Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary Ias 10 Earp
Summary Ias 10 Earp
Uploaded by
Muhammad Tufail DogarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary Ias 10 Earp
Summary Ias 10 Earp
Uploaded by
Muhammad Tufail DogarCopyright:
Available Formats
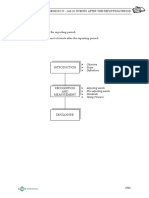
Events After Reporting Period
Objective:
To prescribe
When to adjust FS
Disclosure of DOA
Disclosure of events ARP
Requirments if entity is not going concern.
Scope:
Accounting for events ARP
Disclosures of events ARP
Defintion:
Are those (favaourable or unfavourable) that OCCUR between the end of reporting perioid and the date when financial
statements are authorised for issue. Such events can be adjusting or non adjusting depending the conditions/circumstances.
Adjusting events:
“Events that provide evidence of conditions that (already) existed at the end of reporting date.”
ایسے واقعات جو ان حاالت کے بارے میں ثبوت فراہم کریں جو رپورٹنگ ڈیٹ پر (پہلے سے) موجود ہوں۔
ہمیں پتا بعد میں چال ہو۔،ایک ایسا واقعہ جو پہلے ہوچکا ہے
Treatment:
Adjust the amounts recognise in FS to reflect the adjusting events.
Update the relevant disclosures in the light of new informtion.
List of Adjusting Events:
1. Discovery of fraud/error after reporting period
2. Asset impairment after reporting period
3. Cost of asset purchased before the year end but paid after the year end
4. Proceeds of asset disposed off before the year end but received after the year end
5. Payment of profit sharing or bonus payment when there is present obligatin at the year end
6. Settelment of a court case
7. Sale of inventory after reporting period that requires adjustment in NRV
8. IAS-10 specifically mentions that
if a customer's bankruptcy is announced after the reporting period,
and there is no indication that
the bankruptcy was solely due to events after the reporting period
it is considered an adjusting event.
Non-adjusting events:
Events that are indicative (provide hints) of conditions that arsoe after the end reporting period.
Treatment:
Do not adjust the amounts recognise in FS.
Diclose (Nature and Financail Effect) if the event is material.
List of Non-adjusting events:
1. Annoucing a plan to discontinue an operaion
2. Annoucing, commencing and implementation of major re-structuring
3. Change in exchange rate after reporting period
4. Change in tax rates/; laws after reporitng period
5. Decline in the fair value of investment after reporting period
6. Dividend declared after reporting period
7. Disposal of major subsidary
8. Disposal of asset after reporting period
9. Destruction of plant due to flood or fire
10. Litigation arising out of events after reporting period
11. Major business combination
12. Major ordinary and potential share transaction after reporting period
13. Purchase of asset after reporting period
14. Significant commitments after reporting period
Disclosure requirment of Non-adjusting events:
An entity shall disclose the following for each material category of non-adjusting event after the reporting period:
The nature of the event; and
An estimate of its financial effect
or a statement that such an estimate can not be made
Date of Autorisation:
Definiton:
It refers to the date when the financial statements are approved by an entity's board of directors or equivalent body for release
to stakeholders.
Approving FS for release can change based on;
The management structure,
Statutory requirements
Procedures followed in preparing and finalising the financial statements.
Diclosure:
An entity shall disclose;
The date when the financial statements were authorised for issue
Who gave that authorisation
Importance of date of authorisation:
The financial statements do not reflect events after this date.
Section 232 of Company’s Act, 2017:
Approved by the board of the company
Signed on behalf of the board by CEO and at least one director of the company.
In case of a listed company also sigend by CFO.
Going Concern:
Refers to the assumption that the entity will continue its operations for the foreseeable future.
Explanation:
It means a business is expected to:
Meet its financial obligations when due.
Operate for at least the next 12 months
Not liquidate or go bankrupt in the near future
Indication of Going Concern Issue:
Deterioration in operating results
Deterioration in Financial position.
When Going Concern assumption is not appropriate:
An entity shall not prepare its financial statements on a going concern basis if management determines after the reporting
period either:
That it intends to liquidate the entity
That it intends to cease trading
That it has no realistic alternative but to do so. (License is cancelled/Heavy losses)
In that case, financial statements are prepared on alternative basis.
o Assests are measured at realizable value.
o Liabilities are measured at settelment value.
Factors that lead to Going Concern Problem:
1.Difficulty of major customer
2.Shortage of important supplies
3.Cruicial non current asset falling out of use
4.Emergence of highly effective competitor
5.Decline in value of investment due to change in market conditons
6.Decline in NRV of line of inventory below its cost
Note:
When the Going Concern Problem arises,
financial statements ar ADJUSTED.
Even the going concern issue arises after
the reporitng peirod.
You might also like
- IAL AS Accounting General FormatDocument44 pagesIAL AS Accounting General FormatRajibul Haque Shumon100% (2)
- Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management: Frank K. Reilly & Keith C. BrownDocument41 pagesInvestment Analysis and Portfolio Management: Frank K. Reilly & Keith C. BrownWasim Bin ArshadNo ratings yet
- ICAEW Financial Accounting Past Papers Combined 2010-2013Document130 pagesICAEW Financial Accounting Past Papers Combined 2010-2013Ahmed Raza Tanveer100% (3)
- Topic 5 Events After Reporting Period 4studentsDocument22 pagesTopic 5 Events After Reporting Period 4studentsputerimanggis11No ratings yet
- NAS 10 ICAN Revision Classes IDocument9 pagesNAS 10 ICAN Revision Classes ISujan ShresthaNo ratings yet
- IAS 10 - Events After Reporting DateDocument8 pagesIAS 10 - Events After Reporting DateKhuraim Abu BakrNo ratings yet
- Ias 10 Events After The Reporting Date (2021)Document8 pagesIas 10 Events After The Reporting Date (2021)Nolan TitusNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 MFRS 110 3 Event - After - Reporting PeriodDocument14 pagesTopic 6 MFRS 110 3 Event - After - Reporting Perioddini sofia100% (1)
- Ias 10 Events After The Reporting Period: Fact SheetDocument8 pagesIas 10 Events After The Reporting Period: Fact SheetRJNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Events After The Reporting PeriodDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - Events After The Reporting PeriodNURKHAIRUNNISANo ratings yet
- Advanced Accounting Full Notes 11022021 RLDocument335 pagesAdvanced Accounting Full Notes 11022021 RLSivapriya Kamat100% (1)
- Ias 10 & 37 - 1Document4 pagesIas 10 & 37 - 1Abdullah QureshiNo ratings yet
- As 4Document4 pagesAs 4abhishekkapse654No ratings yet
- 150.events After The Reporting PeriodDocument6 pages150.events After The Reporting PeriodMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Ias 10 Events After The Reporting Period SummaryDocument2 pagesIas 10 Events After The Reporting Period Summaryanon_806011137No ratings yet
- 74889bos60524 cp4 U2Document35 pages74889bos60524 cp4 U2Bala Guru Prasad TadikamallaNo ratings yet
- ACCA - F3 Chapter-19-1Document10 pagesACCA - F3 Chapter-19-1Nile NguyenNo ratings yet
- Module 3 ICAI Material 3 - Ind AS10Document31 pagesModule 3 ICAI Material 3 - Ind AS10siva883No ratings yet
- Nas 10Document11 pagesNas 10anujnepal9595No ratings yet
- Ind As 10Document13 pagesInd As 10mohd52No ratings yet
- Ias 10Document15 pagesIas 10hasan sohailNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Ind As 10: Events After The Reporting Period: After Studying This Unit, You Will Be Able ToDocument31 pagesUnit 2: Ind As 10: Events After The Reporting Period: After Studying This Unit, You Will Be Able TovijaykumartaxNo ratings yet
- Fa 3 Chapter 5 Events After The Reporting PeriodDocument6 pagesFa 3 Chapter 5 Events After The Reporting PeriodKristine Florence TolentinoNo ratings yet
- ACC1026 Topic 8Document64 pagesACC1026 Topic 8Ceae SeaNo ratings yet
- 2022 Ias 10Document4 pages2022 Ias 10gmimranhossain996No ratings yet
- 74704bos60485 Inter p1 cp7 U1Document13 pages74704bos60485 Inter p1 cp7 U1Just KiddingNo ratings yet
- Encoded Pas 1012Document13 pagesEncoded Pas 1012Marielle De LeonNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Events After The Reporting DateDocument12 pagesAccounting For Events After The Reporting DateEjaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document8 pagesChapter 10Mark Kenneth ParagasNo ratings yet
- Ifrs at A Glance: IAS 10 Events After The ReportingDocument4 pagesIfrs at A Glance: IAS 10 Events After The ReportingJozelle Grace PadelNo ratings yet
- Events After The Reporting PeriodDocument1 pageEvents After The Reporting PeriodFaye RagosNo ratings yet
- Objective: Session 29 - Ias 10 Events After The Reporting PeriodDocument4 pagesObjective: Session 29 - Ias 10 Events After The Reporting PeriodZohair HumayunNo ratings yet
- Module 017 Week006-Finacct3 Notes To The Financial StatementsDocument5 pagesModule 017 Week006-Finacct3 Notes To The Financial Statementsman ibeNo ratings yet
- 01 Events After Balance Sheet DateDocument3 pages01 Events After Balance Sheet DateMd. Iqbal HasanNo ratings yet
- #08 PAS 10 (Events After Reporting Period)Document2 pages#08 PAS 10 (Events After Reporting Period)Zaaavnn Vannnnn100% (1)
- Pas 10 - SummaryDocument1 pagePas 10 - SummaryBirdWin WinNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standards Based On Items Impacting Financial StatementsDocument13 pagesAccounting Standards Based On Items Impacting Financial StatementsphotosqueofficialNo ratings yet
- 15 As4Document7 pages15 As4Selvi balanNo ratings yet
- Events After The Reporting Date: Accounting Standard For Local Bodies (ASLB) 14Document14 pagesEvents After The Reporting Date: Accounting Standard For Local Bodies (ASLB) 14kshitijsaxenaNo ratings yet
- 2.ind As 10Document4 pages2.ind As 10Suman SharmaNo ratings yet
- NAS 10 - SummaryDocument2 pagesNAS 10 - Summarysitoulamanish100No ratings yet
- ACC2001 Lecture 6Document44 pagesACC2001 Lecture 6michael krueseiNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Part 2 Event After Reporting Period - A232Document14 pagesTopic 6 - Part 2 Event After Reporting Period - A232balqisNo ratings yet
- LKAS 10 Events After The Reporting Period LKAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities Contigent AssetsDocument63 pagesLKAS 10 Events After The Reporting Period LKAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities Contigent AssetsKogularamanan NithiananthanNo ratings yet
- As 2Document170 pagesAs 2Udit RajNo ratings yet
- Nepal Accounting Standard 10: Events After The Reporting PeriodDocument8 pagesNepal Accounting Standard 10: Events After The Reporting Periodsandeep gyawaliNo ratings yet
- Events After The Reporting Period (MFRS)Document14 pagesEvents After The Reporting Period (MFRS)ShasabellaNo ratings yet
- As PDFDocument158 pagesAs PDFShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- IND AS On Fixed AssetsDocument1 pageIND AS On Fixed Assetschandrakumar k pNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 13 - ISA-560,-MMZ - Compatibility ModeDocument13 pagesLecture - 13 - ISA-560,-MMZ - Compatibility ModeSourav MahadiNo ratings yet
- MFRS 110 Events After The Reporting PeriodDocument8 pagesMFRS 110 Events After The Reporting PeriodSiti Aisyah MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standards: 2.1 AS 4: Contingencies and Events Occurring After The Balance Sheet DateDocument0 pagesAccounting Standards: 2.1 AS 4: Contingencies and Events Occurring After The Balance Sheet DateThéotime HabinezaNo ratings yet
- Finacc 2 6Document7 pagesFinacc 2 6Marielle De LeonNo ratings yet
- LKAS 10 - Events After The Reporting Period - 1556879250 - LKAS 10 - Events After The Reporting PeriodDocument10 pagesLKAS 10 - Events After The Reporting Period - 1556879250 - LKAS 10 - Events After The Reporting PeriodSineth NeththasingheNo ratings yet
- 66638bos53803 cp1Document170 pages66638bos53803 cp1417 Rachit SinglaNo ratings yet
- Ias 10&11Document35 pagesIas 10&11Fariha TasnimNo ratings yet
- Events After The Reporting Date: (Based On Corresponding IPSAS 14)Document13 pagesEvents After The Reporting Date: (Based On Corresponding IPSAS 14)ratiNo ratings yet
- NAS 10 IFRS Reference NoteDocument11 pagesNAS 10 IFRS Reference NoteSujan ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 10 Events After The Reporting PeriodDocument13 pagesIndian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 10 Events After The Reporting PeriodNikhil BabuNo ratings yet
- Quick Notes - MFRS108, MFRS110, MFRS137Document4 pagesQuick Notes - MFRS108, MFRS110, MFRS137Ayda S.No ratings yet
- Events After The Reporting Period: By:-Yohannes NegatuDocument13 pagesEvents After The Reporting Period: By:-Yohannes NegatuEshetie Mekonene AmareNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standards (Group-Ii) : AS - 4: Contingencies and Events Occurring After The Balance Sheet DateDocument14 pagesAccounting Standards (Group-Ii) : AS - 4: Contingencies and Events Occurring After The Balance Sheet DateNitin pandeyNo ratings yet
- Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument4 pagesStatement of Comprehensive Incomebobo tangaNo ratings yet
- DT QB - Capital Gain - Cma CA CsDocument29 pagesDT QB - Capital Gain - Cma CA Cslaplovely544No ratings yet
- Project Report For Manufacturing & Trading of SpicesDocument10 pagesProject Report For Manufacturing & Trading of SpicesSHRUTI AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- To Study The Growth of Mutual Funds Regarding Salaried IndividualsDocument84 pagesTo Study The Growth of Mutual Funds Regarding Salaried Individualschoprapratham764No ratings yet
- Journal To Trial BalanceDocument19 pagesJournal To Trial BalanceIrfan Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- AFM Unit 6Document23 pagesAFM Unit 6harsh singhNo ratings yet
- VOO FactsheetDocument2 pagesVOO FactsheetmartijnNo ratings yet
- Voucher 2023 03 01Document1 pageVoucher 2023 03 01Mir Mazhar Ali MagsiNo ratings yet
- The Altman Z ScoreDocument2 pagesThe Altman Z ScoreNidhi PopliNo ratings yet
- Laporan Keuangan 2020 TeleDocument3 pagesLaporan Keuangan 2020 TeleMT Project EnokNo ratings yet
- Admission of PartnerDocument6 pagesAdmission of PartnerYutika DoshiNo ratings yet
- Draft Public Offering and Trading of Securities DirectiveDocument139 pagesDraft Public Offering and Trading of Securities DirectiveMehari MacNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Working Capital Management at HLL Lifecare Ltd.Document72 pagesAnalysis of Working Capital Management at HLL Lifecare Ltd.Sarangi UthamanNo ratings yet
- Contoh Working Paper-2Document7 pagesContoh Working Paper-2YOLANDA FELY AGASANo ratings yet
- Current AccountDocument15 pagesCurrent AccountMathan RNo ratings yet
- Basic Blank Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) TemplateDocument3 pagesBasic Blank Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) TemplateNamitNo ratings yet
- Ukk 2023 P2-Kunci Jawaban RevDocument47 pagesUkk 2023 P2-Kunci Jawaban RevSaepul RohmanNo ratings yet
- Class 3 - Assurance TopicsDocument13 pagesClass 3 - Assurance TopicsPurple BeastNo ratings yet
- Phu Nhuan Jewelry Joint Stock Company: Financial Analysis ofDocument28 pagesPhu Nhuan Jewelry Joint Stock Company: Financial Analysis ofVân Trang TrầnNo ratings yet
- HDFC Credit Risk Debt Fund - 31 August 2021Document16 pagesHDFC Credit Risk Debt Fund - 31 August 2021Gurvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Intel Corporation Is A Leading Manufacturer of Semiconductor Chips TheDocument1 pageIntel Corporation Is A Leading Manufacturer of Semiconductor Chips TheLet's Talk With HassanNo ratings yet
- Loans - 38614136897 - 01 04 2020 - 31 03 2022Document3 pagesLoans - 38614136897 - 01 04 2020 - 31 03 2022gopal cNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting (Pilot Paper)Document13 pagesManagement Accounting (Pilot Paper)Sujan SanjayNo ratings yet
- WB - Paper-17 CMA FINALDocument131 pagesWB - Paper-17 CMA FINALvijaykumartaxNo ratings yet
- Investment Appraisal 1: Process and MethodsDocument22 pagesInvestment Appraisal 1: Process and MethodsAshura ShaibNo ratings yet
- FM 03 Time Value of MoneyDocument14 pagesFM 03 Time Value of MoneyPrathmesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- DCF Method and Relative ValuationDocument40 pagesDCF Method and Relative ValuationMeghaNo ratings yet