Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 4
Module 4
Uploaded by
saehalaire0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesModule 4
Module 4
Uploaded by
saehalaireCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
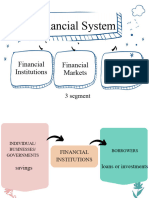
Module 4: Credit Transactions ~ Development banks
OUTLINE Financial institutions dedicated to fund new
and upcoming businesses and economic
NATURE OF CREDIT development projects by providing equity
BASES AND SOURCES capital or loan.
CLASSIFICATIONS OF CREDIT
~ Investment Bank
CREDIT INSTRUMENTS
Financial institutions that provide large
amounts of long-term fixed capital,
Credit primarily established firms. It generally
takes an equity stake in the borrower firm to
A legal agreement to receive cash, goods, or exercise some influence on its direction and
services now and pay for them in the future. operations
~ Savings and Loan Associations
WHY USE CREDIT? Associations that accept savings at interest
Avoid paying cash for large outlays and lend money to savers chiefly for home
Meet financial emergency mortgage loans and may other related
Convenience services.
Investment Purposes ~ Finance Companies
Installment Sales Finance Companies
Consumer Finance Companies
SOURCE OF CREDIT:
Commercial Finance Companies
~ Individual Money Lenders
~ Credit Unions
Lend his surplus to those in need so that it
Corporate organizations which lend savings
will bring income to him
of members to some of the members of the
~ Retail Stores group
~ Pawnshops ~ Insurance Companies
~ Commercial Banks Issues insurance contracts with those who
wish to provide for such contingencies like
Engage in the grant of loans not only to
death or fire. They receive premiums and
businessmen, but also to individuals for
pay out money on the occurrence of the
personal purposes
particular contingencies.
~ Savings Bank
Financial institution whose primary purpose
~ Other Sources
is accepting savings deposits and paying
interest on those deposits Social Security System
Government Service Insurance System
~ Rural Bank
PAG – IBIG
Financial institutions that help rationalize Other Government Agencies
the developing regions or country to finance
their needs specially the projects regarding
agricultural progress
Check credit report regularly.
Types of Credit
Credit Cards
Installment Loans
Service Credit
Revolving Credit
Student Loans
IOU
Single Payment Credit
Credit Cards
Plastic cards with electronic information
that can be used by the holder to make
purchases or obtain cash advances using
a line of credit made available by the
card-issuing financial institution.
Installment Loan
CREDIT POLICIES
A loan in which the amount of payment
May vary from one business to another and the number of payments are
Credit Terms predetermined, such as an automobile
Terms and conditions which credit is loan.
granted.
Credit Periods ◦ Fixed payment
Amount of time within which the ◦ Set period of time
customer is expected to remit payment in
part or in full ◦ Set or varying interest rates
Credit Limit ◦ Examples: Car loans and
A limit with respect to the amount or mortgages
value that a customer can obtain from
the source. Revolving Credit
A type of credit that does NOT have a
fixed number of payments, such as a
How to establish credit? credit card.
Bank accounts ◦ No stated payoff time
Employment history
Residence history ◦ Limit to credit
Utilities in borrower’s name
◦ Minimum monthly payments
Department store or gas credit car
◦ Finance charges
How to maintain a good credit rating?
◦ Example: credit card
Establish a good credit history.
Pay monthly balance on time. Service Credit
Use credit cards sparingly and stay within
A member's earned service, prior
the limit.
service, and purchased service.
Do not move balance to other cards.
Student Loans Lowers credit score
Difficulty getting a loan
Loans offered to students to assist in
payment of the costs of professional
education. These loans usually charger
lower interest than other loans, and are
also usually issued by the government.
Allows a person to finance their
education and defer payments until after
graduation.
Risks of Credit
Interest
Overspending
Debt
Identity Theft
Responsibilities of Credit
Know the real cost of debt.
Don’t use credit to live beyond your means.
It is all about the details...read the fine print!
Pay as much as you can, as early as you can.
Warning Signs of Credit Abuse
Delinquent Payments
Default Notices
Repossession
Collection Agencies
Judgment Lien
Garnishment
Financial Consequences of Debt
Overspending
Paying high interest rates
You might also like
- FinanceDocument5 pagesFinancecrist.jahnskieNo ratings yet
- Finance MidtermDocument4 pagesFinance MidtermHoney GubalaneNo ratings yet
- Individual Money LendersDocument5 pagesIndividual Money LendersMa. Kristine Laurice AmancioNo ratings yet
- Categories Bank Money Lender: Company's TypesDocument5 pagesCategories Bank Money Lender: Company's Typesowenlo876No ratings yet
- Emily Qfin101thursDocument2 pagesEmily Qfin101thursEmily ResuentoNo ratings yet
- Dipali Project ReportDocument58 pagesDipali Project ReportAshish MOHARENo ratings yet
- Full Notes MBF22408T Credit Risk and Recovery ManagementDocument90 pagesFull Notes MBF22408T Credit Risk and Recovery ManagementSheetal DwevediNo ratings yet
- Unit I MBF22408T Credit Risk and Recovery ManagementDocument17 pagesUnit I MBF22408T Credit Risk and Recovery ManagementSheetal DwevediNo ratings yet
- Credit TransactionsDocument26 pagesCredit TransactionssaehalaireNo ratings yet
- Consumer CreditDocument3 pagesConsumer CreditHAIFA DAYANA BT DAZUKINo ratings yet
- Modern Banking: Measures of The Money Supply, Functions and Types of Financial Institutions, and Modern E-BankingDocument16 pagesModern Banking: Measures of The Money Supply, Functions and Types of Financial Institutions, and Modern E-BankingnripendunandyNo ratings yet
- Types of Credit Facilities - Lyst3256Document3 pagesTypes of Credit Facilities - Lyst3256shakeel ahmedNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Credit TransactionsDocument27 pagesModule 4 Credit Transactionslord kwantoniumNo ratings yet
- Money and BankingpptDocument19 pagesMoney and BankingpptSania ZaheerNo ratings yet
- BF Continuation 2Document6 pagesBF Continuation 2Clarisse PauyaNo ratings yet
- Sources of L& S TERm FinanceDocument17 pagesSources of L& S TERm FinanceD Attitude KidNo ratings yet
- Banking Products and Services - Course PresentationDocument171 pagesBanking Products and Services - Course Presentationnimitjain10No ratings yet
- Banking FinanceDocument9 pagesBanking FinanceAstik TripathiNo ratings yet
- Banking Products: and ServicesDocument171 pagesBanking Products: and ServicesJagriti SinghNo ratings yet
- Arranging Funds ModuleDocument34 pagesArranging Funds ModulekylieNo ratings yet
- Social Studies ProjectDocument5 pagesSocial Studies ProjectMarshelleeNo ratings yet
- Nature and Function of CreditDocument28 pagesNature and Function of CreditJennifer Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- SecruDocument29 pagesSecruPooja SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Sources of CapitalDocument42 pagesChapter 5 - Sources of CapitalLIEW YU LIANGNo ratings yet
- Pooja Project ReportDocument62 pagesPooja Project ReportAshish MOHARENo ratings yet
- Credit and Collection Week 4Document69 pagesCredit and Collection Week 4ephesians320laiNo ratings yet
- Bank CreditDocument5 pagesBank Creditnhan thanhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Consumer CreditDocument35 pagesChapter 4 - Consumer CredithaziqNo ratings yet
- Lender DefinitionDocument8 pagesLender Definitionako akoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document29 pagesChapter 4Irene Mae BeldaNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Consumer Loans - 3rd Unit NotesDocument18 pagesEvaluating Consumer Loans - 3rd Unit NotesDr VIRUPAKSHA GOUD GNo ratings yet
- Commercial Lendings by BanksDocument65 pagesCommercial Lendings by Banksvivek satviNo ratings yet
- Types of Credit Instruments & Its FeaturesDocument22 pagesTypes of Credit Instruments & Its Featuresninpra94% (18)
- Chapter 7Document12 pagesChapter 7Muskan KumariNo ratings yet
- Financial Syste - Financial InstitutionDocument15 pagesFinancial Syste - Financial Institutionjennifer.tuguinayNo ratings yet
- Takeover of Home Loans: Internet Banking SBI-Quick-LinksDocument2 pagesTakeover of Home Loans: Internet Banking SBI-Quick-LinksOm ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Sources of Funds: Business FinanceDocument3 pagesSources of Funds: Business FinancePrecious Nicole SantosNo ratings yet
- Consumer CreditDocument33 pagesConsumer CreditNeeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Debentures and BondDocument16 pagesDebentures and Bondbishal bothraNo ratings yet
- Credit Rating:: Working Capital LoansDocument7 pagesCredit Rating:: Working Capital Loansdon faperNo ratings yet
- Personal FinanceDocument10 pagesPersonal FinanceBianca MalinabNo ratings yet
- Based On The Purpose of The CreditDocument5 pagesBased On The Purpose of The CreditAn DoNo ratings yet
- Business FinanceDocument20 pagesBusiness FinanceKim Bryan A. GaliasNo ratings yet
- Basics of Banking - Study NotesDocument13 pagesBasics of Banking - Study NotesTanmoy GhoshNo ratings yet
- Banking Unit 4Document12 pagesBanking Unit 4PaatrickNo ratings yet
- Project ppt.-1Document21 pagesProject ppt.-1Shraddha TripathiNo ratings yet
- Debt DefinitionDocument18 pagesDebt Definitionako akoNo ratings yet
- Loans and AdvancesDocument18 pagesLoans and AdvancesAnupam RoyNo ratings yet
- Security AssetsDocument45 pagesSecurity AssetsLalita BarveNo ratings yet
- Master in Business Finance: Praloy Majumder Icai Mumbai May 2010Document38 pagesMaster in Business Finance: Praloy Majumder Icai Mumbai May 2010praloy66No ratings yet
- FAR Finals ReviewerDocument5 pagesFAR Finals ReviewerJulie Anne DanteNo ratings yet
- Overview of Changing Financial ServicesDocument14 pagesOverview of Changing Financial ServicesNazmul H. PalashNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS FINANCE PresentationDocument55 pagesBUSINESS FINANCE Presentationjeanetteanneborje08No ratings yet
- Develop Understanding of Debt and Consumer CreditDocument5 pagesDevelop Understanding of Debt and Consumer CreditJemal SeidNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER VII COMMERCIAL BANKING 3rd RevisionDocument21 pagesCHAPTER VII COMMERCIAL BANKING 3rd RevisionEunice VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- BANKING Report2Document18 pagesBANKING Report2Ryan Dave GarciaNo ratings yet
- Essay 1Document3 pagesEssay 1api-607929863No ratings yet
- Conflict in AfghanistanDocument10 pagesConflict in AfghanistanAamir HussainNo ratings yet
- Analysis Essay (SFA)Document1 pageAnalysis Essay (SFA)saihtookhantkyaw22No ratings yet
- Analysis of Essay of Youth and Age': Francis Bacon 'The Great Philosopher'Document4 pagesAnalysis of Essay of Youth and Age': Francis Bacon 'The Great Philosopher'muhammad shahidNo ratings yet
- Soal AdrianiDocument3 pagesSoal AdrianiAhmad SupianNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCheat SheetSharon SagerNo ratings yet
- Contractual Claims References Version 7Document301 pagesContractual Claims References Version 7SSalma70100% (13)
- Ramayana - The Essence of The VedasDocument18 pagesRamayana - The Essence of The Vedasthink_sriNo ratings yet
- William Shakespeare's SonnetsDocument5 pagesWilliam Shakespeare's Sonnetsgabryela22No ratings yet
- Model Answer - Final Revision SEC.1 - Term 2Document5 pagesModel Answer - Final Revision SEC.1 - Term 2Mahmoud IbrahimNo ratings yet
- The Divine Interpretation:: A Study of Metaphor in Dante's InfernoDocument5 pagesThe Divine Interpretation:: A Study of Metaphor in Dante's InfernoStephanie BorgesNo ratings yet
- The Tragical History of Doctor Faustus by Christopher MarloweDocument8 pagesThe Tragical History of Doctor Faustus by Christopher MarloweJOSUE BARRIOSNo ratings yet
- Approaches To The Study of Social Problems: The Person-Blame ApproachDocument4 pagesApproaches To The Study of Social Problems: The Person-Blame ApproachsnehaoctNo ratings yet
- Sonic R. SystemDocument2 pagesSonic R. Systemthang 1No ratings yet
- Haitham Samir C.V - FinalDocument5 pagesHaitham Samir C.V - FinalElizabeth SmithNo ratings yet
- Yrrel Janzedrick Cristobal SalesDocument5 pagesYrrel Janzedrick Cristobal SalesClark InternationalNo ratings yet
- Epic of Sundiata PaperDocument4 pagesEpic of Sundiata PaperAdel MahjoubNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Quezon City, Metro Manila: Ouse F EpresentativesDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Quezon City, Metro Manila: Ouse F EpresentativesKabataan Party-ListNo ratings yet
- Civ Pro 1 Module 3 1Document26 pagesCiv Pro 1 Module 3 1Ammar KattoulaNo ratings yet
- Voluntarism - IEPDocument1 pageVoluntarism - IEPLeandro BertoncelloNo ratings yet
- Genre Analysis On Racial StereotypeDocument4 pagesGenre Analysis On Racial Stereotypeapi-316855715No ratings yet
- Dialogues in The RestaurantDocument2 pagesDialogues in The RestaurantZsuzsa SzékelyNo ratings yet
- The Bias of The World - Curating After Szeemann & Hopps - The Brooklyn RailDocument14 pagesThe Bias of The World - Curating After Szeemann & Hopps - The Brooklyn RailALEJANDRA DUEÑASNo ratings yet
- 40 Values ChecklistDocument1 page40 Values ChecklistCarina LindseyNo ratings yet
- Environment Position PaperDocument6 pagesEnvironment Position PaperJenlisa KimanobanNo ratings yet
- MPA - Policy Paper (R.simbahon)Document80 pagesMPA - Policy Paper (R.simbahon)Robert SimbahonNo ratings yet
- Noting and DraftingDocument42 pagesNoting and DraftingJyoti Sinha100% (2)
- Jesus of Levi and JudahDocument40 pagesJesus of Levi and JudahAntony Hylton100% (1)
- Criminal Complaint For Mustafa Rahsad BushDocument13 pagesCriminal Complaint For Mustafa Rahsad BushinforumdocsNo ratings yet
- Smeaheia Dataset License - Gassnova and EquinorDocument5 pagesSmeaheia Dataset License - Gassnova and EquinorZainab AdedejiNo ratings yet