Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LP P3 W15 by Sheraz 6th - 10 TH Nov 2023
LP P3 W15 by Sheraz 6th - 10 TH Nov 2023
Uploaded by
sheraz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesOriginal Title
LP P3 W15 by Sheraz 6th -10 th Nov 2023
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesLP P3 W15 by Sheraz 6th - 10 TH Nov 2023
LP P3 W15 by Sheraz 6th - 10 TH Nov 2023
Uploaded by
sherazCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
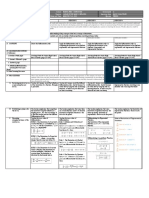
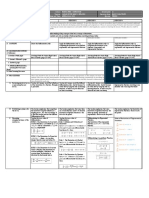
The Science School - LESSON PLAN Teacher Name Mr.
Sheraz Shafique
Subject Pure Maths 3 Class A2 Number of blocks per week 5 Date 6 – 10th Nov, 2023
th
Topic Differential Equations Sub Topic Integration as a reverse of Differentiation
Target Understands and uses different laws of integration to solve problems
Criteria To be able to use integration to find the integrals of various functions
Correct use of the method, Correct steps and sequence, Answer accuracy
Objectives Actions of the pupils and the teacher in the lesson Vocabulary Assessment Tasks Time Resources Homework
(formal/informal)
Things to understand: Prior Knowledge: Teacher will start by asking questions from the Differential The students will be assessed Pure Given in
pupils related to the concepts of Integration from previous chapter equation on their ability to demonstrate 5X40= Mathemati Table
What is the power rule of integration? their understanding of 200 cs 3 by
What is a differential Integration and How to
What is the usage of integration in daily life? minut Sue
equation? formulate a simple es Pemberto
How can you find the equation of curve with the help of
statement involving a n and
What is the difference integration?
rate of change as a Topical
Class Activity: differential equation
between a general and
After assessing the prior knowledge of the students about
a particular solution of the general rules of integration and building on that find by integration, a
a differential equation? concept, the pupils will be asked to describe some rules to general form of
solve a differential equation and will explore examples 10.1 solution for a first
What is the technique and 10.2. order differential
of separating the Action of Pupils: equation in which the
variables are
variables in differential After performing the activities the students will apply the
separable
equations? acquired concepts to solve the examples from the textbook
using the rules of integration and answer the following use an initial condition
What is the method to to find a particular
form a differential questions; solution
equation from a interpret the solution of
How to use differentiation to find the integration of
problem different expressions a differential equation
How to use the natural log to find the integration of in the context of a
a function with its derivative in the numerator problem being
Things to do: How to use the substitution method to find the modelled by the
formulate a simple integration equation
statement involving a How to use of partial fractions in integration
rate of change as a How to use the integration by parts to find the area Informal Assessment
differential equation
under the curve Prior Knowledge
find by integration, a Investigation: Investigate the applications of Integration as an Class Discussion
general form of solution anti of derivatives to find the equation of curve.
for a first order dy/dx = 2x + 3, etc.
differential equation in Formal Assessment
Examples:
which the variables are (Classwork)
separable Pupils will do examples from the book
Days Topic Classwork Homework
Monday Chapter 10 Examples Ex 10A Q1 to
10.1, Exp 10.2 Q4
and Exp 10.3
Tuesday Chapter 10 Ex 10A Q 5 to Ex 5B Q1 to
Q10 Q3
Wednesday Chapter 10 Exp 10.4 to Ex 10A Q11
Exp 10.6 to Q15D Q1
to Q5
use an initial condition
to find a particular Thursday Chapter 10 Ex 10B Q 4 to Ex 5D
solution Q8
Friday Ex 10B full
interpret the solution of exercise
a differential equation
in the context of a Feedback from Students: (question-answer session from the
problem being pupils to verbally assess their understanding)
modelled by the Students will participate in the class discussions and once there is
equation no ambiguity, they will follow the instructions and do the written
task on their work- books
One-on-one support/feedback will be given on spot-checking of
written task
Conclusion:
Students will summarize all the key points used to
Formulate a simple statement involving a rate of change
as a differential equation
find by integration, a general form of solution for a first
order differential equation in which the variables are
separable
find a particular solution by using an initial condition
interpret the solution of a differential equation in the
context of a problem being modelled by the equation
Attitudes Content to be covered
Listening, helping & guiding others Ch5: Pure Mathematics 3 by Sue Pemberton
You might also like
- McGraw-Hill Education Beginning Spanish Grammar: A Practical Guide to 100+ Essential SkillsFrom EverandMcGraw-Hill Education Beginning Spanish Grammar: A Practical Guide to 100+ Essential SkillsNo ratings yet
- Teacher Math Lesson 13 8th GradeDocument32 pagesTeacher Math Lesson 13 8th GradeErin100% (1)
- Secondary Progression Test - Stage 8 English Paper 1 PDFDocument12 pagesSecondary Progression Test - Stage 8 English Paper 1 PDFMaram70% (10)
- Discrete StructuresDocument174 pagesDiscrete StructuresIdham Muqoddas100% (1)
- Life Extension: A Practical Scientific Approach - The Life Extension Weight Loss Program - Pearson, Durk Shaw, SandyDocument392 pagesLife Extension: A Practical Scientific Approach - The Life Extension Weight Loss Program - Pearson, Durk Shaw, Sandypdf ebook free download100% (4)
- Paetep Observation 12-5Document7 pagesPaetep Observation 12-5api-312265721No ratings yet
- BTVS 5x16 "The Body" Audio CommentaryDocument12 pagesBTVS 5x16 "The Body" Audio CommentarynjzNo ratings yet
- 3 Vector Worksheet PDFDocument3 pages3 Vector Worksheet PDFnabil anwar16 Anwar Year 10100% (1)
- EPA07 Maxxforce 11, 13 Diagnostic Manual-1Document190 pagesEPA07 Maxxforce 11, 13 Diagnostic Manual-1Manuel Alejandro Velez NavaNo ratings yet
- LP P3 W18 by Sheraz 27thnov - 01st Dec 2023Document2 pagesLP P3 W18 by Sheraz 27thnov - 01st Dec 2023sherazNo ratings yet
- LP P3 W16 by Sheraz 13th - 17th Nov 2023Document2 pagesLP P3 W16 by Sheraz 13th - 17th Nov 2023sherazNo ratings yet
- LP P3 W14 by Sheraz 30 Oct-03 Nov 2023Document2 pagesLP P3 W14 by Sheraz 30 Oct-03 Nov 2023sherazNo ratings yet
- LP P1 W3 T2 by Sheraz 15th Jan - 19th Jan 2024Document2 pagesLP P1 W3 T2 by Sheraz 15th Jan - 19th Jan 2024sherazNo ratings yet
- LP P3 W3 T2 by Sheraz 15th Jan - 19th Jan 2024Document3 pagesLP P3 W3 T2 by Sheraz 15th Jan - 19th Jan 2024sherazNo ratings yet
- LP P3 W1&W2 T2 by Sheraz 3rd Jan - 12th Jan 2023Document3 pagesLP P3 W1&W2 T2 by Sheraz 3rd Jan - 12th Jan 2023sherazNo ratings yet
- TG-Basic Cal Q3 W26Document5 pagesTG-Basic Cal Q3 W26JohnNo ratings yet
- LP P3 W10 T1 by Sheraz 02-06 Oct 2023Document1 pageLP P3 W10 T1 by Sheraz 02-06 Oct 2023sherazNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4Document3 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4Mark Laurence RubioNo ratings yet
- UNIT Plan Math MYP2 2ndDocument10 pagesUNIT Plan Math MYP2 2ndkolawoleNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On AlgebraDocument5 pagesLesson Plan On AlgebrasairajNo ratings yet
- General Math DLL For SHS - (More DLL at Depedtambayanph - Blogspot.com) Q1, Week 02Document2 pagesGeneral Math DLL For SHS - (More DLL at Depedtambayanph - Blogspot.com) Q1, Week 02Gerry Areola Aquino100% (1)
- MYP2 Algebraic Terms and ExpressionsDocument6 pagesMYP2 Algebraic Terms and ExpressionsYomna SherifNo ratings yet
- Cabuloan National High School: Week 3Document8 pagesCabuloan National High School: Week 3Pia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Ubject ODE ATH Eacher Onah Ebian AmpusDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Ubject ODE ATH Eacher Onah Ebian AmpusMonah DebianNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Log: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofJay MellizaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - College Algebra (New)Document5 pagesSyllabus - College Algebra (New)Is JulNo ratings yet
- Grade 09 Iplan First QuarterDocument15 pagesGrade 09 Iplan First QuarterJessa Jean OrnopiaNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan of 3rd MPDocument10 pagesUnit Plan of 3rd MPkolawoleNo ratings yet
- Knowledge: Sskill: Attitude:: Instructional PlanDocument2 pagesKnowledge: Sskill: Attitude:: Instructional PlanLeah Yaun MuñezNo ratings yet
- LP P1 W1&W2 T2 by Sheraz 3rd Jan - 12th Jan 2023Document2 pagesLP P1 W1&W2 T2 by Sheraz 3rd Jan - 12th Jan 2023sherazNo ratings yet
- DLP Math 7 11-14-22Document3 pagesDLP Math 7 11-14-22FairyLeen PitogoNo ratings yet
- Appendix F. 4S Self-Learning Module 3Document21 pagesAppendix F. 4S Self-Learning Module 3Reliza Amahan SenoNo ratings yet
- MYP 5 (Math-Unit 1) PlannerDocument6 pagesMYP 5 (Math-Unit 1) PlannerMona AhmedNo ratings yet
- DLL - GenMath - Q1, Week 03Document2 pagesDLL - GenMath - Q1, Week 03YojlynOznerolNo ratings yet
- ST Instruction and ManagementDocument2 pagesST Instruction and Managementapi-295344110No ratings yet
- Instructional Project - 1 Bloom's Taxonomy Tuba Demirci Maths TeacherDocument12 pagesInstructional Project - 1 Bloom's Taxonomy Tuba Demirci Maths Teacherapi-611116992No ratings yet
- Comparing FunctionsDocument4 pagesComparing Functionsمحمد أحمد عبدالوهاب محمدNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map 1Document14 pagesCurriculum Map 1Joriel ValdesNo ratings yet
- Cockshott Ubd TemplateDocument2 pagesCockshott Ubd Templateapi-532636489No ratings yet
- ChapterDocument15 pagesChapteralabarbaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Mar 27 31Document5 pagesWeek 7 Mar 27 31Sarah Rivie Mae BeloroNo ratings yet
- DS101Document8 pagesDS101chinkee026No ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument3 pagesDifferential EquationskaplanramizzNo ratings yet
- UNIT PLAN 1 Year 2 MathsDocument9 pagesUNIT PLAN 1 Year 2 MathsSITI NUR'AIN BINTI MOHD SAID MoeNo ratings yet
- Module 2chDocument21 pagesModule 2chChris LynNo ratings yet
- A1 U4 LP Identifying Zeros of Equations AAPR3Document48 pagesA1 U4 LP Identifying Zeros of Equations AAPR3Via Terrado CañedaNo ratings yet
- Module 2. 4S Self-Learning ModuleDocument19 pagesModule 2. 4S Self-Learning ModuleReliza Amahan SenoNo ratings yet
- Week 7Document5 pagesWeek 7Sarah Rivie Mae BeloroNo ratings yet
- Cabuloan National High School: Pia P. Dela CruzDocument8 pagesCabuloan National High School: Pia P. Dela CruzPia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Math Ed 447 Numerical Analysis - UpdatedDocument5 pagesMath Ed 447 Numerical Analysis - UpdatedMagneto Eric Apollyon ThornNo ratings yet
- General Math DLL For SHS - (More DLL at WWW - Depedtambayanph.net) ) Q1, Week 03Document2 pagesGeneral Math DLL For SHS - (More DLL at WWW - Depedtambayanph.net) ) Q1, Week 03IreneRoseMotasNo ratings yet
- DLP 2Document15 pagesDLP 2Pablo JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Gmath Q2 W1Document3 pagesGmath Q2 W1nadyNo ratings yet
- General Math DLL For Shs q1 Week 02 1 CompressDocument5 pagesGeneral Math DLL For Shs q1 Week 02 1 CompressBal BaniasNo ratings yet
- Pearson - MYP Maths - Unit Plan - Sample - Y1 Ch7Document6 pagesPearson - MYP Maths - Unit Plan - Sample - Y1 Ch7world of farhanbilalaiquNo ratings yet
- Group H - Unit Planner Phase 1Document3 pagesGroup H - Unit Planner Phase 1api-383918624No ratings yet
- SELF ASSESSMENT For Grade 9 StudentsDocument4 pagesSELF ASSESSMENT For Grade 9 Studentsrichard aballeNo ratings yet
- Myp Math Extended Unit 04Document6 pagesMyp Math Extended Unit 04vato otavNo ratings yet
- DLL - 2Document3 pagesDLL - 2mercy sacriz0% (1)
- General Math For K11Document2 pagesGeneral Math For K11MelanioNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - 4 and 5 Standard - Unit Plans - Harrison, Huizink, Sproat-Clements, Torres-Skoumal - Second Edition - Oxford 2021Document37 pagesMathematics - 4 and 5 Standard - Unit Plans - Harrison, Huizink, Sproat-Clements, Torres-Skoumal - Second Edition - Oxford 2021783087690qq.comNo ratings yet
- Functions and Linear RelationshipsDocument75 pagesFunctions and Linear RelationshipsJoana PérezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningErwin B. NavarroNo ratings yet
- Understanding by Design Lesson PlanDocument18 pagesUnderstanding by Design Lesson Planchazzman311No ratings yet
- Grade 7 w3Document3 pagesGrade 7 w3Neuford Dawaton GatanNo ratings yet
- MATH UN RL GR7 DecimalsandFractionsDocument3 pagesMATH UN RL GR7 DecimalsandFractionsMatemáticas Sergio CuautleNo ratings yet
- LP P3 W16 by Sheraz 13th - 17th Nov 2023Document2 pagesLP P3 W16 by Sheraz 13th - 17th Nov 2023sherazNo ratings yet
- LP P3 W14 by Sheraz 30 Oct-03 Nov 2023Document2 pagesLP P3 W14 by Sheraz 30 Oct-03 Nov 2023sherazNo ratings yet
- LP P3 W2 T1 by Sheraz 07-11 Aug 2023Document1 pageLP P3 W2 T1 by Sheraz 07-11 Aug 2023sherazNo ratings yet
- LP P1 W3 T1 by Sheraz 15-18 Aug 2023Document1 pageLP P1 W3 T1 by Sheraz 15-18 Aug 2023sherazNo ratings yet
- LP P1 W2 T1 by Sheraz 07-11 Aug 2023Document1 pageLP P1 W2 T1 by Sheraz 07-11 Aug 2023sherazNo ratings yet
- Circle Properties PDFDocument29 pagesCircle Properties PDFsherazNo ratings yet
- A-Level Maths 9709-Paper 42-2024Document10 pagesA-Level Maths 9709-Paper 42-2024sherazNo ratings yet
- Entrance VIII MathsDocument11 pagesEntrance VIII MathssherazNo ratings yet
- Entrance VI MathsDocument6 pagesEntrance VI MathssherazNo ratings yet
- Identifying The Form of Digital Marketing Strategy Most Effective To Millennial's Brand PerceptionDocument16 pagesIdentifying The Form of Digital Marketing Strategy Most Effective To Millennial's Brand PerceptionElisabeth HenangerNo ratings yet
- Boosting ART Uptake and Retention Among HIV Infected Women and Their InfantsDocument4 pagesBoosting ART Uptake and Retention Among HIV Infected Women and Their InfantsDouglas ChukwuNo ratings yet
- KJV The American Patriot's Bible - The Book of JamesDocument10 pagesKJV The American Patriot's Bible - The Book of JamesThomas Nelson BiblesNo ratings yet
- Section 5 Mechatronics SystemDocument3 pagesSection 5 Mechatronics SystemАлексейNo ratings yet
- Installation and Trouble Shooting Manual: Top Drive Drilling EquipmentDocument48 pagesInstallation and Trouble Shooting Manual: Top Drive Drilling EquipmentAlejandro Hernadez100% (1)
- 2021 Florida Complex League Schedule - REVISED 6.3.21Document4 pages2021 Florida Complex League Schedule - REVISED 6.3.21Josh Norris100% (1)
- 02 Question Paper English XDocument8 pages02 Question Paper English XnischithNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Spoken Words With UsagesDocument377 pagesDictionary of Spoken Words With UsageskszonyiNo ratings yet
- PW Select October 2016Document22 pagesPW Select October 2016Publishers WeeklyNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter 1Document63 pages09 - Chapter 1Yash SoniNo ratings yet
- Rough Draft - Project 3Document12 pagesRough Draft - Project 3api-593346566No ratings yet
- Group 4Document25 pagesGroup 4Gemmadel Galang DuaquiNo ratings yet
- Genesys Inbound VoiceDocument6 pagesGenesys Inbound VoiceparidimalNo ratings yet
- General System TheoryDocument307 pagesGeneral System TheoryCarlos Luiz100% (3)
- Wesleyan University-Philippines: Basic Education Department PahintulotDocument1 pageWesleyan University-Philippines: Basic Education Department Pahintulotthyme 02No ratings yet
- Ravlt (Cast)Document6 pagesRavlt (Cast)Pau NndNo ratings yet
- Phillips, Crystals, Defects and Microstructures (CUP, 2004) (ISBN 0521790050)Document808 pagesPhillips, Crystals, Defects and Microstructures (CUP, 2004) (ISBN 0521790050)Ebru Coşkun100% (1)
- Arabic LessonsDocument72 pagesArabic LessonsNoor-uz-Zamaan AcademyNo ratings yet
- Physics DPP 5Document3 pagesPhysics DPP 5Hitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Office2016 AssignmentDocument2 pagesOffice2016 Assignmentapi-400730798No ratings yet
- Fei 2017Document6 pagesFei 2017PRADHAP DNo ratings yet
- Acharya LifeDocument19 pagesAcharya LifeAnand SwamiNo ratings yet
- AWS-PRACT AWS Cloud Practitioner EssentialsDocument1 pageAWS-PRACT AWS Cloud Practitioner EssentialsEdwin VasquezNo ratings yet
- Asian RegionalismDocument13 pagesAsian RegionalismAxel NeoNo ratings yet