prosthodontics
Uploaded by
20182141Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Maxillofacial Prosthodontics CourseDocument98 pagesMaxillofacial Prosthodontics CourseFBI LUC1FeR80% (10)
- Oral Physiology ReviewerDocument20 pagesOral Physiology ReviewerCamille Baybay100% (1)
- Clinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFDocument29 pagesClinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFshagufta lailaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab 3rd ShiftDocument39 pagesAnaphy Lab 3rd Shift202210161No ratings yet
- Mouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsDocument52 pagesMouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsIrfan FalahNo ratings yet
- The Oral CavityDocument55 pagesThe Oral CavityMeren NagaNo ratings yet
- Trans Savi Oto Lec 07 Anatomy and Physiology of Oral Cavity and Pharynx 1st SemDocument16 pagesTrans Savi Oto Lec 07 Anatomy and Physiology of Oral Cavity and Pharynx 1st SemJoherNo ratings yet
- Stomodeum Palate TongueDocument5 pagesStomodeum Palate Tonguekopipaym8No ratings yet
- Review Antomical Structures in The Oral CavityDocument2 pagesReview Antomical Structures in The Oral CavityJiger FunteraNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesDigestive Systemlim.angelyne0126No ratings yet
- Lec04 - Assessing Mouth, Throat, Abdomen and RectumDocument23 pagesLec04 - Assessing Mouth, Throat, Abdomen and RectumIRISH MANIAGONo ratings yet
- Maxillofacial ProstheticsDocument7 pagesMaxillofacial Prostheticsmoondreamerm2No ratings yet
- Od - Finals 1Document18 pagesOd - Finals 1Duc QuocNo ratings yet
- Digestive System (Reviewer)Document13 pagesDigestive System (Reviewer)Kate Dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesDigestive SystemCUESCANO, CRISTEL G. BSMT 2-ANo ratings yet
- Complete DentureDocument5 pagesComplete DentureElyssa Jane F. TanNo ratings yet
- B-M of Human Teeth - 1Document10 pagesB-M of Human Teeth - 1Magd NabilNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity (Mouth Cavity) : Dr. Aymen Ahmed Warille DR Moahip MohamedDocument57 pagesOral Cavity (Mouth Cavity) : Dr. Aymen Ahmed Warille DR Moahip MohamedNada MohammedNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity, Oropharynx & Sore ThroatDocument14 pagesOral Cavity, Oropharynx & Sore ThroatDong YaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument15 pagesDigestive SystemHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- Lecture (2) Oral Cavity, Palate and TongueDocument11 pagesLecture (2) Oral Cavity, Palate and TongueReem ZohairNo ratings yet
- (PLM) Oral Cavity Salivary Glands Pharynx and EsophagusDocument9 pages(PLM) Oral Cavity Salivary Glands Pharynx and EsophagusJovilyn SilongaNo ratings yet
- ORAL PHYSIOLOGY CoverageDocument31 pagesORAL PHYSIOLOGY Coveragelesterliclican22No ratings yet
- ASSESSING MOUTH, THROAT, NOSE and SINUSESDocument13 pagesASSESSING MOUTH, THROAT, NOSE and SINUSESKenneth Andre Batuyog TecsonNo ratings yet
- 3 - Speech - AboDocument34 pages3 - Speech - Abomarymahmoud73737No ratings yet
- Airway ManagementDocument8 pagesAirway ManagementMichael Sedano100% (1)
- Oral Physiology and OcclusionDocument64 pagesOral Physiology and OcclusionFrances SyNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument105 pagesOral CavityAisha AbbasNo ratings yet
- 14 Digestive SystemDocument19 pages14 Digestive SystemPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption: Digestive System of HumanDocument4 pagesDigestion and Absorption: Digestive System of HumanrajaijahNo ratings yet
- Cleft Palate And/or Velopharyngeal Dysfunction: Assessment and Treatment Education Committee, ASHA Special Interest Division 5Document1 pageCleft Palate And/or Velopharyngeal Dysfunction: Assessment and Treatment Education Committee, ASHA Special Interest Division 5Ali SundoroNo ratings yet
- Oral AnatomyDocument2 pagesOral Anatomybellaespeleta5No ratings yet
- The Digestive System and Body MetabolismnotesDocument31 pagesThe Digestive System and Body MetabolismnotesJared Bien TagolimotNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledLeyluhgheylNo ratings yet
- Akash Tongue FinalDocument74 pagesAkash Tongue FinalSuraj kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Gi BNSDocument117 pagesGi BNSBibika MallaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Digestive SystemDocument10 pagesLesson 4 Digestive SystemJulio De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Facial PrimordiaDocument8 pagesFacial PrimordiaALEXIS MOIRAH CALIGAGANNo ratings yet
- T8. Obturartoare-VI 3 PersDocument12 pagesT8. Obturartoare-VI 3 PersOanaA.IanculescuNo ratings yet
- Digestive and Body MetabolismDocument25 pagesDigestive and Body MetabolismGuenNo ratings yet
- Tongue Prosthesis PDFDocument4 pagesTongue Prosthesis PDFMrinmayee ThakurNo ratings yet
- FetalPigDissectionLab 000Document11 pagesFetalPigDissectionLab 000Hermione MalfoyNo ratings yet
- m1 - m2 Oral OccluDocument16 pagesm1 - m2 Oral OccluJane Krystia TeodoroNo ratings yet
- STUDENTS' NOTES ON Assessment of Mouth, Throat, Nose andDocument8 pagesSTUDENTS' NOTES ON Assessment of Mouth, Throat, Nose andRolandNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Swallowing: Table 1Document6 pagesPhysiology of Swallowing: Table 1Nelly ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System2 OllanasDocument3 pagesRespiratory System2 OllanasKirsten AletheaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy - Chapter 23 - Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesAnaphy - Chapter 23 - Respiratory SystemAileen DemaguilaNo ratings yet
- Simply Put - ENT NOSE LECTURESDocument38 pagesSimply Put - ENT NOSE LECTURESCedric KyekyeNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Landmarks, Physiology and Myology of Facial ExpressionDocument89 pagesAnatomical Landmarks, Physiology and Myology of Facial ExpressionJawad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Development of Palate and Tongue NotesDocument9 pagesDevelopment of Palate and Tongue NotesClarisse MendozaNo ratings yet
- Tongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDocument100 pagesTongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDr Mohit Dhawan100% (19)
- L. 10 The Oral CavityDocument79 pagesL. 10 The Oral CavityAsfoor gake1No ratings yet
- Oral Habits Part 2 Tongue ThrustingDocument45 pagesOral Habits Part 2 Tongue ThrustingSudeep M. Choudhary100% (1)
- Development of PalateDocument41 pagesDevelopment of PalateNahid zafarNo ratings yet
- Digestive System AnatomyDocument3 pagesDigestive System AnatomyJo Marchianne PigarNo ratings yet
- All About AppliancesDocument15 pagesAll About AppliancesAlmekhlafiNo ratings yet
- Periodontology 1 Compiled PDFDocument598 pagesPeriodontology 1 Compiled PDFCrypto ManiacNo ratings yet
- The Articulatory SystemDocument4 pagesThe Articulatory SystemDianne MaeNo ratings yet
- 4 Walton2018Document6 pages4 Walton2018meeNo ratings yet
- Deleterious Effects of Oral Habits: A ReviewDocument4 pagesDeleterious Effects of Oral Habits: A ReviewDrshubhankar Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- OHNS--Otolaryngology; Head and Neck surgery: pocket field guideFrom EverandOHNS--Otolaryngology; Head and Neck surgery: pocket field guideNo ratings yet
- Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disorders in DogsDocument14 pagesOral Manifestations of Systemic Disorders in DogsLatifa Putri FajrNo ratings yet
- Introduction To English For Law (TLE 0813)Document11 pagesIntroduction To English For Law (TLE 0813)ilham naylaNo ratings yet
- Bridging The Gap Nasoalveolar Moulding in Early Cleft Palate RehabilitationDocument15 pagesBridging The Gap Nasoalveolar Moulding in Early Cleft Palate RehabilitationcdentistacesarmNo ratings yet
- Bilateral Macrostomia: Interesting Case SeriesDocument4 pagesBilateral Macrostomia: Interesting Case Seriesahmed bouzouidaNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Care For Patients With Cleft PalateDocument6 pagesProsthodontic Care For Patients With Cleft PalateShraddha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- JKCD 6Document5 pagesJKCD 6sulistyowati_rnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 Kelainan Tumbuh Kembang MaksilofasialDocument62 pagesLecture 13 Kelainan Tumbuh Kembang MaksilofasialKIH 20162017No ratings yet
- Bilateral Cleft Lip ReconstructionDocument14 pagesBilateral Cleft Lip ReconstructionHusni mubarakNo ratings yet
- Jurnal ObturatorDocument4 pagesJurnal ObturatorEuginia YosephineNo ratings yet
- Prominent Premaxilla Management On Bilateral Cleft Lip and PalateDocument5 pagesProminent Premaxilla Management On Bilateral Cleft Lip and PalateMuhammad Alif SatrioNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing Part 3Document20 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing Part 3Edralee VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Presurgical Infant Orthopedics For Cleft Lip and PDocument6 pagesPresurgical Infant Orthopedics For Cleft Lip and PPark JiminNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip Surgery A Practical GuideDocument89 pagesCleft Lip Surgery A Practical GuideJasadet JetsadaNo ratings yet
- As Ii Case Study Dy Florendo Gascon PDFDocument26 pagesAs Ii Case Study Dy Florendo Gascon PDFDennis GasconNo ratings yet
- Tools and Education For Speech Clarity and Feeding: 2014 Product CatalogDocument17 pagesTools and Education For Speech Clarity and Feeding: 2014 Product CatalogElectra ZenNo ratings yet
- FINAL NP2 Cramsheet 2Document7 pagesFINAL NP2 Cramsheet 2Zero TwoNo ratings yet
- Cleft Rhinoplasty CMEDocument13 pagesCleft Rhinoplasty CMENaveed KhanNo ratings yet
- Converse: Chapter 43 The Unilateral Cleft Lip Ross H. Musgrave, William S. Garrett, Jr. HistoryDocument20 pagesConverse: Chapter 43 The Unilateral Cleft Lip Ross H. Musgrave, William S. Garrett, Jr. Historyisrael0105111082No ratings yet
- Critically Ill PaedsDocument53 pagesCritically Ill Paedsdayang rohanaNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip - PalateDocument14 pagesCleft Lip - Palateragupathyr100% (1)
- Classification of Maxillofacial Defects: A Review ArticleDocument7 pagesClassification of Maxillofacial Defects: A Review ArticleIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Barbara Tritz Defeat Dental DecayDocument663 pagesBarbara Tritz Defeat Dental DecayAndrea SirahNo ratings yet
- Use of Local and Axial Pattern Flaps For Reconstruction of The Hard and Soft Palate PDFDocument9 pagesUse of Local and Axial Pattern Flaps For Reconstruction of The Hard and Soft Palate PDFJose Luis Granados SolerNo ratings yet
- Rays of HopeDocument3 pagesRays of HopeKathryn100% (1)
- Cleft Lip & PalateDocument24 pagesCleft Lip & PalateBheru Lal0% (1)
- 10-16-02 Cleft Lip and Palate Part 2 TEKNIKDocument93 pages10-16-02 Cleft Lip and Palate Part 2 TEKNIKSulistyawati WrimunNo ratings yet
- Common Health Problems That Develop During Infancy MPNDocument14 pagesCommon Health Problems That Develop During Infancy MPNShaii Whomewhat GuyguyonNo ratings yet
- ICD 2009 V 2.7 3729 514 2629 10 10Document177 pagesICD 2009 V 2.7 3729 514 2629 10 10ali mustofaNo ratings yet
- Ca2 Pedia Quiz RationalizedDocument5 pagesCa2 Pedia Quiz RationalizedRegieLimos100% (2)
GROUP 4 - Maxillofacial Prosthodontics
GROUP 4 - Maxillofacial Prosthodontics
Uploaded by
20182141Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GROUP 4 - Maxillofacial Prosthodontics
GROUP 4 - Maxillofacial Prosthodontics
Uploaded by
20182141Copyright:
Available Formats
CLINICAL CONFERENCE - PROSTHODONTICS 2
MAXILLOFACIAL - “Roof” of oral cavity and “floor”
of nasal cavity and maxillary
PROSTHODONTICS sinuses
- It separates the oral cavity from
TOPIC OUTLINE: nasal cavity
A. Obturators ● Soft palate
A.1 Basic Concepts - Dynamic separator of oral and
A.2 Case Presentation nasal cavity
A.3 Problem-Solving
Respiration
MAXILLOFACIAL PROSTHODONTICS ● Expiration
- is a branch of prosthodontics concerned - Air passes from the lungs, through the
with the restoration and/or pharynx, and then through the
replacement of the stomatognathic oropharynx
and associated facial structures with - Either the air then passes behind the
prosthesis that may or may not be soft palate into the nasopharynx, the
removed on a regular or elective basis nasal cavity, and out the nose, or the
- is a specialty of dentistry which deals soft palate elevates to block the
with the rehabilitation of patients with nasopharynx and the air passes out the
acquired and congenital defects of the oral cavity
head and neck region
● Inspiration
- It focuses on optimizing the - Air passes in the opposite direction,
rudimentary functions of speech and through either the nasal or the oral
swallowing cavity
- These functions are disrupted - For appropriate separation of these
because of congenital, organic, cavities during speech, respiration, and
traumatic, or surgical swallowing, the soft palate elevates in
abnormalities involving the oral the middle third to separate the
cavity and related anatomical oropharynx and nasopharynx
structures.
Speech
- Maxillofacial prosthesis may be: ● Soft palate elevates
1. Extraoral - Part of the facial or cranial ● Pharyngeal wall moves anteriorly and
structure (eye, ear or nose) is missing medially but less dramatic than
and a nonliving substitute or prosthesis sphincteric movement
is used to rehabilitate the part ● Velopharyngeal closure is the
2. Intraoral - Refers to defects in and functional movement of soft palate and
involving the oral cavity, for which pharyngeal wall during speech and
prosthesis may be used to rehabilitate swallowing
the defective area ○ Nasal sound: n, m, ng
○ All oral sounds require that air be
I. BASIC CONCEPTS: impounded in the oral cavity by
ANATOMICAL AND PHYSIOLOGICAL the elevation of the soft palate and
CONSIDERATIONS: NORMAL FUNCTION closure of the pharyngeal walls
Superior Aspect of the Oral Cavity
● Hard palate Inferior Aspect of the Oral Cavity
- Includes the tongue, muscles, and
tissues of the floor of mouth, and the
mandible
GROUP 4: DESTOR, EGENIAS, GAANO, ORENA, PATIU, PEREZ, POJ-AGAN, RATUITA
CLINICAL CONFERENCE - PROSTHODONTICS 2
- These inferior structures act in concert
- Generally require
during speech
some form of
● Tongue - primary articulator
prosthesis
Mastication Class IV - Completed cleft of
● Tongue constantly moves the food the palate involving
bolus on the occlusal surfaces alveolar ridges as well
- Forms the food into a mass and as lip on both right
pushes the mass posteriorly and left sides
against the hard palate and into - Generally require
the oropharynx some form of
● Soft palate simultaneously elevates as prosthesis
the pharynx squeezes
- The pharyngeal squeeze pushes
the food into the esophagus 3. Central nervous system trauma
4. Head injuries and cerebrovascular
accidents
FUNCTIONAL DEFICITS OF SPEECH AND 5. Surgery
6. Neoplastic disease
SWALLOWING
7. Closure of the surgical site
1. Congenital defects
8. Velopharyngeal closure or defects in
2. Cleft palate
hard palate
Class I - Clefts involving the Prosthetic Considerations
soft palate only ● Facial form
- Of these four classes, - Altered facial contours in patients
the class I type are who received trauma or surgical
surgically correctable resection
and usually do not - It may take several months after an
require any prosthesis operation or trauma for the soft
tissues to reach a final, stable position
Class II - Clefts involving the
- These changes necessitate:
soft and hard palate
- Fabrication of interim
up to the incisive
prostheses and repeated
foramen
prosthesis adjustments to
- The soft palate can be
conform to soft tissue
surgically corrected if
changes
the cleft of the hard
palate is not
correctable; the
Loss of Vertical Opening and Altered
prosthetic assistance
is provided for it Mandibular Movements
Causes:
Class III - Clefts of the soft and ● Surgical resection
hard palate involve - trauma to oral cavity structure
the alveolar ridge and - resection of the posterior aspect of the
continuous with the hard palate
lip on one side
GROUP 4: DESTOR, EGENIAS, GAANO, ORENA, PATIU, PEREZ, POJ-AGAN, RATUITA
CLINICAL CONFERENCE - PROSTHODONTICS 2
- muscles of mastication (medial and Border Molding Peripheries of Maxillary
lateral muscles) are frequently detached Resections and Hard Palate Defects: Patient
from the maxilla or partially resected. Movements
Trismus - Border molding the posterior and lateral
- Immediate result of muscular trauma area of a maxillectomy requires that the
leading to decreased vertical opening patient go through head and mandible
and range of motion of the mandible. movements similar to border molding the
- Manual exercise is given to improve velopharyngeal area.
range of motion and opening. - Swallowing is important to move the cut
edge of the soft palate
● Clinical significance:
- Oral hygiene, prosthetic treatment, and Testing the Prosthetic “Seal” between the Oral
manipulation of food bolus will be Cavity and the Nasal Cavity
difficult. - Drinking liquids is the usual test for
prosthetic closure of an anatomical defect
Processed Bases in the soft or hard palate
- Soft tissue and bony undercuts exist ● Patient should be in upright position
after an oral cavity surgery or when swallowing
maxillectomy that may be used as ● Listening to speech sounds is the usual
prosthetic-bearing surfaces way to test for appropriate separation of
- Prosthetic-bearing surfaces are airflow from the oral cavity and nasal
important in achieving accurate occlusal cavity
plane and centric position records. ➔ Test for possible hypernasality, have the
- Using processed bases and denture patient say the word “beat.” Then, pinch
adhesive will aid in achieving accurate the patient’s nares closed and have him or
records her say “beat”
○ If there is a difference in the sound
● Clinical significance: of the word “beat” with and
- Processed bases will allow the clinician without pinching the nares, air is
to judge prosthesis retention and inappropriately escaping around the
position of soft tissues supported by the prosthesis periphery.
base. ○ If the word “beat” sounds more like
“meat,” there is inappropriate air
Border Molding the Velopharyngeal Area: escape.
Patient Movements ➔ Test for hyponasality, have the patient say
- An impression to restore missing tissues the phrase, “Momma made lemon jam.”
of the soft palate and pharynx ○ If the phrase sounds more like
- After placement of the impression “Bobba, bade lebon jab.”, the air is
material, the patient is asked to swallow. not allowed to escape from the oral
- The patient will then open and close the cavity through the nose.
mouth, move the mandible from side to ○ Therefore, prosthesis may be too
side, turn the head from side to side, large or overextended; however,
place the chin down to the chest, move creating hyponasal speech with an
the head from side to side, and extend obturator is uncommon. It is more
the head backward likely that the obturator is
satisfactory, but that the patient
really is congested in the nasal
passages.
GROUP 4: DESTOR, EGENIAS, GAANO, ORENA, PATIU, PEREZ, POJ-AGAN, RATUITA
CLINICAL CONFERENCE - PROSTHODONTICS 2
Side note: - The patient who undergoes maxillary
Ang paginom ng tubig anf kadalasang resection is rehabilitated in three
ginagawa to test if may tamang prosthetic phases, namely:
closure sa cases na may defect sa soft or hard o surgical obturator
palate. Same test kanina na naka-swallow pero o interim obturator, and
naka upright position ang patient. Test for o definitive obturator.
possible hypernasality. Hypernasality—excessive
nasal resonance on vowels and voiced oral 1) Surgical obturator prosthesis
consonants. Hyponasality—too little or absent - aka immediate surgical prosthesis,
resonance on nasal consonants and adjacent immediate temporary obturator,
vowels, especially /i/ and /u. So have the patient surgical baseplate
say the word “beat”. Then pinch the patient’s - a temporary maxillofacial prosthesis
nares closed and say “beat”… (please refer the inserted during or immediately
slide) following surgical or traumatic loss of a
portion or all of one or both maxillary
bones and contiguous alveolar
OBTURATOR structures (i.e. gingival tissue, teeth).
- a maxillofacial prosthesis used to close a - This prosthesis allows the patient to
congenital or acquired tissue opening, take oral nutrition immediately
primarily of the hard palate and/or postoperatively
contiguous alveolar/soft tissue - Speech is generally quite normal with
structures (GPT7) this prosthesis
- This prosthesis will be in service for
Uses of obturator approximately 5 to 10 days
1. Provides a stable matrix for surgical - Frequent revisions of surgical obturators
packing are necessary during the ensuing
2. Reduce oral contamination healing phase (approximately six
3. Speech is effective post operatively months).
4. Permits deglutition - Further surgical revisions may
5. Reduce the psychological impact of require fabrication of another
surgery surgical obturator
6. Reduce period of hospitalization
❖ Goals:
Limitation of obturator a) to support the surgical packing placed in
a) Require insertion and removal the resection cavity created by removal
b) Have redo periodically due to growth of the walls of the maxillary sinus
c) Can be lost or damaged b) to restore continuity of the hard palate
d) May be uncomfortable
e) Poor patient compliance ❖ Fabrication:
o The patient must have a presurgical
MAXILLARY OBTURATOR PROSTHESIS dental examination, and a maxillary
- Required for patients who have cast must be made
undergone tumor resection of the hard o The clinician will also plan
palate for neoplasms that originate in treatment for the patient for
the paranasal sinuses or superior aspect necessary preprosthetic surgery to
of the oral cavity remove epuli, reduce pendulous
tuberosities, and relieve bony
undercuts
GROUP 4: DESTOR, EGENIAS, GAANO, ORENA, PATIU, PEREZ, POJ-AGAN, RATUITA
CLINICAL CONFERENCE - PROSTHODONTICS 2
o A baseplate with routine denture Goal:
extensions or an existing well-fitting - to restore deglutition and speech by
denture may be used for the restoring palatal contours separating
surgical obturator the nasal cavity, maxillary sinus, and
o If the tumor is altering the normal nasopharynx from the oral cavity
contours of the hard palate, the cast
should be altered to restore - Retain and reline the existing denture
appropriate palatal contour may be required before modifying the
o Edentulous surgical obturators must surgical area
be secured by circumzygomatic Relining:
wires, sutures, or bone screws ● Use Denture adhesives
o Retentive holes for zygomatic wires ● The prosthesis is modified with an
are placed bilaterally with a no. 8 intermediate denture liner to conform
round bur in the premolar area to the periphery of the surgical site
through the prosthesis flanges. ● The bulb portion should be kept hollow
during the relining procedure to limit
the weight of the prosthesis
● An ideal material should have enough
body to support itself during the initial
impression procedure and for several
weeks
● As the patient heals, the periphery of
o A single bone screw may be placed the surgical site will become smaller
through the vomer bone, through a and the prosthesis will become
predrilled hole in the midpalate at overextended
the junction of the premaxilla and
hard palate. 3) Definitive obturator
o Removal of the bone screw and - Prosthesis that artificially replaces part
sutures is easily accomplished in an or all of the maxilla and the associated
outpatient setting teeth lost due to surgery or trauma
o Removal of zygomatic wires should
- Fabricated when tissue healing and
be done with the surgeon’s
contraction are complete
assistance and usually requires an
- Fabricated after 6 months or until the
operating room setting
tissues are stable
- Preliminary impression with irreversible
hydrocolloid
2) Interim obturator
- Processed from the postsurgical master
Fabrication:
cast. The interim obturator is delivered ● Preliminary cast should be blocked out
when the surgical obturator is removed ● Border molding the nonsurgical side
- Fabricated either from a new and making the final impression before
impression made from the patient or by border molding the surgical site ensures
adjusting the immediate surgical that the tray is reseated in a consistent
obturator by soft relining material. manner when the surgical site is
- Will be used for 2 to 6 months impressed
● To avoid overextension of the
compound, the clinician must look
GROUP 4: DESTOR, EGENIAS, GAANO, ORENA, PATIU, PEREZ, POJ-AGAN, RATUITA
CLINICAL CONFERENCE - PROSTHODONTICS 2
constantly to the anatomical least form
and landmarks of the surgical site o The inferior extent of the pharyngeal
● There is commonly a soft tissue extension should be at or slightly below
undercut at the junction of the oral the inferior aspect of the pharyngeal
mucosa and skin graft that lines the sphincter
maxillary cavity called a cicatricial line o The overall height of the extension
or scar band should not be more than 1 cm
● Maxillary and mandibular processed o Final impression for closure of the
bases and denture adhesive are used nasopharynx in swallowing by asking
● Place the anterior teeth in an the patient to drink water
end-to-end or reverse horizontal o Ideally, airflow in speech should be
articulatim situation appropriate
● Facial position of the anterior teeth may
be verified at the try-in appointment
● Final evaluation: pressure areas and PROBLEM SOLVING/ TROUBLESHOOTING
border extensions (best done with a
combination of pressure-indicating Troubleshooting an Obturator Prosthesis
paste and tissue-conditioning material) 1. Lack of Retention
● The patient should swallow and go - Overextension of borders in an interim
through all head and jaw movements prosthesis is the result of soft tissue
● A uniform, thin, functionally formed changes, and the prosthesis borders will
coating of material remains with need to be relieved and relined.
obvious “show through” of the acrylic - Adhesives are almost always required
resin in pressure areas for any edentulous obturator prosthesis.
- Patients should masticate as little as
*Soft palate obturator prosthesis possible on the defect side because this
- A soft palate obturator or speech aid tends to unseat the prosthesis.
prosthesis is required for patients who
have a resection of their soft palate or 2. Nasal Reflux
have a soft palate deficit from a cleft
palate - Explain to the patient that the
- When soft palate is resected, patients prosthesis cannot function as a “cork in
will resume swallowing with minimal a bottle,” and some reflux is to be
discomfort, but if the resection is more expected.
extensive, patients may not resume - An upright head position is required
normal swallowing immediately during swallowing.
because of additional surgical o Check the palatal contours with
involvement of the pharynx. In these pressure indicator paste. A
situations, the obturator’s major palatal form that is too low
function will be to restore speech constricts the tongue and
● A posterior extension is added to a unseats the prosthesis. Check
denture prosthesis to contact the the tissue adaptation at the
patient’s pharyngeal wall when it closes posteromedial and
during speech and swallowing posterolateral margins(at the
● Passavant’s ridge: Prominent muscular prosthesis/soft palate junction).
ridge on the pharyngeal wall, present o Place petroleum jelly on the
when the patient says prosthesis surface and
“ahh” functionally disclose the area
GROUP 4: DESTOR, EGENIAS, GAANO, ORENA, PATIU, PEREZ, POJ-AGAN, RATUITA
CLINICAL CONFERENCE - PROSTHODONTICS 2
with a viscous tissue extension and make a new functional
conditioner. If the tissue impression.
conditioner material is thick and
successfully decreases reflux, 2. Hypernasality
this area should be addressed - for appropriate tissue contact in
for a relining procedure. swallowing using a tissue conditioner. If
- When the required relining area is only a uniformly thin coating of material is
1 to 2 cm and the remainder of the evidenced on the obturator and
obturator portion is well fitting, a hypernasality persists, the problem is
chairside relining should be considered. that there is greater pharyngeal wall
- Cut finish lines to demarcate the area constriction in swallowing and limited
indicated by the tissue conditioner. pharyngeal wall movement in speech.,
These finish lines will confine the - pharyngeal constriction is almost always
relining material. An autopolymerizing more pronounced during swallowing
relining resin or a light-cured composite than the constriction during speech.
resin material can be added and border - It usually is not possible to add more
molded in the patient’s mouth. material to the obturator, or the patient
begins to complain of overextension
3. Hypernasality during swallowing.
- When reflux has been minimized but - Increased “compensatory” pharyngeal
hypernasality exists, one should constriction during speech may be seen
consider that the velopharyngeal as time passes. This compensatory
closure may be compromised from movement may increase and eventually
surgery. eliminate hypernasality,
- The soft palate may elevate, but there
may not be enough elevation to close TROUBLESHOOTING PROSTHESES FOR THE
the nasopharynx. PATIENT WITH AN EDENTULOUS
- Clinician should attempt to add a MANDIBULECTOMY
pharyngeal extension, as in the soft
palate obturator prosthesis, over the 1. Unstable Mandibular Denture
inadequately functioning soft palate to - Stability of the base should be
obturate the pharynx evaluated with processed bases at the
time of maxillomandibular relationship
records before placement of wax rims.
II. TROUBLESHOOTING THE SOFT PALATE - Overextension onto movable tissue will
OBTURATOR PROSTHESIS unseat the prosthesis.
- Overextensions should be reduced
1. Prosthesis Feels Too Long before making records.
- The patient complains that they “feel - Unstable at the try-in-inappropriate
the prosthesis in the back” of their tooth position may be unseating the
pharynx. prosthesis.
- The prosthesis should be disclosed with - Denture adhesive often is necessary.
the tissue-conditioning material
because these complaints signal an 2. Inability to Chew or Inability to Chew
overextended prosthesis. beyond a Soft Diet
- if patient continues to complain, it may ● Patients with partial mandibulectomies
be necessary to reduce the entire often have impaired range of motion of
the tongue.
GROUP 4: DESTOR, EGENIAS, GAANO, ORENA, PATIU, PEREZ, POJ-AGAN, RATUITA
CLINICAL CONFERENCE - PROSTHODONTICS 2
- soft diet may be all that the ● (C) Pretreatment extraoral view.
patient can accommodate
despite the insertion of Treatment Plan:
dentures. 1. Impression Phase:
- Hard food requires masticatory ● Use appropriate stock
power that the edentulous impression tray for primary
mandibulectomy patient lacks. impression
● Employ impression compound
CASE REPORT 1: OBTURATORS for primary impression
● Block undercuts in cleft area
PATIENT PROFILE: with modeling wax
Age: 65 years old
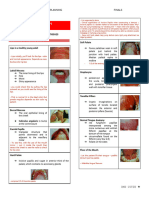
Sex: Female Figure 3.
Medical/Dental History: The patient’s primary
● Born with a congenital cleft lip impressions using an
and palate Impression
● Cleft lip repaired during early Compound.
years; cleft palate not surgically
repaired
● Old denture wearer for seven ● Right Impression - Maxillary Arch
years ● Left Impression - Mandibular Arch
2. Custom Impression Trays:
● Fabricate custom trays using
Figure 1. auto-polymerized acrylic resin
The patient’s old ● Conduct border molding with
denture. green stick impression
compound
Complaint of the patient: ● Adapt type I modeling plastic in
● Poor retention of dentures, the cleft area
leading to difficulty in speaking, ● Record posterior extension by
swallowing, and chewing instructing patient in head
movements
Intraoral Examination: ○ The patient was asked
● Complete unilateral cleft to bend the head
involving anterior alveolar forward slowly, touch
bone, hard palate, and soft the chest, and then
palate move it backward.
● Capture lateral side movements
and phonation for complete
impression
Figure 2. ○ The patient was asked
to do a side-to-side
movement.
○ The patient was also
asked to say ah phonate
● (A) Cleft palate. repeatedly and
● (B) Edentulous mandibular ridge. forcefully.
GROUP 4: DESTOR, EGENIAS, GAANO, ORENA, PATIU, PEREZ, POJ-AGAN, RATUITA
CLINICAL CONFERENCE - PROSTHODONTICS 2
○
The impression surface Figure 5.
was adjusted till the (A) Posttreatment photograph of the patient
patient was satisfied with dentures.
with the speech and (B) (B) Intraoral view with dentures.
comfort. (C) (C) Patient's dentures
3. Secondary Impressions:
● Utilize light-body elastomeric
impression material for detailed 6. Patient Education:
impressions ● Instruct on cleaning and
4. Jaw Relations and Try-On: maintaining complete dentures.
● Record jaw relations ● The patient was satisfied with
● Conduct a try-on to evaluate the aesthetics, speech,
speech, aesthetics, and swallowing, and chewing
swallowing capacity due to improved
○ The patient's speech retention and stability in the
was evaluated using new prosthesis. .
speech tests like 7. Follow-up:
perceptual analyses, ● The patient was recalled for one
resonance frequency week, one month, and six
analyses, and acoustic months to assess any difficulty
analyses. while using the complete
○ There was a marked dentures
improvement in speech.
○ The patient was asked CASE REPORT 2:
to drink water to check Rehabilitation of a Hemimaxillectomy patient
for regurgitation of with Surgical, Interim and Definitive Obturator
liquid during
swallowing. Age: 38 years old
○ The denture prevented Sex: Male
the regurgitation of
liquid during Chief complaint:
swallowing. Overgrowth in the right side of maxilla (7-8
months back).
Intraoral Examination:
Figure 4. Patient The lesion was seen extending from beyond the
Try-On. palatal surface of 17 up to the palatal surface of
14. Swelling had no odontogenic origin. The
tumor was located on a hard palate with a size
5. Final Prosthesis: of 2.9x2.5x1.4 cm.
● Invest and dewax waxed
dentures using conventional
techniques
● Deliver complete dentures with
attention to aesthetics and
function
GROUP 4: DESTOR, EGENIAS, GAANO, ORENA, PATIU, PEREZ, POJ-AGAN, RATUITA
CLINICAL CONFERENCE - PROSTHODONTICS 2
f. On table relining was done with
Extraoral Examination: autopolymerizing clear acrylic resin.
Patient had a square facial Thus the surgical obturator was inserted
form and a straight facial immediately following the surgery.
profile. No extraoral
swelling or deviation was
seen.
Preoperative CT scan:
Diagnosis:
Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma
Treatment Plan:
1. SURGICAL OBTURATOR g. After initial healing was completed, the
● Placed at the time of tumor resection in obturator was relined
the operating room h. Impression compounds followed by
● The surgical obturator must terminate tissue conditione rs were used.
short of skin graft-mucosal junction i. Later it was processed with clear heat
Steps: cure acrylic resin.
a. Diagnostic impressions of upper and j. After 1-1.5 months the patient was
lower arch were made with irreversible recalled for the fabrication of interim
hydrocolloid impression material. The obturator.
impressions were poured into dental
stone. 2. INTERIM OBTURATOR
b. The operating surgeon gave the marking
for surgical resection ● Processed from the postsurgical master
c. The presurgical cast was trimmed and cast.
ball end clasp were placed for retention ● It is placed when the surgical dressing is
d. After completing the wax-up, the clear removed.
heat cured surgical obturator was ● Serves the patient for 4–6 months till
obtained with conventional denture the maxillary defect heals and matures.
processing
Steps:
a. A stock tray of appropriate size was
used to record the impression.
b. The undercuts in the medial wall were
blocked out with gauze lubricated with
petroleum jelly.
e. The tumor mass was resected, with c. Floss was tied to gauze for easy
leaving a safety margin of healthy retrieval. The lateral wall of the defect
tissues by the operating surgeon was first recorded with an impression
compound.
GROUP 4: DESTOR, EGENIAS, GAANO, ORENA, PATIU, PEREZ, POJ-AGAN, RATUITA
CLINICAL CONFERENCE - PROSTHODONTICS 2
d. Retention grooves were made into h. Indirect retention provided with rests
compounds for interlocking. on canine, lateral incisor
e. Later a wash made with irreversible i. Central incisor provided with rest seat
hydrocolloid impression material and proximal plate.
f. A hollow bulb obturator was processed j. Altered cast technique was used to
with clear heat cured acrylic resin. record the soft tissue. For which, a
g. Wrap around clasp was used to custom tray was fabricated over the
improve retention. It was checked into master cast which contained the
the patient's mouth and then delivered framework. The lateral border of defect
was recorded with the impression
compound. Later retentive holes were
made into the compound. A wash was
made with a tissue conditioner.
3. DEFINITIVE OBTURATOR
● It was processed at least 3-4 months
after completing chemotherapy and
radiotherapy.
Steps:
a. A diagnostic cast was obtained for k. The master cast was sectioned along
surveying. the hard tissue to provide retention
b. Framework design groves. The impression was seated on
c. Mouth preparation the cast. It was reversed and beading
d. Impression was made with vinyl and boxing was done. Later it was
polysiloxane in a custom tray. (FIG 12) poured with dental stone.
e. The master cast was poured into die
stone and a cast partial denture
framework was fabricated over it.
(FIG13)
l. A layer of hard wax (Cavex Set up Hard)
was adapted over the framework placed
on the obtained cast from altered cast
technique
m. Modelling wax was used for fabricating
f. Complete palate as the major connector wax rims. Jaw relation was recorded.
was designed.
g. Direct retainer was planned on the right
first premolar and embrasure clasp
between the right first and second
molars.
GROUP 4: DESTOR, EGENIAS, GAANO, ORENA, PATIU, PEREZ, POJ-AGAN, RATUITA
CLINICAL CONFERENCE - PROSTHODONTICS 2
x. Installation
y. Recall after a week
n. The record was transferred to the
articulator and mounted.
o. Following teeth selection, the teeth
setting was completed. The obturator
was tried in the patient's mouth.
p. Waxed up articulator was then References:
processed to obtain heat cured clear PROSTHODONTIC TREATMENT FOR
hollow bulb obturator. EDENTULOUS PATIENTS: COMPLETE DENTURES
q. 1 mm spacer with modelling wax was AND IMPLANT-SUPPORTED PROSTHESES 12th
adapted over the defect area. 3-4 tissue edition by Zarb-Bolender Copyright © 2004,
stops were made. Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved
r. A thin layer of autopolymerizing acrylic Roslan, Husniyati & Shahabudin, Saadiah.
resin was adapted over the wax. (2018). Palatal obturator prosthesis: A clinical
s. Later the shell was filled with salt and case report. Cumhuriyet Dental Journal. 21.
closed with a lid made from 55-60. 10.7126/cumudj.340121
autopolymerizing resin.
Rehabilitation of a hemimaxillectomy patient
with surgical, interim and definitive obturator: A
case report. . The Journal of Prosthodontics and
Dental Materials (JPDM). (n.d.).
https://jpdm-ips-mnm.com/rehabilitation-of-a-
hemimaxillectomy-patient-with-surgical-interim
-and-definitive-obturator-a-case-report/?fbclid=
t. The shell was removed. Two holes were
IwAR1lLATwWcZarZgKI6QRM5QDQQ3lZnmSyCd
made into the shell for removing the
Xolvg6CLtxsdMI6eypPTkHrQ
salt. The modelling wax was removed.
u. The heat cured resin adapted over the
defect area; the shell was then
positioned over it.
v. The heat cured resin was adapted over
the remainder cavity and the flask was
closed and clamps placed over it.
w. The processing was completed.
GROUP 4: DESTOR, EGENIAS, GAANO, ORENA, PATIU, PEREZ, POJ-AGAN, RATUITA
You might also like
- Maxillofacial Prosthodontics CourseDocument98 pagesMaxillofacial Prosthodontics CourseFBI LUC1FeR80% (10)
- Oral Physiology ReviewerDocument20 pagesOral Physiology ReviewerCamille Baybay100% (1)
- Clinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFDocument29 pagesClinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFshagufta lailaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab 3rd ShiftDocument39 pagesAnaphy Lab 3rd Shift202210161No ratings yet
- Mouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsDocument52 pagesMouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsIrfan FalahNo ratings yet
- The Oral CavityDocument55 pagesThe Oral CavityMeren NagaNo ratings yet
- Trans Savi Oto Lec 07 Anatomy and Physiology of Oral Cavity and Pharynx 1st SemDocument16 pagesTrans Savi Oto Lec 07 Anatomy and Physiology of Oral Cavity and Pharynx 1st SemJoherNo ratings yet
- Stomodeum Palate TongueDocument5 pagesStomodeum Palate Tonguekopipaym8No ratings yet
- Review Antomical Structures in The Oral CavityDocument2 pagesReview Antomical Structures in The Oral CavityJiger FunteraNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesDigestive Systemlim.angelyne0126No ratings yet
- Lec04 - Assessing Mouth, Throat, Abdomen and RectumDocument23 pagesLec04 - Assessing Mouth, Throat, Abdomen and RectumIRISH MANIAGONo ratings yet
- Maxillofacial ProstheticsDocument7 pagesMaxillofacial Prostheticsmoondreamerm2No ratings yet
- Od - Finals 1Document18 pagesOd - Finals 1Duc QuocNo ratings yet
- Digestive System (Reviewer)Document13 pagesDigestive System (Reviewer)Kate Dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesDigestive SystemCUESCANO, CRISTEL G. BSMT 2-ANo ratings yet
- Complete DentureDocument5 pagesComplete DentureElyssa Jane F. TanNo ratings yet
- B-M of Human Teeth - 1Document10 pagesB-M of Human Teeth - 1Magd NabilNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity (Mouth Cavity) : Dr. Aymen Ahmed Warille DR Moahip MohamedDocument57 pagesOral Cavity (Mouth Cavity) : Dr. Aymen Ahmed Warille DR Moahip MohamedNada MohammedNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity, Oropharynx & Sore ThroatDocument14 pagesOral Cavity, Oropharynx & Sore ThroatDong YaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument15 pagesDigestive SystemHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- Lecture (2) Oral Cavity, Palate and TongueDocument11 pagesLecture (2) Oral Cavity, Palate and TongueReem ZohairNo ratings yet
- (PLM) Oral Cavity Salivary Glands Pharynx and EsophagusDocument9 pages(PLM) Oral Cavity Salivary Glands Pharynx and EsophagusJovilyn SilongaNo ratings yet
- ORAL PHYSIOLOGY CoverageDocument31 pagesORAL PHYSIOLOGY Coveragelesterliclican22No ratings yet
- ASSESSING MOUTH, THROAT, NOSE and SINUSESDocument13 pagesASSESSING MOUTH, THROAT, NOSE and SINUSESKenneth Andre Batuyog TecsonNo ratings yet
- 3 - Speech - AboDocument34 pages3 - Speech - Abomarymahmoud73737No ratings yet
- Airway ManagementDocument8 pagesAirway ManagementMichael Sedano100% (1)
- Oral Physiology and OcclusionDocument64 pagesOral Physiology and OcclusionFrances SyNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument105 pagesOral CavityAisha AbbasNo ratings yet
- 14 Digestive SystemDocument19 pages14 Digestive SystemPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption: Digestive System of HumanDocument4 pagesDigestion and Absorption: Digestive System of HumanrajaijahNo ratings yet
- Cleft Palate And/or Velopharyngeal Dysfunction: Assessment and Treatment Education Committee, ASHA Special Interest Division 5Document1 pageCleft Palate And/or Velopharyngeal Dysfunction: Assessment and Treatment Education Committee, ASHA Special Interest Division 5Ali SundoroNo ratings yet
- Oral AnatomyDocument2 pagesOral Anatomybellaespeleta5No ratings yet
- The Digestive System and Body MetabolismnotesDocument31 pagesThe Digestive System and Body MetabolismnotesJared Bien TagolimotNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledLeyluhgheylNo ratings yet
- Akash Tongue FinalDocument74 pagesAkash Tongue FinalSuraj kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Gi BNSDocument117 pagesGi BNSBibika MallaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Digestive SystemDocument10 pagesLesson 4 Digestive SystemJulio De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Facial PrimordiaDocument8 pagesFacial PrimordiaALEXIS MOIRAH CALIGAGANNo ratings yet
- T8. Obturartoare-VI 3 PersDocument12 pagesT8. Obturartoare-VI 3 PersOanaA.IanculescuNo ratings yet
- Digestive and Body MetabolismDocument25 pagesDigestive and Body MetabolismGuenNo ratings yet
- Tongue Prosthesis PDFDocument4 pagesTongue Prosthesis PDFMrinmayee ThakurNo ratings yet
- FetalPigDissectionLab 000Document11 pagesFetalPigDissectionLab 000Hermione MalfoyNo ratings yet
- m1 - m2 Oral OccluDocument16 pagesm1 - m2 Oral OccluJane Krystia TeodoroNo ratings yet
- STUDENTS' NOTES ON Assessment of Mouth, Throat, Nose andDocument8 pagesSTUDENTS' NOTES ON Assessment of Mouth, Throat, Nose andRolandNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Swallowing: Table 1Document6 pagesPhysiology of Swallowing: Table 1Nelly ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System2 OllanasDocument3 pagesRespiratory System2 OllanasKirsten AletheaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy - Chapter 23 - Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesAnaphy - Chapter 23 - Respiratory SystemAileen DemaguilaNo ratings yet
- Simply Put - ENT NOSE LECTURESDocument38 pagesSimply Put - ENT NOSE LECTURESCedric KyekyeNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Landmarks, Physiology and Myology of Facial ExpressionDocument89 pagesAnatomical Landmarks, Physiology and Myology of Facial ExpressionJawad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Development of Palate and Tongue NotesDocument9 pagesDevelopment of Palate and Tongue NotesClarisse MendozaNo ratings yet
- Tongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDocument100 pagesTongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDr Mohit Dhawan100% (19)
- L. 10 The Oral CavityDocument79 pagesL. 10 The Oral CavityAsfoor gake1No ratings yet
- Oral Habits Part 2 Tongue ThrustingDocument45 pagesOral Habits Part 2 Tongue ThrustingSudeep M. Choudhary100% (1)
- Development of PalateDocument41 pagesDevelopment of PalateNahid zafarNo ratings yet
- Digestive System AnatomyDocument3 pagesDigestive System AnatomyJo Marchianne PigarNo ratings yet
- All About AppliancesDocument15 pagesAll About AppliancesAlmekhlafiNo ratings yet
- Periodontology 1 Compiled PDFDocument598 pagesPeriodontology 1 Compiled PDFCrypto ManiacNo ratings yet
- The Articulatory SystemDocument4 pagesThe Articulatory SystemDianne MaeNo ratings yet
- 4 Walton2018Document6 pages4 Walton2018meeNo ratings yet
- Deleterious Effects of Oral Habits: A ReviewDocument4 pagesDeleterious Effects of Oral Habits: A ReviewDrshubhankar Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- OHNS--Otolaryngology; Head and Neck surgery: pocket field guideFrom EverandOHNS--Otolaryngology; Head and Neck surgery: pocket field guideNo ratings yet
- Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disorders in DogsDocument14 pagesOral Manifestations of Systemic Disorders in DogsLatifa Putri FajrNo ratings yet
- Introduction To English For Law (TLE 0813)Document11 pagesIntroduction To English For Law (TLE 0813)ilham naylaNo ratings yet
- Bridging The Gap Nasoalveolar Moulding in Early Cleft Palate RehabilitationDocument15 pagesBridging The Gap Nasoalveolar Moulding in Early Cleft Palate RehabilitationcdentistacesarmNo ratings yet
- Bilateral Macrostomia: Interesting Case SeriesDocument4 pagesBilateral Macrostomia: Interesting Case Seriesahmed bouzouidaNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Care For Patients With Cleft PalateDocument6 pagesProsthodontic Care For Patients With Cleft PalateShraddha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- JKCD 6Document5 pagesJKCD 6sulistyowati_rnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 Kelainan Tumbuh Kembang MaksilofasialDocument62 pagesLecture 13 Kelainan Tumbuh Kembang MaksilofasialKIH 20162017No ratings yet
- Bilateral Cleft Lip ReconstructionDocument14 pagesBilateral Cleft Lip ReconstructionHusni mubarakNo ratings yet
- Jurnal ObturatorDocument4 pagesJurnal ObturatorEuginia YosephineNo ratings yet
- Prominent Premaxilla Management On Bilateral Cleft Lip and PalateDocument5 pagesProminent Premaxilla Management On Bilateral Cleft Lip and PalateMuhammad Alif SatrioNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing Part 3Document20 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing Part 3Edralee VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Presurgical Infant Orthopedics For Cleft Lip and PDocument6 pagesPresurgical Infant Orthopedics For Cleft Lip and PPark JiminNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip Surgery A Practical GuideDocument89 pagesCleft Lip Surgery A Practical GuideJasadet JetsadaNo ratings yet
- As Ii Case Study Dy Florendo Gascon PDFDocument26 pagesAs Ii Case Study Dy Florendo Gascon PDFDennis GasconNo ratings yet
- Tools and Education For Speech Clarity and Feeding: 2014 Product CatalogDocument17 pagesTools and Education For Speech Clarity and Feeding: 2014 Product CatalogElectra ZenNo ratings yet
- FINAL NP2 Cramsheet 2Document7 pagesFINAL NP2 Cramsheet 2Zero TwoNo ratings yet
- Cleft Rhinoplasty CMEDocument13 pagesCleft Rhinoplasty CMENaveed KhanNo ratings yet
- Converse: Chapter 43 The Unilateral Cleft Lip Ross H. Musgrave, William S. Garrett, Jr. HistoryDocument20 pagesConverse: Chapter 43 The Unilateral Cleft Lip Ross H. Musgrave, William S. Garrett, Jr. Historyisrael0105111082No ratings yet
- Critically Ill PaedsDocument53 pagesCritically Ill Paedsdayang rohanaNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip - PalateDocument14 pagesCleft Lip - Palateragupathyr100% (1)
- Classification of Maxillofacial Defects: A Review ArticleDocument7 pagesClassification of Maxillofacial Defects: A Review ArticleIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Barbara Tritz Defeat Dental DecayDocument663 pagesBarbara Tritz Defeat Dental DecayAndrea SirahNo ratings yet
- Use of Local and Axial Pattern Flaps For Reconstruction of The Hard and Soft Palate PDFDocument9 pagesUse of Local and Axial Pattern Flaps For Reconstruction of The Hard and Soft Palate PDFJose Luis Granados SolerNo ratings yet
- Rays of HopeDocument3 pagesRays of HopeKathryn100% (1)
- Cleft Lip & PalateDocument24 pagesCleft Lip & PalateBheru Lal0% (1)
- 10-16-02 Cleft Lip and Palate Part 2 TEKNIKDocument93 pages10-16-02 Cleft Lip and Palate Part 2 TEKNIKSulistyawati WrimunNo ratings yet
- Common Health Problems That Develop During Infancy MPNDocument14 pagesCommon Health Problems That Develop During Infancy MPNShaii Whomewhat GuyguyonNo ratings yet
- ICD 2009 V 2.7 3729 514 2629 10 10Document177 pagesICD 2009 V 2.7 3729 514 2629 10 10ali mustofaNo ratings yet
- Ca2 Pedia Quiz RationalizedDocument5 pagesCa2 Pedia Quiz RationalizedRegieLimos100% (2)