Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Polo Poster ISCA - 2022
Polo Poster ISCA - 2022
Uploaded by
LUTHIEN orquideaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Polo Poster ISCA - 2022
Polo Poster ISCA - 2022
Uploaded by
LUTHIEN orquideaCopyright:
Available Formats
MANAGEMENT OF NYSTAGMUS
C. Polo MD 1 , J. Cena MD 2
1 Hospital Piñero, Buenos Aires (Argentina)
2 Hospital Vilela, Rosario (Argentina)
Nystagmus is defined as an involuntary rhythmic oscillation of the eyes.
Nystagmus in Albinism is an Infantile nystagmus, which usually appears in the first 3e6 months of life, leads to reduced visual acuity due to the excessive motion of images
on the retina, and also the movement of images away from the fovea. The characteristics of Nystagmus in albinism are variable in each patient.
The therapeutic alternatives we have are: carbonic anhydrase inhibitors in drops to minimize it. Other options are the use of contact lenses and surgery to improve
torticollis or minimize its frequency.
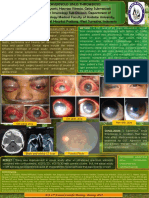
In this poster we present three cases where these treatments were used.
CASE 1 CASE 2 CASE 3
NYSTAGMUS AND STRABISMUS TREATMENT WITH TOPICAL CONTACT LENS
SURGERY BRINZOLAMIDE
PREOPERATORY: Visual acuity : 20/200 BE
Patient with esotropia and nystagmus Visual acuity :LE 20/100 RE 20/70 Pendular Nystagmus
Visual acuity : 20/100 BE Pendular Nystagmus
Pendular Nystagmus
POSTOPERATORY
Visual acuity : 20/70 BE
Ortotropia
Plsusoptix: Improvement of fixation and
stabilization of nystagmus.
After 1 year with topic Brinzolamide:
Visual Acuity 20/50 Visual acuity : 20/100 BE with Contact Lens with
Improvement of quality vision and fixation astigmatism correction and iris print
Pendular Nystagmus with minimal improvement
CONCLUSION: The treatment of nystagmus in Albinism has as its main objective improve both visual acuity, increasing stability in fixation, such as
compensatory torticollis in the case of exists and the aesthetic aspect of the nystagmus, decreasing its intensity.
The first therapeutic step in the treatment of patients with nystagmus is to correct the refractive error with glasses or contact lenses, since these
patients present typically a high astigmatism in favor of the rule. I know can add prisms to improve head posture and, in cases where the
nystagmus decreases with convergence, it might be indicated to add ˜ base prisms temporary to stimulate convergence. In any casegood
response to prisms is a good indicator of the response to surgery.
Among the indications for surgical treatment are find: torticollis, since these patients present a nystagmus block with gaze and strabismus; and
improvement of nystagmus with convergence. The most commonly surgical techniques used are retroinsertion, resection, and tenotomy, or a
combination thereof. The retroinsertion of the muscles that have their action in the direction of the torticollis aim to move the eyes in that
direction, bringing the eyes to the locked position in primary position, thus improving the abnormal posture of the head.
Other authors propose a retroinsertion of the 4 horizontal muscles behind the equator to decrease the torsional effect of the muscles .
Tenotomy could also be an option therapeutic in these patients, since it could interrupt the proprioceptive circuit present in the nerve endings
of the tendinoscleral junction, which would lead to a decreased response to the nystagmus signal.
Regarding medical treatment, multiple options have been proposed over the years with different results, among which we can highlight the
botulinum toxin and the carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (Brinzolamide).
The effect of anhydrase inhibitors carbonica is based on the same principles as tenotomy, that is, blocking the proprioceptive circuit of the
junction tendon-sclera. Previous studies show that this effect It is obtained both by administering them orally and by route topical.
Bibliography
Topical brinzolamide (Azopt) versus placebo in the treatment of infantile nystagmus syndrome (INS).
Hertle RW, Yang D, Adkinson T, Reed M.
Br J Ophthalmol. 2015 Apr;99(4):471-6. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2014-305915. Epub 2014 Oct 21.
Nieves-Moreno M, et al. Brinzolamida tópica en el nistagmo congénito: Estudio retrospectivo. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol.
2017. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.oftal.2017.06.001
Effects of topical brinzolamide on infantile nystagmus syndrome waveforms: eyedrops for nystagmus.
Dell'osso LF, Hertle RW, Leigh RJ, Jacobs JB, King S, Yaniglos S.
J Neuroophthalmol. 2011 Sep;31(3):228-33. doi: 10.1097/WNO.0b013e318223d0a9.
PMID: 21709585
You might also like
- Final I. Competency-checklist-VenipunctureDocument2 pagesFinal I. Competency-checklist-Venipuncturejohn100% (4)
- Case Presentation On MIDocument40 pagesCase Presentation On MIKaku Manisha85% (13)
- El Borno FusionDocument112 pagesEl Borno FusionneareastspineNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Treatment of Excessive Gingival DisplayDocument12 pagesPeriodontal Treatment of Excessive Gingival DisplayJuan Carlos CárcamoNo ratings yet
- Ematrix Training DocumentDocument2 pagesEmatrix Training DocumentmadilynmcoleNo ratings yet
- Diagnosa NistagmusDocument66 pagesDiagnosa Nistagmusriesky912No ratings yet
- Effective Treatment of Platysma Bands With.15Document1 pageEffective Treatment of Platysma Bands With.15AbdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Joint Bone Spine 2017 VionnetDocument5 pagesJoint Bone Spine 2017 VionnetChristiano TanuriNo ratings yet
- Compare Two Splints 2005Document9 pagesCompare Two Splints 2005Hồ TiênNo ratings yet
- A Small Study of The Relationship BetweeDocument3 pagesA Small Study of The Relationship BetweeDr. Hilder HernandezNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Ocular Myasthenia Gravis.8Document3 pagesTreatment of Ocular Myasthenia Gravis.8nitaNo ratings yet
- ) Nystagmus: Otorhinolaryngology Clinics May 2012Document8 pages) Nystagmus: Otorhinolaryngology Clinics May 2012Evan DionesiaNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous PharmacologyDocument32 pagesMiscellaneous PharmacologyAbdul Rehman SafdarNo ratings yet
- Pharm - Ther. Eye, Ear & SkinDocument21 pagesPharm - Ther. Eye, Ear & Skintutor tujuhNo ratings yet
- 1933 0693 Article p1372Document8 pages1933 0693 Article p1372florin jescuNo ratings yet
- Nervio AlveolarDocument3 pagesNervio AlveolarLuis GustavoNo ratings yet
- Current & Emerging Therapies For Managing Glaucoma - HVDocument17 pagesCurrent & Emerging Therapies For Managing Glaucoma - HVHerdy VeristianNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Optic NeuritisDocument4 pagesTreatment of Optic NeuritisGufront MustofaNo ratings yet
- YNSA Treatment of StrokeDocument4 pagesYNSA Treatment of StrokeHendrawan PratamaNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms Underlying Nystagmus: Richard V AbadiDocument4 pagesMechanisms Underlying Nystagmus: Richard V AbadiLeonardoCampanelliNo ratings yet
- CryosurgeryDocument6 pagesCryosurgeryLuiz Gabriel SignorelliNo ratings yet
- Compensatory Head Posture and Neck Problems: Is There An Association? A Cohort Study of Nystagmus PatientsDocument5 pagesCompensatory Head Posture and Neck Problems: Is There An Association? A Cohort Study of Nystagmus PatientsRositamundiNo ratings yet
- 2018 Total Mandibular Reconstruction Following Diffuse Sclerosing OsteomyelitisDocument5 pages2018 Total Mandibular Reconstruction Following Diffuse Sclerosing OsteomyelitisBladimirNo ratings yet
- Neuritis VestibularDocument12 pagesNeuritis VestibularMahesa Kurnianti Putri100% (1)
- Anaesthetic Considerations For Strabismus Surgery in Children and AdultsDocument12 pagesAnaesthetic Considerations For Strabismus Surgery in Children and AdultschdoankNo ratings yet
- Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders.15Document33 pagesNeuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders.15Marco Macavilca CruzNo ratings yet
- Clinical Study of Intraocular Pressure Changesfollowing Nd-Yag Laser Iridotomy in Angle Closure DiseaseDocument15 pagesClinical Study of Intraocular Pressure Changesfollowing Nd-Yag Laser Iridotomy in Angle Closure DiseaseIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Preventive Treatment of Migraine Whichdrugs To Choose Own ExperienceDocument3 pagesPreventive Treatment of Migraine Whichdrugs To Choose Own ExperiencenadyaNo ratings yet
- Fsurg 09 843982Document7 pagesFsurg 09 843982fachriybalafifNo ratings yet
- Acta 91 78Document3 pagesActa 91 78Gonzalo CastroNo ratings yet
- Cobb - Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel ReleaseDocument8 pagesCobb - Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel ReleaseJohnny WangNo ratings yet
- Levodopa (Combined With CarbidopaDocument4 pagesLevodopa (Combined With CarbidopaEugene MercadoNo ratings yet
- Pelosin 2013Document10 pagesPelosin 2013QuocNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia in Ophthal Mic SurgeryDocument98 pagesAnesthesia in Ophthal Mic SurgeryT Z BenNo ratings yet
- Infantile Periocular Capillary Hemangioma An Unusual PresentationDocument2 pagesInfantile Periocular Capillary Hemangioma An Unusual PresentationAngela Mitchelle NyanganNo ratings yet
- Botulinum Toxin in The Treatment of Facial ParalysisDocument10 pagesBotulinum Toxin in The Treatment of Facial ParalysisLeandro Henrique da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Corneal Neurotization: A Novel Solution To Neurotrophic KeratopathyDocument9 pagesCorneal Neurotization: A Novel Solution To Neurotrophic KeratopathyJosé Castro SoaresNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Value of Nystagmus: Spontaneous and Induced Ocular OscillationsDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Value of Nystagmus: Spontaneous and Induced Ocular OscillationsPrincella MonicaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal GlaucomaDocument5 pagesJurnal GlaucomaAshabul AnharNo ratings yet
- Mecanic 4Document5 pagesMecanic 4omarNo ratings yet
- CST - PPTX NewDocument1 pageCST - PPTX NewLiyanti RinceNo ratings yet
- A Study On Effectiveness of Low Level Laser Therapy and Mcconnell Taping in Subjects With Infrapatellar BursistisDocument4 pagesA Study On Effectiveness of Low Level Laser Therapy and Mcconnell Taping in Subjects With Infrapatellar BursistisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Nej M 199804233381702Document7 pagesNej M 199804233381702Syafrial BarawasNo ratings yet
- Low Laser TherapyDocument2 pagesLow Laser TherapySuzana PoloncaNo ratings yet
- Finzel 2019Document6 pagesFinzel 2019syahrulNo ratings yet
- New Technique For Cryoneuroablation of The Proximal Greater Occipital Nerve 2019Document8 pagesNew Technique For Cryoneuroablation of The Proximal Greater Occipital Nerve 2019stogicza agnesNo ratings yet
- Pott's Disease MEDICAL MANAGEMENTDocument3 pagesPott's Disease MEDICAL MANAGEMENTRuby Anna BorceNo ratings yet
- Emergency Management: Angle-Closure GlaucomaDocument1 pageEmergency Management: Angle-Closure GlaucomaSitti HazrinaNo ratings yet
- Lambru2021 2Document12 pagesLambru2021 2Deyvid CapeloNo ratings yet
- Temporary Blindness After Inferior Alveolar Nerve BlockDocument2 pagesTemporary Blindness After Inferior Alveolar Nerve BlockIbramanto WarganegaraNo ratings yet
- Re-Evaluating The Treatment of Acute Optic Neuritis: ReviewDocument10 pagesRe-Evaluating The Treatment of Acute Optic Neuritis: ReviewGufront MustofaNo ratings yet
- KyphosisDocument7 pagesKyphosisjhenz11_25No ratings yet
- Manajemen Diplopia 1Document4 pagesManajemen Diplopia 1LailyIraFauziyyahNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Outline ScriptDocument4 pagesTrigeminal Neuralgia Outline ScriptRogerQuxNo ratings yet
- Casani 2011Document8 pagesCasani 2011Anamaria SNo ratings yet
- Hao, K. 2019. Application of Ozone Therapy in Interventional MedicineDocument4 pagesHao, K. 2019. Application of Ozone Therapy in Interventional MedicineMoi RoksNo ratings yet
- The FACIAL NERVE Current Trends in Diagnosis, Treatment, and RehabilitationDocument17 pagesThe FACIAL NERVE Current Trends in Diagnosis, Treatment, and RehabilitationkrazeedoctorNo ratings yet
- Treatment - of - Perioral - Dystonia - With - Botu20160214 25964 1k8rnph With Cover Page v2Document7 pagesTreatment - of - Perioral - Dystonia - With - Botu20160214 25964 1k8rnph With Cover Page v2runit nangaliaNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Neuralgia - A Practical GuideDocument12 pagesTrigeminal Neuralgia - A Practical Guide전영우No ratings yet
- Tendinopathy GuidelinesDocument26 pagesTendinopathy GuidelinesArdis CaniNo ratings yet
- 1330 FullDocument5 pages1330 FullMaxend Arselino SilooyNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma Case ReportDocument9 pagesGlaucoma Case Reportsuci caraswatiNo ratings yet
- 1 Septic CST Dr. PutriDocument4 pages1 Septic CST Dr. Putriرغد القرنيNo ratings yet
- Small Fiber Neuropathy and Related Syndromes: Pain and NeurodegenerationFrom EverandSmall Fiber Neuropathy and Related Syndromes: Pain and NeurodegenerationSung-Tsang HsiehNo ratings yet
- HIFU Beginner PDFDocument56 pagesHIFU Beginner PDFWaelNo ratings yet
- Benefir PackageDocument115 pagesBenefir PackageSourav KumarNo ratings yet
- Operating Room Technique Write Up PAPA SLRCDocument43 pagesOperating Room Technique Write Up PAPA SLRCShane Vlademier ParadoNo ratings yet
- Oral and Maxillofacial Trauma - Fonseca - Primary ManagementDocument7 pagesOral and Maxillofacial Trauma - Fonseca - Primary ManagementyogeshNo ratings yet
- TURBT - Transurethral Resection of Bladder TumorDocument6 pagesTURBT - Transurethral Resection of Bladder TumorDaywalker PedragozaNo ratings yet
- Giant Cell Tumor - CompleteDocument35 pagesGiant Cell Tumor - CompletewildanmalikNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT ON SHOCK (SEPTIC SHOCK) (AutoRecovered) (AutoRecovered)Document17 pagesASSIGNMENT ON SHOCK (SEPTIC SHOCK) (AutoRecovered) (AutoRecovered)SabariNo ratings yet
- 15 Sample Clinical Sciences QuestionsDocument5 pages15 Sample Clinical Sciences QuestionsGizemNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches For Intraabdominal Masses in AdultsDocument6 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment Approaches For Intraabdominal Masses in AdultsMelfi Triani SiskaNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of NeckDocument37 pagesSurgical Anatomy of Neckaishwarya raviNo ratings yet
- Alpha & PH StatDocument46 pagesAlpha & PH Statambitiousamit1No ratings yet
- Aorta Delivers Blood Bladder Lungs Kidney Nephron Renal Vein Returns Blood Skin Ureter UrethraDocument2 pagesAorta Delivers Blood Bladder Lungs Kidney Nephron Renal Vein Returns Blood Skin Ureter UrethraMarc Jeff GabasaNo ratings yet
- كتاب العملي باطنه وجراحهDocument103 pagesكتاب العملي باطنه وجراحهnoranhassanshams0No ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System: Anup PanthiDocument67 pagesGastrointestinal System: Anup PanthiMadhav KhanalNo ratings yet
- 00.docii 2020 Renal - UrogenitalDocument13 pages00.docii 2020 Renal - Urogenitalanderson ndabishakaNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Method of Three Dimensional Technique For The Detection of AmpC Beta-LactamasesDocument7 pagesA Simplified Method of Three Dimensional Technique For The Detection of AmpC Beta-LactamasesInternational Medical PublisherNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument2 pagesEctopic Pregnancyعبد الله الحربيNo ratings yet
- 14 CR Muthia Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma Which Detected in Ascitic Fluid SmearDocument8 pages14 CR Muthia Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma Which Detected in Ascitic Fluid Smearmuttaqin95No ratings yet
- Gow Gates TechniqueDocument3 pagesGow Gates TechniqueAlanNo ratings yet
- Phacoemulsification Made EasyDocument2 pagesPhacoemulsification Made EasymidoNo ratings yet
- Hisham Hussein Mohamed Ahmed - Gynaecomastia Paper Dr. AymanDocument14 pagesHisham Hussein Mohamed Ahmed - Gynaecomastia Paper Dr. Aymanhoremheb1100% (1)
- 5 10.1111@clr.13698Document31 pages5 10.1111@clr.13698josephineNo ratings yet
- DR Daniel Samadi MD PC - Pediatric ENT NJDocument7 pagesDR Daniel Samadi MD PC - Pediatric ENT NJPediatric ENT NJ by Dr Daniel SamadiNo ratings yet
- Surgery of Conotruncal AnomaliesDocument623 pagesSurgery of Conotruncal AnomaliesLyse lilyNo ratings yet
- DefibrillationDocument25 pagesDefibrillationAnisha Bagaria100% (2)
- TABELA NCM MedicamentosDocument240 pagesTABELA NCM MedicamentosNit_suNo ratings yet