Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GCSE Structures and Bonding Summary Sheet
GCSE Structures and Bonding Summary Sheet
Uploaded by
Babalola TomisinCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GCSE Structures and Bonding Summary Sheet
GCSE Structures and Bonding Summary Sheet
Uploaded by
Babalola TomisinCopyright:
Available Formats
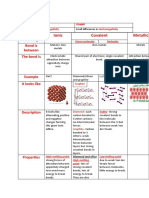
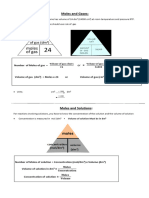
GCSE Summary: Properties of different structures
Structure Properties Explanation
Giant ionic structure High melting points and boiling points. The strong electrostatic forces between positive and
negative ions require lots of energy to overcome.
Lattice of positive and
Do not conduct electricity as solids. Solid: the ions are in fixed positions.
negative ions strongly Conduct electricity as liquids/solutions. Liquid/solution: The ions are free to move.
attracted together
Simple molecular structure Low melting and boiling points. Although the covalent bonds between the atoms in
molecules are strong, the intermolecular forces
Strong covalent bonds between the molecules are weak and little energy is
needed to overcome them.
Weak intermolecular Do not conduct electricity. The molecules are neutral so there are no moving
forces charges.
Giant covalent/macromolecular structure High melting and boiling points. There are strong covalent bonds throughout the
structure which require lots of energy to overcome.
Do not conduct electricity, except graphite. Diamond/Silica: There are no moving charges.
Strong covalent bonds Graphite: There are delocalised electrons.
Metallic structure High melting and boiling points. The strong electrostatic forces between positive ions
and delocalised electrons require lots of energy to
Positive ions
overcome.
Delocalised electrons
from the outer shells
of the metal atoms
You might also like
- Potassium TrihydrateDocument5 pagesPotassium TrihydrateTeresa Davis60% (15)
- Ap Unit2 Worksheet AnswersDocument7 pagesAp Unit2 Worksheet Answersburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Property Explanation: Liquid StateDocument9 pagesProperty Explanation: Liquid StateNothing NameNo ratings yet
- 2.2. How Bonding and Structure Are Related To The Properties of SubstancesDocument1 page2.2. How Bonding and Structure Are Related To The Properties of SubstancesatemisgoddesofhuntNo ratings yet
- Structure and BondingDocument1 pageStructure and BondingeohomegrownappsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Structure..Document6 pagesChemical Bonding Structure..rachelNo ratings yet
- Ionic Molecular Covalent Network Covalent MetallicDocument2 pagesIonic Molecular Covalent Network Covalent MetallicLeah RualesNo ratings yet
- Bonding (Diamond, Graphite, Fullerene and Silicon-Dioxide)Document1 pageBonding (Diamond, Graphite, Fullerene and Silicon-Dioxide)Safe GuardNo ratings yet
- c3 Structure and BondingDocument2 pagesc3 Structure and BondingNavdha SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry Notes 5Document3 pagesCsec Chemistry Notes 5debestieNo ratings yet
- Bonding A LevelDocument2 pagesBonding A LevelHamzah ArabicaNo ratings yet
- Practice Worksheet of Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesPractice Worksheet of Chemical Bondingch khakanNo ratings yet
- 4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedDocument23 pages4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedFN5052023 PRAMITA MAHENDRANNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure-ReviewDocument1 pageBonding and Structure-Reviewcandyli3788No ratings yet
- 4-Properties Relating To Structure Revision SheetDocument6 pages4-Properties Relating To Structure Revision SheetalvaressaschaNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding ReportDocument7 pagesCovalent Bonding ReportGun TnNo ratings yet
- Forces of AttractionDocument21 pagesForces of AttractionDoveNo ratings yet
- Bonding Knowledge OrganiserDocument1 pageBonding Knowledge Organisermya thet htar sweNo ratings yet
- O Level Pure Chem SummaryDocument75 pagesO Level Pure Chem SummaryEdcademiaNo ratings yet
- The Properties of CompoundsDocument1 pageThe Properties of CompoundssuazopalaoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Zoe 171121Document2 pagesChemistry Zoe 171121NavNo ratings yet
- SCINOTESDocument2 pagesSCINOTESMark Beduya CuffeeNo ratings yet
- Bonding and StructureDocument20 pagesBonding and StructureYusma KhanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Implication of Wave Particle DualityDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure: Implication of Wave Particle Dualityguiller139No ratings yet
- Types of CrystalsDocument12 pagesTypes of CrystalsSpace MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Chemical PropertiesDocument32 pagesLesson 3 Chemical PropertiesJohann LeoncitoNo ratings yet
- Bonding A Level NotesDocument5 pagesBonding A Level NotesWashington NyakaviNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document25 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Anonymous BW2VsFifi9No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding SummaryDocument8 pagesChemical Bonding SummaryKiara LimNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes On StructuresDocument7 pagesChem Notes On StructuresHey thereNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds HWDocument1 pageChemical Bonds HWquinlanNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3 - BondingDocument15 pages3.1.3 - BondingaprildazzleNo ratings yet
- 5c. CrystalsDocument5 pages5c. CrystalsUnknownKidNo ratings yet
- Scientific MethodDocument26 pagesScientific Methodclarisse.ionicNo ratings yet
- AQA Combined Science Structure and BondingDocument2 pagesAQA Combined Science Structure and Bondingali.a.226No ratings yet
- IB SL Chemistry NotesDocument5 pagesIB SL Chemistry NotesArsh SheikhNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileDocument17 pagesCovalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileMahi QuaziNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 002Document7 pagesGen Chem 002jazz vergsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding O LevelDocument1 pageChemical Bonding O LevelChong56No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChemical BondingSANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesMetallic Bondingonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- Summary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesSummary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesAnonymous L7ZuSkR100% (1)
- Paper 2Document21 pagesPaper 2John SonbolNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument1 pageBondingdavid.andrijanicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document3 pagesChapter 5s1062579No ratings yet
- Structure: Physical Properties Ionic Comp Covalent Compound Metal Iodine Diamond GraphiteDocument2 pagesStructure: Physical Properties Ionic Comp Covalent Compound Metal Iodine Diamond GraphiteAnonymous ATvkkrtr2yNo ratings yet
- DifferencebetweenionicandcovalentompoundsDocument2 pagesDifferencebetweenionicandcovalentompoundsRammohan Balaji PrasadNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds and StructureDocument17 pagesChemical Bonds and StructureEddie EvansNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument2 pagesIonic Bondingdigjhon6No ratings yet
- Bonding and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesBonding and Properties of Substancesdan964No ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsDocument4 pagesLecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsmartinNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document2 pagesCH 7Heather SiuNo ratings yet
- Energy Bands in Solid 6Document4 pagesEnergy Bands in Solid 6S.M. Abdul Mannan MahdiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Chemical BondingQutub KhanNo ratings yet
- 06 CB Notes 2022Document6 pages06 CB Notes 2022Fitri armaya Jeffri (Greendaless)No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Chemical BondingDocument10 pagesGrade 9 Chemical BondingAmonique DaveyNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding Revision QuestionsDocument1 pageCovalent Bonding Revision Questionsrachael.knightNo ratings yet
- Atoms CombiningDocument12 pagesAtoms Combiningshehryar khanNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 IB Bridging Course Chemistry: Flow of This SectionDocument10 pagesGrade 10 IB Bridging Course Chemistry: Flow of This SectionMarc LoNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument40 pagesChemical BondingabuhurairabscNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- Physics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPhysics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Online VolunteeringDocument15 pagesOnline VolunteeringBabalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- MYP Science Level 2 Unit 1 Summative AssessmentDocument9 pagesMYP Science Level 2 Unit 1 Summative AssessmentBabalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Full Instructions Week 7 May 20 26Document41 pagesScience 9 Full Instructions Week 7 May 20 26Babalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- s40328 018 0225 0Document26 pagess40328 018 0225 0Babalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- SI Units - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument3 pagesSI Units - Chemistry LibreTextsBabalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- The Challenges of Social Work Practice in NigeriaDocument9 pagesThe Challenges of Social Work Practice in NigeriaBabalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- Preview: Electrical Resistance and Ohm's LawDocument10 pagesPreview: Electrical Resistance and Ohm's LawBabalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- Int 2019 1002 Spseintro.1Document1 pageInt 2019 1002 Spseintro.1Babalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- Basin and PeDocument37 pagesBasin and PeBabalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- Energies 12 00650Document20 pagesEnergies 12 00650Babalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- 3 Chaardee+and+Jankaew 4 1 13-25Document13 pages3 Chaardee+and+Jankaew 4 1 13-25Babalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- Christmas & New Year Day: Food IdeaDocument27 pagesChristmas & New Year Day: Food IdeaBabalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- 3D Reservoir Modeling ProjectsDocument9 pages3D Reservoir Modeling ProjectsBabalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- Peterson 1985Document48 pagesPeterson 1985Babalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- Publications Energy 93 105 01 EgDocument19 pagesPublications Energy 93 105 01 EgBabalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- Department of Earth Sciences, The Universiiy of Beak, Leeds L.S2 9JT (Great Britain)Document15 pagesDepartment of Earth Sciences, The Universiiy of Beak, Leeds L.S2 9JT (Great Britain)Babalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- Tang2022 Article RegressionModelingForLaminarFlDocument10 pagesTang2022 Article RegressionModelingForLaminarFlBabalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- 1-4 Introduction To Electrochemistry - RedoxDocument24 pages1-4 Introduction To Electrochemistry - RedoxCtstrphyNo ratings yet
- Separate Chemistry: Higher Tier in BoldDocument16 pagesSeparate Chemistry: Higher Tier in BoldzipperNo ratings yet
- The World's Most Extensive Selection of Ductless Fume Hoods.Document9 pagesThe World's Most Extensive Selection of Ductless Fume Hoods.Alejandro Ceron GuerreroNo ratings yet
- 2-Synthetic Methods Chap 2Document81 pages2-Synthetic Methods Chap 2MahsaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Education - April 1995 - Vella - Principles of Bioinorganic Chemistry by S J Lippard and J M Berg PP 411Document1 pageBiochemical Education - April 1995 - Vella - Principles of Bioinorganic Chemistry by S J Lippard and J M Berg PP 411Neeraj MundaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RefiningDocument8 pagesIntroduction To RefiningAnubhav ChandilNo ratings yet
- C C..Ii..M M.. Iin ND Du Us Sttrriie Es S Iin NC C..: FootnoteDocument2 pagesC C..Ii..M M.. Iin ND Du Us Sttrriie Es S Iin NC C..: FootnoteIan FletcherNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0928493122000443 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S0928493122000443 MainmrshirafatimaNo ratings yet
- Module 11 Carbohydrates Lecture 29 Carbohydrates I: C H O + 6O 6CO 6H O Energy Oxidation Photosynthesis + + GlucoseDocument5 pagesModule 11 Carbohydrates Lecture 29 Carbohydrates I: C H O + 6O 6CO 6H O Energy Oxidation Photosynthesis + + GlucoseRajiv KalsiNo ratings yet
- Wendy Myers Toxic Metals That Cause Fatigue EguideDocument22 pagesWendy Myers Toxic Metals That Cause Fatigue EguideMarcelo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Anabaena VariabilisDocument2 pagesAnabaena VariabilisHafsa QaderNo ratings yet
- Write The Letter That Best Answers The Question or Completes The Statement On The Line ProvidedDocument10 pagesWrite The Letter That Best Answers The Question or Completes The Statement On The Line ProvidedLama AshiNo ratings yet
- Enviornmental Chemistry 60 QuestionsDocument62 pagesEnviornmental Chemistry 60 QuestionsShyam SubediNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Worksheet Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Worksheet Chemical BondingShashwatNo ratings yet
- 2013 Yan Synthesis of Fiber Crosslinking Cationic Latex and Its Effect On Surface Properties ofDocument6 pages2013 Yan Synthesis of Fiber Crosslinking Cationic Latex and Its Effect On Surface Properties ofMohammed JamaliNo ratings yet
- Chemical OrganizationDocument16 pagesChemical OrganizationYousef EshaweeNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan Chemistry s3Document7 pagesSkema Jawapan Chemistry s3Fazliawati MahayuddinNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Laboratory Report OutlineDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry Laboratory Report OutlineAminaNo ratings yet
- Summative Test - Biotech2022Document6 pagesSummative Test - Biotech2022Joan VillarcaNo ratings yet
- Soil Properties School ProjectDocument25 pagesSoil Properties School ProjectMike VadenNo ratings yet
- Microwave-Assisted Rapid Synthesis of Well-Shaped MOF-74 (Ni) For CO E Cient CaptureDocument12 pagesMicrowave-Assisted Rapid Synthesis of Well-Shaped MOF-74 (Ni) For CO E Cient Capturelucas perezNo ratings yet
- Mole ObjectiveDocument26 pagesMole ObjectiveDevil WalkerNo ratings yet
- Chemical Storage Guidelines SiDocument2 pagesChemical Storage Guidelines SiIndranil MitraNo ratings yet
- JEESankalp Practice Paper-01Document16 pagesJEESankalp Practice Paper-01jayeshsadafule383No ratings yet
- Cbse Question Paper 2019 (Set-1) Class 11 Chemistry Mahanhi Palanjall Vldyamandir, PrayagrajDocument5 pagesCbse Question Paper 2019 (Set-1) Class 11 Chemistry Mahanhi Palanjall Vldyamandir, PrayagrajBibha KumariNo ratings yet
- Phrases Clauses and SentencesDocument15 pagesPhrases Clauses and SentencesAnanto Arya FahresyNo ratings yet
- Cementation in FPDDocument53 pagesCementation in FPDNiharika SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions Sheet - 1 PDFDocument3 pagesPractice Questions Sheet - 1 PDFbadisa booksNo ratings yet