Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Coordination Chemistry
Coordination Chemistry
Uploaded by
Kushagra AgrawalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Coordination Chemistry
Coordination Chemistry
Uploaded by
Kushagra AgrawalCopyright:
Available Formats
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions
®
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
COORDINATION CHEMISTRY
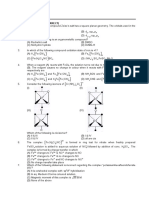
1. Match the electronic configurations in List-I with appropriate metal complex ions in List-II and choose
the correct option. [Atomic Number: Fe = 26, Mn = 25, Co = 27] [JEE(Advanced) 2023]
List-I List-II
(P) t 62g e 0g (1) [Fe(H2O)6]2+
2+
(Q) t 32g e 2g (2) [Mn(H2O)6]
(R) e 2 t 32 (3) [Co(NH3)6]3+
(S) 4
t 2g e 2g (4) [FeCl4]–
(5) [CoCl4]2–
(A) P → 1; Q → 4; R → 2; S → 3 (B) P → 1; Q → 2; R → 4; S → 5
(C) P → 3; Q → 2; R → 5; S → 1 (D) P → 3; Q → 2; R → 4; S → 1
2. The complex(es), which can exhibit the type of isomerism shown by [Pt(NH3)2Br2], is(are)
[en = H2NCH2CH2NH2] [JEE(Advanced) 2023]
(A) [Pt(en)(SCN)2] (B) [Zn(NH3)2Cl2]
(B) [Pt(NH3)2Cl4] (D) [Cr(en)2(H2O)(SO4)]+
3. LIST-I contains metal species and LIST-II contains their properties.
LIST-I LIST-II
4–
(I) [Cr(CN)6] (P) t2g orbitals contain 4 electrons
(II) [RuCl6]
2–
(Q) µ(spin-only) = 4.9 BM
2+
(III) [Cr(H2O)6] (R) low spin complex ion
2+
(IV) [Fe(H2O)6] (S) metal ion in 4+ oxidation state
4
(T) d species
[Given : Atomic number of Cr = 24, Ru = 44, Fe = 26]
Metal each metal species in LIST-I with their properties in LIST-II, and choose the correct option
[JEE(Advanced) 2022]
(A) I → R, T; II → P, S; III → Q, T; IV → P, Q
(B) I → R, S; II → P, T; III → P, Q; IV → Q, T
(C) I → P, R; II → R, S; III → R, T; IV → P, T
(D) I → Q, T; II → S, T; III → P, T; IV → Q, R
4. The calculated spin only magnetic moments of [Cr(NH3)6]3+ and [CuF6]3– in BM, respectively, are
(Atomic numbers of Cr and Cu are 24 and 29, respectively) [JEE(Advanced) 2021]
(A) 3.87 and 2.84 (B) 4.90 and 1.73
(C) 3.87 and 1.73 (D) 4.90 and 2.84
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions ®
5. The total number of possible isomers for [Pt(NH3)4Cl2]Br2 is ______ . [JEE(Advanced) 2021]
6. The pair(s) of complexes wherein both exhibit tetrahedral geometry is(are)
(Note: py = pyridine
Given: Atomic numbers of Fe, Co, Ni and Cu are 26, 27, 28 and 29, respectively)
[JEE(Advanced) 2021]
– 2– – 2–
(A) [FeCl4] and [Fe(CO)4] (B) [Co(CO)4] and [CoCl4]
2–
(C) [Ni(CO)4] and [Ni(CN)4] (D) [Cu(py)4]+ and [Cu(CN)4]3–
7. Choose the correct statement(s) among the following : [JEE(Advanced) 2020]
–
(A) [FeCl4] has tetrahedral geometry.
(B) [Co(en)(NH3)2Cl2]+ has 2 geometrical isomers.
(C) [FeCl4]– has higher spin-only magnetic moment than [Co(en)(NH3)2Cl2]+.
(D) The cobalt ion in [Co(en)(NH3)2Cl2]+ has sp3d2 hybridization.
8. In an experiment, 𝑚 grams of a compound X (gas/liquid/solid) taken in a container is loaded in a balance
as shown in figure I below. In the presence of a magnetic field, the pan with X is either deflected upwards
(figure II), or deflected downwards (figure III), depending on the compound X. Identify the correct
statement(s) [JEE(Advanced) 2020]
(I) (II) (III)
Balanced ; Upward deflection ; Downward deflection ;
Magnetic field absent Magnetic field present Magnetic field present
m X
N S N S
magnet
(A) If X is H2O(l), deflection of the pan is upwards.
(B) If X is K4[Fe(CN)6](s), deflection of the pan is upwards.
(C) If X is O2(g), deflection of the pan is downwards.
(D) If X is C6H6(l), deflection of the pan is downwards.
9. Total number of cis N–Mn–Cl bond angles (that is, Mn–N and Mn–Cl bonds in cis positions) present in a
molecule of cis-[Mn(en)2Cl2] complex is ____ (en = NH2CH2CH2NH2) [JEE(Advanced) 2019]
10. The correct statement(s) regarding the binary transition metal carbonyl compounds is (are)
(Atomic numbers : Fe = 26, Ni = 28) [JEE(Advanced) 2018]
(A) Total number of valence shell electrons at metal centre in Fe(CO)5 or Ni(CO)4 is 16
(B) These are predominantly low spin in nature
(C) Metal - carbon bond strengthens when the oxidation state of the metal is lowered
(D) The carbonyl C–O bond weakens when the oxidation state of the metal is increased
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions
®
11. Among the species given below, the total number of diamagnetic species is____.
–
H atom, NO2 monomer, O2 (superoxide), dimeric sulphur in vapour phase,
Mn3O4, (NH4)2[FeCl4], (NH4)2[NiCl4], K2MnO4, K2CrO4 [JEE(Advanced) 2018]
3+
12. The correct option(s) regarding the complex [Co(en) (NH3)3(H2O)] :-
(en = H2NCH2CH2NH2) is (are) [JEE(Advanced) 2018]
(A) It has two geometrical isomers
(B) It will have three geometrical isomers if bidentate 'en' is replaced by two cyanide ligands
(C) It is paramagnetic
3+
(D) It absorbs light at longer wavelength as compared to [Co(en) (NH3)4]
13. Match each set of hybrid orbitals from LIST-I with complex (es) given in LIST-II.
LIST-I LIST-II
2
P. dsp 1. [FeF6]4–
3
Q. sp 2. [Ti(H2O)3Cl3]
R. sp3d2 3. [Cr(NH3)6]3+
S. d2sp3 4. [FeCl4]2–
5. Ni(CO)4
6. [Ni(CN)4]2–
The correct option is [JEE(Advanced) 2018]
(A) P → 5; Q → 4,6; R → 2,3; S → 1 (B) P → 5,6; Q → 4; R → 3; S → 1,2
(C) P → 6; Q → 4,5; R → 1; S → 2,3 (D) P → 4,6; Q → 5,6; R → 1,2; S → 3
14. Addition of excess aqueous ammonia to a pink coloured aqueous solution of MCl2. 6H2O (X) and NH4Cl
gives an octahedral complex Y in the presence of air. In aqueous solution, complex Y behaves as 1 : 3
electrolyte. The reaction of X with excess HCl at room temperature results in the formation of a blue
coloured complex Z. The calculated spin only magnetic moment of X and Z is 3.87 B.M., whereas it is
zero for complex Y.
Among the following options, which statements is(are) correct ? [JEE(Advanced) 2017]
2 3
(A) The hybridization of the central metal ion in Y is d sp
(B) Z is tetrahedral complex
(C) Addition of silver nitrate to Y gives only two equivalents of silver chloride
(D) When X and Z are in equilibrium at 0°C, the colour of the solution is pink
– –
15. The number of geometric isomers possible for the complex [CoL2Cl2] (L = H2NCH2CH2O ) is
[JEE(Advanced) 2016]
2+ 2+ 2+
16. The geometries of the ammonia complexes of Ni , Pt and Zn , respectively , are :
[JEE(Advanced) 2016]
(A) octahedral, square planar and tetrahederal
(B) square planar, octahederal and tetrahederal
(C) tetrahederal, square planar and octahederal
(D) octahederal , tetrahederal and square planar
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions ®
3+ – –
17. For the octahedral complexes of Fe in SCN (thiocyanato-S) and in CN ligand environments, the
difference between the spin only magnetic moments in Bohr magnetons (when approximated to the
nearest integer) is
[Atomic number of Fe = 26] [JEE(Advanced) 2015]
18. The correct statement(s) about Cr2+ and Mn3+ is (are)
[Atomic numbers of Cr = 24 and Mn = 25] [JEE(Advanced) 2015]
(A) Cr2+ is a reducing agent
(B) Mn3+ is an oxidizing agent
(C) Both Cr2+ and Mn3+ exhibit d4 electronic configuration
(D) When Cr2+ is used as a reducing agent, the chromium ion attains d5 electronic configuration
19. In the complex acetylbromidodicarbonylbis(triethylphosphine)iron(II), the number of Fe–C bond(s) is-
[JEE(Advanced) 2015]
20. Among the complex ions, [Co(NH2-CH2-CH2-NH2)2Cl2] , [CrCl2(C2O4)2]3–, [Fe(H2O)4(OH)2]+,
+
[Fe(NH3)2(CN)4]–, [Co(NH2-CH2-CH2-NH2)2(NH3)Cl]2+ and [Co(NH3)4(H2O)Cl]2+, the number of
complex ion(s) that show(s) cis-trans isomerism is - [JEE(Advanced) 2015]
21. A list of species having the formula XZ4 is given below :
XeF4, SF4, SiF4, BF4 , BrF4 , [Cu(NH3)4]2+, [FeCl4]2–, [CoCl4]2– and [PtCl4]2–.
– –
Defining shape on the basis of the location of X and Z atoms, the total number of species having a square
planar shape is [JEE(Advanced) 2014]
22. Match each coordination compound in List-I with an appropriate pair of characteristics from List-II and
select the correct answer using the code given below the lists.
{en = H2NCH2CH2NH2 ' atomic numbers ; Ti = 22 ; Cr = 24 ; Co = 27 ; Pt = 78}
[JEE(Advanced) 2014]
List-I List-II
(P) [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]Cl (1) Paramagnetic and exhibits ionisation isomerism
(Q) [Ti(H2O)5Cl](NO3)2 (2) Diamagnetic and exhibits cis-trans isomerism
(R) [Pt(en)(NH3)Cl]NO3 (3) Paramagnetic and exhibits cis-trans isomerism
(S) [Co(NH3)4(NO3)2]NO3 (4) Diamagnetic and exhibits ionisation isomerism
Code :
P Q R S
(A) 4 2 3 1
(B) 3 1 4 2
(C) 2 1 3 4
(D) 1 3 4 2
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions
®
SOLUTIONS
1. Ans. (D)
II
Sol. 1. [Fe(H 2O)6 ]+2
WFL
eg
6
configuration 3d
t2g
t2g4 eg2(S)
II
2. [Mn(H 2O)6 ]+2
WFL
eg
configuration 3d5
t2g
t2g3 eg2(Q)
III
3. [Co(NH3 )6 ]+3
SFL
eg
configuration 3d6
t2g
t2g6 eg0(P)
III
4. [Fe Cl4 ]Θ
WFL
t2
configuration 3d5
e
e 2
t23(R)
II
5. [Co Cl4 ]–2
WFL
t2
configuration 3d7
e
4 3
e t2 (None)
2. Ans. (C, D)
+2
Sol. [Pt(NH3 ) 2 Br2 ]
Hybridisation : dsp2 , geometry : square planar
Br NH 3 Br NH 3
II II
Pt Pt
Br NH 3 NH 3 Br
cis trans
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions ®
(A) [Pt(en)(SCN)2] : square planar, cis–trans not possible
(B) [Zn(NH3)2Cl2] : tetrahedral, cis–trans not possible
(C) [Pt(NH3)2Cl4] : octahedral, cis–trans possible
Cl NH 3
Cl NH 3 Cl Cl
IV IV
Pt Pt
Cl NH 3 Cl Cl
Cl NH 3
cis trans
(D) [Cr(en)2(H2O)SO4]+ : Octahedral
H2 O
III
en Cr en
SO4
trans
3. Ans. (A)
4–
Sol. (1) [Cr(CN)6]
+2 4 0
Cr = [Ar]18 3d 4s ; low spin complex
P,R,T
(2) [RuCl6]2–
+4 4 0
Ru = [Kr]364d 5s ; low spin complex
P,R,S,T
(3) [Cr(H2O)6]2+
Cr+2 = [Ar]183d44s0 ; high spin complex
Q,T
(4) [Fe(H2O)6]2+
Fe+2 = [Ar]183d6 ; High spin complex
P,Q
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions
®
4. Ans. (A)
Sol. [Cr(NH3)6]3+
⇒ [Ar]3d
3+ 3
Cr
In presence of NH3 ligand eg
t2g
Number of unpaired electrons = 3
=µ n ( n + 2 ) B.M.
=µ 3 ( 3 + 2 ) B.M.
µ = 15 B.M.
⇒ 3.87 B.M.
[CuF6]3–
Cu3+ ⇒ [Ar]3d8
In presence of F– Ligand
Cu3+ ⇒ eg
t2g
Number of unpaired electrons = 2
=µ n ( n + 2 ) B.M.
=µ 2 ( 2 + 2 ) ⇒ 8 B.M. ⇒ 2.84 B.M
5. Ans. (6)
Sol. Isomers
(I) [Pt (NH3)4 Cl2]Br2 ⇒ G.I. = 2
(II) [Pt (NH3)4 Br2] Cl2 ⇒ G.I. = 2
(III) [Pt (NH3)4 BrCl] Br.Cl ⇒ G.I. = 2
I, II, III are ionisation isomers of each other, each having 2 geometrical isomers.
Total possible isomers will be 6
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions ®
6. Ans. (A, B, D)
Sol. (A)
–
[FeCl4]
Fe [Ar] 3d64s2
+3
Fe [Ar] 3d54s0
–
Cl is W.F.L. and does not pair up the unpaired electron of central metal atom.
3d 4s 4p
3+ 5 –
∴ Fe (d ) in[FeCl4]
sp3
2– Tetrahedral
[Fe(CO)4]
6 2
Fe [Ar] 3d 4s
2– 8 2
Fe [Ar] 3d 4s 3d 4s 4p
2– 10 2–
∴ Fe (d ) in [Fe(CO)4]
sp3
Tetrahedral
(B)
–
[Co(CO)4]
7 2
Co [Ar] 3d 4s
8 2
Co–1 [Ar] 3d 4s 4s 4p
∴ Co (d ) in [Co(CO)4]
– 10 –
sp3
2–
[CoCl4] Tetrahedral
7 2
Co [Ar] 3d 4s
7
Co+2 [Ar] 3d 4s0
Cl– is W.F.L. and does not pair up the unpaired electron of central metal atom.
4s 4p
∴ Co2+ (d7) in [CoCl4]2–
sp3
Tetrahedral
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions
®
(C)
[Ni(CO)4]
8 2
Ni [Ar] 3d 4s
0 8 2
Ni [Ar] 3d 4s
4s 4p
∴ Ni (d10) in [Ni(CO)4]
sp3
Tetrahedral
[Ni(CN)4]2–
8 2
Ni [Ar] 3d 4s
Ni+2 [Ar] 3d84s0
CN– is S.F.L. and pair up the unpaired electron of central metal atom.
4s 4p
∴ Ni (d8) in [Ni(CN)4]2–
dsp2
Square planar
(D) [Cu(py)4]
Cu [Ar] 3d104s1
Cu+1 [Ar] 3d104s0
4s 4p
∴Cu (d ) in [Cu(py)4]
+1 10 +
sp3
Tetrahedral
[Cu(CN)4]3
Cu [Ar] 3d104s1
Cu+1 [Ar] 3d104s0
CN– is S.F.L. and pair up the unpaired electron of central metal atom.
4s 4p
∴ Cu (d ) in [Cu(CN)4]
+1 10 3–
sp3
Tetrahedral
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions ®
7. Ans. (A, C)
Sol.
(A) [FeCl4]–
't2'
∆t < P
3+
Fe : [Ar]3d5
'e'
– 3
[FeCl4] is sp hybridised and has tetrahedral geometry with 5 unpaired electrons.
+
(B) [Co(en)(NH3)2Cl2] has three geometrical isomers.
NH3 NH3
Cl–
H2N Cl– H2N NH3 NH3
H2N
H2C H2C H2C
Co3+ Co3+ Co3+
H2C H2C
Cl– H2C
H2N H2N Cl– H2N NH3
–
NH3 Cl Cl–
–
(C) [FeCl4]
't2'
∆t < P
3+
Fe : [Ar]3d5
'e'
Number of unpaired electrons (n) = 5
Spin only magnetic moment = n(n + 2) B.M.
= 5.92 B.M.
+
[Co(en)(NH3)2Cl2]
'eg'
Co
3+
: [Ar]3d6 ∆O > P
't2g'
Number of unpaired electrons (n) = 0
Spin only magnetic moment = n(n + 2) B.M. = 0
10
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions
®
+
(D) [Co(en)(NH3)2Cl2]
'eg'
Co3+ : [Ar]3d6 ∆O > P
't2g'
[Co(en)(NH3)2Cl2]+ is d2sp3 hybridised and has octahedral geometry with 0 unpaired electron.
8. Ans. (A, B, C)
Sol. Paramagnetic compound (X) are attracted towards magnetic field and the pan is deflected downwards.
While the Diamagnetic compound (X) are repelled by magnetic field and pan is deflected upward.
(A) X ⇒ H2O → Diamagnetic (correct)
(B) X ⇒ K4[Fe(CN)6](s) → Diamagnetic (correct)
Here Fe2+ + Strong field ligand → 3d6 ⇒ [t2g6, eg0]
(C) X ⇒ O2 → Paramagnetic (correct)
Here O2(g) is paramagnetic due to two-unpaired electrons present in π* (antibonding orbitals).
(D) X ⇒ C6H6 () → Diamagnetic (Incorrect)
It is due to presence of 0 unpaired electrons.
9. Ans. (6.00)
cis[M(en) 2Cl 2
Sol.
N (1)
Cl N(2) Cl(a)— Mn — N (1)
(a)
Cl(a)— Mn — N (2)
Mn Cl(a)— Mn — N(4)
Cl(b)— Mn — N(1)
Cl (b) N(3) Cl(b)— Mn — N(3)
N(4) Cl(b)— Mn — N (4)
Number of cis (Cl—Mn—N) = 6
10. Ans. (B, C)
Sol. (A) [Fe(CO5)] & [Ni(CO)4] complexes have 18-electrons in their valence shell.
(B) Carbonyl complexes are predominantly low spin complexes due to strong ligand field.
(C) As electron density increases on metals (with lowering oxidation state on metals), the extent of
synergic bonding increases. Hence M–C bond strength increases
(D) While positive charge on metals increases and the extent of synergic bond decreases and hence C–O
bond becomes stronger.
11
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions ®
11. Ans. (1)
Sol.
* H-atom = Paramagnetic
1
1s
* NO2 = N odd electron species Paramagnetic
O O
O2 (superoxide) = One unpaired electrons in π* M.O.
–
* Paramagnetic
S2 (in vapour phase) = same as O2, two unpaired e s are present in π* M.O.
–
* Paramagnetic
+2 +4
* Mn3O4 = 2 MnO . MnO 2 Paramagnetic
* (NH4)2[FeCl4] = Fe+2 = 3d6 4s0
Cl Cl Cl Cl Paramagnetic
sp3- hybridisation
* (NH4)2 [NiCl4] = Ni = 3d8 4s2
+2
Ni = 3d8 4s0
Cl Cl Cl Cl Paramagnetic
3
sp - hybridisation
O–
* K2MnO4 = 2K+ Mn Paramagnetic
, Mn+6 = [Ar] 3d1
O O–
O
O
* K2CrO4 = 2K+ Cr – , Cr+6 = [Ar] 3d0 Diamagnetic
O –
O
O
12. Ans. (A, B, D)
+3
Sol. (A) [Co(en)(NH3)3(H2O)] complex is type of [M(AA)b3c] have two G.I.
b b
A b A b
M M
A b A c
c b
12
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions
®
(B) If (en) is replaced by two cynide ligand, complex will be type of [Ma3b2c] and have 3 G.I.
c c c
a a a b a b
M M M
a b a b b a
b a a
(C) [Co(en)(NH3)3(H2O)]3+ have d6 configuration (t62g) on central metal with SFL therefore it is
dimagnetic in nature.
(D) Complex [Co(en)(NH3)3(H2O)]3+ have lesser CFSE (∆O) value than [Co(en)(NH3)4]3+ therefore
complex [Co(en)(NH3)3(H2O)]+ absorbs longer wavelength for d–d transition.
13. Ans. (C)
4–
Sol. [1] [FeF6]
3d 4s 4p 4d
2+ 6
Fe = [Ar]3d , Fe+2 :
Hyb : sp3d 2
[2] [Ti (H2O)3Cl3]
3d 4s 4p
+3 1
Ti = [Ar]3d , Ti+3 :
Hyb : d 2 sp3
[3] [Cr(NH3)6]3+
3d 4s 4p
+3 3 +3
Cr = [Ar]3d , Cr :
Hyb : d2 sp3
[4] [FeCl4]2–
3d 4s 4p
2+ 6 +2
Fe = [Ar]3d , Fe :
Hyb : sp3
[5] [Ni(CO)4]
Ni : 3d8 4s2 3d 4s 4p
Ni :
13
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions ®
Back pairing of electrons due to presence of strong field ligand
3d 4s 4p
Ni :
Hyb. : sp3
2–
[6] [Ni (CN)4]
4s 4p
Ni2+ : 3d8 2+
Ni :
Electron pairing take place due to presence of S.F.L.
4s 4p
2+
Ni :
Hyb. : dsp2
14. Ans. (A, B, D)
II III
Sol. Excess NH4OH/NH4Cl
[Co(H2O)6]Cl2 Air/O2
[Co(NH3)6]Cl3
Pink (X) (Y)
2+ – 2–
[Co(H2O)6] + 4Cl [CoCl4]
(X) (excess) (Z) blue c
2 3
(A) Hybridisation of (Y) is d sp as NH3 is strong field ligand
2– 3 –
(B) [CoCl4] have sp hybridisation as Cl is weak field ligand
III
(C) [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 + 3AgNO3(aq.) → 3AgCl
(Y)
[Co(H 2 O)6 ]2 + + 4Cl –
(D) [CoCl 4 ]2 − + 6H 2 O ∆H = (–)ve (exothermic)
(Blue) (Pink)
When ice is added to the solution the equilibrium shifts right hence pink colour will remain predominant
So, correct answer is (A ,B & D)
15. Ans. (5)
Sol. [CoL2Cl2]– (L = H2NCH2CH2O–)
[Co(H2NCH2CH2O)2 Cl2]
↓
It is [M(AB)2C2] type of complex
A A B
C B C B C A
M M M
C A C B C A
B , A , B
C C
A A A B
M and M
B B B A
C C
Total geometrical isomers = 5
14
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions
®
16. Ans. (A)
Sol. Metal ion Complex with NH3 Geometry
2+ 2+
Ni [Ni(NH3)6] Octahedral
2+ 2+
Pt [Pt(NH3)4] Square planar
2+ 2+
Zn [Zn(NH3)4] Tetrahedral
So, option (A) is correct.
17. Ans. (4)
3– 3–
Sol. [Fe(CN)6] [Fe(SCN)6]
Fe+3 = 3d5 Fe+3 = 3d5
C N is S.F.L SCN is W.F.L
∆0 > P ∆0 < P
µ= n(n + 2) B.M. µ= n(n + 2) B.M.
n = number of unpaired electron = 1 n = number of unpaired electron = 5
µ = 1.73 B.M. µ = 5.92 B.M.
difference = 5.92 – 1.73 = 4.19
Ans. ≈ 4
18. Ans. (A, B, C)
+2
Sol. (A) Cr is a reducing agent : CORRECT STATEMENT
+2
Cr is a reducing agent as its configuration changes from d4 to d3 and Cr+3 having a half filled t2g level in
presence of H2O
Cr+2 → Cr+3 + e¯
3d44sº 3
3d 4sº
(B) Mn+3 is a oxidizing agent : CORRECT STATEMENT
The change from Mn+3 to Mn+2 results in the half filled (d5) configuration which has extra stability
+ e¯
Mn
+3
→ Mn+2
3d44sº 3d54sº
[extra stable half filled (d5) configuration]
(C) Both Cr+2 and Mn+3 exhibit d4 electronic configuration : CORRECT STATEMENT
Cr+2 → 3d44sº
Mn+3 → 3d44sº
(D) When Cr+2 is used as reducing agent chromium ion attain d5 electronic configuration : INCORECT
Cr+2 → Cr+3 + e¯
3d44sº 3d34sº
Reducing agent It attain d3 electronic configuration
15
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
JEE Advanced Chemistry 10 Years Topicwise Questions with Solutions ®
19. Ans. (3)
Sol. Structure of complex
º
O C2H5
Br C P C2H5
(1) C2H5
Fe (II)
O (3) (2) C2H5
C C P C2H5
CH3 C2H5
O
Total number of Fe–C bonds are 3
20. Ans. (6)
Sol. Total number of complex ions which show cis-trans isomerism
Complex ion Complex type Isomers
+
[Co(NH2–CH2–CH2–NH2)2Cl2] [M(AA)2b2] 1 cis + 1 trans
3–
[CrCl2(C2O4)2] [M(AA)2b2] 1 cis + 1 trans
[Fe(H2O)4(OH)2]+ [Ma4b2] 1 cis + 1 trans
[Fe(NH3)2(CN)4]¯ [Ma4b2] 1 cis + 1 trans
[Co(NH2–CH2–CH2–NH2)2(NH3)Cl]+2 [M(AA)2bc] 1 cis + 1 trans
+2
[Co(NH3)4(H2O)Cl] [Ma4bc] 1 cis + 1 trans
All six complex ions show cis-trans isomerism
21. Ans. (4)
Sol. XeF4, BrF4 , [Cu(NH3)4]2+ , [PtCl4]2– are square planar
–
SF4 – Sea saw
SiF4 , BF4 , [FeCl4]2–, [CoCl4]2– are tetrahedral
–
22. Ans. (B)
Sol. (P) [CrIII(NH3)4Cl2]Cl : (1) Complex given in (P) is Paramagnetic & show two geometrical
(3 unpaired electrons) isomerism (cis and trans) (does not show ionization isomer)
(Q) [TiIII(H2O)5Cl](NO3)2 (2) Complex given in (Q) is paramagnetic show ionization isomerism
(1 unpaired electrons)
(R) [PtII(en)(NH3)Cl]NO3 (3) Complex given in (R) is diamagnetic and show ionization
(1 unpaired electrons) isomerism
(S) [CoIII(NH3)4(NO3)2]NO3 (4) Complex given in (S) is diamagnetic does not show ionization
(0 unpaired electrons) isomerism show geometrical isomerism
16
For More Material Join: @JEEAdvanced_2024
You might also like
- Quiz - Coordination Compounds PDFDocument2 pagesQuiz - Coordination Compounds PDFAman JaiswalNo ratings yet
- UT - 08 Advanced Paper - 1 Practice Paper - Chemistry MetallurgyDocument5 pagesUT - 08 Advanced Paper - 1 Practice Paper - Chemistry Metallurgyshreshthagupta2111No ratings yet
- Guided Revision Plan-Score AdvancedDocument5 pagesGuided Revision Plan-Score AdvancedPratham PatelNo ratings yet
- DPP5 COR1 Advanced-20Document10 pagesDPP5 COR1 Advanced-20tikam chandNo ratings yet
- DPP - 03 - Coordination CompoundDocument4 pagesDPP - 03 - Coordination CompoundPHANINDRA MNo ratings yet
- C Ch-18 Co-Ordination CompoundsDocument7 pagesC Ch-18 Co-Ordination Compoundsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- 003 ????? Coordination Compounds DPP 04 of Lecture 07 LakDocument3 pages003 ????? Coordination Compounds DPP 04 of Lecture 07 LakStockPlusIndiaNo ratings yet
- Tranisition Elements-03 - Assignments (New)Document13 pagesTranisition Elements-03 - Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- D and F Block Elements - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGoDocument13 pagesD and F Block Elements - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGobaklesneha125No ratings yet
- Coordination Compound-1Document38 pagesCoordination Compound-1Sambhav SinghalNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds Ex Ii 1632118773652Document8 pagesCoordination Compounds Ex Ii 1632118773652Abhijeet0% (1)
- DPP 05Document17 pagesDPP 051234dvsvNo ratings yet
- Diwali Assignment INORGANIC 12thDocument12 pagesDiwali Assignment INORGANIC 12thRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- GUJCET - D22 Mar 2024Document17 pagesGUJCET - D22 Mar 2024aadityabhagchandaniNo ratings yet
- DPP - Coordination ChemistryDocument8 pagesDPP - Coordination ChemistryHarishNo ratings yet
- The D-F-Block ElementsDocument49 pagesThe D-F-Block Elementsdevansh dewanNo ratings yet
- M-Caps-27: Chemistry: NEET & AIIMS 2018-19Document5 pagesM-Caps-27: Chemistry: NEET & AIIMS 2018-19Vishal SinghNo ratings yet
- Senior - 2020 - Class - 12 - Chemistry - Objective Questions - Coordination CompoundsDocument4 pagesSenior - 2020 - Class - 12 - Chemistry - Objective Questions - Coordination CompoundsJijendarNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry - Practice Sheet - Lakshya JEE 2024Document4 pagesCoordination Chemistry - Practice Sheet - Lakshya JEE 2024Vedant JainNo ratings yet
- 11 April 23 Evening Chem EnglishDocument14 pages11 April 23 Evening Chem EnglishHaina KumariNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundDocument19 pagesCoordination CompoundJatindra PatelNo ratings yet
- Tejas Prayas JEE (2024) : Coordination CompoundDocument4 pagesTejas Prayas JEE (2024) : Coordination Compoundshubharambh665No ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2018 Paper - 1 Question With Solution - ChemistryDocument13 pagesJEE Advanced 2018 Paper - 1 Question With Solution - ChemistrySanju PatelNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds-T-4Document3 pagesCoordination Compounds-T-4sharavaravindNo ratings yet
- Yakeen NEET 2.0 (Legend) : Chemistry Coordination CompoundsDocument3 pagesYakeen NEET 2.0 (Legend) : Chemistry Coordination CompoundsJagaηηath ΚabiNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsRESONANCE APSPDocument34 pagesCoordination CompoundsRESONANCE APSPGOURISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Topic TestDocument3 pagesChemistry Topic TestSri Dattagiri Maharaj Education SocietyNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordination Compound Ex-4 Solution For Vedantu TatvaDocument9 pagesCo-Ordination Compound Ex-4 Solution For Vedantu TatvaAbhinav ThapliyalNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds Final RevisionDocument3 pagesCoordination Compounds Final RevisionROWA new year CelebrationNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Online Exam 2019: Questions & Solutions (Memory Based)Document5 pagesJEE Main Online Exam 2019: Questions & Solutions (Memory Based)Ihtisham Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- 21.coordination Compound, D & F Block Transition ElementsDocument21 pages21.coordination Compound, D & F Block Transition ElementsQwerty100% (1)
- Coordination MCQDocument11 pagesCoordination MCQMohammad Khaier KaliliNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Kit (Chemistry-200 L) -Vol. 2 - 看图王 PDFDocument60 pagesTutorial Kit (Chemistry-200 L) -Vol. 2 - 看图王 PDFAijin JiangNo ratings yet
- C - Ch-03 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument4 pagesC - Ch-03 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structuremysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- D and F Block and CoordinationDocument2 pagesD and F Block and Coordinationneeravgoyal06No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument25 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructurehadhivkdNo ratings yet
- 02 - Coordination CompoundsDocument8 pages02 - Coordination CompoundsNithin KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- BG C494 VWKC M4 JZ 4 Er LCBDocument17 pagesBG C494 VWKC M4 JZ 4 Er LCBpinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Online Exam 2019: (Memory Based Paper)Document6 pagesJEE Main Online Exam 2019: (Memory Based Paper)Deepak SainiNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions - Chapter 25Document7 pagesSample Questions - Chapter 25Rasel Islam100% (2)
- Inorganic 2Document10 pagesInorganic 2jitesh100kushwahaNo ratings yet
- 19.coordination Compounds - WatermarkDocument29 pages19.coordination Compounds - WatermarkMayank GoelNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Coordination SolutionDocument12 pagesUnit 5 Coordination Solutionsuryansh.yt9641No ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds (Exercise+Answers)Document32 pagesCoordination Compounds (Exercise+Answers)Hanukkah100% (1)
- JEE Main CHEMISTRY 2024 Question Papers With Answer Key PDFDocument5 pagesJEE Main CHEMISTRY 2024 Question Papers With Answer Key PDFnetraynahar2006No ratings yet
- LPP-Transition Elements and Coordination Compounds: Te Te Te EtDocument4 pagesLPP-Transition Elements and Coordination Compounds: Te Te Te EtYash TandonNo ratings yet
- Cordination Compounds DPP 4Document3 pagesCordination Compounds DPP 4yash agarwalNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsDocument10 pagesCoordination Compoundsyogesh khandlaNo ratings yet
- Institute Test PDF ReportDocument8 pagesInstitute Test PDF ReportIshan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Co-Ordination CompoundsDocument2 pagesAssignment On Co-Ordination CompoundsMayank MundadaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry AssignmentDocument11 pagesInorganic Chemistry AssignmentK VIKASNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsDocument18 pagesCoordination CompoundsAksa Merlin ThomasNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compound Level-0 Part IDocument3 pagesCoordination Compound Level-0 Part IAnumuskan KashyapNo ratings yet
- Che Neet 3Document5 pagesChe Neet 3pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Co OrdinateDocument72 pagesCo OrdinateMotivational BabaNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compound 2Document2 pagesCoordination Compound 2ngpresidntNo ratings yet
- Test - D18 Dec 2022Document9 pagesTest - D18 Dec 2022PrinceNo ratings yet
- 6 Cordination Compoundc PDFDocument19 pages6 Cordination Compoundc PDFbruhaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-Coordination CompoundsDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank-Coordination CompoundsMohamed zidan khanNo ratings yet
- Main Group Metal Coordination Polymers: Structures and NanostructuresFrom EverandMain Group Metal Coordination Polymers: Structures and NanostructuresNo ratings yet
- Adv Funct Materials - 2021 - Collins - Scaffold Fabrication Technologies and Structure Function Properties in Bone TissueDocument23 pagesAdv Funct Materials - 2021 - Collins - Scaffold Fabrication Technologies and Structure Function Properties in Bone TissueIsworo RukmiNo ratings yet
- ISO 8573 - Parte 2Document52 pagesISO 8573 - Parte 2caio vinicius da silva vieira100% (1)
- Chapter Twenty OneDocument17 pagesChapter Twenty Oneabdullaammar090No ratings yet
- Blasting & Painting Inspection Report Format For Bottom Plate 01Document7 pagesBlasting & Painting Inspection Report Format For Bottom Plate 01ABEC Trombay siteNo ratings yet
- CHE4613LAB7Document6 pagesCHE4613LAB7Huda AlkhouriNo ratings yet
- Self Compacting ConcreteDocument46 pagesSelf Compacting ConcreteJeet Pawar80% (5)
- Chapter 4 ADocument39 pagesChapter 4 AnajwaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Transport in Cells MSDocument17 pages1.3 Transport in Cells MSMethyl OrangeNo ratings yet
- Mineral Preservatives in The Wood of Stradivari and GuarneriDocument9 pagesMineral Preservatives in The Wood of Stradivari and Guarneriponbohacop100% (1)
- Class - XII Periodic Test - II Portions - 2023 - 24Document2 pagesClass - XII Periodic Test - II Portions - 2023 - 24Adithya SNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Process Safety Formula of Chemical Compounds Name Ammonia Ammonium HydroxideDocument7 pages4.1 Process Safety Formula of Chemical Compounds Name Ammonia Ammonium Hydroxideİlkin İbrahimliNo ratings yet
- Advanced Technologies For Ammonia Plants - CASALE GROUPDocument83 pagesAdvanced Technologies For Ammonia Plants - CASALE GROUPWael MansourNo ratings yet
- 2 Assay Techniques in Clinical Chemistry-Supplemental MateriDocument7 pages2 Assay Techniques in Clinical Chemistry-Supplemental MateriIbnul Islam Abdellah100% (1)
- HV-EHV Cables Synthetic Isolation DegassingDocument16 pagesHV-EHV Cables Synthetic Isolation DegassingAmina Malek AyaNo ratings yet
- Typical Sections - Editable (Autosaved)Document157 pagesTypical Sections - Editable (Autosaved)sandeepNo ratings yet
- 氯化聚丙烯 MSDSDocument5 pages氯化聚丙烯 MSDSThảo ThuNo ratings yet
- Nullifire SC902 - Safety Data Sheet Part B V9.0Document9 pagesNullifire SC902 - Safety Data Sheet Part B V9.0ANIBAL LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Organic Nomenclature Bank 1Document18 pagesOrganic Nomenclature Bank 1talaaty599No ratings yet
- 3.6 Revision Guide Organic Analysis AqaDocument3 pages3.6 Revision Guide Organic Analysis Aqashafiqur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Fitri BHPDocument3 pagesFitri BHPekadwiyantiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lab ReportDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Lab ReportJabin Sta. TeresaNo ratings yet
- STULZ CyberAir DX IOM OCS0135Document55 pagesSTULZ CyberAir DX IOM OCS0135Bùi LinhNo ratings yet
- Membrane Separations-1408Document62 pagesMembrane Separations-1408shashwatNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat Zenith: Gol - AntibiotikaDocument3 pagesDaftar Obat Zenith: Gol - AntibiotikaNetriNo ratings yet
- Avantor Chemical Price List 2019-2020-RANKEMDocument84 pagesAvantor Chemical Price List 2019-2020-RANKEMVikki PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 TEST BANK Chapter 7 TEST BANKDocument61 pagesChapter 7 TEST BANK Chapter 7 TEST BANKangelineNo ratings yet
- Pitting Corrosion of MetalsDocument6 pagesPitting Corrosion of MetalsRahamat ShaikNo ratings yet
- Iso 20558 2 2018 PDFDocument9 pagesIso 20558 2 2018 PDFlartaNo ratings yet
- KR10150 Rev02Document2 pagesKR10150 Rev02KOUAME EDYMAIN FRANCISNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: R Cell RDocument15 pagesElectrochemistry: R Cell RSsNo ratings yet