Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MMM Poster Finl
MMM Poster Finl
Uploaded by
Parth Dalal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageMMM Poster Finl
MMM Poster Finl
Uploaded by
Parth DalalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
SYMEA028-Parth Dalal
Pimpri Chinchwad Education Trust’s
SYMEA030-Dhruva Damle
Pimpri Chinchwad College of Engineering SYMEA036-Vivek Deshmukh
SYMEA043-Dwaipayan Dhar
Metrology & Mechanical Measurement SYMEA054-Pratik Ghodke
IE2 Assignment: Sensor Selection.
Transducer Selection for Room Temperature Monitoring: Thermocouple Transducer Selection for Monitoring the Steering angle and rate of
rotation of steering wheel: Angle Sensor
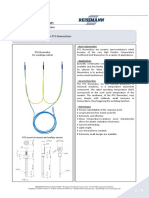
Fig. 1.1: Thermocouple Fig.1.2: Thermocouple
IMG Source: Directindustry.com Image source: Wikimedia Commons
Fig.2.2 Schematic Diagram
Image Source:digikey.in
Working
Advantages & Capabilities Working
Working
Advantages & Capabilities:
Thermocouples utilize the Seebeck effect, Speed: Angle sensors offer fast and efficient
Wide Temperature Range: Thermocouples
where a voltage is produced across the data capture, ideal for high-volume
can measure a wide range of temperatures, .
junction of two different metals under a packaging lines.
from cryogenic temperatures to extremely
temperature gradient. This voltage is
high temperatures encountered in furnaces. Versatility: Angle sensors are available in
proportional to the temperature difference
Ruggedness: They are robust and can various Categories like touchless, Shaft-type,
between the measuring and reference
withstand harsh industrial environments, Hollow-Shaft, multi-turn angle sensors.
junctions. By measuring this voltage and
including high temperatures and mechanical
referencing calibration tables or equations Integration: Angle sensors can easily
shocks.
specific to the thermocouple type, the integrate with existing Steering system and
Fast Response Time: Thermocouples have
temperature can be accurately determined. data can be acquired.
a rapid response time, making them suitable
for applications where quick temperature
measurements are required.
Static Characteristics Static Characteristics
Range: Typically, from -200°C to 2300°C. Precision: The angle sensors have high
Comparison with Other
Accuracy: Varies based on the type and precision, down to 0.1. Options
construction, but can achieve accuracies Comparison with Other Options Sensitivity: High sensitivity, immediate output AMR based Sensors: Less angle range upto
within a few degrees Celsius. after specific input. 180deg as compared to hall effect which provides
Sensitivity: Higher sensitivity compared 360deg.
RTDs(Resistance Temperature Detector):
to other temperature measurement While RTDs offer higher accuracy and GMR based Sensors: High angle resolution,
devices. stability in a narrower temperature range, they Dynamic Characteristics less accuracy and deflects with temperature
are more susceptible to damage in high- change.
Dynamic Characteristics
temperature environments and typically
Response Time: Fast response time, Response Time: The time taken for the sensor to
require more complex signal conditioning.
usually within a few seconds. decode the inputs after it is presented.
Infrared Pyrometers: Although they offer Durability: Resistance to environmental factors
Linearity: Generally linear within the
non-contact temperature measurement, they
specified temperature range. like dust, moisture, and shock.
may not be suitable for all applications,
Drift: Minimal drift over time, ensuring especially those with obstructions or varying Connectivity: Options for wired or wireless
stable and reliable measurements. emissivity. It’s expensive. connection to interface with other systems.
You might also like
- Isuzu 4fb1 Engine ManualDocument3 pagesIsuzu 4fb1 Engine ManualGermán40% (10)
- YSICatalog 1998Document85 pagesYSICatalog 1998danielNo ratings yet
- Industrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionFrom EverandIndustrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- How To Estimate Operating Costs PDFDocument5 pagesHow To Estimate Operating Costs PDFKimberly ConleyNo ratings yet
- 9 Electricity Test - CircuitsDocument5 pages9 Electricity Test - CircuitsRahmonGreen100% (1)
- Temperature Sensor GuideDocument12 pagesTemperature Sensor Guideriver147No ratings yet
- S4-P2 Conkle WirelessSensorTechnologiesDocument28 pagesS4-P2 Conkle WirelessSensorTechnologiesasndmpNo ratings yet
- Mini Project ReportDocument14 pagesMini Project ReportfatinNo ratings yet
- IR Inspection Program For Fired Heater Mechanical Integrity: New Product!Document1 pageIR Inspection Program For Fired Heater Mechanical Integrity: New Product!bazil17No ratings yet
- Still Will: TestsDocument3 pagesStill Will: TestsDanilo FortesNo ratings yet
- Technical Note: Cooled Vs Uncooled Thermal ImagingDocument4 pagesTechnical Note: Cooled Vs Uncooled Thermal ImagingGallegos MONo ratings yet
- Labaratory Report.Document6 pagesLabaratory Report.Mary Grace SecondesNo ratings yet
- Imu20 Data SheetDocument2 pagesImu20 Data SheetDevis DexvilsNo ratings yet
- Physics QuestionsDocument15 pagesPhysics QuestionsMoniruzzaman MahadiNo ratings yet
- Revised Blog Content - MAY 2019Document5 pagesRevised Blog Content - MAY 2019Rugged MonitoringNo ratings yet
- DSC-8000 8500-Specifications English PDFDocument3 pagesDSC-8000 8500-Specifications English PDFDanny KurniaNo ratings yet
- Shield Fire Detection and Evacuation System 12 15Document4 pagesShield Fire Detection and Evacuation System 12 15eng.abdullrahmanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Fault Monitoring Using GSM Technology: April 2016Document4 pagesThermal Power Plant Fault Monitoring Using GSM Technology: April 2016Sporada TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Thermal Actuators Powering InnovationDocument10 pagesThermal Actuators Powering Innovationmahi04087No ratings yet
- DE28 Differential Pressure Transmitter: Block Schematic DiagramDocument4 pagesDE28 Differential Pressure Transmitter: Block Schematic Diagramsudarsana 6185091jaNo ratings yet
- TigerTech PredictiveMaintenance 1Document2 pagesTigerTech PredictiveMaintenance 1Música BNo ratings yet
- Thermocouple Attachment Unit PDFDocument2 pagesThermocouple Attachment Unit PDFvjvijay88No ratings yet
- Design-Of-Early-Fault-Detection-Technique-F - 2014 - International-Journal-of-ElDocument7 pagesDesign-Of-Early-Fault-Detection-Technique-F - 2014 - International-Journal-of-ElM Firdaus AhmadNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Miscllanious MeasurementDocument10 pagesUnit 6 Miscllanious Measurement08 Dadarkar Mujtaba MEANo ratings yet
- Data Sheet PTCDocument8 pagesData Sheet PTCjjermanNo ratings yet
- SRC PosterDocument1 pageSRC PosterShivam SinghNo ratings yet
- Application Note Solar IndustryDocument2 pagesApplication Note Solar IndustryAll4UyenNo ratings yet
- Lfa 457 Thermal TesterDocument12 pagesLfa 457 Thermal TesterlbnxxxxNo ratings yet
- Temperature Sensitivity of A Quartz Crystal Microbalance For TGA in Space AnnotatedDocument5 pagesTemperature Sensitivity of A Quartz Crystal Microbalance For TGA in Space AnnotatedNg Zi XuanNo ratings yet
- AN38 Achieving Millikelvin Temperature StabilityDocument8 pagesAN38 Achieving Millikelvin Temperature Stabilityum usuarioNo ratings yet
- 50 52 53 - T M - Dec 15 - ThermographyDocument3 pages50 52 53 - T M - Dec 15 - ThermographyJai SharmaNo ratings yet
- Shri Sai Polytechnic Chandrapur: Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument14 pagesShri Sai Polytechnic Chandrapur: Department of Electrical EngineeringrutujaraipureNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Electrical and Thermal Characteristics of Load-Relay Circuit Using Thermal ImagingDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Electrical and Thermal Characteristics of Load-Relay Circuit Using Thermal ImagingChethan GowdaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Management of Integrated Circuits in Burn-In EnvironmentDocument5 pagesThermal Management of Integrated Circuits in Burn-In EnvironmentRahmat HidayatNo ratings yet
- Why Use Temperature Transmitters Instead of Direct Wiring?Document4 pagesWhy Use Temperature Transmitters Instead of Direct Wiring?Ika WidyaNo ratings yet
- Sensores de Proximidade.Document48 pagesSensores de Proximidade.catraioNo ratings yet
- Eee-Vii-Industrial Drives and Applications U2Document9 pagesEee-Vii-Industrial Drives and Applications U2SimranNo ratings yet
- What's The Difference Between Capacitive and Thermal Inclination Sensors ?Document5 pagesWhat's The Difference Between Capacitive and Thermal Inclination Sensors ?Antonio TakeshiNo ratings yet
- Thermocouple Principles and ApplicationsDocument14 pagesThermocouple Principles and ApplicationsGhada SaeedNo ratings yet
- Heatsink EfficiencyDocument6 pagesHeatsink EfficiencyHarryNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Temperature Solutions - Rugged MonitoringDocument23 pagesFiber Optic Temperature Solutions - Rugged MonitoringRugged MonitoringNo ratings yet
- Online Thermal Vibration Balancing of GeneratorDocument7 pagesOnline Thermal Vibration Balancing of GeneratorduhaimNo ratings yet
- Thermocouple Type Instruments Construction Principle of Operation - Electrical4uDocument7 pagesThermocouple Type Instruments Construction Principle of Operation - Electrical4unitish kumarNo ratings yet
- Étalonnage Des Capteurs de ForceDocument13 pagesÉtalonnage Des Capteurs de ForceWadie KhatiNo ratings yet
- Assignment1-Temperature Devices MARTIN MI-202Document5 pagesAssignment1-Temperature Devices MARTIN MI-202alexisNo ratings yet
- 19mt4251 SSC Manual FinalDocument49 pages19mt4251 SSC Manual FinalR.MADHU SUDHANAN HICET STAFF EIENo ratings yet
- Research of The Inverse Time Characteristic Curve For The Electronic Thermal RelayDocument4 pagesResearch of The Inverse Time Characteristic Curve For The Electronic Thermal RelayGeorge MateiNo ratings yet
- Other Types of TransducersDocument17 pagesOther Types of TransducersCrichelleMaeNo ratings yet
- Product Information: Motor and Machine ProtectionDocument9 pagesProduct Information: Motor and Machine ProtectionMarcos Gomez PeresNo ratings yet
- Thermal ImagingDocument3 pagesThermal ImagingarsalNo ratings yet
- Product Information: NTC-thermistorsDocument3 pagesProduct Information: NTC-thermistorsRicardo CruzNo ratings yet
- Tec4 127 71 31 17 03Document3 pagesTec4 127 71 31 17 03jemosqueraNo ratings yet
- MelTemp - Users ManualDocument16 pagesMelTemp - Users ManualGabriel DillNo ratings yet
- IN150 ProHeat 35 LiquidCooled Induction System EnglishDocument4 pagesIN150 ProHeat 35 LiquidCooled Induction System EnglishYousefNo ratings yet
- First Choice: For Every JobDocument8 pagesFirst Choice: For Every JobNatanael Gadelha Diniz SilvestreNo ratings yet
- MC - Field Engineer RACWDocument12 pagesMC - Field Engineer RACWSRK ACADEMY OF EDUCATIONNo ratings yet
- Exp-1. Evacuative Tube ConcentratorDocument8 pagesExp-1. Evacuative Tube ConcentratorWaseem Nawaz MohammedNo ratings yet
- Wireless Connecting Rod Temperature Measurements For Reciprocating Compressor MonitoringDocument12 pagesWireless Connecting Rod Temperature Measurements For Reciprocating Compressor MonitoringZubair KhanNo ratings yet
- Towards Standard Testing Materials For High Temperature So - 2015 - Energy ProceDocument11 pagesTowards Standard Testing Materials For High Temperature So - 2015 - Energy Procepaween saetaeNo ratings yet
- Leine Linde Rotary EncodersDocument16 pagesLeine Linde Rotary EncodersDeepak JainNo ratings yet
- DTI-1000 STS-050, - 100,-102: Digital Temperature Indicator and STS Reference SensorsDocument10 pagesDTI-1000 STS-050, - 100,-102: Digital Temperature Indicator and STS Reference Sensorssara kubikaNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Torque of A Combustion Engine.: ICMSC 2018Document5 pagesMeasuring The Torque of A Combustion Engine.: ICMSC 2018Hanafi AjahNo ratings yet
- Applications: Infrared ThermometerDocument2 pagesApplications: Infrared Thermometerana jumanaNo ratings yet
- ADMModule - S11 12PS-IIIa-2Document28 pagesADMModule - S11 12PS-IIIa-2Lebz Ricaram33% (3)
- Industrial Training ReportDocument25 pagesIndustrial Training Reportankitsingh19092003No ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration Quiz SCDocument2 pagesAerobic Respiration Quiz SCapi-323720899No ratings yet
- 2016 Ehv Ac DC TransmissionDocument3 pages2016 Ehv Ac DC TransmissionNaren Singh TanwarNo ratings yet
- Whitener TopWhite BSPB Pande-Sujit enDocument6 pagesWhitener TopWhite BSPB Pande-Sujit enMayra Scavino ValderramaNo ratings yet
- CON3301 - PPT 5 Energy (2017)Document40 pagesCON3301 - PPT 5 Energy (2017)楊子慶No ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy ReviewsDocument22 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy ReviewsNatsolar IngenieriaNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Coatings Nov 2013Document46 pagesPipeline Coatings Nov 2013vincent.w.stone6724100% (3)
- EPS 205 Frequently Asked Questions 2 8.28 PDFDocument32 pagesEPS 205 Frequently Asked Questions 2 8.28 PDFDarshan Diesel100% (2)
- 1200 Macro ExamplesDocument21 pages1200 Macro ExamplessheetalnathNo ratings yet
- Cooling SystemDocument2 pagesCooling SystemSuharto ZuhriNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems ExergyDocument5 pagesSample Problems ExergySamer Al-MimarNo ratings yet
- Sobbi (1993) Porfirias Estables en Soluciones - PphotocatalisisDocument8 pagesSobbi (1993) Porfirias Estables en Soluciones - PphotocatalisisHenry ArceoNo ratings yet
- Design Basis For MV Drive and Motor - RADocument3 pagesDesign Basis For MV Drive and Motor - RANavaneetha KrishnanNo ratings yet
- 2 Valvula Reductora Presion Ayvaz BDV25 PDFDocument2 pages2 Valvula Reductora Presion Ayvaz BDV25 PDFjoaquin torrano veraNo ratings yet
- EHS EnglishDocument12 pagesEHS Englishgeraldine.18074No ratings yet
- Single Buoy Mooring ProcedureDocument3 pagesSingle Buoy Mooring ProcedureKannan100% (1)
- Film Capacitors For Industrial ApplicationsDocument32 pagesFilm Capacitors For Industrial ApplicationsArifujjaman SumonNo ratings yet
- Lead Acid BatteryDocument14 pagesLead Acid Batterydaabgchi50% (2)
- Introduction and Customer Information: Left Side View of John Deere 250D and 300D Dump Truck (Manufactured 2002-)Document470 pagesIntroduction and Customer Information: Left Side View of John Deere 250D and 300D Dump Truck (Manufactured 2002-)Juan Carlos Cruz Rodriguez100% (1)
- EMS Awareness ACN-L1 PDFDocument37 pagesEMS Awareness ACN-L1 PDFSiddharth RajmohanNo ratings yet
- Palava - Instruction Manual For Smart Electricity MeterDocument9 pagesPalava - Instruction Manual For Smart Electricity MeterPrathamesh ShevaleNo ratings yet
- 1822 Further.c n06Document6 pages1822 Further.c n06Nghĩa Nguyễn HữuNo ratings yet
- ME-112 Thermodynamics Assignment: Question No:1Document12 pagesME-112 Thermodynamics Assignment: Question No:1Mairaj NaseemNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion & Work Power Energy (11th) WADocument23 pagesCircular Motion & Work Power Energy (11th) WASwarnlata MishraNo ratings yet
- WI-NG-6460-002-065 Work Instruction For Circuit Breaker Fail Protection (5062) Rev00Document6 pagesWI-NG-6460-002-065 Work Instruction For Circuit Breaker Fail Protection (5062) Rev00Mohamed NasrNo ratings yet
- Biogeometry Newsletter 7 Nov 2013Document3 pagesBiogeometry Newsletter 7 Nov 2013zbhabhaNo ratings yet