Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsUnit 2 Components
Unit 2 Components
Uploaded by
ngaymaithinhvuonghnCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- CauhoiDocument9 pagesCauhoinguyen hoang phucNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.3-2: Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesInformation Sheet 1.3-2: Learning ObjectivesDan JamesNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.3-2: Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesInformation Sheet 1.3-2: Learning ObjectivesDan JamesNo ratings yet
- TRANSISTORSDocument3 pagesTRANSISTORSIndri SuciNo ratings yet
- Com 223 SimplifiedDocument4 pagesCom 223 SimplifiedKroosNo ratings yet
- Electronic Components (Active vs. Passive)Document5 pagesElectronic Components (Active vs. Passive)Djinn CooNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 2 Activities: Grade 9 Seatwork ActivityDocument5 pagesQ2 Module 2 Activities: Grade 9 Seatwork ActivityIsiah Milan GloriNo ratings yet
- 1 Basic Electronics P1 NotesDocument18 pages1 Basic Electronics P1 NotesEphraem RobinNo ratings yet
- InductorsDocument15 pagesInductorsjoelsilvera874No ratings yet
- InductorsDocument15 pagesInductorsjoelsilvera874No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics M1Document13 pagesBasic Electronics M1roshansingh906585730No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics L1Document19 pagesBasic Electronics L1msellereneNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentsDocument3 pagesElectronic ComponentsAudelio CerezoNo ratings yet
- 3 FC 93 D 5Document3 pages3 FC 93 D 5wkanda techNo ratings yet
- BEC Notes Lecture 2 by Ur Engineering FriendDocument7 pagesBEC Notes Lecture 2 by Ur Engineering Friendapjvlogs0No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument202 pagesUntitledSidharth KapoorNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Electrical ComponentsDocument7 pagesThe Basics of Electrical ComponentsLeunamme G. ComendadorNo ratings yet
- Remote Control LED: Final ProjectDocument18 pagesRemote Control LED: Final ProjectNoman MustafaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Bridge CourseDocument23 pagesBasic Electronics Bridge Courseswarupa.23iseNo ratings yet
- Inductors (Presentation)Document24 pagesInductors (Presentation)joelsilvera874No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics (ES-112)Document29 pagesBasic Electronics (ES-112)Bharat LalNo ratings yet
- Communication With Laser BeamDocument17 pagesCommunication With Laser BeamJagruti MulayNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentsDocument4 pagesElectronic ComponentsvenomousessenceNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Components and Test EquipmentDocument16 pagesBasic Electronic Components and Test EquipmentkamleshyadavmoneyNo ratings yet
- Unit Four (Cuarta Unidad)Document7 pagesUnit Four (Cuarta Unidad)Madewill DuránNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing (NCII) Quarter 4 Module 1 Testing Electronic Components (Tec)Document12 pagesComputer Systems Servicing (NCII) Quarter 4 Module 1 Testing Electronic Components (Tec)Xyreel LagurasNo ratings yet
- Credit-3 Basic ElectronicsDocument66 pagesCredit-3 Basic ElectronicsRamNo ratings yet
- Electronic Materials-G5Document15 pagesElectronic Materials-G5Joana MendoNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Ces - Grade 7 - Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument8 pagesWeek 4 - Ces - Grade 7 - Basic Electronic ComponentsCarl Michael BermudezNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor DevicesDocument12 pagesSemiconductor DevicesElizabeth GogovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Electronic Components & SignalsDocument12 pagesChapter 1. Electronic Components & SignalsPavankumar Gosavi100% (2)
- Instrument and ElectronicsDocument12 pagesInstrument and ElectronicsAshfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cristobal, Rowela - Research Work #4Document17 pagesCristobal, Rowela - Research Work #4rowela cristobalNo ratings yet
- Branches of ElectronicsDocument2 pagesBranches of ElectronicsRyan Patricio Varona100% (1)
- Active & PassiveDocument3 pagesActive & Passivevirendra.aryaNo ratings yet
- Passive Vs Active DevicesDocument4 pagesPassive Vs Active DevicesANGELYN TI-ADNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument10 pagesBasic ElectronicsFrancess Mae AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Interns H 22Document24 pagesInterns H 22www.chandangowda1128No ratings yet
- Electronics Comprises The Physics, Engineering, Technology and Applications That Deal With TheDocument7 pagesElectronics Comprises The Physics, Engineering, Technology and Applications That Deal With TheAditya JainNo ratings yet
- PurshimutuDocument15 pagesPurshimutuwww.chandangowda1128No ratings yet
- Electronics: Electronics Comprises The Physics, Engineering, TechnologyDocument10 pagesElectronics: Electronics Comprises The Physics, Engineering, TechnologyirayoNo ratings yet
- Electronic Component: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesElectronic Component: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSai KarthikNo ratings yet
- Physics 12th Board Proj LaserDocument15 pagesPhysics 12th Board Proj Lasermichelledamian3431No ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument6 pagesTransistorsdeepakvasavaNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument5 pagesComputer Hardwareodunmoolorun dorcasNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument33 pagesLab ManualsimeeraataaddeseeNo ratings yet
- What Are Transistors? Define and Discuss Their Types and FunctionsDocument1 pageWhat Are Transistors? Define and Discuss Their Types and FunctionsPrincess CassidyNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document28 pagesCH 3eyobeshete01No ratings yet
- Analog Electronics - Study Material Author Sarat Kumar Muduli, Mahesweta PattanaikDocument70 pagesAnalog Electronics - Study Material Author Sarat Kumar Muduli, Mahesweta PattanaikvhanzchaprotzNo ratings yet
- EDCDocument7 pagesEDCSrijal KumariNo ratings yet
- Applying Quality StandardDocument58 pagesApplying Quality StandardmardyNo ratings yet
- Robotics HW 3-1Document3 pagesRobotics HW 3-1Awesomus BerjaNo ratings yet
- Clap SwitchDocument16 pagesClap SwitchPiyush RamawatNo ratings yet
- Electronic Materials and Components Introduction To ComponentsDocument23 pagesElectronic Materials and Components Introduction To Componentsazmeer pashaNo ratings yet
- Ayeza Physics AssignmentDocument5 pagesAyeza Physics Assignmentmitraskills83No ratings yet
- Basic Circuit ComponentsDocument3 pagesBasic Circuit ComponentsJhoker SudzNo ratings yet
- What Is Electric Resistance?Document39 pagesWhat Is Electric Resistance?Abdelrhman ElkholyNo ratings yet
- A Printed Circuit BoardDocument7 pagesA Printed Circuit BoardmrhailgvnNo ratings yet
- De Great Tech Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument2 pagesDe Great Tech Basic Electronic Componentsowusu ericNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic OscillationDocument30 pagesElectromagnetic OscillationLokendra Joshi100% (1)
- Autonomous Hazardous Materials Handling Mobile RobotDocument88 pagesAutonomous Hazardous Materials Handling Mobile RobotMomen A. DiabNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 - CH28-31 Test 3Document17 pagesPhysics 2 - CH28-31 Test 3Matheus GroberioNo ratings yet
- US4907483Document23 pagesUS4907483cristianoufo2No ratings yet
- Design Analysis of An Electric Induction Furnace For Melting Aluminum ScrapDocument8 pagesDesign Analysis of An Electric Induction Furnace For Melting Aluminum ScrapToughla Zita LongningNo ratings yet
- Elektrisola Datasheet AlDocument4 pagesElektrisola Datasheet AlCarlos CaraballoNo ratings yet
- Tài Liệu Bếp Từ ElectroluxDocument49 pagesTài Liệu Bếp Từ ElectroluxchuminhNo ratings yet
- SAILOR 6000 MF-HF 150-250-500W Installation Manual 98-130890-CDocument80 pagesSAILOR 6000 MF-HF 150-250-500W Installation Manual 98-130890-CBeneDict Ben D100% (1)
- 400Hz ConverterDocument2 pages400Hz ConverterIlham WaskitoNo ratings yet
- Circuits 2 Laboratory L31A: ScoreDocument20 pagesCircuits 2 Laboratory L31A: ScoreNicoNo ratings yet
- Cblephpl 06Document6 pagesCblephpl 06Harishni ArulvasagamNo ratings yet
- Senior Physics Ipe Imp Question Bank 2019-20Document10 pagesSenior Physics Ipe Imp Question Bank 2019-20Soumendu KonaeNo ratings yet
- RF Design MCQ-1Document16 pagesRF Design MCQ-1JeyavelNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Components in Solar Inverter V1 - YunluDocument36 pagesMagnetic Components in Solar Inverter V1 - YunluMeng ZhongNo ratings yet
- Training 400 KV SubstaionDocument69 pagesTraining 400 KV SubstaionDeepak Yadav100% (1)
- XII Phy New Chap 07 Alternating Current 91 A&R Items Full ChapterDocument5 pagesXII Phy New Chap 07 Alternating Current 91 A&R Items Full ChapterjaidityaNo ratings yet
- Sanyo Air Conditioner ManualDocument85 pagesSanyo Air Conditioner ManualrjjmejNo ratings yet
- Asrs Report by RakshaDocument85 pagesAsrs Report by RakshaRaksha Harsh KaushikNo ratings yet
- 005 Xii Phy Sample Question Paper 03Document11 pages005 Xii Phy Sample Question Paper 03Upendra MandalNo ratings yet
- Detailed Solution of IES 2103 (ECE) Objective Paper - I: Set - A'Document12 pagesDetailed Solution of IES 2103 (ECE) Objective Paper - I: Set - A'vijaynarayan guptaNo ratings yet
- 15537540281Document20 pages15537540281RohanNo ratings yet
- EE QuestionsDocument25 pagesEE QuestionsJohn Raymond LumanlanNo ratings yet
- Design Challenges For Distributed Power Systems, 2006Document15 pagesDesign Challenges For Distributed Power Systems, 2006g2908699No ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Electricity and Electronics 6Th Edition Stan Gibilisco Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Electricity and Electronics 6Th Edition Stan Gibilisco Online Ebook All Chapter PDFjames.pickett954100% (13)
- High-Precision Rogowski Coils For Improved Relay Protection, Control and MeasurementsDocument2 pagesHigh-Precision Rogowski Coils For Improved Relay Protection, Control and Measurementskhaled1512No ratings yet
- Resonant Circuits11Document28 pagesResonant Circuits11Srujana Dec100% (1)
- Panasonic GLP23A Chasis SchematicsDocument39 pagesPanasonic GLP23A Chasis SchematicsAngelescuO100% (1)
- 12V To 24V DC DC ConverterDocument4 pages12V To 24V DC DC ConverterDavid Arrata ParralesNo ratings yet
- Revised Curriculum of Electrical Engineering (UET) 2019Document169 pagesRevised Curriculum of Electrical Engineering (UET) 2019Qazi Faiz Ullah Qazi Zaki UllahNo ratings yet
- Paper 10Document8 pagesPaper 10zeeltarpara97560No ratings yet
Unit 2 Components
Unit 2 Components
Uploaded by
ngaymaithinhvuonghn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Unit 2 components
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesUnit 2 Components
Unit 2 Components
Uploaded by
ngaymaithinhvuonghnCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Unit 2: Components
Reading and Speaking 1
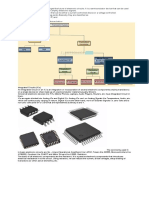
1. How can electronic components be classified?
- Electronic components can be classified into three main categories:
passive, active, electromechanical.
2. What is the MOSFET? What are its advantages?
- The MOSFET was the first truly compact transistor that could be
miniaturized and mass-produced for a wide range of uses. Its
advantages include high scalability, affordability low power
consumption, and high density.
3. What is the electronic components?
- An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical
entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their
associated fields.
4. What is the difference between passive component and active
component?
- Active components rely on a source of energy. Passive components
can’t rely on a source of power.
Reading and Speaking 2
1. How many types of transistor? What are they? What is the difference
between them?
- There are two types of transistors, a bipolar transistor has terminals
labeled base, collector, and emitter. For a field-effect transistor, the
terminals are labeled gate, source, and drain.
2. What are most transistors made from?
- Most transistors are made from very pure silicon, and some
germanium.
3. What does the essential usefulness of a transistor come from?
- The essential usefulness of a transistor comes from its ability to use a
small signal applied between one pair of its terminals to control a
much larger signal at another pair of terminals
4. What is a transistor? What is it composed?
- A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch
electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of
semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for
connection to an external circuit.
Reading and Speaking 3
1. What advantages do integrated circuits have over discrete circuits?
Does they have any disadvantages? If yes, what are they?
- Advantages: cost and performance
- Disadvantage: high design cost
2. How are integrated circuits classified?
- Analog ICs, Digital ICs, and Mixed-Signal ICs
3. What equipments are integrated circuits used now?
- Computers, mobile phones, and other digital home
4. How were integrated circuits made practical?
- Integrated circuits were made practical by technological advancements
in metal–oxide–silicon (MOS) semiconductor device fabrication
Reading and Speaking 4
1. How many passive electronic components are mentioned in the
passages? What are they?
- Resistors, capacitors and inductors
2. What is a capacitor? What do most capacitors contain? Where are
capacitors widely used? What are they used for?
- A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field.
It is a passive electronic component with two terminals. Capacitors are
widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical
devices.
3. What is an inductor? What does an inductor typically consist of?
- An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two
terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field
when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists
of an insulated wire wound into a coil around a core.
4. What is a resistor? How is its electrical function specified?
- A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that
implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.
You might also like
- CauhoiDocument9 pagesCauhoinguyen hoang phucNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.3-2: Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesInformation Sheet 1.3-2: Learning ObjectivesDan JamesNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.3-2: Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesInformation Sheet 1.3-2: Learning ObjectivesDan JamesNo ratings yet
- TRANSISTORSDocument3 pagesTRANSISTORSIndri SuciNo ratings yet
- Com 223 SimplifiedDocument4 pagesCom 223 SimplifiedKroosNo ratings yet
- Electronic Components (Active vs. Passive)Document5 pagesElectronic Components (Active vs. Passive)Djinn CooNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 2 Activities: Grade 9 Seatwork ActivityDocument5 pagesQ2 Module 2 Activities: Grade 9 Seatwork ActivityIsiah Milan GloriNo ratings yet
- 1 Basic Electronics P1 NotesDocument18 pages1 Basic Electronics P1 NotesEphraem RobinNo ratings yet
- InductorsDocument15 pagesInductorsjoelsilvera874No ratings yet
- InductorsDocument15 pagesInductorsjoelsilvera874No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics M1Document13 pagesBasic Electronics M1roshansingh906585730No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics L1Document19 pagesBasic Electronics L1msellereneNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentsDocument3 pagesElectronic ComponentsAudelio CerezoNo ratings yet
- 3 FC 93 D 5Document3 pages3 FC 93 D 5wkanda techNo ratings yet
- BEC Notes Lecture 2 by Ur Engineering FriendDocument7 pagesBEC Notes Lecture 2 by Ur Engineering Friendapjvlogs0No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument202 pagesUntitledSidharth KapoorNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Electrical ComponentsDocument7 pagesThe Basics of Electrical ComponentsLeunamme G. ComendadorNo ratings yet
- Remote Control LED: Final ProjectDocument18 pagesRemote Control LED: Final ProjectNoman MustafaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Bridge CourseDocument23 pagesBasic Electronics Bridge Courseswarupa.23iseNo ratings yet
- Inductors (Presentation)Document24 pagesInductors (Presentation)joelsilvera874No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics (ES-112)Document29 pagesBasic Electronics (ES-112)Bharat LalNo ratings yet
- Communication With Laser BeamDocument17 pagesCommunication With Laser BeamJagruti MulayNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentsDocument4 pagesElectronic ComponentsvenomousessenceNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Components and Test EquipmentDocument16 pagesBasic Electronic Components and Test EquipmentkamleshyadavmoneyNo ratings yet
- Unit Four (Cuarta Unidad)Document7 pagesUnit Four (Cuarta Unidad)Madewill DuránNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing (NCII) Quarter 4 Module 1 Testing Electronic Components (Tec)Document12 pagesComputer Systems Servicing (NCII) Quarter 4 Module 1 Testing Electronic Components (Tec)Xyreel LagurasNo ratings yet
- Credit-3 Basic ElectronicsDocument66 pagesCredit-3 Basic ElectronicsRamNo ratings yet
- Electronic Materials-G5Document15 pagesElectronic Materials-G5Joana MendoNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Ces - Grade 7 - Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument8 pagesWeek 4 - Ces - Grade 7 - Basic Electronic ComponentsCarl Michael BermudezNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor DevicesDocument12 pagesSemiconductor DevicesElizabeth GogovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Electronic Components & SignalsDocument12 pagesChapter 1. Electronic Components & SignalsPavankumar Gosavi100% (2)
- Instrument and ElectronicsDocument12 pagesInstrument and ElectronicsAshfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cristobal, Rowela - Research Work #4Document17 pagesCristobal, Rowela - Research Work #4rowela cristobalNo ratings yet
- Branches of ElectronicsDocument2 pagesBranches of ElectronicsRyan Patricio Varona100% (1)
- Active & PassiveDocument3 pagesActive & Passivevirendra.aryaNo ratings yet
- Passive Vs Active DevicesDocument4 pagesPassive Vs Active DevicesANGELYN TI-ADNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument10 pagesBasic ElectronicsFrancess Mae AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Interns H 22Document24 pagesInterns H 22www.chandangowda1128No ratings yet
- Electronics Comprises The Physics, Engineering, Technology and Applications That Deal With TheDocument7 pagesElectronics Comprises The Physics, Engineering, Technology and Applications That Deal With TheAditya JainNo ratings yet
- PurshimutuDocument15 pagesPurshimutuwww.chandangowda1128No ratings yet
- Electronics: Electronics Comprises The Physics, Engineering, TechnologyDocument10 pagesElectronics: Electronics Comprises The Physics, Engineering, TechnologyirayoNo ratings yet
- Electronic Component: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesElectronic Component: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSai KarthikNo ratings yet
- Physics 12th Board Proj LaserDocument15 pagesPhysics 12th Board Proj Lasermichelledamian3431No ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument6 pagesTransistorsdeepakvasavaNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument5 pagesComputer Hardwareodunmoolorun dorcasNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument33 pagesLab ManualsimeeraataaddeseeNo ratings yet
- What Are Transistors? Define and Discuss Their Types and FunctionsDocument1 pageWhat Are Transistors? Define and Discuss Their Types and FunctionsPrincess CassidyNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document28 pagesCH 3eyobeshete01No ratings yet
- Analog Electronics - Study Material Author Sarat Kumar Muduli, Mahesweta PattanaikDocument70 pagesAnalog Electronics - Study Material Author Sarat Kumar Muduli, Mahesweta PattanaikvhanzchaprotzNo ratings yet
- EDCDocument7 pagesEDCSrijal KumariNo ratings yet
- Applying Quality StandardDocument58 pagesApplying Quality StandardmardyNo ratings yet
- Robotics HW 3-1Document3 pagesRobotics HW 3-1Awesomus BerjaNo ratings yet
- Clap SwitchDocument16 pagesClap SwitchPiyush RamawatNo ratings yet
- Electronic Materials and Components Introduction To ComponentsDocument23 pagesElectronic Materials and Components Introduction To Componentsazmeer pashaNo ratings yet
- Ayeza Physics AssignmentDocument5 pagesAyeza Physics Assignmentmitraskills83No ratings yet
- Basic Circuit ComponentsDocument3 pagesBasic Circuit ComponentsJhoker SudzNo ratings yet
- What Is Electric Resistance?Document39 pagesWhat Is Electric Resistance?Abdelrhman ElkholyNo ratings yet
- A Printed Circuit BoardDocument7 pagesA Printed Circuit BoardmrhailgvnNo ratings yet
- De Great Tech Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument2 pagesDe Great Tech Basic Electronic Componentsowusu ericNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic OscillationDocument30 pagesElectromagnetic OscillationLokendra Joshi100% (1)
- Autonomous Hazardous Materials Handling Mobile RobotDocument88 pagesAutonomous Hazardous Materials Handling Mobile RobotMomen A. DiabNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 - CH28-31 Test 3Document17 pagesPhysics 2 - CH28-31 Test 3Matheus GroberioNo ratings yet
- US4907483Document23 pagesUS4907483cristianoufo2No ratings yet
- Design Analysis of An Electric Induction Furnace For Melting Aluminum ScrapDocument8 pagesDesign Analysis of An Electric Induction Furnace For Melting Aluminum ScrapToughla Zita LongningNo ratings yet
- Elektrisola Datasheet AlDocument4 pagesElektrisola Datasheet AlCarlos CaraballoNo ratings yet
- Tài Liệu Bếp Từ ElectroluxDocument49 pagesTài Liệu Bếp Từ ElectroluxchuminhNo ratings yet
- SAILOR 6000 MF-HF 150-250-500W Installation Manual 98-130890-CDocument80 pagesSAILOR 6000 MF-HF 150-250-500W Installation Manual 98-130890-CBeneDict Ben D100% (1)
- 400Hz ConverterDocument2 pages400Hz ConverterIlham WaskitoNo ratings yet
- Circuits 2 Laboratory L31A: ScoreDocument20 pagesCircuits 2 Laboratory L31A: ScoreNicoNo ratings yet
- Cblephpl 06Document6 pagesCblephpl 06Harishni ArulvasagamNo ratings yet
- Senior Physics Ipe Imp Question Bank 2019-20Document10 pagesSenior Physics Ipe Imp Question Bank 2019-20Soumendu KonaeNo ratings yet
- RF Design MCQ-1Document16 pagesRF Design MCQ-1JeyavelNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Components in Solar Inverter V1 - YunluDocument36 pagesMagnetic Components in Solar Inverter V1 - YunluMeng ZhongNo ratings yet
- Training 400 KV SubstaionDocument69 pagesTraining 400 KV SubstaionDeepak Yadav100% (1)
- XII Phy New Chap 07 Alternating Current 91 A&R Items Full ChapterDocument5 pagesXII Phy New Chap 07 Alternating Current 91 A&R Items Full ChapterjaidityaNo ratings yet
- Sanyo Air Conditioner ManualDocument85 pagesSanyo Air Conditioner ManualrjjmejNo ratings yet
- Asrs Report by RakshaDocument85 pagesAsrs Report by RakshaRaksha Harsh KaushikNo ratings yet
- 005 Xii Phy Sample Question Paper 03Document11 pages005 Xii Phy Sample Question Paper 03Upendra MandalNo ratings yet
- Detailed Solution of IES 2103 (ECE) Objective Paper - I: Set - A'Document12 pagesDetailed Solution of IES 2103 (ECE) Objective Paper - I: Set - A'vijaynarayan guptaNo ratings yet
- 15537540281Document20 pages15537540281RohanNo ratings yet
- EE QuestionsDocument25 pagesEE QuestionsJohn Raymond LumanlanNo ratings yet
- Design Challenges For Distributed Power Systems, 2006Document15 pagesDesign Challenges For Distributed Power Systems, 2006g2908699No ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Electricity and Electronics 6Th Edition Stan Gibilisco Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Electricity and Electronics 6Th Edition Stan Gibilisco Online Ebook All Chapter PDFjames.pickett954100% (13)
- High-Precision Rogowski Coils For Improved Relay Protection, Control and MeasurementsDocument2 pagesHigh-Precision Rogowski Coils For Improved Relay Protection, Control and Measurementskhaled1512No ratings yet
- Resonant Circuits11Document28 pagesResonant Circuits11Srujana Dec100% (1)
- Panasonic GLP23A Chasis SchematicsDocument39 pagesPanasonic GLP23A Chasis SchematicsAngelescuO100% (1)
- 12V To 24V DC DC ConverterDocument4 pages12V To 24V DC DC ConverterDavid Arrata ParralesNo ratings yet
- Revised Curriculum of Electrical Engineering (UET) 2019Document169 pagesRevised Curriculum of Electrical Engineering (UET) 2019Qazi Faiz Ullah Qazi Zaki UllahNo ratings yet
- Paper 10Document8 pagesPaper 10zeeltarpara97560No ratings yet