Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medical Term Chapter05
Medical Term Chapter05
Uploaded by
sweetiepotamusCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Medical Term Chapter05
Medical Term Chapter05
Uploaded by
sweetiepotamusCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 5
The Skeletal System
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Word Parts
Arthr/o Joint Kinesi/o Movement
Brachi/o Arm My/o Muscle
Carp/o Wrist Myel/o Bone marrow
Cervic/o Neck Orth/o Straight
Chondr/o Cartilage Os/te/o Bone
Cost/o Rib Ped/o Foot, Child
Crani/o Cranium Spondyl/o Vertebrae
Dactyl/o Finger, Toe Thorac/o Chest
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #1
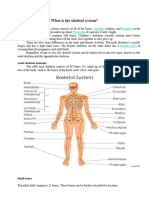
Skeleton
o 206 bones
o Rigid but articulating (movable at joints) framework
for muscles and other tissues
o Protects vital organs
o Stores minerals
o Makes blood cells
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #2
Skeleton divided into two parts: axial and appendicular
o Axial
Skull
Chest
Spinal column
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #3
Skeleton divided into two parts: axial and appendicular
o Appendicular
Arms
Legs
Shoulder
Pelvic bones
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #4
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #5
Ligaments: bands of tissue that connect two bones
together
Tendons: attach muscles to bone
Joints (articulations): places where bones come together
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #6
Ossification
o Bone formation
o Begins early in fetal development when skeleton is
composed mostly of cartilage
o Osseous tissue: connective tissue with mature bone
cells called osteocytes
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #7
Parts of the long bone:
o Diaphysis—shaft
o Epiphysis—each end of a long bone
o Epiphyseal plate—growth area of a long bone
o Medullary cavity—inside of the diaphysis
o Marrow—tissue that produces blood cells
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #8
Compact bone—hard, dense bone and makes up
diaphysis
Spongy bone—mesh-like bone tissue found in epiphyses
Periosteum—membrane covering the bone surfaces
Endosteum—inner surface of medullary cavity lined with
thin layer of cells
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #9
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #10
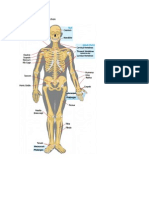
Axial skeleton
o Cranium (head)
o Thorax
o Vertebral column
o Cranial bones enclose and protect brain
Frontal bone; two parietal bones; two temporal
bones; occipital bone
Joined by cranial sutures
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #11
Main facial bones:
o Nasal bone—forms the bridge of the nose
o Zygomatic bones—form the cheeks
o Maxilla—immovable upper jawbone
o Mandible—movable lower jawbone
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #12
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #13
Thorax
o Breastplate or thoracic cage
o 12 thoracic vertebrae, 12 ribs, costal (rib) cartilages,
sternum
o Major organs inside thoracic cage: heart and lungs
o Rib pairs attached to correspondingly numbered
vertebrae (back bones)
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #14
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #15
Spinal column
o Five sections of vertebrae
o Prefix letter (C for cervical, T for thoracic, L for
lumbar), followed by number indicating placement on
column
7 cervical vertebrae
12 thoracic vertebrae
5 lumbar vertebrae
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #16
Spinal column
o At the base of spinal column are the sacrum and
coccyx
o Sacrum formed by five fused sacral vertebrae
o Coccyx contains three to five fused coccygeal
vertebrae
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #17
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #18
Appendicular skeleton
o Body’s appendages (upper limbs and lower limbs)
o Areas to which appendages are attached: shoulder
and pelvic girdles
o Clavicle: collarbone
o Scapula: shoulder blade
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #19
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #20
Appendicular skeleton
o Humerus: long arm bone extending from shoulder
and ending at elbow
o Forearm: ulna and radius
o Wrist: eight bones in two rows, called carpal bones
o Metacarpals: hand bones
o Phalanges: bones that make up the fingers
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #21
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #22
Appendicular skeleton
o Hip bone (os coxae): fusion of three bones—ilium,
ischium, pubis
o Femur: long bone that extends from hip to knee
o Tibia and fibula: long bones that extend from knee to
ankle
o Talus: ankle bone
o Patella: kneecap
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #23
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #24
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #25
Joints
o Or articulation is place where bones come together
o Synarthrosis: joint with no movement (cranium)
o Amphiarthrosis: joint with little movement
(vertebrae)
o Diarthrosis or synovial: joint with free movement
(knee)
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #26
Joints
o Cartilage: connective tissue that enables movement
o Bursae: spaces within connective tissue filled with
synovial fluid
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Structure and Function #27
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Disorders Related to the Skeletal System
#1
Sprain: tear in a ligament
Fractures: broken bone
o Simple fracture (closed fracture): no open skin
o Compound fracture (open fracture): broken bone
protrudes through the skin
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Disorders Related to the Skeletal System
#2
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Disorders Related to the Skeletal System
#3
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Disorders Related to the Skeletal System
#4
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Disorders Related to the Skeletal System
#5
Bone disorders
o Osteomyelitis: inflammation caused by bacteria
o Osteoporosis: decrease in bone density and mass
o Rickets: causing bowed legs in children
o Osteomalacia: bone softening in adulthood
o Osteosarcoma: tumor of the bone
o Chondrosarcoma: tumor that arises in cartilage
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Disorders Related to the Skeletal System
#6
Joint disorders
o Arthritis: joint inflammation
o Osteoarthritis: general wear and tear on joints
o Rheumatoid arthritis (RA: immunologic abnormality)
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Disorders Related to the Skeletal System
#7
Spine disorders
o Herniated disc: disc that protrudes into vertebral
canal and puts pressure on spinal nerve
o Kyphosis (humpback): compression fractures of
vertebrae
o Lordosis: abnormal curvature in lumbar region
o Scoliosis: sideways curvature of spine
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Disorders Related to the Skeletal System
#8
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Diagnostic Tests, Treatments, and
Surgical Procedures
Reduction: realignment of broken bone
Traction: elastics or pulley and weights to maintain
alignment
Casts and splints to immobilize broken bone
Medication for pain and inflammation and/or physical
therapy
Arthrocentesis: drains fluid and relieves pressure in joint
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Practice and Practitioners
Orthopedics: orthopedic medicine
Orthopedic surgeons: coordinate patient care with
physical therapists, occupational therapists, kinesiologists
Rheumatologist: physician who specializes in treatment
of joint disorders and arthritic conditions
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Abbreviations
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Practice Exercise #1
What is a compound fracture?
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Answer to Practice Exercise #1
A compound fracture involves a break in the bone that
protrudes through the skin.
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Practice #2
What is scoliosis?
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Answer to Practice #2
Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine.
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Practice #3
Identify these word parts:
o carp/o
o lumb/o
o phalang/o
o dactyl/o
o brachi/o
o myel/o
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Answer to Practice #3
Identify these word parts:
o carp/o: wrist
o lumb/o: lower back
o phalang/o: bones of fingers and toes
o dactyl/o: fingers, toes
o brachi/o: arm
o myel/o: bone marrow
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Practice #4
Identify these abbreviations:
o ACL
o ROM
o Fx
o TKA
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Answer to Practice #4
Identify these abbreviations:
o ACL: anterior cruciate ligament
o ROM: range of motion
o Fx: fracture
o TKA: total knee arthroplasty
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Practice #5
Analyze this term:
Amphiarthrosis
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Answer to Practice #5
Analyze this term:
Amphi- arthr/ -osis
↓ ↓ ↓
P R S
↓ ↓ ↓
Both Joint Abnormal
sides condition
Amphiarthrosis is a joint with
little movement.
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Practice #6
Analyze this term:
Osteogenesis
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Answer to Practice #6
Analyze this term:
Oste/ o/ -genesis
↓ ↓ ↓
R CV S
↓ ↓
Bone origin
Osteogenesis refers to the
formation of bone.
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Practice #7
Analyze this term:
Arthralgia
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Answer to Practice #7
Analyze this term:
Arthr -algia
↓ ↓
R S
↓ ↓
Joint pain
Arthralgia is pain in a joint.
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Practice #8
Analyze this term:
Osteomalacia
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Answer to Practice #8
Analyze this term:
Oste/ o/ -malacia
↓ ↓ ↓
R CV S
↓ ↓
Bone softening
Osteomalacia is softening of the
bone.
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Practice #9
Analyze this term:
Arthroscopy
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Answer to Practice #9
Analyze this term:
Arthr/ o/ -scopy
↓ ↓ ↓
R CV S
↓ ↓
Joint Use of
instrumen
t for
viewing
Arthroscopy is an examination of the inside of a joint viewed with
an instrument.
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Practice #10
Analyze this term:
Costectomy
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
Answer to Practice #10
Analyze this term:
Cost -ectomy
↓ ↓
R S
↓ ↓
Ribs Surgical
removal of
Costectomy is the surgical
removal of a rib.
Copyright © 2019 Wolters Kluwer · All Rights Reserved
You might also like
- Feasibility StudyDocument5 pagesFeasibility StudyKath Garcia50% (4)
- Tesla Motors Expansion StrategyDocument26 pagesTesla Motors Expansion StrategyVu Nguyen75% (4)
- Skeletal SystemDocument28 pagesSkeletal SystemAivee SumulongNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Reading Comprehension Exercises - 126764Document5 pagesSkeletal System Reading Comprehension Exercises - 126764Lucianny FilionNo ratings yet
- 08chapter8theskeletalsystem Appendicularskeleton 170828041008Document40 pages08chapter8theskeletalsystem Appendicularskeleton 170828041008Saif JalaliNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesSkeletal SystemWynne Michael David GogoNo ratings yet
- Module 4 SKELETAL SYSTEMDocument23 pagesModule 4 SKELETAL SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology: The Skeletal System: The Appendicular SkeletonDocument39 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology: The Skeletal System: The Appendicular SkeletonJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument28 pagesSkeletal SystemExequielNo ratings yet
- Skeletal PartsDocument6 pagesSkeletal PartsResa MagusaraNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument9 pagesThe Skeletal SystemLili PredescuNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Report PDFDocument86 pagesSkeletal System Report PDFMarian Elaine RufilaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Skeletal SystemDocument48 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Skeletal SystemAster fayisaNo ratings yet
- Support, Movement and LocomotionDocument3 pagesSupport, Movement and LocomotionAhmad Barrun Nidhom83% (23)
- Unit Three: General Anatomy of The of Skeletal System (Osteology)Document78 pagesUnit Three: General Anatomy of The of Skeletal System (Osteology)Gifti DemisseNo ratings yet
- Movement IIDocument17 pagesMovement IIPurple LovahhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Human Skeletal SystemKristine DomacenaNo ratings yet
- Exp-4, To Study The General Features of Axial and Appendicular Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesExp-4, To Study The General Features of Axial and Appendicular Skeletal SystemKeshab KapoorNo ratings yet
- Locomotion Notes by AhmedfjDocument3 pagesLocomotion Notes by AhmedfjruesNo ratings yet
- Systems of The BodyDocument144 pagesSystems of The BodyTweetie Borja DapogNo ratings yet
- Prepared Lesson On Skeletal System: By: Crisanto C. SaunilDocument26 pagesPrepared Lesson On Skeletal System: By: Crisanto C. SaunilChris Catanus SaunilNo ratings yet
- The Axial Skeleton PDFDocument9 pagesThe Axial Skeleton PDFElvin EzuanNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Skeletal SystemDocument25 pagesWeek 6 Skeletal SystemDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Movement and Locomotion Question Bank For Class 9Document7 pagesMovement and Locomotion Question Bank For Class 9piyushmandal4567No ratings yet
- Skeletal System Anatomy: Skull Mandible Temporal BoneDocument5 pagesSkeletal System Anatomy: Skull Mandible Temporal BoneMichael Villamor100% (1)
- Raz lr30 Hardstuffbones CLRDocument10 pagesRaz lr30 Hardstuffbones CLRapi-268605530No ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Skeletal System-Notes of LessonDocument4 pagesChapter-6 Skeletal System-Notes of Lessonjothishree24121980No ratings yet
- The Importance of Your Skeletal SystemDocument18 pagesThe Importance of Your Skeletal SystemChris DavisNo ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument19 pagesBody SystemsSiria PinedaNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthrology Nur PDFDocument133 pagesOsteoarthrology Nur PDFAngelNo ratings yet
- 20201012-20201019-1149-Skeletal SystemDocument61 pages20201012-20201019-1149-Skeletal Systemdrin zekaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesSkeletal SystemJovi Floresca AberinNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesThe Skeletal SystemJessa Mae BanquirigNo ratings yet
- ch-8 Our SkeletalDocument8 pagesch-8 Our Skeletalxhtk3em03zNo ratings yet
- Skeleton System QuizDocument3 pagesSkeleton System Quizhardik321No ratings yet
- Human Skeletal System BLOGDocument8 pagesHuman Skeletal System BLOG622752No ratings yet
- Skeleton - Movement and LocomtionDocument5 pagesSkeleton - Movement and Locomtion9 A 10 Jerome Justin DasNo ratings yet
- Materi Human SkeletonDocument6 pagesMateri Human SkeletonRicky UchihaNo ratings yet
- Module Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesModule Skeletal SystemEMEM QUENNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY I Lecture 02, GENERAL ANATOMY 2, Skeletal System, BonesDocument42 pagesANATOMY I Lecture 02, GENERAL ANATOMY 2, Skeletal System, BonesHalima NazarNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument8 pagesDefinitionJamesNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Week 1 3Document51 pagesSkeletal System Week 1 3Nichole Balao-asNo ratings yet
- Theskeletalsystemanatomy 181202101855Document52 pagesTheskeletalsystemanatomy 181202101855Sandhiya KNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesSkeletal SystemMaureen Tianson DomingoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Skelital SystemDocument6 pagesStructure and Functions of The Skelital SystemLucshaan GaneshadasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter24 Muscukoskeletal AssessmentDocument31 pagesChapter24 Muscukoskeletal AssessmentMARY ANNE JUDE ANTHONYNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System 2017Document10 pagesSkeletal System 2017sonali voraNo ratings yet
- Human Skeletal SystemDocument37 pagesHuman Skeletal SystembhikasNo ratings yet
- WEEK 5 LAB EXERCISE - Skeletal SystemDocument14 pagesWEEK 5 LAB EXERCISE - Skeletal SystemG4 AMOYO ANGELICA NICOLENo ratings yet
- Ms. Karen B. Adriano, RN, LPT: Skeletal SystemDocument38 pagesMs. Karen B. Adriano, RN, LPT: Skeletal SystemKevin AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Science Four Lesson 1.1A Your Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesScience Four Lesson 1.1A Your Skeletal SystemSara GNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Fact FileDocument2 pagesSkeletal System Fact FileAsma AbbasNo ratings yet
- The Bones and The MusclesDocument35 pagesThe Bones and The MusclesJohn Christian CastroNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Prepared By: GENER R. RODELASDocument31 pagesSkeletal System: Prepared By: GENER R. RODELASgener r. rodelasNo ratings yet
- 2 Skeletal System (Simple)Document41 pages2 Skeletal System (Simple)Mario RectoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Grade 7-The Human SkeletonDocument19 pagesLesson 2 Grade 7-The Human SkeletonSAMI DHAOUINo ratings yet
- Midterm Assignment 1Document5 pagesMidterm Assignment 1R Jay LagdaminNo ratings yet
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology: 14 EditionDocument62 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology: 14 EditionTalha AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System AnatomyDocument6 pagesSkeletal System AnatomymanuelaristotleNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System PowerpointDocument40 pagesSkeletal System PowerpointLee KaiYangNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of A Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesStructure and Function of A Skeletal Systemapi-280073172No ratings yet
- The Health Care Facility CH-4Document34 pagesThe Health Care Facility CH-4sweetiepotamusNo ratings yet
- Microbio Skin and Eyes LectureDocument30 pagesMicrobio Skin and Eyes LecturesweetiepotamusNo ratings yet
- DGTipsheet31EnjoyFoodsFromManyCultures PDFDocument1 pageDGTipsheet31EnjoyFoodsFromManyCultures PDFsweetiepotamusNo ratings yet
- Plant Sterols and Stanols in The Management of Blood Cholesterol LevelsDocument18 pagesPlant Sterols and Stanols in The Management of Blood Cholesterol LevelssweetiepotamusNo ratings yet
- Understanding Food Principles and PreparationDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Food Principles and PreparationsweetiepotamusNo ratings yet
- 3 Day Food Recall Day 1 Breakfast Lunch Dinner SnacksDocument1 page3 Day Food Recall Day 1 Breakfast Lunch Dinner SnackssweetiepotamusNo ratings yet
- Nail Care Lesson 2Document5 pagesNail Care Lesson 2Tin TinNo ratings yet
- GRP 3 Keesha & Marie Faye Abdellah Power Point FINALDocument10 pagesGRP 3 Keesha & Marie Faye Abdellah Power Point FINALevangelo22656No ratings yet
- Math 8 Q3 Module 5 With Answer KeyDocument13 pagesMath 8 Q3 Module 5 With Answer KeyJimcris villamorNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire For Tourist Satisfaction in Taiwanese Hot Springs TourismDocument2 pagesQuestionnaire For Tourist Satisfaction in Taiwanese Hot Springs TourismAmeer Akram100% (5)
- Cisco GGSNDocument386 pagesCisco GGSNtrunto0% (1)
- Hdat2en 4 52Document156 pagesHdat2en 4 52blahh12345689No ratings yet
- Cyber CrimeDocument366 pagesCyber CrimeRufino Gerard MorenoNo ratings yet
- Mass, Volume, and Density: Goals Shape Formula Symbols Table 2.1Document5 pagesMass, Volume, and Density: Goals Shape Formula Symbols Table 2.1SandyNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Factual Report Text "ROSE"Document9 pagesAnalyzing Factual Report Text "ROSE"Muhammad Taufiq GunawanNo ratings yet
- Nile International Freight ServicesDocument19 pagesNile International Freight ServicessameerhamadNo ratings yet
- C H A P T E R TWO: Corporate Strategy Decisions and Their Marketing ImplicationsDocument20 pagesC H A P T E R TWO: Corporate Strategy Decisions and Their Marketing ImplicationsHrishikesh MahapatraNo ratings yet
- 核心單字3000Level3 A-IDocument12 pages核心單字3000Level3 A-IShulin ChenNo ratings yet
- C161 Occupational Health Services ConventionDocument7 pagesC161 Occupational Health Services ConventionKeith RhodesNo ratings yet
- Eskom, ABB Reach R1.5bn Settlement For Kusile Cost OverrunDocument3 pagesEskom, ABB Reach R1.5bn Settlement For Kusile Cost OverrunNokukhanya MntamboNo ratings yet
- Harga Daikin ACDocument9 pagesHarga Daikin ACIlham CaisarNo ratings yet
- Experience With The Munster-Type Below-Elbow Prosthesis, A Preliminary ReportDocument5 pagesExperience With The Munster-Type Below-Elbow Prosthesis, A Preliminary ReportrehabeasyNo ratings yet
- Plasticity - Rubber PDFDocument3 pagesPlasticity - Rubber PDFsujudNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis of Complex Networks 2011Document501 pagesStructural Analysis of Complex Networks 2011kemalihsan_17959No ratings yet
- Phil CSR Case StudiesDocument26 pagesPhil CSR Case StudiesA Niknok MaifiosoNo ratings yet
- Summary of Maximum Load and Energy Consumption of Kwara State Goevrnment Mdas in Ilorin MetropolisDocument61 pagesSummary of Maximum Load and Energy Consumption of Kwara State Goevrnment Mdas in Ilorin MetropolisAbdulyekini AhmaduNo ratings yet
- Fitel S199M24 Spec SheetDocument1 pageFitel S199M24 Spec SheetcolinyNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity of Cocoa Pod Husk PDFDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity of Cocoa Pod Husk PDFTài ColeNo ratings yet
- Ongc V Saw PipesDocument9 pagesOngc V Saw PipesManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- TC-42X1 Part 1Document50 pagesTC-42X1 Part 1Pedro SandovalNo ratings yet
- FSM 2000Document52 pagesFSM 2000aram_hNo ratings yet
- Instructional Methods For Teaching Social Studies: A Survey of What Middle School Students Like and Dislike About Social Studies InstructionDocument4 pagesInstructional Methods For Teaching Social Studies: A Survey of What Middle School Students Like and Dislike About Social Studies InstructionShally GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mapa de Concessões 1 1Document1 pageMapa de Concessões 1 1Venkat PachaNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 13 KINETIC THEORY With SOLUTIONSDocument6 pagesPhysics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 13 KINETIC THEORY With SOLUTIONSSk ShivamNo ratings yet