Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hematology in Practice - The Complete Blood Count
Hematology in Practice - The Complete Blood Count
Uploaded by
Ciel AnnCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Schalms Veterinary Hematology 7Th Edition Marjory B Brooks All ChapterDocument67 pagesSchalms Veterinary Hematology 7Th Edition Marjory B Brooks All Chapterefrain.blair179100% (13)
- Haematology Notes - 3rd EdDocument100 pagesHaematology Notes - 3rd EdSally Brit100% (1)
- Cytology Laboratory DoneDocument22 pagesCytology Laboratory DoneUthaya Kumar100% (1)
- Post Analytical Phase of Laboratory TestingDocument7 pagesPost Analytical Phase of Laboratory TestingClarisse De Guzman100% (1)
- Delta Checks in The Clinical Laboratory 2019Document24 pagesDelta Checks in The Clinical Laboratory 2019birlikteyizNo ratings yet
- Chang TransfusionMed2014 DisclaimerDocument7 pagesChang TransfusionMed2014 Disclaimerteresa.cuautleNo ratings yet
- Hil 303990R7Document8 pagesHil 303990R7KHALIDNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Clinical Biochemistry 2Document27 pagesBasic Concepts of Clinical Biochemistry 2O. floriceNo ratings yet
- Ey Vaz Zadeh 2007Document10 pagesEy Vaz Zadeh 2007Zain-Alabdeen Haithem LaftaNo ratings yet
- Pereira 2018Document6 pagesPereira 2018UnknownNo ratings yet
- TTG ProcedureDocument8 pagesTTG ProcedureAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Pr-02958 - TM Brochure Ortho Sera Id-Mts Manual Pr-02958Document4 pagesPr-02958 - TM Brochure Ortho Sera Id-Mts Manual Pr-02958Son NguyenNo ratings yet
- Hema - Sop 2024Document31 pagesHema - Sop 2024Raki DallasNo ratings yet
- Quality ControlDocument10 pagesQuality Controlbunniecaronan113003No ratings yet
- BioPharm - Scale Down - Downstream PDFDocument10 pagesBioPharm - Scale Down - Downstream PDFGeetanjali HubliNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance of Laboratory Results: A Challenge in Health Care ManagementDocument6 pagesQuality Assurance of Laboratory Results: A Challenge in Health Care Managementrizkiyah prabawantiNo ratings yet
- ERBA ELite 3 ControlsDocument1 pageERBA ELite 3 ControlsGlobalindo Center MedicalNo ratings yet
- Role of Nursing Personnel in Laboratory Testing: August 2018Document6 pagesRole of Nursing Personnel in Laboratory Testing: August 2018John Alexander Hurtado ParraNo ratings yet
- Annalof Nursing PrimarycareDocument6 pagesAnnalof Nursing PrimarycarefatmanajehNo ratings yet
- ISBT Science Series - 2008 - RamanDocument28 pagesISBT Science Series - 2008 - RamanWong Jia AnnNo ratings yet
- Dalenberg 2013Document19 pagesDalenberg 2013Yash NaykaNo ratings yet
- Test For Different Immunological Principles Mary Jesreth V. BayasDocument15 pagesTest For Different Immunological Principles Mary Jesreth V. BayasMJ VergaraNo ratings yet
- Linical Aboratory O: S H, MT (Ascp) SH B A. K, E D, Mls (Ascp), Cls (Nca)Document5 pagesLinical Aboratory O: S H, MT (Ascp) SH B A. K, E D, Mls (Ascp), Cls (Nca)Tito LeopardoNo ratings yet
- BANDERASDocument4 pagesBANDERASSamuel FuentesNo ratings yet
- Astm E1326Document5 pagesAstm E1326samuellepedealbaNo ratings yet
- Verification of Molecular Assays: Rent EatonDocument4 pagesVerification of Molecular Assays: Rent EatonCristian AgostiniNo ratings yet
- Proficiency Testing Technical Brief 18A - tcm18 214885Document2 pagesProficiency Testing Technical Brief 18A - tcm18 214885RONALD ALFONSO PACHECO TORRESNo ratings yet
- Bakal 1995Document3 pagesBakal 1995Residencia Cirugia GeneralNo ratings yet
- Standard Additions Myth and RealityDocument6 pagesStandard Additions Myth and RealitytogatorNo ratings yet
- Lab Dept: Hematology Test Name: Reticulocyte Count: General InformationDocument2 pagesLab Dept: Hematology Test Name: Reticulocyte Count: General InformationTanveerNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Blood Smear Pathologist ToolDocument3 pagesPeripheral Blood Smear Pathologist ToolSimon HafeniNo ratings yet
- IFU HemaologyDocument2 pagesIFU HemaologyShujat RazaqNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry - Quality Management and InformaticsDocument5 pagesClinical Chemistry - Quality Management and Informaticsrosellae.No ratings yet
- Robustness Assessent in Computer Assisted Liquid HPLC Procedures Based On Desirability FunctionsDocument10 pagesRobustness Assessent in Computer Assisted Liquid HPLC Procedures Based On Desirability FunctionsAngel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance & Quality ControlDocument5 pagesQuality Assurance & Quality ControlErica Mae Macabingkel100% (1)
- Methods: Stefaan Derveaux, Jo Vandesompele, Jan HellemansDocument4 pagesMethods: Stefaan Derveaux, Jo Vandesompele, Jan HellemansmnkjhpNo ratings yet
- Nova Biomedical Nova Statstrip Xpress Glucose Meter Manual Original 1Document84 pagesNova Biomedical Nova Statstrip Xpress Glucose Meter Manual Original 1AzeertyNo ratings yet
- Position Paper On Particle Sizing - Sample Preparation, Method Validation and Data PresentationDocument3 pagesPosition Paper On Particle Sizing - Sample Preparation, Method Validation and Data PresentationAdamNo ratings yet
- Validation Protocol For New Methods or Instruments in The Clinical LaboratoryDocument6 pagesValidation Protocol For New Methods or Instruments in The Clinical LaboratorymohammedNo ratings yet
- MICRT Quality ControlDocument23 pagesMICRT Quality ControlMohamed AldamanhouryNo ratings yet
- User Guide: Blood Glucose Monitoring SystemDocument30 pagesUser Guide: Blood Glucose Monitoring SystemVince CentenoNo ratings yet
- TEa GuidelinesDocument20 pagesTEa GuidelinesNacho BressánNo ratings yet
- Essential Laboratory KnowledgeDocument23 pagesEssential Laboratory KnowledgeUhuebor DavidNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Quality Control: An OverviewDocument32 pagesLaboratory Quality Control: An OverviewanggaririnNo ratings yet
- SOP For ABO GroupingDocument5 pagesSOP For ABO GroupingDUKENo ratings yet
- Hepa e Hepatitis-A-Antibody MetDocument19 pagesHepa e Hepatitis-A-Antibody MetKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- cIL Ix1: A Multi-Rule Shewhart Chart For Quality Control in Clinical ChemistryDocument9 pagescIL Ix1: A Multi-Rule Shewhart Chart For Quality Control in Clinical ChemistryJustino WaveleNo ratings yet
- Xpert HCV Viral Load Brochure Ceivd 3043-02Document4 pagesXpert HCV Viral Load Brochure Ceivd 3043-02sharenNo ratings yet
- Spiking Into Aqueous Samples: Standard Guide ForDocument6 pagesSpiking Into Aqueous Samples: Standard Guide Formohdhafizmdali100% (1)
- A74719D-Establishing Appropriate QC Ranges For ImmunoAssayDocument4 pagesA74719D-Establishing Appropriate QC Ranges For ImmunoAssaydar alhikmahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Automation-and-POCTDocument32 pagesChapter 3 Automation-and-POCTNida RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Corneal Asymmetry Analysis by Pentacam Scheimpflug Tomography For Keratoconus DiagnosisDocument13 pagesCorneal Asymmetry Analysis by Pentacam Scheimpflug Tomography For Keratoconus DiagnosisJuanes MagnoNo ratings yet
- Screening and Diagnostic TestsDocument34 pagesScreening and Diagnostic TestsQuỳnh Anh Phạm HoàngNo ratings yet
- Clinical ChemistryDocument19 pagesClinical Chemistrythrowawy100% (2)
- Laboratory Procedure Manual: C-Reactive Protein Serum NephelometryDocument13 pagesLaboratory Procedure Manual: C-Reactive Protein Serum NephelometryFadlan HafizhNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Analytical Methods Used For Regulation of Foods and DrugsDocument10 pagesEvaluation of Analytical Methods Used For Regulation of Foods and DrugsrenatoandaraNo ratings yet
- GPP Pipetting Calibration and Technique ENDocument4 pagesGPP Pipetting Calibration and Technique ENveneta gizdakovaNo ratings yet
- Method Development and Validation For Estimation of Dosulepin in Pure and Dosage Form by Using HPLCDocument8 pagesMethod Development and Validation For Estimation of Dosulepin in Pure and Dosage Form by Using HPLCBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0039625720300709 MainDocument23 pages1 s2.0 S0039625720300709 Mainneha midhaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Laboratory Investigations: A Guide for Nurses, Midwives and Health ProfessionalsFrom EverandUnderstanding Laboratory Investigations: A Guide for Nurses, Midwives and Health ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Labs & Imaging for Primary Eye Care: Optometry In Full ScopeFrom EverandLabs & Imaging for Primary Eye Care: Optometry In Full ScopeNo ratings yet
- Quick guide to Laboratory Medicine: a student's overviewFrom EverandQuick guide to Laboratory Medicine: a student's overviewNo ratings yet
- Routine Laboratory Evaluation of CoagulationDocument7 pagesRoutine Laboratory Evaluation of CoagulationGilo IlaganNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 11 - Blood)Document22 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 11 - Blood)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Mls Imls Content Guideline PDFDocument11 pagesMls Imls Content Guideline PDFswasahmedNo ratings yet
- Nattokinase - 2008Document7 pagesNattokinase - 2008nataleebellaNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Leech TherapyDocument24 pagesMedicinal Leech TherapyKingNo ratings yet
- Potential Adverse Effects of Long-Term Consumption of Fatty AcidsDocument11 pagesPotential Adverse Effects of Long-Term Consumption of Fatty Acidstaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation and Hemostasis in Neurosurgery PDFDocument404 pagesAnticoagulation and Hemostasis in Neurosurgery PDFAleksandar DimovskiNo ratings yet
- The Platelet Rich Plasma ProcedureDocument2 pagesThe Platelet Rich Plasma ProcedurekaisalanaafidaNo ratings yet
- Produktkatalog Fresenius Kabi Transfusion Technolo-Q SmpFCuAau2bGekq5W8jXHusten LjM97QZf MP7CADocument206 pagesProduktkatalog Fresenius Kabi Transfusion Technolo-Q SmpFCuAau2bGekq5W8jXHusten LjM97QZf MP7CACampaign MediaNo ratings yet
- Quality Standards For Sample Processing, Transportation, and Storage in Hemostasis TestingDocument11 pagesQuality Standards For Sample Processing, Transportation, and Storage in Hemostasis TestingGunay AliyevaNo ratings yet
- Blood Workbook To Assist With Conscience Matters Involving BloodDocument18 pagesBlood Workbook To Assist With Conscience Matters Involving BloodRicky YauNo ratings yet
- DIC Blood Component TherapyDocument30 pagesDIC Blood Component TherapySameer KumarNo ratings yet
- Antifibrinolytic Therapy and Perioperative ConsiderationsDocument14 pagesAntifibrinolytic Therapy and Perioperative Considerationsandrey wahyudiNo ratings yet
- Physiology of CoagulationDocument44 pagesPhysiology of CoagulationXee JayNo ratings yet
- CT BTDocument20 pagesCT BTZainMalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2DannyNo ratings yet
- Serum Vs Plasma: Which Specimen Should You UseDocument48 pagesSerum Vs Plasma: Which Specimen Should You UseTanveerNo ratings yet
- Swift River Medication AdministrationDocument4 pagesSwift River Medication AdministrationmattNo ratings yet
- Blood Physiology MainDocument68 pagesBlood Physiology MainOmenaalaNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders: Drg. Gita Dwi Jiwanda Sovira, M.KesDocument26 pagesBleeding Disorders: Drg. Gita Dwi Jiwanda Sovira, M.KessaskiakonitaNo ratings yet
- Postpartum HemorrhageDocument22 pagesPostpartum HemorrhageReynaldiReikyHadiwijayaNo ratings yet
- I RECOVER Post Vaccine ProtocolDocument58 pagesI RECOVER Post Vaccine ProtocolJohnny SmithNo ratings yet
- Blood Products. Preparation of Blood ComponentsDocument32 pagesBlood Products. Preparation of Blood ComponentsSanthiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Full Blood PictureDocument1 pageFull Blood PictureGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Hematology - Handbookfor Personal UseDocument156 pagesHematology - Handbookfor Personal Useuber6791100% (1)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY LAB - Hanbook of Pathophysiology SevastreDocument192 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY LAB - Hanbook of Pathophysiology Sevastredorina0101No ratings yet
- Bact AlertDocument10 pagesBact Alertwulan3daysNo ratings yet
- Lab. Act. #5 - Blood and HematopoiesisDocument8 pagesLab. Act. #5 - Blood and HematopoiesisDan OdviarNo ratings yet
Hematology in Practice - The Complete Blood Count
Hematology in Practice - The Complete Blood Count
Uploaded by
Ciel AnnOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hematology in Practice - The Complete Blood Count
Hematology in Practice - The Complete Blood Count
Uploaded by
Ciel AnnCopyright:
Available Formats
HEMATOLOGY | THEORIES & PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS ~ Ate Medtech ~
Kathleen S. Langreo, RMT, MLS (ASCPi) April 2024 Edition
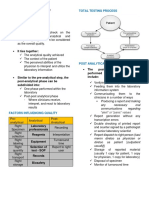
I. BASIC HEMATOLOGY LABORATORY PRACTICE PRE-ANALYTIC VARIABLES POST-ANALYTIC VARIABLES
~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~
A. THE MICROSCOPE
DELTA CHECKS NOTES AND CONCENSUS FOR THE
HEMATOLOGY LABORATORY SCIENTIST
✓ can help detect errors in specimen identification, specimen
integrity, errors in manual data entry, analytical errors
✓ based upon the total expected variation, which must include
biological and analytical variation
MICROSCOPE PART FUNCTION ✓ unlikely that consecutive results obtained on one patient will vary
can be opened and closed to increase significantly unless a substantial change has occurred with the
or reduce the volume of light directed patient’s medical status
toward the image ✓ multiple delta checks failing on several tests performed on a
Iris Diaphragm single patient means a strong possibility that the patient or
minimal light may be useful for specimen was misidentified
unstained materials or images with low ✓ not useful for every analyte; best used in stable analytes with little
refractive index (e.g., unstained
day-to-day variation that are measured frequently such as red
materials)
blood cell (RBC) indices (MCV, MCH, MCHC), electrolytes, or
4x (scanner), 10x (low power), 40x (high
Objective Lenses liver function tests (ALT/SGPT, AST/SGOT)
dry), 50x (oil), and 100x(oil)
MICROSCOPE CARE INSTRUCTIONS
✓ Do not let non-oil lenses get in contact with oil on slides
✓ Only use lens papers specifically made to clean objective lenses
✓ Wipe and remove oil from oil objectives every after use
MICROSCOPE USE TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDES
✓ To ensure fine details of immature cells are properly and clearly
seen, use 100x oil-immersion lenses and ensure that the
diaphragm is fully opened for maximum light
✓ Blurred 40x high power objective may be due to oil contamination,
use lens paper to remove any residual oil
B. QUALITY ASSURANCE IN HEMATOLOGY
QUALITY INDICATOR PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS
historical check on a specific
sample from latest result or
from previous cumulative
results
standard of variation between
delta checks must be
established
Delta Checks
if variation in a result exceeds
the established standard, flags
will be shown and a need for
investigation on the cause of
failed deltas must be identified
failed delta checks may prompt
for additional validation,
corrective action and reflex
testing if necessary ✓ suggested delta check limits for MCV is +/-5 fL and MCHC
manual methods or additional variation +/-5.0 g/dL for 24 hours up to 1 week interval
tests (e.g., differential count, ✓ delta checks are not recommended for other hematology
Reflex Testing manual slide review) added by parameters including hemoglobin, hematocrit, RBC count, WBC
the technologist in order to count or platelet count. Acute changes in these parameters are
ensure accuracy of results common in hospital patients and the false positive rate is
displayed next to a specific unacceptably high
result often indicating the need ✓ standards of troubleshooting abnormal platelet counts must
Flaggings
for extra validation prior to
include checking for platelet clumping or RBC fragments through
release of results
Twitter: @medtechlyfe | Facebook Group: Pinoy Medtechs Abroad
PAGE 1 OF 8
Contact: atemedtech@gmail.com
HEMATOLOGY | THEORIES & PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS ~ Ate Medtech ~
Kathleen S. Langreo, RMT, MLS (ASCPi) April 2024 Edition
flaggings in the histograms or manual checking of the blood
smear CAPILLARY PUNCTURE
✓ clinical correlation plays an important role in interpreting delta ✓ The middle or ring finger of the non-dominant hand is
~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~
failures (e.g.,creatinine results in patients with renal failure rise preferred (least painful areas)
and fall depending on their dialysis schedule, patients receiving ✓ Warming the finger or heel can help improve blood flow and
contrast media for imaging often have elevated creatinine values ensure free flowing blood without the need to greatly pinch the
postprocedure that return to normal within a few days) area (gentle pressure is allowed)
✓ Order of draw:
1. hematology specimens
C. SPECIMEN COLLECTION
2. chemistry specimens
3. blood bank specimens
SAMPLE COLLECTION BEST PRACTICES ✓ Always wipe off the first drop of blood to avoid tissue fluid
✓ Practice proper patient identification using minimum of 2 contamination
major unique patient identifiers, preferably full name and
birthday. Do not identify using questions answerable by
II. THE COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
YES/NO
A. HEMATOPOIESIS PRINCIPLES
✓ Labelling must be done at the patient’s bedside and never
leave the patient’s room until labelling is done. Pre-labeling of
tubes should not be practiced. THE BONE MARROW
✓ Use of re-usable tourniquets is discouraged especially for ✓ The bone marrow assumes the primary role in hematopoiesis in
patients at risk for infection. If no choice, practice disinfection the adult human (intramedullary hematopoiesis) while the liver and
of tourniquets after each use. spleen can also become sites of hematopoiesis if needed
✓ Gloves should be used at all times and must be changed per (extramedullary hematopoiesis).
patient. ✓ Prime locations for bone marrow in an adult is the iliac crest
✓ Practice hand hygiene every after each blood draw. (located in the pelvic area) and the sternum (located in the chest
area).
RECOMMENDED ORDER OF DRAW (ETS) ✓ The bone marrow’s normal M:E ratio is 3:1 to 4:1. White blood
cells have a much shorter life span than red blood cells—6 to 10
1. Blood culture bottles 6. Sodium heparin (dark green
2. Non-additive tube/plain top) hours for neutrophils as opposed to 120 days for erythrocytes—
tube 7. Plasma-separator tube/PST and must be produced at a much higher rate for normal
3. Coagulation tube (light (light green top) hematopoiesis.
blue top) 8. EDTA (purple or pink top) ✓ Circumstances within the bone marrow (e.g., infiltration of leukemic
4. Clot activator tube (red top) 9. Blood tube with ACD (pale cells, tumor) may diminish its normal hematopoietic capability and
5. Serum-separator tube/SST yellow) force the spleen and liver to perform. This can be correlated to the
(red- grey tiger top or gold 10. Oxalate or fluoride tubes hepatomegaly and splenomegaly that can occur in different
top) (light grey top) hematologic malignancies.
“B C R H E S” THE SPLEEN (Hematopoiesis, Reservoir, Filtration, Immunologic)
Blood Coagulation Red top, Heparin EDTA Sodium ✓ In cases of splenic rupture or trauma, large numbers of platelets
culture Citrate tube clot activator, fluoride, may be spilled into the peripheral circulation and predispose
serum anti-glycolytic patients to unwanted clotting events
separator agent ✓ Older red blood cells that have lost their elasticity and deformability
EFFECTS OF CARRY-OVER in the last days of their 120-day life span and are culled from the
(PROPER ORDER OF DRAW IS NOT FOLLOWED) circulation by splenic phagocytes
✓ EDTA contamination can cause falsely increased potassium in ✓ Red blood cells that are filled with inclusions (e.g., Howell-Jolly
chemistry results bodies, Heinz bodies, Pappenheimer bodies) are selectively
✓ Clot activator may cause falsely shortened PT and aPTT reviewed and cleared from the cell within the spleen. Inclusions are
results “pitted” and pulled from the red blood cell without destroying the
✓ Bacteria from non-sterile caps of previous tubes may cellular integrity, and red blood cells are left to continue their
contaminate blood culture samples if not collected first journey through the circulation.
✓ Antibody-coated red blood cells have their antibodies removed
PATIENT IDENTIFIERS within the spleen and usually reappear in the peripheral circulation
MAJOR MINOR as spherocytes, a smaller, more compact red blood cell structure
▪ First name and last name ▪ Unique hospital number with a shortened life span
▪ Middle name spelling ▪ Medical record number ✓ The spleen plays a valuable role in promoting phagocytic activity
▪ Date of birth ▪ Chart number
for encapsulated organisms (Haemophilus influenzae,
Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis) that helps the
DETAILS NEEDED FOR LABELLING reticuloendothelial system (RES) of the body to get rid of these
MAJOR MINOR organisms.
▪ Patient’s first name and last ▪ Unique hospital number ✓ Individuals that had their spleens removed may be vulnerable to
name ▪ Medical record number infections
▪ Middle name/middle initial ▪ Chart number
▪ Date of birth ▪ Ordering physician
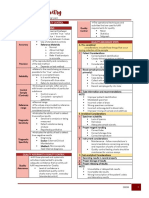
B. THE COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT (CBC/FBC)
▪ Time and date collected ▪ Status (STAT, routine)
▪ Phlebotomist ▪ Specimen # and/or Barcode
(if applicable) THE 9 MAJOR COMPONENTS OF A COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
TIPS FOR VERY SMALL VEINS
✓ Warm the arm/area to promote vasodilation
✓ Tap the vein while the arm is tied with tourniquet to promote
distension.
✓ Ask the patient to clench and unclench their first several times
(not recommended for measurements affected by arm
exercise such as lactic acid and potassium)
✓ Use winged collecting cannula /”butterfly” or a needle with
higher gauge (23-25)
Twitter: @medtechlyfe | Facebook Group: Pinoy Medtechs Abroad
PAGE 2 OF 8
Contact: atemedtech@gmail.com
HEMATOLOGY | THEORIES & PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS ~ Ate Medtech ~
Kathleen S. Langreo, RMT, MLS (ASCPi) April 2024 Edition
- reduced flexibility of
red cells on
~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~
prolonged storage
at room temperature
- K2EDTA or
Na2EDTA
- macrocytosis
- hyponatremia
- polycythemia vera
(PCV)
- narrower tubes than
- borosilicate tubes
recommended
- deoxygenated blood
Others - soda lime tubes
- reading of the buffy
- loss of blood due to
coat
improper sealing
MAJOR CBC PARAMETERS (HGB, HCT, RBC, WBC) RED BLOOD CELL (RBC)
HEMOGLOBIN ✓ counted on single-channel impedance counters in automated
RBCs are lysed leaving a analyzers
hemoglobin solution to ✓ data are plotted on a frequency distribution graph, or volume
measure absorbance/optical distribution histogram, with relative number on the y-axis and
Cyanmethemoglobin Method –
density volume (channel number equivalent to a specific volume) on the
gold standard for Hb
measurement x-axis
can have significant variability ✓ manual methods using hemocytometers have high inaccuracy
especially in confined patients and have been replaced by automated methods
on IV therapy
FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN HEMOGLOBIN MEASUREMENTS INTERPRETATION OF RBC HISTOGRAMS
HIGH HB LOW HB The normal red cell distribution NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
▪ carboxyhemoglobin (>10%) ▪ clotting curve is Gaussian (bell-shaped) CURVE
▪ cryoglobulins ▪ dilution/contamination with and the peak of the curve should
▪ in-vivo hemolysis iv fluid fall within the normal MCV range
▪ heparin contamination ▪ hemorrhage/blood loss (80-100 fL)
▪ hyperbilirubinemia/icterus (trauma, surgery,
▪ lipemia/hyperlipidemia gastrointestinal bleeds,
▪ increased monoclonal menstruation, phlebotomy)
proteins/hyperproteinemia ▪ chronic renal insufficiency
▪ lysis-resistant rbcs (Hb S, Hb ▪ metastatic cancer
C disease) ▪ chemotherapy The red cell distribution curve HETEROGENOUS RBC
▪ hyperleukocytosis ▪ nutritional deficiencies (Vit will get wider as the red cells POPULATION
▪ polycythemia vera (PCV) B12, folate, poor diet) vary more in size.
▪ sample not mixed properly ▪ bone marrow failure Thus, a narrow distribution curve
▪ patient is a neonate/newborn ▪ anemias (iron deficiency, indicates a homogenous
or living at high altitudes hemolysis) population of red cells; the wider
▪ cardiac or pulmonary ▪ chronic the distribution curve, the more
diseases (compensatory diseases/inflammation heterogenous the population of
mechanism) red cells.
HEMATOCRIT
calculated parameter from the measured
MCV and RBC count in automated A population of cells that are of RBC SHIFT TO THE LEFT
analyzers similar size, but not the size of
normal RBCs, will produce a
HCT = (RBC x MCV) peak that is shifted in one
may be manually measured by the
10 direction or the other from the
microhematocrit method (recommended
to get the average of at least 3 different peak that represents normal
replicate measurements for precision) RBCs.
FACTORS OF HIGH FACTORS OF LOW An RBC population with a low
MICROHEMATOCRIT MICROHEMATOCRIT MCV will be shifted to the left on
the histogram display.
RBC SHIFT TO THE RIGHT
- use of liquid EDTA
Dilution instead of powdered/dry
effect EDTA (0.5% lower) As the MCV of a red blood cell
- IV fluid contamination population increases, the RBC
distribution curve will move
farther to the right on the display.
- longer centrifugation
- increased centrifugal
- shorter period of
Trapped force
centrifugation
plasma - elevated ESR due to
- decreased
factors patient condition DIMORPHIC RBC
centrifugal force
- increased plasma POPULATION
proteins When two distinct populations of
- microcytosis (e.g. - excess EDTA (RBC red blood cells are present in a
iron deficiency or shrinkage) sample, the red blood cell
Red cell thalassemia trait) - K3EDTA (about 2% histogram may have more than
factors - sickle cell trait or lower) one peak.
sickle cell disease - fully oxygenated blood
- spherocytosis - hypernatremia
Twitter: @medtechlyfe | Facebook Group: Pinoy Medtechs Abroad
PAGE 3 OF 8
Contact: atemedtech@gmail.com
HEMATOLOGY | THEORIES & PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS ~ Ate Medtech ~
Kathleen S. Langreo, RMT, MLS (ASCPi) April 2024 Edition
FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN RBC COUNTS MCHC (g/dL) =Hgb (g/dL) x 100 the amount of hemoglobin per
Hct (%) red blood cell
~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~
HIGH RBC LOW RBC
▪ hyperleukocytosis ▪ in vitro hemolysis Normal Range: 32-26 g/dL
▪ cryoglobulins ▪ RBC agglutination (cold
CAUSES OF SHIFTS IN MCH & MCHC VALUES
▪ giant platelets agglutinins, rouleaux)
▪ sample not mixed prior to ▪ dilution with IV fluid HIGH MCH & MCHC LOW MCH & MCHC
running ▪ nucleated RBCs ▪ lipemia ▪ low sodium/electrolyte
▪ polycythemia vera (PCV) and ▪ RBC fragmentation ▪ in vitro/in vivo hemolysis imbalance
other proliferative diseases (MAHAs, mechanical ▪ hyperbilirubinemia/icteric ▪ lead poisoning
▪ living at high altitudes damage, schistocytes, burn) sample (>25-25 mg/dL) ▪ microcytic anemia (iron
▪ cardiac or pulmonary ▪ clotted sample ▪ RBC agglutination/cold agg’ns deficiency, chronic
diseases (compensatory ▪ hemorrhage ▪ hyper/paraproteinemia disease/inflammation,
mechanism) ▪ bone marrow failure (due to ▪ presence of lyse-resistant sideroblastic)
▪ excess EPO therapy or EPO- tumors, proliferation of RBCs/abnormal RBCs (sickle ▪ thalassemias
secreting tumors abnormal cells, aplasia) cells, xerocytosis, hemoglobin
▪ COPD ▪ renal failure (decreased or C crystals, spherocytosis,
▪ severe dehydration failure to produced EPO) AIHA)
▪ anemias ▪ hyperleukocytosis
Rule of Threes (3’s) WHITE BLOOD CELL (WBC)
✓ Correlation checks between the hemoglobin and hematocrit ✓ principle for counting is impedance and/or optical/light scatter
✓ Failure to fall within the correlation check may be an indicator systems such as fluorescence flow cytometry (red cells are
of post-analytic error the need for corrective actions lysed leaving WBCs which are stained for differentiation)
(reviewing a peripheral smear, tracing the origin of the ✓ forward-angle light scatter (FSC) correlates with cell volume,
samples, or other investigation) primarily because of diffraction of light.
✓ Formula: ✓ side-scatter light (SSC) results from refraction and reflection of
1. Hgb = RBC x 3 light from larger structures inside the cell and correlates with
2. Hct (±3) = Hgb x 3 degree of internal complexity (nuclear and granular details)
3. RBC (±0.3) = Hb÷3 ✓ side-fluorescence light (SFL) shows the amount of nucleic acids
RBC PARAMETERS (INDICES (MCV, MCHC, MCH) and RDW and cell organelles
✓ scattergrams vary by instrument so it is important to use
RBC Indices Formula
machine-specific interpretation guidelines provided to your
MCV (fL) = Hct (%) × 10___ MCHC (g/dL) = Hgb (g/dL) x
facility
100
✓ knowledge of common machine flaggings is essential
RBC count (x1012/L) Hct (%)
Normal Range: 80-100 fL Normal Range: 32-36 g/dL
GENERAL
MCH (pg) =__Hgb (g/dL) x 10__ INTERPRETATION OF WBC SCATTERGRAMS
RBC count (x1012/L)
Normal Range: 27-31 pg
MEAN CORPUSCULAR VOLUME (MCV)
Normal Range: 80-100 fL one of the most stable
MCV (fL) = Hct (%) × 10___
12 parameters in a CBC with little
RBC count (x10 /L) variability even in confined
patients on IV therapy
*** any significant shift in MCV
that cannot be explained as a may help determine sample
result of the listed circumstances integrity, pre-analytic and
below should prompt the
analytic sample qualities
laboratory to investigate a
possible sample mismatch or good delta check parameter
misidentification
CAUSES OF SHIFTS IN MCV VALUE
HIGH MCV LOW MCV
▪ cold agglutinins ▪ low sodium/electrolyte
▪ microaggregates of RBCs imbalance/hypo-osmolar
▪ transfusion therapy states
▪ reticulocytosis/polychromasia ▪ lipemia
▪ paraproteinemia ▪ icteric samples
▪ severe hyperglycemia (>600 ▪ hemolysis
mg/dL or >33 mmol/L) ▪ RBC fragments (MAHAs)
▪ rouleaux ▪ microcytic anemia (iron
▪ EDTA whole blood storage at deficiency, chronic
room temp for 1-4 days disease/inflammation,
▪ hyperleukocytosis sideroblastic)
▪ round macrocytosis (liver ▪ hemoglobinopathy
diseases) ▪ thalassemia
▪ megaloblastic anemia (Vit ▪ lead poisoning
B12/folate deficiency) ▪ pregnancy
▪ hyperosmolar states
MEAN CORPUSCULAR HEMOGLOBIN (MCH) & MEAN
CORPUSCULAR HEMOGLOBIN CONCENTRATION (MCHC)
MCH (pg) = Hgb (g/dL) × 10_
RBC count (x1012/L) the average weight of
Normal Range: 27-31 pg hemoglobin in a given
amount of red blood cells
Twitter: @medtechlyfe | Facebook Group: Pinoy Medtechs Abroad
PAGE 4 OF 8
Contact: atemedtech@gmail.com
HEMATOLOGY | THEORIES & PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS ~ Ate Medtech ~
Kathleen S. Langreo, RMT, MLS (ASCPi) April 2024 Edition
FLAGGINGS DESCRIPTION
Positive Judgment/ indicates that analysis values or
~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~
Auto-validation Failure measured morphology exceeded the
predefined machine criteria and
a.) Diff: abnormal blood needs extra validation steps prior to
cell differentiation release
b.) Morph: abnormal
morphology doing manual smear review of the
c.) Count: counted sample with such flaggings is
value unreliable needed
may indicate the presence of
abnormal/atypical mononuclear cells
Monocytosis/ which are often mistakenly read as
Leukocytosis Present/ monocytes or lymphocytes by the
Atypical Lymphocytes/ machine
Blasts???
do manual differential count to
validate results
may indicate
microclots/microaggregates in the MORE EXAMPLES OF NORMAL WBC SCATTERGRAMS
sample often mistakenly counted as (WILL VARY DEPENDING ON THE ANALYZER USED)
RBC Agglutination? WBCs due to their size
PLT Clumps?
counted measurements are
unreliable, do manual estimated
counts for validation/checking
instrument failed to categorize cells
counted during differential counting
Gray Area in
Scattergram
do manual smear review to check for
abnormal/atypical WBCs
indicates that there was no analysis
error or abnormality detected by the
Negative Judgment/ analyser
Auto-validated
results may be released without the
need for extra validation
different cell clusters in the
scattergram cannot be differentiated
(may be due to abnormal cells, WBC
aggregation or significant presence
WBC Abnormal of nRBCs)
Scattergram
scan the slide for abnormal cells and
nRBCs and do manual differential
and WBC count correction if deemed
necessary
indicates that the instrument has
detected cells in the region for left
shift (band cells) in the scattergram
when band
cells are present, they are included
Left Shift?
in the neutrophil population
a manual smear review may be
indicated to look out for immature
granulocytes, toxic granulation or
vacuolation of neutrophils
Note: Manual smear review and differential counting criteria will
all depend on a laboratory’s standard operating procedures.
Twitter: @medtechlyfe | Facebook Group: Pinoy Medtechs Abroad
PAGE 5 OF 8
Contact: atemedtech@gmail.com
HEMATOLOGY | THEORIES & PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS ~ Ate Medtech ~
Kathleen S. Langreo, RMT, MLS (ASCPi) April 2024 Edition
✓ the RDW is not a determination of “normal” red blood cell size.
The cell population may be mostly large or mostly small cells
~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~
and the RDW will be within the reference range. When the cells
are observed on a smear, they will not be cells of typical size but
would have uniformly small (RBC left shift) or big (RBC right
shift) population
FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN WBC COUNTS
HIGH WBC LOW WBC
▪ presence of platelet clumps ▪ WBC aggregation/clumping
▪ giant platelets ▪ RBC agglutination
▪ cryoglobulinemia ▪ blood diluted with IV fluid
▪ presence of organisms/bacteria ▪ bone marrow
▪ adipose tissue/fat globules failure/suppression
▪ fibrin clumps ▪ myelodysplastic syndromes
▪ lyse-resistant RBCs (sickle ▪ hypersplenism
cells, Hgb S, Hgb C) ▪ aplastic anemia
▪ nRBCs ▪ HIV/AIDS
▪ carcinoma cells ▪ autoimmune disorders
▪ leukemia/lymphoma/ (SLE, rheumatoid arthritis)
myeloproliferative disorders ▪ congenital
▪ septicemia/infections immunodeficiency
▪ leukemoid reactions syndromes
▪ hypersensitivity reactions ▪ chemotherapy/radiation
▪ stress (trauma, shock, reactive) therapy
OTHER CBC PARAMETERS (RDW, PLT COUNT, RETICS)
RED CELL DISTRIBUTION WIDTH (RDW)
✓ a mathematical calculation that gives insight into the amount of
anisocytosis (variation in size) and, to some degree,
poikilocytosis (variation in shape) in a peripheral smear
✓ normal value for RDW is 11.5% to 14.5%
✓ an increase in the RDW is observed when the size of the RBCs
varies within the red cell populations. This is physiologically a
mix of different cell sizes and is known as anisocytosis
✓ a wide peak on an RBC histogram would represent an RDW
above the reference range and the population of cells would be
variable in size when observed microscopically
Twitter: @medtechlyfe | Facebook Group: Pinoy Medtechs Abroad
PAGE 6 OF 8
Contact: atemedtech@gmail.com
HEMATOLOGY | THEORIES & PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS ~ Ate Medtech ~
Kathleen S. Langreo, RMT, MLS (ASCPi) April 2024 Edition
PLATELET COUNT
✓ platelet counts are best performed on anticoagulated venous FUNGAL ELEMENTS IN BLOOD
~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~
blood obtained by a clean, trauma-free venipuncture
✓ instruments count platelets by impedance, light-scattering,
optical fluorescence technology or a combined techniques of
the three
✓ platelet aggregation often leads to instrument ‘flags’, abnormal
histograms of platelet distribution and abnormal white cell
scatter plots
✓ it is of utmost importance to examine a blood film for the
presence of fibrin strands, platelet aggregates, platelet
satellitism and giant platelets whenever a platelet count is
unexpectedly low
✓ when platelet aggregation is antibody-mediated, accurate
counts can usually be obtained on specimens taken into
citrate or heparin rather than EDTA (use correction factor)
FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN PLATELET COUNTS
HIGH PLT LOW PLT
▪ presence of microcytic red ▪ partial clotting of specimen
cells/fragmented RBCs and platelet activation due to
(MAHAs, severe burns) poor venipuncture technique GIANT PLATELETS
▪ white cell fragments counted or traumatic blood draw
as platelets (fragments All ▪ EDTA-induced platelet
instruments of leukemic blast aggregation
cells, hairy cells or lymphoma ▪ platelet satellitism
cells) ▪ storage of blood at 4°C for
▪ cryoglobulins/cryoproteinemia more than 24 hours
▪ reactive process in IDA ▪ EDTA-induced platelet
▪ bacteria/fungi in blood phagocytosis by neutrophils
sample and monocytes
▪ high heat artefacts ▪ giant platelets falling above
▪ lipemic samples upper threshold for platelet
▪ in vitro hemolysis count
▪ microcytosis (<50-60 fL MCV) ▪ dilution with IV fluid
▪ polycythemia vera (PCV) ▪ giant platelets disorders
▪ essential thrombocythemia ▪ decreased production (Vit
▪ reactive (splenectomy, post- B12, folate deficiency,
surgery, compensation after cancer, leukemia, radiation
blood loss) and chemotherapy, RETICULOCYTE COUNT
▪ primary myelofibrosis HIV/AIDS) ✓ young red cells, newly released from the bone marrow, that
▪ CML ▪ increased destruction (ITP, still contain ribosomal RNA seen by supravital staining (new
dengue, autoimmune methylene blue, brilliant cresyl blue)
diseases, PTP, DIC, TTP) ✓ seen on Romanowsky-stained smears as slightly larger cells
bluish cells described as “polychromatophilic” (basophilia due
PLATELET SATELLITISM to remaining RNA combined with acidophilia of hemoglobin)
✓ increased numbers observed on Romanowsky-stained blood
smears is termed “polychromasia”
✓ the normal reticulocyte rate is 0.5%-2.0% in adults and 2.0%-
6.0% in newborns
✓ effective means of assessing bone marrow red blood cell
generation or response to anemia
FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN RETICULOCYTE COUNT
HIGH RETICS LOW/NORMAL RETICS
PLATELET CLUMPING ▪ reticulocytosis is the ▪ bone marrow
appropriate response in depression/suppression
anemic stress conditions (tumors,
▪ hemolysis (immune/non- malignancies, aplastic
immune causes) anemia, infiltration)
▪ hemorrhage/bleeding ▪ congenital conditions of bone
▪ hemoglobinopathies marrow inefficiency
▪ RBC membrane defects ▪ myelodysplastic syndromes
▪ MAHAs ▪ liver diseases/alcoholic liver
▪ failure
Anemia without
reticulocytosis
can indicate
inadequate
bone marrow
response/poor
compensation.
Twitter: @medtechlyfe | Facebook Group: Pinoy Medtechs Abroad
PAGE 7 OF 8
Contact: atemedtech@gmail.com
HEMATOLOGY | THEORIES & PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS ~ Ate Medtech ~
Kathleen S. Langreo, RMT, MLS (ASCPi) April 2024 Edition
RETICULOCYTES STAINED WITH SUPRAVITAL STAINS
~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~ Ate Medtech Notes ~
APPROACH TO RETICULOCYTE COUNT IN ANEMIAS
POLYCHROMASIA OBSERVED ON PERIPHERAL BLOOD
SMEARS (ROMANOWSKY-STAINS)
Twitter: @medtechlyfe | Facebook Group: Pinoy Medtechs Abroad
PAGE 8 OF 8
Contact: atemedtech@gmail.com
You might also like
- Schalms Veterinary Hematology 7Th Edition Marjory B Brooks All ChapterDocument67 pagesSchalms Veterinary Hematology 7Th Edition Marjory B Brooks All Chapterefrain.blair179100% (13)
- Haematology Notes - 3rd EdDocument100 pagesHaematology Notes - 3rd EdSally Brit100% (1)
- Cytology Laboratory DoneDocument22 pagesCytology Laboratory DoneUthaya Kumar100% (1)
- Post Analytical Phase of Laboratory TestingDocument7 pagesPost Analytical Phase of Laboratory TestingClarisse De Guzman100% (1)
- Delta Checks in The Clinical Laboratory 2019Document24 pagesDelta Checks in The Clinical Laboratory 2019birlikteyizNo ratings yet
- Chang TransfusionMed2014 DisclaimerDocument7 pagesChang TransfusionMed2014 Disclaimerteresa.cuautleNo ratings yet
- Hil 303990R7Document8 pagesHil 303990R7KHALIDNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Clinical Biochemistry 2Document27 pagesBasic Concepts of Clinical Biochemistry 2O. floriceNo ratings yet
- Ey Vaz Zadeh 2007Document10 pagesEy Vaz Zadeh 2007Zain-Alabdeen Haithem LaftaNo ratings yet
- Pereira 2018Document6 pagesPereira 2018UnknownNo ratings yet
- TTG ProcedureDocument8 pagesTTG ProcedureAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Pr-02958 - TM Brochure Ortho Sera Id-Mts Manual Pr-02958Document4 pagesPr-02958 - TM Brochure Ortho Sera Id-Mts Manual Pr-02958Son NguyenNo ratings yet
- Hema - Sop 2024Document31 pagesHema - Sop 2024Raki DallasNo ratings yet
- Quality ControlDocument10 pagesQuality Controlbunniecaronan113003No ratings yet
- BioPharm - Scale Down - Downstream PDFDocument10 pagesBioPharm - Scale Down - Downstream PDFGeetanjali HubliNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance of Laboratory Results: A Challenge in Health Care ManagementDocument6 pagesQuality Assurance of Laboratory Results: A Challenge in Health Care Managementrizkiyah prabawantiNo ratings yet
- ERBA ELite 3 ControlsDocument1 pageERBA ELite 3 ControlsGlobalindo Center MedicalNo ratings yet
- Role of Nursing Personnel in Laboratory Testing: August 2018Document6 pagesRole of Nursing Personnel in Laboratory Testing: August 2018John Alexander Hurtado ParraNo ratings yet
- Annalof Nursing PrimarycareDocument6 pagesAnnalof Nursing PrimarycarefatmanajehNo ratings yet
- ISBT Science Series - 2008 - RamanDocument28 pagesISBT Science Series - 2008 - RamanWong Jia AnnNo ratings yet
- Dalenberg 2013Document19 pagesDalenberg 2013Yash NaykaNo ratings yet
- Test For Different Immunological Principles Mary Jesreth V. BayasDocument15 pagesTest For Different Immunological Principles Mary Jesreth V. BayasMJ VergaraNo ratings yet
- Linical Aboratory O: S H, MT (Ascp) SH B A. K, E D, Mls (Ascp), Cls (Nca)Document5 pagesLinical Aboratory O: S H, MT (Ascp) SH B A. K, E D, Mls (Ascp), Cls (Nca)Tito LeopardoNo ratings yet
- BANDERASDocument4 pagesBANDERASSamuel FuentesNo ratings yet
- Astm E1326Document5 pagesAstm E1326samuellepedealbaNo ratings yet
- Verification of Molecular Assays: Rent EatonDocument4 pagesVerification of Molecular Assays: Rent EatonCristian AgostiniNo ratings yet
- Proficiency Testing Technical Brief 18A - tcm18 214885Document2 pagesProficiency Testing Technical Brief 18A - tcm18 214885RONALD ALFONSO PACHECO TORRESNo ratings yet
- Bakal 1995Document3 pagesBakal 1995Residencia Cirugia GeneralNo ratings yet
- Standard Additions Myth and RealityDocument6 pagesStandard Additions Myth and RealitytogatorNo ratings yet
- Lab Dept: Hematology Test Name: Reticulocyte Count: General InformationDocument2 pagesLab Dept: Hematology Test Name: Reticulocyte Count: General InformationTanveerNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Blood Smear Pathologist ToolDocument3 pagesPeripheral Blood Smear Pathologist ToolSimon HafeniNo ratings yet
- IFU HemaologyDocument2 pagesIFU HemaologyShujat RazaqNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry - Quality Management and InformaticsDocument5 pagesClinical Chemistry - Quality Management and Informaticsrosellae.No ratings yet
- Robustness Assessent in Computer Assisted Liquid HPLC Procedures Based On Desirability FunctionsDocument10 pagesRobustness Assessent in Computer Assisted Liquid HPLC Procedures Based On Desirability FunctionsAngel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance & Quality ControlDocument5 pagesQuality Assurance & Quality ControlErica Mae Macabingkel100% (1)
- Methods: Stefaan Derveaux, Jo Vandesompele, Jan HellemansDocument4 pagesMethods: Stefaan Derveaux, Jo Vandesompele, Jan HellemansmnkjhpNo ratings yet
- Nova Biomedical Nova Statstrip Xpress Glucose Meter Manual Original 1Document84 pagesNova Biomedical Nova Statstrip Xpress Glucose Meter Manual Original 1AzeertyNo ratings yet
- Position Paper On Particle Sizing - Sample Preparation, Method Validation and Data PresentationDocument3 pagesPosition Paper On Particle Sizing - Sample Preparation, Method Validation and Data PresentationAdamNo ratings yet
- Validation Protocol For New Methods or Instruments in The Clinical LaboratoryDocument6 pagesValidation Protocol For New Methods or Instruments in The Clinical LaboratorymohammedNo ratings yet
- MICRT Quality ControlDocument23 pagesMICRT Quality ControlMohamed AldamanhouryNo ratings yet
- User Guide: Blood Glucose Monitoring SystemDocument30 pagesUser Guide: Blood Glucose Monitoring SystemVince CentenoNo ratings yet
- TEa GuidelinesDocument20 pagesTEa GuidelinesNacho BressánNo ratings yet
- Essential Laboratory KnowledgeDocument23 pagesEssential Laboratory KnowledgeUhuebor DavidNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Quality Control: An OverviewDocument32 pagesLaboratory Quality Control: An OverviewanggaririnNo ratings yet
- SOP For ABO GroupingDocument5 pagesSOP For ABO GroupingDUKENo ratings yet
- Hepa e Hepatitis-A-Antibody MetDocument19 pagesHepa e Hepatitis-A-Antibody MetKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- cIL Ix1: A Multi-Rule Shewhart Chart For Quality Control in Clinical ChemistryDocument9 pagescIL Ix1: A Multi-Rule Shewhart Chart For Quality Control in Clinical ChemistryJustino WaveleNo ratings yet
- Xpert HCV Viral Load Brochure Ceivd 3043-02Document4 pagesXpert HCV Viral Load Brochure Ceivd 3043-02sharenNo ratings yet
- Spiking Into Aqueous Samples: Standard Guide ForDocument6 pagesSpiking Into Aqueous Samples: Standard Guide Formohdhafizmdali100% (1)
- A74719D-Establishing Appropriate QC Ranges For ImmunoAssayDocument4 pagesA74719D-Establishing Appropriate QC Ranges For ImmunoAssaydar alhikmahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Automation-and-POCTDocument32 pagesChapter 3 Automation-and-POCTNida RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Corneal Asymmetry Analysis by Pentacam Scheimpflug Tomography For Keratoconus DiagnosisDocument13 pagesCorneal Asymmetry Analysis by Pentacam Scheimpflug Tomography For Keratoconus DiagnosisJuanes MagnoNo ratings yet
- Screening and Diagnostic TestsDocument34 pagesScreening and Diagnostic TestsQuỳnh Anh Phạm HoàngNo ratings yet
- Clinical ChemistryDocument19 pagesClinical Chemistrythrowawy100% (2)
- Laboratory Procedure Manual: C-Reactive Protein Serum NephelometryDocument13 pagesLaboratory Procedure Manual: C-Reactive Protein Serum NephelometryFadlan HafizhNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Analytical Methods Used For Regulation of Foods and DrugsDocument10 pagesEvaluation of Analytical Methods Used For Regulation of Foods and DrugsrenatoandaraNo ratings yet
- GPP Pipetting Calibration and Technique ENDocument4 pagesGPP Pipetting Calibration and Technique ENveneta gizdakovaNo ratings yet
- Method Development and Validation For Estimation of Dosulepin in Pure and Dosage Form by Using HPLCDocument8 pagesMethod Development and Validation For Estimation of Dosulepin in Pure and Dosage Form by Using HPLCBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0039625720300709 MainDocument23 pages1 s2.0 S0039625720300709 Mainneha midhaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Laboratory Investigations: A Guide for Nurses, Midwives and Health ProfessionalsFrom EverandUnderstanding Laboratory Investigations: A Guide for Nurses, Midwives and Health ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Labs & Imaging for Primary Eye Care: Optometry In Full ScopeFrom EverandLabs & Imaging for Primary Eye Care: Optometry In Full ScopeNo ratings yet
- Quick guide to Laboratory Medicine: a student's overviewFrom EverandQuick guide to Laboratory Medicine: a student's overviewNo ratings yet
- Routine Laboratory Evaluation of CoagulationDocument7 pagesRoutine Laboratory Evaluation of CoagulationGilo IlaganNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 11 - Blood)Document22 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 11 - Blood)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Mls Imls Content Guideline PDFDocument11 pagesMls Imls Content Guideline PDFswasahmedNo ratings yet
- Nattokinase - 2008Document7 pagesNattokinase - 2008nataleebellaNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Leech TherapyDocument24 pagesMedicinal Leech TherapyKingNo ratings yet
- Potential Adverse Effects of Long-Term Consumption of Fatty AcidsDocument11 pagesPotential Adverse Effects of Long-Term Consumption of Fatty Acidstaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation and Hemostasis in Neurosurgery PDFDocument404 pagesAnticoagulation and Hemostasis in Neurosurgery PDFAleksandar DimovskiNo ratings yet
- The Platelet Rich Plasma ProcedureDocument2 pagesThe Platelet Rich Plasma ProcedurekaisalanaafidaNo ratings yet
- Produktkatalog Fresenius Kabi Transfusion Technolo-Q SmpFCuAau2bGekq5W8jXHusten LjM97QZf MP7CADocument206 pagesProduktkatalog Fresenius Kabi Transfusion Technolo-Q SmpFCuAau2bGekq5W8jXHusten LjM97QZf MP7CACampaign MediaNo ratings yet
- Quality Standards For Sample Processing, Transportation, and Storage in Hemostasis TestingDocument11 pagesQuality Standards For Sample Processing, Transportation, and Storage in Hemostasis TestingGunay AliyevaNo ratings yet
- Blood Workbook To Assist With Conscience Matters Involving BloodDocument18 pagesBlood Workbook To Assist With Conscience Matters Involving BloodRicky YauNo ratings yet
- DIC Blood Component TherapyDocument30 pagesDIC Blood Component TherapySameer KumarNo ratings yet
- Antifibrinolytic Therapy and Perioperative ConsiderationsDocument14 pagesAntifibrinolytic Therapy and Perioperative Considerationsandrey wahyudiNo ratings yet
- Physiology of CoagulationDocument44 pagesPhysiology of CoagulationXee JayNo ratings yet
- CT BTDocument20 pagesCT BTZainMalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2DannyNo ratings yet
- Serum Vs Plasma: Which Specimen Should You UseDocument48 pagesSerum Vs Plasma: Which Specimen Should You UseTanveerNo ratings yet
- Swift River Medication AdministrationDocument4 pagesSwift River Medication AdministrationmattNo ratings yet
- Blood Physiology MainDocument68 pagesBlood Physiology MainOmenaalaNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders: Drg. Gita Dwi Jiwanda Sovira, M.KesDocument26 pagesBleeding Disorders: Drg. Gita Dwi Jiwanda Sovira, M.KessaskiakonitaNo ratings yet
- Postpartum HemorrhageDocument22 pagesPostpartum HemorrhageReynaldiReikyHadiwijayaNo ratings yet
- I RECOVER Post Vaccine ProtocolDocument58 pagesI RECOVER Post Vaccine ProtocolJohnny SmithNo ratings yet
- Blood Products. Preparation of Blood ComponentsDocument32 pagesBlood Products. Preparation of Blood ComponentsSanthiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Full Blood PictureDocument1 pageFull Blood PictureGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Hematology - Handbookfor Personal UseDocument156 pagesHematology - Handbookfor Personal Useuber6791100% (1)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY LAB - Hanbook of Pathophysiology SevastreDocument192 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY LAB - Hanbook of Pathophysiology Sevastredorina0101No ratings yet
- Bact AlertDocument10 pagesBact Alertwulan3daysNo ratings yet
- Lab. Act. #5 - Blood and HematopoiesisDocument8 pagesLab. Act. #5 - Blood and HematopoiesisDan OdviarNo ratings yet