Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fibre Crops
Fibre Crops
Uploaded by
parth.dhameja0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesFibre Crops
Fibre Crops
Uploaded by
parth.dhamejaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
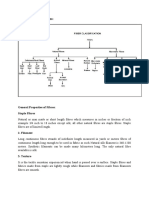
Fibre crops
(Parth D) Introduction: Good morning to one and all today
our group is going to brief you all about fibre crops.
(Parth T)What are fibre crops?
Fibre crops are field crops known for their fibre which are,
traditionally used to make paper, cloth or rope. Fiber crops
are called "fiber crops" because they are cultivated primarily
for the fibers they produce. These fibers are used in various
industries to make textiles, paper, and other products.
Examples of fiber crops include cotton, flax, hemp, and jute.
There are 2 fibre crops that are we going talk about today.
Cotton and Jute:
1) (Parth P) Cotton: Cotton is a soft, fluffy fibre that grows
in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of
cotton plants. It is one of the most important fiber crops
in the world, used in a variety of products from clothing
to home furnishings. It grows in dry tropical and sub-
tropical regions of the world. The major cultivators of
cotton are USA, India, China, Egypt, Pakistan And
Russia. India has the largest area in cotton production.
Recently India has surpassed China as the largest
producer of cotton in the world. In India about 70 percent
of total cotton is produced in Maharashtra, Gujrat,
Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Rajasthan.
What are the requirements for growing cotton: Tropical and
sub tropical climates are the best places to grow cotton. It
require a long period of sunshine and moderate rainfall
during the time of sowing.
(Parth D) Jute: Jute, often called the "golden fiber," is a fast-
growing natural plant fiber similar to bamboo. It's strong,
affordable, and eco-friendly. India and China are the world's
largest jute producers, with India's main producing region
being West Bengal. Jute is used for various products,
including sacks, bags, mats, ropes, and twine. Its rapid growth
and biodegradability make it environmentally friendly.
Requirements for growing jute: Jute cultivation is supported
by clayey loam or sandy loam soil. Excessive rainfall and
water logging is harmful for jute plants. Generally, March to
May is the sowing season for jute plants in India, but it also
depends on the rainfall and soil type of the specific region.
Depending on the time of sowing, the harvesting can be done
between June and September. Hot and humid climate with
temperature ranging from 24°C to 37°C is ideal for jute
plantation.
(Parth P)Ending: Thank you all for giving us your time and we
hope u liked the presentation.
You might also like
- Validating The Brain Injury GuidelinesDocument9 pagesValidating The Brain Injury GuidelinesMarcus CezilloNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument2 pagesBusiness PlanShradha Gupta100% (1)
- DuctDocument100 pagesDuctSam100% (3)
- Zoomlion TC6520-10D - Foundation - 101114Document32 pagesZoomlion TC6520-10D - Foundation - 101114achsangantengNo ratings yet
- Jute Jute Products AssignmentDocument12 pagesJute Jute Products AssignmentSuaiba SebaNo ratings yet
- Jute and CottonDocument15 pagesJute and CottonDeepika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Agriculture: Nitrogen CycleDocument5 pagesAgriculture: Nitrogen CycleVikash SoniNo ratings yet
- Cotton and JuteDocument7 pagesCotton and JutedarshanpandaNo ratings yet
- Organization StudyDocument59 pagesOrganization StudysharonjohneyNo ratings yet
- Seed FiberDocument57 pagesSeed FiberMurad HossainNo ratings yet
- Mid Term TEX 111Document8 pagesMid Term TEX 111Mainur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Cotton - A Natural Fiber: Free Days. The Most Important Cotton-Growing Countries Are The USA, China, India, PakistanDocument3 pagesCotton - A Natural Fiber: Free Days. The Most Important Cotton-Growing Countries Are The USA, China, India, PakistancieloypiedraNo ratings yet
- CottonDocument9 pagesCottonh.wasif457No ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Study On Jute FiberDocument51 pagesA Comprehensive Study On Jute FiberAsad Amir100% (2)
- Fiber CropsDocument3 pagesFiber Cropsmalath bash100% (1)
- Ecofriendly Usage of JUTE and Its HARVESTINGDocument5 pagesEcofriendly Usage of JUTE and Its HARVESTINGsouvik paulNo ratings yet
- Project SreenathDocument42 pagesProject SreenathSreenath SudhakaranNo ratings yet
- Unconventional Fibre PlantsDocument18 pagesUnconventional Fibre PlantsRajendra Singh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process and Properties of Cotton FiberDocument25 pagesManufacturing Process and Properties of Cotton FibersandhyaRanimohanty100% (4)
- Fiber, Yarn, Fabrics 3Document18 pagesFiber, Yarn, Fabrics 3Mahadi HabibNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Job Satisfaction by KishoreDocument83 pagesProject Report On Job Satisfaction by KishoreYellaturi Siva Kishore ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cotton Hai YeDocument7 pagesCotton Hai Yerahul0751No ratings yet
- Jute 123Document2 pagesJute 123shmlnajeeb1No ratings yet
- The Plant The Fibre Producers: Cotton Is Almost Pure CelluloseDocument3 pagesThe Plant The Fibre Producers: Cotton Is Almost Pure CelluloseVasudha NagpalNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Study On Jute Fiber PDFDocument51 pagesA Comprehensive Study On Jute Fiber PDFRenato GuimaraesNo ratings yet
- Fibre Crops, Bamboo, Timber - FinalDocument109 pagesFibre Crops, Bamboo, Timber - Finalsggdgd100% (1)
- JuteDocument16 pagesJuteAviral VermaNo ratings yet
- Fiber To FabricsDocument36 pagesFiber To Fabricskirtinagda100% (5)
- Jute Presentation IBDocument18 pagesJute Presentation IBRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- JUTE Plant Time PaperDocument6 pagesJUTE Plant Time PaperAbdulroheem AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Botanical Classification of CottonDocument6 pagesBotanical Classification of Cottontex_hasan_014No ratings yet
- CottonDocument2 pagesCottonXeniya777No ratings yet
- YE 101 Lecture-6 Jute 2nd PartDocument34 pagesYE 101 Lecture-6 Jute 2nd Partjiban srNo ratings yet
- The Word Textile Comes From The Latin Verb Texere, Meaning To Weave. TraditionallyDocument16 pagesThe Word Textile Comes From The Latin Verb Texere, Meaning To Weave. TraditionallysanketNo ratings yet
- Indian Cash Crops - Cotton, Jute & RubberDocument8 pagesIndian Cash Crops - Cotton, Jute & RubberUdit BalyanNo ratings yet
- Safari - 17-Sep-2020 at 2:07 PMDocument1 pageSafari - 17-Sep-2020 at 2:07 PMSantosh J Yadav's FriendNo ratings yet
- 5 Sustainable Material To Look Out For in 2023Document5 pages5 Sustainable Material To Look Out For in 2023Srija dasNo ratings yet
- How Feasible Is Paper Made of JuteDocument3 pagesHow Feasible Is Paper Made of JuteMohammad Shahjahan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The Jute Industry of IndiaDocument4 pagesAn Overview of The Jute Industry of IndiaRSBALAKUMARNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument66 pagesProjectkarthikeyan.artsNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document14 pagesUnit 7Dr. Shriram KunjamNo ratings yet
- Cotton: Botanical NameDocument14 pagesCotton: Botanical NameGowardhanNo ratings yet
- Operations Research ReportDocument30 pagesOperations Research ReportVenkatesh RajuNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Fibre To Fabric Sample QuestionsDocument3 pagesGrade 6 Fibre To Fabric Sample Questionsmohamedaahil12318No ratings yet
- Statement of The Problem:: Fiber Seeds Genus Cellulose Shrub Americas Africa India Mexico Australia AfricaDocument7 pagesStatement of The Problem:: Fiber Seeds Genus Cellulose Shrub Americas Africa India Mexico Australia AfricaMark Angelo DiazNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-Cotton PDFDocument25 pagesUnit 4-Cotton PDFFuad HamidNo ratings yet
- Fiber Plants & DiscussionDocument10 pagesFiber Plants & DiscussionvishcrimeNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Study of Textile From Fiber To FashionDocument10 pagesComprehensive Study of Textile From Fiber To Fashiondeepakshi.inNo ratings yet
- Types of Fibres - Class 6, Fibre To FabricDocument5 pagesTypes of Fibres - Class 6, Fibre To FabricPriyaNo ratings yet
- Nylon - : Plastic Molecular WeightDocument3 pagesNylon - : Plastic Molecular WeightStela WinxNo ratings yet
- Advanced Technologies For Textile and Fashion IndustryDocument5 pagesAdvanced Technologies For Textile and Fashion Industryfamilia -gentileNo ratings yet
- Sheet - Introduction To CottonDocument7 pagesSheet - Introduction To CottonNafim Al SadikNo ratings yet
- Environmentally Friendly, Eco-Friendly Products, Natural Products, Biodegradable Plastics, Natural Dyes and Pigments, Jute Products, Natural FibersDocument9 pagesEnvironmentally Friendly, Eco-Friendly Products, Natural Products, Biodegradable Plastics, Natural Dyes and Pigments, Jute Products, Natural FibersJahangir Alam KallalNo ratings yet
- A Treatise On Cotton FiberDocument5 pagesA Treatise On Cotton FiberRobotrixNo ratings yet
- 6825 29541 1 PBDocument7 pages6825 29541 1 PBNKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - PART 1-NATURAL (Cotton)Document67 pagesChapter 2 - PART 1-NATURAL (Cotton)XuanNo ratings yet
- Classification of FibresDocument12 pagesClassification of FibresARYAN RATHORENo ratings yet
- CoirDocument34 pagesCoirMithun KiruthiNo ratings yet
- Hemp Hurds as Paper-Making Material United States Department of Agriculture, Bulletin No. 404From EverandHemp Hurds as Paper-Making Material United States Department of Agriculture, Bulletin No. 404No ratings yet
- The Green Wardrobe Guide: Finding Eco-Chic Fashions That Look Great and Help Save the PlanetFrom EverandThe Green Wardrobe Guide: Finding Eco-Chic Fashions That Look Great and Help Save the PlanetNo ratings yet
- en 12676 1 00 Anti Glare Systems For Roads PDFDocument31 pagesen 12676 1 00 Anti Glare Systems For Roads PDFLidia GheraliuNo ratings yet
- Load Balancing in LteDocument5 pagesLoad Balancing in LteAli AnisNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument3 pagesReview of Related LiteratureGap SeamanNo ratings yet
- External BallisticsDocument16 pagesExternal Ballisticsblowmeasshole1911100% (1)
- BENNING HD600 (R2 10) 3baDocument2 pagesBENNING HD600 (R2 10) 3bamoumtazzNo ratings yet
- Dukane TS200 Technical ManualDocument9 pagesDukane TS200 Technical ManualTom MaboetieNo ratings yet
- Malaysian Earth Science Olympiad - Set 1Document5 pagesMalaysian Earth Science Olympiad - Set 1Lee Sun TaiNo ratings yet
- FADECDocument4 pagesFADECAman OjhaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline ParasitologyDocument6 pagesCourse Outline ParasitologyNichole SilverioNo ratings yet
- Ap English Literature and Composition 2022 FRQDocument6 pagesAp English Literature and Composition 2022 FRQAnitaNo ratings yet
- Composite FailureDocument28 pagesComposite FailurerhinemineNo ratings yet
- Abekavo PreliminaryDocument11 pagesAbekavo PreliminaryAdah EneNo ratings yet
- Clinical Skills Cranial Nerves I To VI Students Copy 2019Document4 pagesClinical Skills Cranial Nerves I To VI Students Copy 2019carlosNo ratings yet
- Aviation ReportDocument22 pagesAviation ReportNguyen LinhNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Cummins 6LTAA8.9 G2Document4 pagesCatalogue Cummins 6LTAA8.9 G2akbar muslim100% (1)
- Drinking Games Sarah Levy Full ChapterDocument67 pagesDrinking Games Sarah Levy Full Chapterivan.jones400100% (9)
- Nissan Pathfider 2005 ManualDocument84 pagesNissan Pathfider 2005 ManualDragos StefanNo ratings yet
- 4.drug Metabolism (Biotransformation)Document33 pages4.drug Metabolism (Biotransformation)Osama KhanNo ratings yet
- TRANSMISSION CONTROL VALVE (2 - 2) - Wheel Loader Komatsu WA120-1 - TORQUE CONVERTER AND TRANSMISSION 777partsDocument2 pagesTRANSMISSION CONTROL VALVE (2 - 2) - Wheel Loader Komatsu WA120-1 - TORQUE CONVERTER AND TRANSMISSION 777partsashraf elsayedNo ratings yet
- 100-Meter Sprint Running Event Analysis and Programming ofDocument109 pages100-Meter Sprint Running Event Analysis and Programming ofphilemon tam100% (1)
- Safepro Fire - DLP - PPT - Fire Suppression - SafeproDocument21 pagesSafepro Fire - DLP - PPT - Fire Suppression - SafeproSUHAIL SafePro Fire0% (1)
- About CargilDocument2 pagesAbout CargilVarsha KastureNo ratings yet
- Environment and Society 1St Ed Edition Magnus Bostrom Full ChapterDocument67 pagesEnvironment and Society 1St Ed Edition Magnus Bostrom Full Chapterbetty.barabas349100% (10)
- Adobe Corporate Office, NoidaDocument7 pagesAdobe Corporate Office, NoidaChaahat SoniNo ratings yet
- Оймсны машинDocument3 pagesОймсны машинLyracism UguumurNo ratings yet
- TextileDocument29 pagesTextileEkta BhagatNo ratings yet