Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec)
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec)
Uploaded by
KhaLid ErjaliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec)
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec)
Uploaded by
KhaLid ErjaliCopyright:
Available Formats
IPsec- Internet Protocol Security
IPsec is framework that help us to protect IP traffic on the
network layer .
IP protocol itself does not have any security features at all IPSEC can protect our
traffic with the following features:
Confidentiality: By encrypting our data , nobody expect the
sender and receiver will be able to read our data
Intergrity : We want to make sure that nobody changes the data in
our packet , by calculating a hash value , the sender and receiver
will be able to check if changes have been made to the packet
Authentication: The sender an receiver will authenticate the
each other to make sure that we are really talking to with the
device we intend to .
Anti-reply: Even if packet is encrypted and authenticated , an
attacker could try to capture these packets and send them again.
By using sequence number, IPSEC will not transmit any duplicate
packets.
Before we can protect any IP Packet we need to IPsec peer that
builds IPsec Tunnel.
To establish the IPsec tunnel , we use protocol called IKE (Internet Key Exchange)
IPsec- Internet Protocol Security 1
There are two phases to build an IPsec Tunnel:
1. IKE version 1
2. IKE Version 2
In IKE phase 1, two peers will negotiate about the encryption, authentication,
hashing and the other protocols that they want to use some other parameter that
are required. In the phase, an ISAKMP (internet security Association and key
Management Protocol) session established . This is also called the ISAKMP tunnel
or IKE phase 1 tunnel .
The collection of parameter that the two devices will use is called SA (security
Association)
The IKE phase 1 tunnels is only used for management traffic . We use this tunnel
as secure method to established the second tunnel called IKE Phase 2 tunnel or
IPSEC Tunnel and for the management traffic like keepalives.
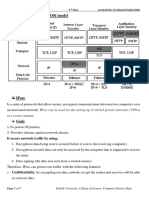
Here is a picture of our two router completed IKE Phase 2
IPsec- Internet Protocol Security 2
Once the IKE phase 2 is completed, we have an IKE phase 2 tunnel (or IPsec
Tunnel) that we can use to protect our data. The user data will sent through the
IKE phase 2 tunnel .
IKE builds the tunnel for us but it does not authenticate or
encrypt user data. We use two other protocol for this:
AH ( Authentication Header)
ESP ( Encapsulating security Payload)
💡 AH and ESP both offer authentication and integrity but only ESP
supports encryption. Because of this, ESP is the most popular choice
nowadays.
Both protocol support two different modes:
Transport Mode
Tunnel Mode
The main difference of between the two is that with the transport mode we will
use the original IP Header wile in Tunnel mode , we use new IP Header :
IPsec- Internet Protocol Security 3
Transport is often between two devices that want to protect some
insecure traffic . (example telnet traffic)
Tunnel Mode is technically used for site to site VPNs where we
need to encapsulate the original IP packet since these are mostly
private IP address and it cant be routed on the internet.
The Entire process of IPSEC consists of Five step:
Initiation: something has to trigger the creation of our tunnels. For example
when you configure IPsec on a router, you use an access-list to tell the router
what data to protect. When the router receives something that matches the
access-list, it will start the IKE process. It’s also possible to manually initiate
the tunnel.
IKE phase 1: we negotiate a security association to build the IKE phase 1
tunnel (ISAKMP tunnel).
IKE phase 2: within the IKE phase 1 tunnel, we build the IKE phase 2 tunnel
(IPsec tunnel).
Data transfer: we protect user data by sending it through the IKE phase 2
tunnel.
IPsec- Internet Protocol Security 4
Termination: when there is no user data to protect then the IPsec tunnel will
be terminated after awhile.
IPsec- Internet Protocol Security 5
You might also like
- IPSEC VPN Troubleshooting Scenarios 1662193543Document24 pagesIPSEC VPN Troubleshooting Scenarios 1662193543shan1512No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Time Domain Response First Order SystemDocument11 pagesChapter 5 Time Domain Response First Order SystemZiad ObeidNo ratings yet
- 39-IPSEC Site To Site VPNsDocument4 pages39-IPSEC Site To Site VPNsZoubert AnasNo ratings yet
- Security Protocols in The Osi Model: IpsecDocument7 pagesSecurity Protocols in The Osi Model: IpsecEvan ahmed abdulkadirNo ratings yet
- IPSEC Tunnel Config and ExplainDocument5 pagesIPSEC Tunnel Config and Explaindakodo3166No ratings yet
- Internet Protocol (IP) : Internet Protocol (IP) : It Is The Method or Protocol by Which Data IsDocument11 pagesInternet Protocol (IP) : Internet Protocol (IP) : It Is The Method or Protocol by Which Data IsMirza SulmamNo ratings yet
- IPsec is designed to provide interoperableDocument2 pagesIPsec is designed to provide interoperablepunitdubey.eceNo ratings yet
- Expt 09 MinorDocument2 pagesExpt 09 Minorsakshi gaikwadNo ratings yet
- IPSecDocument25 pagesIPSecDinesh ParasharNo ratings yet
- L2TP., IP SecDocument18 pagesL2TP., IP Secmahsa ahmadzaiNo ratings yet
- Web SecurityDocument17 pagesWeb SecurityUchiha SasukeNo ratings yet
- Ipsec: 4 Key Functions or Services of Ipsec Are As FollowsDocument9 pagesIpsec: 4 Key Functions or Services of Ipsec Are As FollowsRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Network Security EssentialsDocument33 pagesNetwork Security EssentialsMin LwinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 NDS REPORTDocument20 pagesAssignment 2 NDS REPORTZhen WeiNo ratings yet
- Ipsec Implementation: Leah M. Pakula Jonathan Pass Kevin Fleming Oleg Morozov Jeff BrownDocument23 pagesIpsec Implementation: Leah M. Pakula Jonathan Pass Kevin Fleming Oleg Morozov Jeff BrowneswaranslmNo ratings yet
- VPN Detailed Notes 1664625366Document12 pagesVPN Detailed Notes 1664625366awa fayeNo ratings yet
- Advanced Features of Linux Strongswan The Opensource VPN SolutionDocument17 pagesAdvanced Features of Linux Strongswan The Opensource VPN SolutionThinh LeNo ratings yet
- Ipsec Site-To-Site VPN TutorialDocument3 pagesIpsec Site-To-Site VPN TutorialVisakh VijayNo ratings yet
- IPsec - 2 Problems (Eng)Document19 pagesIPsec - 2 Problems (Eng)Marina HuberNo ratings yet
- Ip Security: Submitted To: Prof, Abdul HananDocument17 pagesIp Security: Submitted To: Prof, Abdul HananArslan Kamran JuttNo ratings yet
- VPN Interview Questions and AnswersDocument7 pagesVPN Interview Questions and AnswersMD IRFANNo ratings yet
- What Is VPNTDocument3 pagesWhat Is VPNTVineeth BabuNo ratings yet
- IPSECDocument4 pagesIPSECtoyisi5546No ratings yet
- The Idea To Encrypt and Seal The Transport and Application Layer Data During Transmission Also Offer Integrity Protection Is Called IP SecurityDocument18 pagesThe Idea To Encrypt and Seal The Transport and Application Layer Data During Transmission Also Offer Integrity Protection Is Called IP Securityrh_rathodNo ratings yet
- Cisco VPNDocument123 pagesCisco VPNChinni ChiNo ratings yet
- Ipsec: Authentication Header (Ah) : The Ah Protocol Provides A Mechanism ForDocument2 pagesIpsec: Authentication Header (Ah) : The Ah Protocol Provides A Mechanism ForGaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- 32-08 Site-to-Site Virtual Private NetworksDocument13 pages32-08 Site-to-Site Virtual Private Networksabhinaskari1No ratings yet
- Internet Key Exchange (IKEv2) ProtocolDocument10 pagesInternet Key Exchange (IKEv2) ProtocolPrashant TiwariNo ratings yet
- IPSec Basics HandoutsDocument20 pagesIPSec Basics HandoutsJame JameNo ratings yet
- IP SecurityDocument10 pagesIP Securitypray71No ratings yet
- Connection SecurityDocument52 pagesConnection SecurityQuangHuyĐoànNo ratings yet
- Virtual Private Networking BasicsDocument14 pagesVirtual Private Networking BasicsManeeshaNo ratings yet
- Demystifying Ipsec VPN'S 1Document21 pagesDemystifying Ipsec VPN'S 1David MaasNo ratings yet
- Crypto Map Based IPsec VPN FundamentalsDocument11 pagesCrypto Map Based IPsec VPN FundamentalsAnonymous GEyA5IrNo ratings yet
- Ipsec and VPN: Ali Bodden Joseph Gonya Miguel MendezDocument30 pagesIpsec and VPN: Ali Bodden Joseph Gonya Miguel MendezshahrianNo ratings yet
- SCCS 420 CH 32 (Internet Security)Document10 pagesSCCS 420 CH 32 (Internet Security)api-3738694No ratings yet
- IP Sec Unit 5 CNSDocument21 pagesIP Sec Unit 5 CNSJaguar cocNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Ip Security: Benefits of IpsecDocument12 pagesUnit-4 Ip Security: Benefits of IpsecLokesh Sai Kumar DasariNo ratings yet
- Lec 16 Network Security Ipsecurity AH ESPDocument29 pagesLec 16 Network Security Ipsecurity AH ESPMehek RichhariaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ipsec: Charlie KaufmanDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Ipsec: Charlie KaufmanSakthi VelNo ratings yet
- VPN Part-1.1Document28 pagesVPN Part-1.1RuRuele RuNo ratings yet
- MindCert Cisco IPsec MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert Cisco IPsec MindMapcpawan_69No ratings yet
- Mikrotik IpsecDocument13 pagesMikrotik IpsecMertol SerbanNo ratings yet
- CNS Chapter 4Document17 pagesCNS Chapter 4Divya shreeNo ratings yet
- NS20 Lecture 3 Internet Protocol Security - IPsecDocument36 pagesNS20 Lecture 3 Internet Protocol Security - IPseceztog006No ratings yet
- ENARSI - Chapter - 20 - Securing DMVPN TunnelsDocument31 pagesENARSI - Chapter - 20 - Securing DMVPN TunnelsAnna DangNo ratings yet
- CF Full Notes PDFDocument240 pagesCF Full Notes PDFKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik IpsecDocument13 pagesMikrotik IpsecMertol SerbanNo ratings yet
- Introduction AjaDocument36 pagesIntroduction AjaRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Ipsec Lab 2Document19 pagesIpsec Lab 2jkararrigasNo ratings yet
- Itexamanswers Net Ccna Security v2 0 Chapter 8 Exam AnswersDocument17 pagesItexamanswers Net Ccna Security v2 0 Chapter 8 Exam AnswersDDDDNo ratings yet
- BCA 4th Sem : Assignment File Introduction To Internet TechnologiesDocument23 pagesBCA 4th Sem : Assignment File Introduction To Internet TechnologiesvjagarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08Document27 pagesChapter 08willy muhammad fauziNo ratings yet
- Security For IP Layer: - What Should It Be?Document25 pagesSecurity For IP Layer: - What Should It Be?Snehal SolankeNo ratings yet
- Apnic Elearning:: Ipsec BasicsDocument34 pagesApnic Elearning:: Ipsec BasicsRajkumar WaghmodeNo ratings yet
- Security Associations (Sas) : VPN OverviewDocument7 pagesSecurity Associations (Sas) : VPN OverviewfxtrendNo ratings yet
- Ipsec: Acknowledgement: All The Figures in This Lecture Note Are From Steve Friedl'SDocument8 pagesIpsec: Acknowledgement: All The Figures in This Lecture Note Are From Steve Friedl'SReeta DuttaNo ratings yet
- 11 IP Sec Services 02 Mar 2021material I 02 Mar 2021 IPSECDocument36 pages11 IP Sec Services 02 Mar 2021material I 02 Mar 2021 IPSECSharath KumarNo ratings yet
- Netts - ISCW10S04 IPsecDocument57 pagesNetts - ISCW10S04 IPsecFabio QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Lab V: Ip Security Protocol (Ipsec) : University of Split, Fesb, CroatiaDocument13 pagesLab V: Ip Security Protocol (Ipsec) : University of Split, Fesb, CroatiaGeorges karamNo ratings yet
- Echo on a Chip - Secure Embedded Systems in Cryptography: A New Perception for the Next Generation of Micro-Controllers handling Encryption for Mobile MessagingFrom EverandEcho on a Chip - Secure Embedded Systems in Cryptography: A New Perception for the Next Generation of Micro-Controllers handling Encryption for Mobile MessagingNo ratings yet
- Thesis 1986 AlKharafiDocument531 pagesThesis 1986 AlKharafiPriyankaNo ratings yet
- AuxiliariesDocument14 pagesAuxiliariesKeadilan Harus Ditegakkan100% (3)
- Database Management System (DBMS) NotesDocument56 pagesDatabase Management System (DBMS) NotesVivekKhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Hitachi FathersdayDocument8 pagesHitachi FathersdayRiverland Welding and Tool SuppliesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Part 1 - Group 2Document48 pagesChapter 4 - Part 1 - Group 2Ahmad SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- ch4 Lesson 5,6Document40 pagesch4 Lesson 5,6Abhi RokXsNo ratings yet
- Class 8 CH 5 Data Handling August 19Document3 pagesClass 8 CH 5 Data Handling August 19shayn budihardjoNo ratings yet
- Development of Asymmetries: Jan E. KronmillerDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Asymmetries: Jan E. KronmillerAdrian Silva SantosNo ratings yet
- Loctite Stycast 2762: Technical Data SheetDocument3 pagesLoctite Stycast 2762: Technical Data SheetankitaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Cooking Eggs - RecipesDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Cooking Eggs - RecipesCristelle Joyce BallicudNo ratings yet
- Ece F314 - 2022Document3 pagesEce F314 - 2022ARCHISHA SINGHNo ratings yet
- 1) Monitor Oracle BackupsDocument5 pages1) Monitor Oracle Backupsjerome MossNo ratings yet
- The UniverseDocument5 pagesThe UniverseAn MaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19 BDocument6 pagesLecture 19 BHongYu HuiNo ratings yet
- SIMATIC S7 Graph For S7-300 400 - Getting StartedDocument24 pagesSIMATIC S7 Graph For S7-300 400 - Getting StartedErica BeasleyNo ratings yet
- 2.software and Hardware Requirement SpecificationDocument3 pages2.software and Hardware Requirement Specificationnaba221085No ratings yet
- Sedemac gc1200 002 Manual For gc1200 ControllersDocument75 pagesSedemac gc1200 002 Manual For gc1200 ControllersKrishnakumar GanesanNo ratings yet
- Welding Symbol Reference ChartDocument2 pagesWelding Symbol Reference ChartAamer MohammedNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Blood Pressure Measurement: M F Pimentel August 26, 2019 Blood Pressure - Biomedical Signal ProcessingDocument59 pagesUnit-4 Blood Pressure Measurement: M F Pimentel August 26, 2019 Blood Pressure - Biomedical Signal Processingpriya dharshiniNo ratings yet
- Asm HandbookDocument2 pagesAsm HandbookLilian RoseNo ratings yet
- CPCS202 08 Arrays 2d S19Document51 pagesCPCS202 08 Arrays 2d S19Al SuNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem in BusinessDocument4 pagesPythagorean Theorem in BusinessDeelanshiNo ratings yet
- Additional Practice Questions - Structural IdealisationDocument9 pagesAdditional Practice Questions - Structural IdealisationXiuming ChenNo ratings yet
- Lab 4-5 Applied Linear Algebra For It - 501032: 1 ExercisesDocument4 pagesLab 4-5 Applied Linear Algebra For It - 501032: 1 ExercisesAnh QuocNo ratings yet
- Aspen HYSYS - Steady States and Dynamic Simulator (EG Plant Exercise) PDFDocument10 pagesAspen HYSYS - Steady States and Dynamic Simulator (EG Plant Exercise) PDFtuan.huu2007No ratings yet
- Chap 123 Final Paper N Aunt ADocument48 pagesChap 123 Final Paper N Aunt AjoannaotawayNo ratings yet
- For All Sanfoundry MCQ (1000+ MCQ) JOIN Telegram GroupDocument472 pagesFor All Sanfoundry MCQ (1000+ MCQ) JOIN Telegram GroupRitesh DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorDocument15 pagesDC GeneratorNhilNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet Powernics 9701 Black Lead Free: Berger Nippon Paint Automotive Coatings Private LimitedDocument2 pagesProduct Data Sheet Powernics 9701 Black Lead Free: Berger Nippon Paint Automotive Coatings Private LimitedSamNo ratings yet