Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acceleration Change of Direction Assignment - 1
Acceleration Change of Direction Assignment - 1
Uploaded by
Study PixCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- New Scientist Essential Guide - No10 - Einstein's UniverseDocument102 pagesNew Scientist Essential Guide - No10 - Einstein's UniverseHieu TrinhNo ratings yet
- Daily Practice Problems (Motion) : Objective DPP - 1.1Document25 pagesDaily Practice Problems (Motion) : Objective DPP - 1.1Mayank SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 1 (Revision) Motion in One Dimension: Bakliwal Tutorials - IITDocument5 pagesPhysics Chapter 1 (Revision) Motion in One Dimension: Bakliwal Tutorials - IITMihica KhareNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 - Circular MotionDocument4 pagesDPP - 01 - Circular Motionshivansh mishra roll no. 30No ratings yet
- CT - Kinematics - Kinematics Practice Sheet - 10062020 - Physics - Kinematics - Sheet - 1 To 10Document21 pagesCT - Kinematics - Kinematics Practice Sheet - 10062020 - Physics - Kinematics - Sheet - 1 To 10Nilesh NagarNo ratings yet
- Kinematics P ME KNM 01-02-03Document3 pagesKinematics P ME KNM 01-02-03Raghav MishraNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Quiz by Ruchir AroraDocument4 pagesKinematics Quiz by Ruchir Arorachaitanya goyalNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion MCQ PDFDocument17 pagesCircular Motion MCQ PDFZIA UR REHMANNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 _ Kinematics Of Circular MotionDocument4 pagesDPP - 01 _ Kinematics Of Circular MotionAnsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Praveen Kumar Pachauri: IIT-JEE - 2020 - 2021Document22 pagesPraveen Kumar Pachauri: IIT-JEE - 2020 - 2021Vibhas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics 11th Test No 4 CH 5 Start To Rotational K.EDocument2 pagesPhysics 11th Test No 4 CH 5 Start To Rotational K.EatfaNo ratings yet
- Think As King Part-1Document3 pagesThink As King Part-1girrajsharma0999No ratings yet
- Z - Kinematics 1-D - CombineDocument24 pagesZ - Kinematics 1-D - CombineAryan SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter #4Document13 pagesChapter #4Malik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- 15 Vector - MidPhase 1 - Physics - QDocument3 pages15 Vector - MidPhase 1 - Physics - QDevansh DuhanNo ratings yet
- 11 TH STD Motion in 2 Dimension, Circular Motion Jee-Neet MCQ Test Paper 02 Jan 2023.Document4 pages11 TH STD Motion in 2 Dimension, Circular Motion Jee-Neet MCQ Test Paper 02 Jan 2023.Rajiv RathodNo ratings yet
- Motion - Daily Home Assignment 04 PDFDocument4 pagesMotion - Daily Home Assignment 04 PDFHarshit SinglaNo ratings yet
- Class - 11 Vedantu Physics Chp-2 Objective Questions With SolutionsDocument26 pagesClass - 11 Vedantu Physics Chp-2 Objective Questions With SolutionsAloke kr. MondalNo ratings yet
- Kinematics LN 1DDocument8 pagesKinematics LN 1D2pwxanqt8aNo ratings yet
- Class 11-Kinematics - 1 Test - MaligaonDocument8 pagesClass 11-Kinematics - 1 Test - MaligaonHimangshuMandalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Circular MotionDocument4 pagesChapter 04 Circular MotionMuhammad AtirNo ratings yet
- QP Class 11Document2 pagesQP Class 11gkr94No ratings yet
- Asaptutor-Motion in A Plane (Gr11-Physics)Document9 pagesAsaptutor-Motion in A Plane (Gr11-Physics)jimmyemandeeNo ratings yet
- Ch-05 Circular Motion: Practice Sheet 01Document5 pagesCh-05 Circular Motion: Practice Sheet 01Vikas GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics DPP - 6Document4 pagesPhysics DPP - 6Hemant JasoriyaNo ratings yet
- Intso Stso Physics Class Vii Motion and Time Worksheet-8Document3 pagesIntso Stso Physics Class Vii Motion and Time Worksheet-8murali.trichyNo ratings yet
- 2 Kinematics 1-D FINAL 1664995471946Document21 pages2 Kinematics 1-D FINAL 1664995471946PRIYATAM IOAANo ratings yet
- Physics Class 11Document9 pagesPhysics Class 11eagleankush5No ratings yet
- 10 KINEMATICS - Doc 1Document4 pages10 KINEMATICS - Doc 1Prabodh GuptNo ratings yet
- KM - Circular MotionDocument1 pageKM - Circular Motionatharva varshneyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Motion in A Plane (PG 09 - 26)Document17 pagesChapter-3 Motion in A Plane (PG 09 - 26)darling deanNo ratings yet
- CD 7 e 4 B 01 B 7 e 4 Ad 1 Aa 95Document18 pagesCD 7 e 4 B 01 B 7 e 4 Ad 1 Aa 95RiteshNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes (Exam)Document6 pagesPhysics Notes (Exam)Christopher MorrisNo ratings yet
- 1.AS-RT PhyDocument2 pages1.AS-RT Phypranshulrai17No ratings yet
- XI Physics KEY Irfan Sanjrani 4TH FNTDocument3 pagesXI Physics KEY Irfan Sanjrani 4TH FNTjaipal singhNo ratings yet
- Work Book # 1: Distance & Displacement, Speed &velocity, Average Speed & Average Velocity 1Document21 pagesWork Book # 1: Distance & Displacement, Speed &velocity, Average Speed & Average Velocity 1Shreyas MishraNo ratings yet
- KINEMATICSDocument53 pagesKINEMATICSSwadhin BarikNo ratings yet
- Aiits 1820 HCT I Jeea Paper 1Document15 pagesAiits 1820 HCT I Jeea Paper 1Axbycz0% (1)
- Motion in 1dDocument12 pagesMotion in 1dkhushi23277No ratings yet
- IX Science Chapter 08 AssignmentDocument8 pagesIX Science Chapter 08 AssignmentARPIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Grav, Rot, SHMDocument4 pagesGrav, Rot, SHMSandeep NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion (Question Paper)Document6 pagesCircular Motion (Question Paper)anchlia12345No ratings yet
- phy class 11 test no 1Document2 pagesphy class 11 test no 1binodkrm826No ratings yet
- MT 3 Medical PaperDocument20 pagesMT 3 Medical PaperRiteshNo ratings yet
- Part-A Single Correct Choice Type (1-5) : MST (Km+Vector)Document4 pagesPart-A Single Correct Choice Type (1-5) : MST (Km+Vector)AtulNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion (MCQ)Document17 pagesCircular Motion (MCQ)mail2sgarg_841221144No ratings yet
- Model Test Paper 1 PDFDocument5 pagesModel Test Paper 1 PDFShaunak ThakarNo ratings yet
- Mock Test - 97 (16 Jan 2023) Rotational DynamicsDocument1 pageMock Test - 97 (16 Jan 2023) Rotational DynamicsparamNo ratings yet
- Neet - 2017 Test Series Two Dimensional Motion & Work Power EnergyDocument4 pagesNeet - 2017 Test Series Two Dimensional Motion & Work Power Energyumved singh yadav100% (1)
- CIRCULAR MOTION JEE PracticeDocument21 pagesCIRCULAR MOTION JEE PracticeDev PatelNo ratings yet
- 2019MTEQtr1G12-STEM - Physics 1Document8 pages2019MTEQtr1G12-STEM - Physics 1Elcid BocacaoNo ratings yet
- Special Class TestDocument73 pagesSpecial Class TestSatyam YadavNo ratings yet
- SPP 01Document6 pagesSPP 01Ryan MittalNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight LineDocument8 pagesMotion in A Straight LinemathsbykeshavNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee Phase Test 1 (Class XI), 16 Aug, 2020: Advanced Paper 2Document11 pagesFiitjee Phase Test 1 (Class XI), 16 Aug, 2020: Advanced Paper 2Mayukh MaityNo ratings yet
- Phyiscs Wallah QuestionsDocument25 pagesPhyiscs Wallah QuestionsFreedom Fighters FanNo ratings yet
- Techno Test Ix (Physics)Document2 pagesTechno Test Ix (Physics)swathyraghavendranNo ratings yet
- Techno Test Ix (Physics)Document2 pagesTechno Test Ix (Physics)swathyraghavendranNo ratings yet
- Course: Circular Motion: Presented by Kailash SharmaDocument29 pagesCourse: Circular Motion: Presented by Kailash SharmaHJNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Introduction To General Physics & Scientific MethodDocument24 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To General Physics & Scientific MethodJamicah Nicole SolisNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Thermochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry Chemistry AP Chapter 23: Nuclear Chemistry 23.1: The Nature of Nuclear ReactionsDocument16 pagesUnit 4: Thermochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry Chemistry AP Chapter 23: Nuclear Chemistry 23.1: The Nature of Nuclear ReactionsPankaj Kumar50% (4)
- Year 12 MockDocument5 pagesYear 12 MockAlvan MmaduwubaNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Electromagnetism - David DugdaleDocument378 pagesEssentials of Electromagnetism - David DugdaleLuis AugustoNo ratings yet
- The Physics of Gamma-Ray BurstsDocument109 pagesThe Physics of Gamma-Ray Bursts龙李No ratings yet
- 5.1 Electric Fields NotesDocument1 page5.1 Electric Fields NotesMouneissa Cisse - NYT.StudentNo ratings yet
- Efficient Hybrid Solar Cells From Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and A Conjugated PolymerDocument5 pagesEfficient Hybrid Solar Cells From Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and A Conjugated Polymerlong tran hoangNo ratings yet
- Can J Chem Eng - 2022 - Pukkella - An Integrated CFD Methodology For Tracking Fluid Interfaces and Solid Distributions in ADocument20 pagesCan J Chem Eng - 2022 - Pukkella - An Integrated CFD Methodology For Tracking Fluid Interfaces and Solid Distributions in AArjun KumarNo ratings yet
- PHD Course Work Syllabus PhysicsDocument5 pagesPHD Course Work Syllabus Physicsmtywrhajd100% (2)
- Half BHZDocument18 pagesHalf BHZShreya DebnathNo ratings yet
- Eugen Merzbacher - Quantum MechanicsDocument670 pagesEugen Merzbacher - Quantum MechanicsMilan Milovanovic100% (1)
- Detectors - Electron Spin ResonanceDocument7 pagesDetectors - Electron Spin ResonancegdgdfgNo ratings yet
- Plasmon-Enhanced Light-Matter Interactions and ApplicationsDocument14 pagesPlasmon-Enhanced Light-Matter Interactions and ApplicationsAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- Dana P. Williams-A Very Short Course On C - Algebras-2019 161ppDocument161 pagesDana P. Williams-A Very Short Course On C - Algebras-2019 161ppDumitru D. DRAGHIANo ratings yet
- Regularity Methods in Tropical Operator Theory: Ho Chi Minh, Le Duan, G. Lindemann and N. GrothendieckDocument12 pagesRegularity Methods in Tropical Operator Theory: Ho Chi Minh, Le Duan, G. Lindemann and N. GrothendieckhahattproNo ratings yet
- Measuring Planck's Constant Using The Photoelectric Effect Purpose: TheoryDocument3 pagesMeasuring Planck's Constant Using The Photoelectric Effect Purpose: TheoryAmrit NumanNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Constituents of The Material World. ContentsDocument6 pagesThe Ultimate Constituents of The Material World. ContentsloparedesNo ratings yet
- NCERT Grade 11 Physics CH 07 System of Particles and Rotational MotionDocument32 pagesNCERT Grade 11 Physics CH 07 System of Particles and Rotational MotionNilanjan BiswasNo ratings yet
- Book 17296 PDFDocument205 pagesBook 17296 PDFREVA ENo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation Lucture 9Document18 pagesEnergy Conservation Lucture 9julia saleemNo ratings yet
- Plasma: Plasma (from Greek πλάσμα, "anything formed"Document7 pagesPlasma: Plasma (from Greek πλάσμα, "anything formed"Maitri ShahNo ratings yet
- Theory and Application For The Scanning Tunneling MicroscopeDocument4 pagesTheory and Application For The Scanning Tunneling MicroscopeIgor LukacevicNo ratings yet
- 2022 AP Chem Summer Assignment ReviewDocument8 pages2022 AP Chem Summer Assignment ReviewDon RengNo ratings yet
- CDW in YbcoDocument48 pagesCDW in YbcoIon IvanNo ratings yet
- CH 22Document63 pagesCH 22mariamNo ratings yet
- PHYS234: Assignment 1 Solutions: Problem 1Document3 pagesPHYS234: Assignment 1 Solutions: Problem 1Erica wangNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics @kvpy - AspirantsDocument5 pagesModern Physics @kvpy - AspirantssagarNo ratings yet
- DPP 1 - Mathematical Tools & Vector PDFDocument2 pagesDPP 1 - Mathematical Tools & Vector PDFRahul BNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/41Document28 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/41Zhongchen TianNo ratings yet
Acceleration Change of Direction Assignment - 1
Acceleration Change of Direction Assignment - 1
Uploaded by
Study PixOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acceleration Change of Direction Assignment - 1
Acceleration Change of Direction Assignment - 1
Uploaded by
Study PixCopyright:
Available Formats
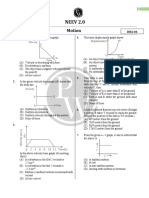
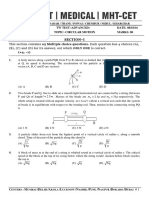
ACCELERATION CHANGE OF DIRECTION
ASSIGNMENT - 1
1. A particle is moving in x–y–plane at 2 m/s along x–axis. 2 seconds later, its velocity is 4 m/s in
a direction making 60° with positive x–axis. Its average acceleration for this period of motion is:-
(A) 5 m/s2 , along y–axis (B) 3 m/s2, along y–axis
(C) 5 m/s2, along at 60° with positive x–axis (D) 3m/s2, at 60° with positive x–axis.
2. The second's hand of a watch has length 6 cm. Speed of end point and magnitude of
difference of velocities at two perpendicular positions will be
(A) 2p & 0 mm/s (B) 2 2 & 4.44 mm/s
(C) 2 2 & 2p mm/s (D) 2p & 2 2 mm/s
3. An object may have :-
(A) Varying speed without having varying acceleration
(B) Varying velocity without having varying speed
(C) Non–zero acceleration without having varying velocity
(D) Non–zero acceleration without having varying speed .
4. Which of the following statements are true for a moving body ?
(A) If its speed changes, its velocity must change and it must have some acceleration
(B) If its velocity changes, its speeds must change and it must have some acceleration
(C) If its velocity changes, its speed may or may not change, and it must have some acceleration
(D) If its speed changes but direction of motion does not change, its velocity may remain constant
5. When a particle is in motion, its acceleration may be in any direction.
6. a particle is rotating in a circle of radius 1m with constant speed 4 m/s. In time 1 s, match the following
(in SI units)
Column I Column II
(A) Displacement (p) 8 sin 2
(B) Distance (q) 4
(C) Average velocity (r) 2 sin 2
(D) Average acceleration (s) 4 sin 2
ANSWER KEYS
1. (B) 2. (D) 3. (A,B,D) 4. (A,C) 5. (T) 6. Straight line
You might also like
- New Scientist Essential Guide - No10 - Einstein's UniverseDocument102 pagesNew Scientist Essential Guide - No10 - Einstein's UniverseHieu TrinhNo ratings yet
- Daily Practice Problems (Motion) : Objective DPP - 1.1Document25 pagesDaily Practice Problems (Motion) : Objective DPP - 1.1Mayank SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 1 (Revision) Motion in One Dimension: Bakliwal Tutorials - IITDocument5 pagesPhysics Chapter 1 (Revision) Motion in One Dimension: Bakliwal Tutorials - IITMihica KhareNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 - Circular MotionDocument4 pagesDPP - 01 - Circular Motionshivansh mishra roll no. 30No ratings yet
- CT - Kinematics - Kinematics Practice Sheet - 10062020 - Physics - Kinematics - Sheet - 1 To 10Document21 pagesCT - Kinematics - Kinematics Practice Sheet - 10062020 - Physics - Kinematics - Sheet - 1 To 10Nilesh NagarNo ratings yet
- Kinematics P ME KNM 01-02-03Document3 pagesKinematics P ME KNM 01-02-03Raghav MishraNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Quiz by Ruchir AroraDocument4 pagesKinematics Quiz by Ruchir Arorachaitanya goyalNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion MCQ PDFDocument17 pagesCircular Motion MCQ PDFZIA UR REHMANNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 _ Kinematics Of Circular MotionDocument4 pagesDPP - 01 _ Kinematics Of Circular MotionAnsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Praveen Kumar Pachauri: IIT-JEE - 2020 - 2021Document22 pagesPraveen Kumar Pachauri: IIT-JEE - 2020 - 2021Vibhas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics 11th Test No 4 CH 5 Start To Rotational K.EDocument2 pagesPhysics 11th Test No 4 CH 5 Start To Rotational K.EatfaNo ratings yet
- Think As King Part-1Document3 pagesThink As King Part-1girrajsharma0999No ratings yet
- Z - Kinematics 1-D - CombineDocument24 pagesZ - Kinematics 1-D - CombineAryan SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter #4Document13 pagesChapter #4Malik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- 15 Vector - MidPhase 1 - Physics - QDocument3 pages15 Vector - MidPhase 1 - Physics - QDevansh DuhanNo ratings yet
- 11 TH STD Motion in 2 Dimension, Circular Motion Jee-Neet MCQ Test Paper 02 Jan 2023.Document4 pages11 TH STD Motion in 2 Dimension, Circular Motion Jee-Neet MCQ Test Paper 02 Jan 2023.Rajiv RathodNo ratings yet
- Motion - Daily Home Assignment 04 PDFDocument4 pagesMotion - Daily Home Assignment 04 PDFHarshit SinglaNo ratings yet
- Class - 11 Vedantu Physics Chp-2 Objective Questions With SolutionsDocument26 pagesClass - 11 Vedantu Physics Chp-2 Objective Questions With SolutionsAloke kr. MondalNo ratings yet
- Kinematics LN 1DDocument8 pagesKinematics LN 1D2pwxanqt8aNo ratings yet
- Class 11-Kinematics - 1 Test - MaligaonDocument8 pagesClass 11-Kinematics - 1 Test - MaligaonHimangshuMandalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Circular MotionDocument4 pagesChapter 04 Circular MotionMuhammad AtirNo ratings yet
- QP Class 11Document2 pagesQP Class 11gkr94No ratings yet
- Asaptutor-Motion in A Plane (Gr11-Physics)Document9 pagesAsaptutor-Motion in A Plane (Gr11-Physics)jimmyemandeeNo ratings yet
- Ch-05 Circular Motion: Practice Sheet 01Document5 pagesCh-05 Circular Motion: Practice Sheet 01Vikas GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics DPP - 6Document4 pagesPhysics DPP - 6Hemant JasoriyaNo ratings yet
- Intso Stso Physics Class Vii Motion and Time Worksheet-8Document3 pagesIntso Stso Physics Class Vii Motion and Time Worksheet-8murali.trichyNo ratings yet
- 2 Kinematics 1-D FINAL 1664995471946Document21 pages2 Kinematics 1-D FINAL 1664995471946PRIYATAM IOAANo ratings yet
- Physics Class 11Document9 pagesPhysics Class 11eagleankush5No ratings yet
- 10 KINEMATICS - Doc 1Document4 pages10 KINEMATICS - Doc 1Prabodh GuptNo ratings yet
- KM - Circular MotionDocument1 pageKM - Circular Motionatharva varshneyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Motion in A Plane (PG 09 - 26)Document17 pagesChapter-3 Motion in A Plane (PG 09 - 26)darling deanNo ratings yet
- CD 7 e 4 B 01 B 7 e 4 Ad 1 Aa 95Document18 pagesCD 7 e 4 B 01 B 7 e 4 Ad 1 Aa 95RiteshNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes (Exam)Document6 pagesPhysics Notes (Exam)Christopher MorrisNo ratings yet
- 1.AS-RT PhyDocument2 pages1.AS-RT Phypranshulrai17No ratings yet
- XI Physics KEY Irfan Sanjrani 4TH FNTDocument3 pagesXI Physics KEY Irfan Sanjrani 4TH FNTjaipal singhNo ratings yet
- Work Book # 1: Distance & Displacement, Speed &velocity, Average Speed & Average Velocity 1Document21 pagesWork Book # 1: Distance & Displacement, Speed &velocity, Average Speed & Average Velocity 1Shreyas MishraNo ratings yet
- KINEMATICSDocument53 pagesKINEMATICSSwadhin BarikNo ratings yet
- Aiits 1820 HCT I Jeea Paper 1Document15 pagesAiits 1820 HCT I Jeea Paper 1Axbycz0% (1)
- Motion in 1dDocument12 pagesMotion in 1dkhushi23277No ratings yet
- IX Science Chapter 08 AssignmentDocument8 pagesIX Science Chapter 08 AssignmentARPIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Grav, Rot, SHMDocument4 pagesGrav, Rot, SHMSandeep NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion (Question Paper)Document6 pagesCircular Motion (Question Paper)anchlia12345No ratings yet
- phy class 11 test no 1Document2 pagesphy class 11 test no 1binodkrm826No ratings yet
- MT 3 Medical PaperDocument20 pagesMT 3 Medical PaperRiteshNo ratings yet
- Part-A Single Correct Choice Type (1-5) : MST (Km+Vector)Document4 pagesPart-A Single Correct Choice Type (1-5) : MST (Km+Vector)AtulNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion (MCQ)Document17 pagesCircular Motion (MCQ)mail2sgarg_841221144No ratings yet
- Model Test Paper 1 PDFDocument5 pagesModel Test Paper 1 PDFShaunak ThakarNo ratings yet
- Mock Test - 97 (16 Jan 2023) Rotational DynamicsDocument1 pageMock Test - 97 (16 Jan 2023) Rotational DynamicsparamNo ratings yet
- Neet - 2017 Test Series Two Dimensional Motion & Work Power EnergyDocument4 pagesNeet - 2017 Test Series Two Dimensional Motion & Work Power Energyumved singh yadav100% (1)
- CIRCULAR MOTION JEE PracticeDocument21 pagesCIRCULAR MOTION JEE PracticeDev PatelNo ratings yet
- 2019MTEQtr1G12-STEM - Physics 1Document8 pages2019MTEQtr1G12-STEM - Physics 1Elcid BocacaoNo ratings yet
- Special Class TestDocument73 pagesSpecial Class TestSatyam YadavNo ratings yet
- SPP 01Document6 pagesSPP 01Ryan MittalNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight LineDocument8 pagesMotion in A Straight LinemathsbykeshavNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee Phase Test 1 (Class XI), 16 Aug, 2020: Advanced Paper 2Document11 pagesFiitjee Phase Test 1 (Class XI), 16 Aug, 2020: Advanced Paper 2Mayukh MaityNo ratings yet
- Phyiscs Wallah QuestionsDocument25 pagesPhyiscs Wallah QuestionsFreedom Fighters FanNo ratings yet
- Techno Test Ix (Physics)Document2 pagesTechno Test Ix (Physics)swathyraghavendranNo ratings yet
- Techno Test Ix (Physics)Document2 pagesTechno Test Ix (Physics)swathyraghavendranNo ratings yet
- Course: Circular Motion: Presented by Kailash SharmaDocument29 pagesCourse: Circular Motion: Presented by Kailash SharmaHJNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Introduction To General Physics & Scientific MethodDocument24 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To General Physics & Scientific MethodJamicah Nicole SolisNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Thermochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry Chemistry AP Chapter 23: Nuclear Chemistry 23.1: The Nature of Nuclear ReactionsDocument16 pagesUnit 4: Thermochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry Chemistry AP Chapter 23: Nuclear Chemistry 23.1: The Nature of Nuclear ReactionsPankaj Kumar50% (4)
- Year 12 MockDocument5 pagesYear 12 MockAlvan MmaduwubaNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Electromagnetism - David DugdaleDocument378 pagesEssentials of Electromagnetism - David DugdaleLuis AugustoNo ratings yet
- The Physics of Gamma-Ray BurstsDocument109 pagesThe Physics of Gamma-Ray Bursts龙李No ratings yet
- 5.1 Electric Fields NotesDocument1 page5.1 Electric Fields NotesMouneissa Cisse - NYT.StudentNo ratings yet
- Efficient Hybrid Solar Cells From Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and A Conjugated PolymerDocument5 pagesEfficient Hybrid Solar Cells From Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and A Conjugated Polymerlong tran hoangNo ratings yet
- Can J Chem Eng - 2022 - Pukkella - An Integrated CFD Methodology For Tracking Fluid Interfaces and Solid Distributions in ADocument20 pagesCan J Chem Eng - 2022 - Pukkella - An Integrated CFD Methodology For Tracking Fluid Interfaces and Solid Distributions in AArjun KumarNo ratings yet
- PHD Course Work Syllabus PhysicsDocument5 pagesPHD Course Work Syllabus Physicsmtywrhajd100% (2)
- Half BHZDocument18 pagesHalf BHZShreya DebnathNo ratings yet
- Eugen Merzbacher - Quantum MechanicsDocument670 pagesEugen Merzbacher - Quantum MechanicsMilan Milovanovic100% (1)
- Detectors - Electron Spin ResonanceDocument7 pagesDetectors - Electron Spin ResonancegdgdfgNo ratings yet
- Plasmon-Enhanced Light-Matter Interactions and ApplicationsDocument14 pagesPlasmon-Enhanced Light-Matter Interactions and ApplicationsAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- Dana P. Williams-A Very Short Course On C - Algebras-2019 161ppDocument161 pagesDana P. Williams-A Very Short Course On C - Algebras-2019 161ppDumitru D. DRAGHIANo ratings yet
- Regularity Methods in Tropical Operator Theory: Ho Chi Minh, Le Duan, G. Lindemann and N. GrothendieckDocument12 pagesRegularity Methods in Tropical Operator Theory: Ho Chi Minh, Le Duan, G. Lindemann and N. GrothendieckhahattproNo ratings yet
- Measuring Planck's Constant Using The Photoelectric Effect Purpose: TheoryDocument3 pagesMeasuring Planck's Constant Using The Photoelectric Effect Purpose: TheoryAmrit NumanNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Constituents of The Material World. ContentsDocument6 pagesThe Ultimate Constituents of The Material World. ContentsloparedesNo ratings yet
- NCERT Grade 11 Physics CH 07 System of Particles and Rotational MotionDocument32 pagesNCERT Grade 11 Physics CH 07 System of Particles and Rotational MotionNilanjan BiswasNo ratings yet
- Book 17296 PDFDocument205 pagesBook 17296 PDFREVA ENo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation Lucture 9Document18 pagesEnergy Conservation Lucture 9julia saleemNo ratings yet
- Plasma: Plasma (from Greek πλάσμα, "anything formed"Document7 pagesPlasma: Plasma (from Greek πλάσμα, "anything formed"Maitri ShahNo ratings yet
- Theory and Application For The Scanning Tunneling MicroscopeDocument4 pagesTheory and Application For The Scanning Tunneling MicroscopeIgor LukacevicNo ratings yet
- 2022 AP Chem Summer Assignment ReviewDocument8 pages2022 AP Chem Summer Assignment ReviewDon RengNo ratings yet
- CDW in YbcoDocument48 pagesCDW in YbcoIon IvanNo ratings yet
- CH 22Document63 pagesCH 22mariamNo ratings yet
- PHYS234: Assignment 1 Solutions: Problem 1Document3 pagesPHYS234: Assignment 1 Solutions: Problem 1Erica wangNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics @kvpy - AspirantsDocument5 pagesModern Physics @kvpy - AspirantssagarNo ratings yet
- DPP 1 - Mathematical Tools & Vector PDFDocument2 pagesDPP 1 - Mathematical Tools & Vector PDFRahul BNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/41Document28 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/41Zhongchen TianNo ratings yet