Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Martinez Rey Poster
Martinez Rey Poster
Uploaded by
Ali DarvishiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Martinez Rey Poster
Martinez Rey Poster
Uploaded by
Ali DarvishiCopyright:
Available Formats
Simulation of a Steam Cracking Reactor with Ethane-propane
Mixtures using COMSOL Multiphysics®
R. Y. 1
Martinez ,
H. S. J. A 1
Amaya , 1
Arenas , Galán2
1. Chemical Engineering Department, Universidad Industrial de Santander, Bucaramanga, Colombia
2. ECOPETROL, Barrancabermeja, Colombia
INTRODUCTION: The Colombian Petroleum Company Figure 4 shows the concentration profiles for the main reactants
(ECOPETROL) needs to increase the production of ethylene and and products at outlet temperature of 1110 K and a 50/50w
propylene from diverse feedstocks. Therefore, this simulation ethane propane mixture. The ethane and propane conversions
studied the pyrolysis of ethane-propane mixtures in an existing are 0.75 and 0.90. Ethylene yield is 0.58 (mol ethylene/ mol
steam-cracking reactor (SCR) which was originally designed for ethane + mole propane). Industrial data yield is 0.60.
ethane cracking.
Parameter Value Unit
Flow 787.65 g/s
Steam/Fluid 0.4 kg/kg
Temperature in 913.2 K
Temperature out 1118.15 K
Average velocity outlet 206.65 m/s
Internal diameter 108 mm
Tube Length straight tube 8.2 m Figure 4. Concentration profiles Figure 5. Temperature profile with a
at T = 1110K 50/50w ethane-propane mixture
Total lenght 90.4 m
35000
Figure 1. The SCR geometry Table 1. Some SCR datasheet 30000
The models revealed a
ETHYLENE PRODUCTION [TON/YEAR]
25000
potential increase in
COMPUTATIONAL METHODS: The radiant section of the 20000
Tnew ethylene production when
15000
SCR was simulated as a plug flow reactor. The coil geometry and Told the old inlet temperature of
10000
its datasheet are shown in Figure 1 and Table 1. A 0D,1D and 2D 5000 797 K is increased to a new
models have been developed using COMSOL Multiphysics®. The 0 temperature of 913 K.
797 913
Chemical Reaction Engineering module was used for the definition TEMPERATURE [K]
of chemical species and reaction kinetics. A modified molecular
Figure 6. Influence of inlet temperature
kinetic model proposed by Froment1 was used. The thermodynamic on ethylene production
properties were calculated using the TEA COCO simulator. For the A fractional factor analysis was performed to study the
0D case, the following balance equations were set up: selectivity to ethylene as a function of outlet temperature and
Mass Balance mass fraction of propane. Results show that propane mass
fraction do not overcome 0.4. Reaction temperature does not
influence ethylene selectivity.
Energy Balance
RESULTS: An example of an ethylene concentration profile for
the 2D model is shown in Figure 2 for a 50/50w ethane-propane
mixture. A validation of the models were carried out with results
obtained by Froment1 and Galán3. The absolute errors for these
results were less than 4% for the reactions products.
%w
Species
0D COMSOL 1D Matlab Froment Figure 5. Respond surface for ethylene selectivity as
a function of propane mass fraction and reaction temperature
H2 2.95 2.69 3.00
CH4 13.61 13.75 12.00
CONCLUSIONS: The results of 0D COMSOL vs industrial data
C2H4 43.38 41.55 38.00 and other models show that absolute errors are less than 4%.
All models were used to detect operational conditions below
C2H6 18.42 21.85 26.00 optimal conditions.
Factor Analysis shows that the propane concentration at the
C3H6 8.77 8.80 8.00
feed has a strong influence on the ethylene selectivity.
Table 2. Comparison of 0D REFERENCES:
COMSOL model with other models 1.Sundaram, K.M. & Froment, G. F. Modelling of thermal cracking kinetics 1. Thermal cracking of
Figure 2. Ethylene concentration profile ethane, propane and their mixture. Chem. Eng. Sci., 32(6), 601-608 (1977)
2.Berreni, M. & Wang, M. Modelling and dynamics optimization of thermal cracking of propane for
For the 0D model, the model was investigated with a 0/100, ethylene manufacture, Comp. & Chem. Eng. 35, 2876-2885 (2011)
25/75, 50/50 75/25 and 100/0 mass relation of ethane/propane. 3.Galán, J. A. Operation conditions for the production of ethylene propylene in an existing SCR,
Master Thesis, Universidad Industrial de Santander, (2016)
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the 2018 COMSOL Conference in Boston
You might also like
- A Mathematical Model For The Production of Low Density Polyethylene in A Tubular ReactorDocument8 pagesA Mathematical Model For The Production of Low Density Polyethylene in A Tubular ReactorAlfredo IllescasNo ratings yet
- Rakha 2018Document13 pagesRakha 2018civilgardelNo ratings yet
- Steinberg 1998Document7 pagesSteinberg 1998Joaquín Tardón MuñozNo ratings yet
- Sundar Am 1981Document6 pagesSundar Am 1981Jhonatan Amaya ArdilaNo ratings yet
- Block DiagramDocument4 pagesBlock DiagramSyafiiqahNo ratings yet
- The Characterisation of Cotton Fabrics and The Interaction With Perfume Molecules by Inverse Gas Chromatography (IGC)Document4 pagesThe Characterisation of Cotton Fabrics and The Interaction With Perfume Molecules by Inverse Gas Chromatography (IGC)api-3733260No ratings yet
- Bed 9Document6 pagesBed 9Mary Grace VelitarioNo ratings yet
- AmoniaDocument35 pagesAmonianoelia cossio0% (1)
- Steam In: Net Heat Value NG Net Heat Value OILDocument2 pagesSteam In: Net Heat Value NG Net Heat Value OILvijendrNo ratings yet
- Steam In: Net Heat Value NG Net Heat Value OILDocument2 pagesSteam In: Net Heat Value NG Net Heat Value OILvijendrNo ratings yet
- Steam In: Net Heat Value NG Net Heat Value OILDocument2 pagesSteam In: Net Heat Value NG Net Heat Value OILvijendrNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S030626192031374X MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S030626192031374X Mainabdullah khanNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemical Engineering National Institute of Technology RourkelaDocument1 pageDepartment of Chemical Engineering National Institute of Technology RourkelaAbhisek AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Lab V - Non-Isothermal CSTR Reactors SimulinkDocument14 pagesLab V - Non-Isothermal CSTR Reactors SimulinkjullyNo ratings yet
- ENC-2020-0329 A Comprehensive Energetic, Exergetic and Heat Transfer Analysis of A Solar Organic Rankine System PowerDocument10 pagesENC-2020-0329 A Comprehensive Energetic, Exergetic and Heat Transfer Analysis of A Solar Organic Rankine System PowerAna Elisa AchilesNo ratings yet
- Optimization of The Synthesis of Carbon Nanotubes To Improve The Efficiency of Chemical Posttreatments of The Prepared MaterialDocument6 pagesOptimization of The Synthesis of Carbon Nanotubes To Improve The Efficiency of Chemical Posttreatments of The Prepared Material¡SrDanecMxNo ratings yet
- ECT Prev. Year End SemDocument4 pagesECT Prev. Year End SemKamal Vijay Ram R SNo ratings yet
- Economic Benefits of High Temperature Ammonia Heat Pumps (Two Case Stories) (Two Case Stories)Document13 pagesEconomic Benefits of High Temperature Ammonia Heat Pumps (Two Case Stories) (Two Case Stories)Sebastian Matías AguillónNo ratings yet
- Solution To Workshop 6-212 Power Cycles: School of Engineering and Sciences Thermodynamics Dr. Jorge Francisco EstelaDocument13 pagesSolution To Workshop 6-212 Power Cycles: School of Engineering and Sciences Thermodynamics Dr. Jorge Francisco EstelaChristian RengifoNo ratings yet
- AE8301 Aero Engineering Thermodynamics, QP, IAT 2 (2020 - 2021) - SDocument2 pagesAE8301 Aero Engineering Thermodynamics, QP, IAT 2 (2020 - 2021) - SGurunath AeroNo ratings yet
- Paper - Thermal Cracking of PropaneDocument13 pagesPaper - Thermal Cracking of PropaneshampexNo ratings yet
- Alternative Cycles Based On Carbon Dioxide For Central Receiver Solar Power PlantsDocument8 pagesAlternative Cycles Based On Carbon Dioxide For Central Receiver Solar Power PlantsSyed Jiaul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Methane Conversion Using Dielectric Barrier Discharge: Comparison With Thermal Process and Catalyst Ef FectsDocument6 pagesMethane Conversion Using Dielectric Barrier Discharge: Comparison With Thermal Process and Catalyst Ef Fectsapi-3728640No ratings yet
- Renewable Acrylonitrile ProductionDocument5 pagesRenewable Acrylonitrile ProductionThomas ChiNo ratings yet
- Assignment AETDDocument2 pagesAssignment AETDPratham M JariwalaNo ratings yet
- Nr210304 ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesNr210304 ThermodynamicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Computer Simulation of An Industrial Ethane-Cracking Furnace OperationDocument5 pagesComputer Simulation of An Industrial Ethane-Cracking Furnace OperationMari Luz Hermoza MamaniNo ratings yet
- Electronica y Electricidad Automotriz 4 Como Funcionan Los Sistemas de Encendido ElectronicoDocument11 pagesElectronica y Electricidad Automotriz 4 Como Funcionan Los Sistemas de Encendido ElectronicoJuan Francisco Garcia ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Main Activities in University of Perugia About Technologies For Greenhouse Gases MitigationDocument16 pagesMain Activities in University of Perugia About Technologies For Greenhouse Gases MitigationbharathimanjulaNo ratings yet
- Direct Dimethyl Ether Synthesis From Kinetic Model: Synthesis Gas: Experiments andDocument11 pagesDirect Dimethyl Ether Synthesis From Kinetic Model: Synthesis Gas: Experiments andFajar Hamida MunfaridiNo ratings yet
- Simulation of The Firebox ofDocument6 pagesSimulation of The Firebox ofAli DarvishiNo ratings yet
- Optimization of A Sofc System: Influence of Design and Operation Parameters On System EfficincyDocument8 pagesOptimization of A Sofc System: Influence of Design and Operation Parameters On System Efficincy10 000 de cartiNo ratings yet
- IR Comparitive Materials Evaluation For Gas Turbine Kesseli Et AlDocument37 pagesIR Comparitive Materials Evaluation For Gas Turbine Kesseli Et AlRizwan MNo ratings yet
- Adv Therm Week 10Document16 pagesAdv Therm Week 10Tegin Berkay BudakNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument4 pagesPower Plant EngineeringKishore KrishNo ratings yet
- Retrofit Design o On Synthesis and P F Heat Exchanger Netw Purification Unit of Me Work (HEN) Ethanol PlantDocument4 pagesRetrofit Design o On Synthesis and P F Heat Exchanger Netw Purification Unit of Me Work (HEN) Ethanol PlantMohamed RefaatNo ratings yet
- Ruta 1Document5 pagesRuta 1DORIS HELENA GUTIÉRREZ LONDOÑONo ratings yet
- Effect of Temperature On Chemical Activation of CNTDocument5 pagesEffect of Temperature On Chemical Activation of CNTDiani MuhandiramNo ratings yet
- Santa Cesaria 1981Document10 pagesSanta Cesaria 1981Jorge LondoñoNo ratings yet
- MT Answer KeyDocument41 pagesMT Answer Keykaviyas.21chemNo ratings yet
- Acetona 1Document1 pageAcetona 1Abigail Salinas Del RioNo ratings yet
- Energy: Yang Wang, Zhijun Zhou, Junhu Zhou, Jianzhong Liu, Zhihua Wang, Kefa CenDocument5 pagesEnergy: Yang Wang, Zhijun Zhou, Junhu Zhou, Jianzhong Liu, Zhihua Wang, Kefa CenKean PascualNo ratings yet
- Urea Technology, Toyo Eng. CompnayDocument20 pagesUrea Technology, Toyo Eng. CompnaySteve WanNo ratings yet
- Separator Efficiency CirculatingloadDocument4 pagesSeparator Efficiency CirculatingloadirfanNo ratings yet
- Recoma 35E: Recoma Sintered Samarium Cobalt MagnetsDocument1 pageRecoma 35E: Recoma Sintered Samarium Cobalt MagnetsNareshNo ratings yet
- 04 Flame Height CalculationsDocument22 pages04 Flame Height CalculationssalcedopozasNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet GeniousDocument2 pagesData Sheet GeniousMarioNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger NetworkDocument34 pagesHeat Exchanger NetworkrovshanbabayevNo ratings yet
- Investigation On The Heating Performance of The Heat Pump Withwaste Heat Recovery For The Electric BusDocument14 pagesInvestigation On The Heating Performance of The Heat Pump Withwaste Heat Recovery For The Electric BusEmre EmlekNo ratings yet
- Stability Testing of PT SN /C Anodic Catalyst For Renewable Hydrogen Production Via Electrochemical Reforming of EthanolDocument9 pagesStability Testing of PT SN /C Anodic Catalyst For Renewable Hydrogen Production Via Electrochemical Reforming of EthanolAntoni GuilhermeNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Diethylacetal: Thermodynamic and Kinetic StudiesDocument9 pagesSynthesis of Diethylacetal: Thermodynamic and Kinetic StudiesrukwavuNo ratings yet
- Techniques and Unique and Characteristic Signatures To Identify Hydrino Are Predicted From Exact Closed-Form Solutions of Atoms and MoleculesDocument51 pagesTechniques and Unique and Characteristic Signatures To Identify Hydrino Are Predicted From Exact Closed-Form Solutions of Atoms and MoleculesAleksandrNo ratings yet
- Small Scale ORC Plant Modeling With The AMESim Simulation ToolDocument10 pagesSmall Scale ORC Plant Modeling With The AMESim Simulation ToolÜlkü Serçin SerçinoğluNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in Thermal Engineering: Thoranis Deethayat, Tanongkiat Kiatsiriroat, Chakkraphan ThawonngamyingsakulDocument5 pagesCase Studies in Thermal Engineering: Thoranis Deethayat, Tanongkiat Kiatsiriroat, Chakkraphan ThawonngamyingsakulKumbamNo ratings yet
- ATD - I IA QP FinalDocument1 pageATD - I IA QP FinalSarita UmadiNo ratings yet
- Efficiency of Inefficient Endoreversible Thermal MachinesDocument7 pagesEfficiency of Inefficient Endoreversible Thermal Machinescarolina coaquiraNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermal Engineering: P. Regulagadda, I. Dincer, G.F. NatererDocument7 pagesApplied Thermal Engineering: P. Regulagadda, I. Dincer, G.F. Natererjhugo_mirandaNo ratings yet
- Binario MEt MEtyDocument4 pagesBinario MEt MEtyHilda Piza PuentesNo ratings yet
- 2001 Latest Urea Technology For Improving Performance and Product Quality PDFDocument20 pages2001 Latest Urea Technology For Improving Performance and Product Quality PDFAviv AL FarisNo ratings yet
- Plasma Water Activation With An Inductive Plasma Torch at Atmospheric PressureDocument1 pagePlasma Water Activation With An Inductive Plasma Torch at Atmospheric Pressureabo obaNo ratings yet
- Simulation of The Firebox ofDocument6 pagesSimulation of The Firebox ofAli DarvishiNo ratings yet
- Pretreatments of Coils To Minimize Coke Formation in Ethylene Furnaces PDFDocument4 pagesPretreatments of Coils To Minimize Coke Formation in Ethylene Furnaces PDFAli DarvishiNo ratings yet
- Coke Deposition by Physical Condensation Oft PDFDocument12 pagesCoke Deposition by Physical Condensation Oft PDFAli DarvishiNo ratings yet
- Future Coils For Ethylene FurnacesDocument2 pagesFuture Coils For Ethylene FurnacesAli DarvishiNo ratings yet
- Integration, Feedstock Optimization Are Key Success Factors For EuropeDocument4 pagesIntegration, Feedstock Optimization Are Key Success Factors For EuropeAli DarvishiNo ratings yet
- FPSO Commissioning Presentation 3Document31 pagesFPSO Commissioning Presentation 3javeedscrib100% (2)
- What Are The Disadvantages of A Canal Solar PVDocument6 pagesWhat Are The Disadvantages of A Canal Solar PVAnumakonda JagadeeshNo ratings yet
- Tds - 25 LPS, Head-150 MTRDocument4 pagesTds - 25 LPS, Head-150 MTRmukherjeemohul25No ratings yet
- Steam Consumption at Sulphitation / Raw Sugar Factories (Boiling House - Recent Trends)Document6 pagesSteam Consumption at Sulphitation / Raw Sugar Factories (Boiling House - Recent Trends)Yadav ShwetaNo ratings yet
- Manuel Partes ElectricoDocument28 pagesManuel Partes ElectricoAndersonNo ratings yet
- 100 Gnomish InventionsDocument10 pages100 Gnomish InventionsRuslan GabbasovNo ratings yet
- 05-Wellhead Xmas TreeDocument38 pages05-Wellhead Xmas TreeVamsi MahantiNo ratings yet
- Ratings of SCRDocument32 pagesRatings of SCRSourav DebnathNo ratings yet
- Fithian Sheets-Green Building Materials PDFDocument13 pagesFithian Sheets-Green Building Materials PDFGemmer BatuyongNo ratings yet
- Test - 02: Class: XI - 2022 (Term-02)Document10 pagesTest - 02: Class: XI - 2022 (Term-02)DhruvJainNo ratings yet
- PowerPact D-Frame Circuit Breakers CatalogDocument68 pagesPowerPact D-Frame Circuit Breakers CatalogDiego Fernando Pérez SantibáñezNo ratings yet
- FlenderTechnical HandbookDocument79 pagesFlenderTechnical HandbookTom TamponNo ratings yet
- Credentialing Achievement Record: Industrial Technology MaintenanceDocument14 pagesCredentialing Achievement Record: Industrial Technology MaintenanceAnilNo ratings yet
- A Ongc HRM Summer ProjectDocument58 pagesA Ongc HRM Summer ProjectAmit SunsaraNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual / A130-H66: Document IdentificationDocument124 pagesOperation Manual / A130-H66: Document IdentificationHalilibrahim CanNo ratings yet
- Nacobre Tarjeta ManualDocument6 pagesNacobre Tarjeta Manualalex castroNo ratings yet
- 6.2. Natural Gas (Treatment)Document45 pages6.2. Natural Gas (Treatment)MaisarahNo ratings yet
- G For The Material Is 82 GN/m2. If The I-Section Is Replaced by A T-Section Made of TheDocument6 pagesG For The Material Is 82 GN/m2. If The I-Section Is Replaced by A T-Section Made of Theክበር ተመስጌንNo ratings yet
- TAD734GE Technical Data 21373062.06Document15 pagesTAD734GE Technical Data 21373062.06Ricardo MarmoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical DryerDocument11 pagesMechanical DryerCharlyn Flores100% (1)
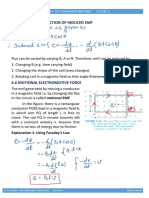
- Methods of Production of Induced Emf: Explanation 1: Using Faraday's LawDocument3 pagesMethods of Production of Induced Emf: Explanation 1: Using Faraday's LawNishita SahNo ratings yet
- 22 Ca08103002z-En 2010Document38 pages22 Ca08103002z-En 2010Laurentiu ApostolNo ratings yet
- 15N41CLGDocument11 pages15N41CLGssarbani720No ratings yet
- 11 Appendix J B 1st-31st March 2020 - 2Document2 pages11 Appendix J B 1st-31st March 2020 - 2Adita DayNo ratings yet
- Pentolite Booster: High Initiating Energy Optimal Blasting EfficiencyDocument2 pagesPentolite Booster: High Initiating Energy Optimal Blasting EfficiencyYoga PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Bentley 1997Document17 pagesBentley 1997michael arjonaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Atomic Structure Measurement Calculation Concept Maps PracticeDocument17 pagesPeriodic Table Atomic Structure Measurement Calculation Concept Maps PracticeleydaNo ratings yet
- An LC CircuitDocument11 pagesAn LC CircuitHRM, BAPEXNo ratings yet
- KGE Catalogue.36165930 PDFDocument2 pagesKGE Catalogue.36165930 PDFAshish MishraNo ratings yet