Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prednisone
Prednisone
Uploaded by
tfish1065Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prednisone
Prednisone
Uploaded by
tfish1065Copyright:
Available Formats
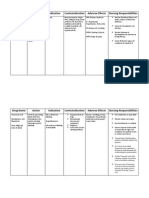
Medication:
Prednisone
Expected Pharmacological Action: Prednisone is in a class of drugs called corticosteroids. Prednisone prevents the release of substances in the body that cause inflammation. Therapeutic Uses: Prednisone is used to treat many different conditions such as allergic disorders, skin conditions, ulcerative colitis arthritis, lupus, psoriasis, or breathing disorders. Side/Adverse Effects: Get emergency medical help if you have any of these signs of an allergic reaction to prednisone: hives; difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Call your doctor at once if you have any of these serious side effects: * blurred vision, eye pain, or seeing halos around lights; * swelling, rapid weight gain, feeling short of breath; * severe depression, unusual thoughts or behavior, seizure (convulsions); * bloody or tarry stools, coughing up blood; * pancreatitis (severe pain in your upper stomach spreading to your back, nausea and vomiting, fast heart rate); * low potassium (confusion, uneven heart rate, extreme thirst, increased urination, leg discomfort, muscle weakness or limp feeling); or * dangerously high blood pressure (severe headache, blurred vision, buzzing in your ears, anxiety, confusion, chest pain, shortness of breath, uneven heartbeats, seizure). Less serious prednisone side effects may include: * sleep problems (insomnia), mood changes; * acne, dry skin, thinning skin, bruising or discoloration; * slow wound healing; * increased sweating headache, dizziness, spinning sensation; * nausea, stomach pain, bloating; or * changes in the shape or location of body fat (especially in your arms, legs, face, neck, breasts, and waist).
Corticosteroids may cause hypernatremia, hypokalemia, fluid retention, and elevation in blood pressure. These mineralocorticoid effects are most significant with fludrocortisone, followed by hydrocortisone and cortisone, then by prednisone and prednisolone. The remaining corticosteroids, betamethasone, dexamethasone, methylprednisolone, and triamcinolone, have little mineralocorticoid activities. However, large doses of any corticosteroid can demonstrate these effects, particularly if given for longer than brief periods. Therapy with corticosteroids should be administered cautiously in patients with preexisting fluid retention, hypertension, congestive heart failure, and/or renal dysfunction. Dietary sodium restriction and potassium supplementation may be advisable. Corticosteroids may elevate serum triglyceride and LDL cholesterol levels if used for longer than brief periods. Patients with preexisting hyperlipidemia may require closer monitoring during prolonged corticosteroid therapy, and adjustments made accordingly in their lipid-lowering regimen Food/Medication Interactions: A total of 659 drugs (2805 brand and generic names) are known to interact with prednisone. Some products that may interact with this drug include: aldesleukin, mifepristone, quinolone antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin), drugs that can cause bleeding/bruising (including antiplatelet drugs such as clopidogrel, "blood thinners" such as warfarin, NSAIDs such as ibuprofen). Aspirin can increase the risk of side effects when used with this medication. However, if your doctor has directed you to take low-dose aspirin for heart attack or stroke prevention (usually at dosages of 81-325 milligrams a day), Nursing Administration: Physician Administer 5mg of Prednisone PO BID as prescribed by
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness: reduce symptoms such as swelling and allergic-type reactions
You might also like
- 1000 Drug CardsDocument33 pages1000 Drug Cardstfish106587% (91)
- AMC Online - Recalls - V3Document167 pagesAMC Online - Recalls - V3Halfida100% (3)
- PREDNISONEDocument4 pagesPREDNISONECay SevillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TramadolDocument14 pagesDrug Study TramadolBianca Freya Porral85% (13)
- Drug Study - Dexamethasone (Decilone)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Dexamethasone (Decilone)mikErlhNo ratings yet
- 100 Must-Read Life-Changing Books PDFDocument161 pages100 Must-Read Life-Changing Books PDFSanjay Roy100% (1)
- Assess Notes Nursing AssessmentDocument206 pagesAssess Notes Nursing Assessmenttostc100% (7)
- Nursing PathosDocument197 pagesNursing PathosDarlene Newcomer0% (1)
- Inhaler Chart 2016 PDFDocument2 pagesInhaler Chart 2016 PDFAlmas TalidaNo ratings yet
- Imci Chart Booklet 2011 - 1 PDFDocument64 pagesImci Chart Booklet 2011 - 1 PDFDanny Irung100% (2)
- Florinef (Fludrocortisone)Document3 pagesFlorinef (Fludrocortisone)E100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyKatrina EstoconingNo ratings yet
- Solu-Cortef (Hydrocortisone)Document3 pagesSolu-Cortef (Hydrocortisone)E100% (2)
- Hydrocortisone TabDocument7 pagesHydrocortisone TabXee JayNo ratings yet
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocument5 pagesSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Fludrocortisone (Florinef)Document17 pagesFludrocortisone (Florinef)passer byNo ratings yet
- High Ceiling Loop Diuretics Thiazides and Realted DiureticsDocument3 pagesHigh Ceiling Loop Diuretics Thiazides and Realted DiureticsDaphne GoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 48 Drugs Affecting Corticosteroid LevelsDocument24 pagesChapter 48 Drugs Affecting Corticosteroid LevelsAshaNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasonetab PDFDocument8 pagesDexamethasonetab PDFFaizaNadeemNo ratings yet
- Hydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationDocument5 pagesHydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationKhaled ElabdNo ratings yet
- CHN Drug StudyDocument10 pagesCHN Drug StudyJoshua Cyryll ComiaNo ratings yet
- CortocosteroidsDocument3 pagesCortocosteroidssindhu mNo ratings yet
- Orticosteroids: Oral MedicationsDocument2 pagesOrticosteroids: Oral MedicationsYanie RuhuputtyNo ratings yet
- High Dose Inhaled Corticosteroides and Steroid Tablets For People With Lung DiseaseDocument12 pagesHigh Dose Inhaled Corticosteroides and Steroid Tablets For People With Lung DiseasekarlosNo ratings yet
- PrednisoneDocument5 pagesPrednisoneMarcus Philip GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Indication Action Side Effects NSG - ConsiderationDocument8 pagesName of Drug Classification Indication Action Side Effects NSG - ConsiderationMaurence John Feliciano LuluquisenNo ratings yet
- Metoprolol and AmiodaroneDocument5 pagesMetoprolol and AmiodaroneNolte BombayNo ratings yet
- Drugs Coronary Ward IIDocument7 pagesDrugs Coronary Ward IITimothy Joy VercelesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders and DrugsDocument149 pagesEndocrine Disorders and DrugsJaypee Fabros Edra100% (1)
- PrednisoneDocument3 pagesPrednisoneapi-3797941100% (1)
- 2 CorticosteroidsDocument30 pages2 CorticosteroidsrikarzNo ratings yet
- Adrenocortical AgentsDocument8 pagesAdrenocortical AgentsKarina Madriaga100% (1)
- Fludrocortisone (Florinef)Document15 pagesFludrocortisone (Florinef)passer by100% (1)
- Pharm Facts4Document2 pagesPharm Facts4Emily CheungNo ratings yet
- Interaksi Obat Klinik Amanatul UmmahDocument64 pagesInteraksi Obat Klinik Amanatul UmmahRiza jatur rahmahNo ratings yet
- Docetaxel - 40mg/ml Injection: InstructionDocument11 pagesDocetaxel - 40mg/ml Injection: InstructionywNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Reference DocumentDocument29 pagesUltimate Reference DocumentShellyza Moledina SajwaniNo ratings yet
- Drug CardsDocument16 pagesDrug Cardsp_dawg100% (7)
- Farmakologi KortikosteroidDocument41 pagesFarmakologi Kortikosteroiddebbyelvira100% (1)
- Prescribing Information: Teva-PrednisoneDocument13 pagesPrescribing Information: Teva-PrednisoneKousar MohammediNo ratings yet
- UWORLDNCLEXreview2021 PDFDocument100 pagesUWORLDNCLEXreview2021 PDFmahshid kianiNo ratings yet
- Jam (Drug Study)Document11 pagesJam (Drug Study)Vincent QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Lascuna-Drug StudyDocument8 pagesLascuna-Drug StudyAiza Pearl LascuñaNo ratings yet
- Losartan PotassiumDocument3 pagesLosartan Potassiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Name Indication Contraindication Drug Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: Route and DosageDocument6 pagesDrug Name Indication Contraindication Drug Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: Route and Dosageسبوكاي100% (1)
- Prednisone TabDocument10 pagesPrednisone TabrantiadrianiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Medications ReviewerDocument4 pagesRespiratory Medications ReviewerKevin VillaranteNo ratings yet
- Product Name: New Zealand Data Sheet Apo-PrednisoneDocument13 pagesProduct Name: New Zealand Data Sheet Apo-PrednisonedomNo ratings yet
- Nursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeDocument5 pagesNursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeSophia limNo ratings yet
- Propylthiouracil DSDocument6 pagesPropylthiouracil DSAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Drugs Increased Risk of DiabetesDocument5 pagesDrugs Increased Risk of Diabetesk9cfxtdfqmNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GranjaDocument5 pagesDrug Study GranjajolibeecaldonaNo ratings yet
- Pharm ReveiwerDocument19 pagesPharm Reveiwerpinedaalexa758No ratings yet
- Drug Study GuideDocument9 pagesDrug Study GuideSh3meeNo ratings yet
- Propylthiouracil 2Document14 pagesPropylthiouracil 2Magdy Ali ELsherbenyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument34 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsMei-mei ZhuangNo ratings yet
- Year 2 AntiallergyDocument19 pagesYear 2 AntiallergyjonaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Hypertension 2012Document13 pagesDrugs For Hypertension 2012Lidya ZhuangNo ratings yet
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyDocument33 pagesEMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyNicole GarciaNo ratings yet
- Methadone Hydro ChlorideDocument4 pagesMethadone Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyDocument8 pagesEMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyShaine WolfeNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Hyper-cortisolism (Cushing Syndrome), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHyper-cortisolism (Cushing Syndrome), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- 101 Really Important Things You Already Know, But Keep Forgetting-ManteshDocument238 pages101 Really Important Things You Already Know, But Keep Forgetting-ManteshJuan MedinaNo ratings yet
- NclexDocument34 pagesNclexErnie John OyaoNo ratings yet
- Emergency NursingDocument35 pagesEmergency NursingEric HugoNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument179 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesTrixie Al Marie75% (4)
- Psychiatric Nursing ReviewDocument26 pagesPsychiatric Nursing ReviewIdionessNo ratings yet
- Nclex ReviewDocument40 pagesNclex Reviewanon-42981396% (27)
- V, V V V#'V VVDocument2 pagesV, V V V#'V VVtfish1065No ratings yet
- BUD AppendixDocument48 pagesBUD AppendixOrnielNo ratings yet
- IMCI Patient Assessment FormDocument2 pagesIMCI Patient Assessment FormDa Bondad67% (3)
- Case Presentation: Alcoholic GastritisDocument18 pagesCase Presentation: Alcoholic Gastritisstancy thomas100% (1)
- TB PresentationDocument13 pagesTB PresentationHafid Iqbal MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Price List PT BMP: Nama Obat Satuan Stok Harga Nett++ (RP)Document98 pagesPrice List PT BMP: Nama Obat Satuan Stok Harga Nett++ (RP)apriantiNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes On ShockDocument3 pagesAdditional Notes On ShockSheniqua GreavesNo ratings yet
- MacrolidesDocument9 pagesMacrolidesAnish Kumar ANo ratings yet
- 52 Q. Medicine 1st Half PDFDocument12 pages52 Q. Medicine 1st Half PDFFahad2036No ratings yet
- Antihelmintics DrugsDocument14 pagesAntihelmintics DrugsSalman AshrafNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease NursingDocument11 pagesCommunicable Disease NursingMelvinFabraÜ100% (1)
- Pleurisy (Pleuritis)Document17 pagesPleurisy (Pleuritis)kamilahfernandezNo ratings yet
- Care of Child Aged 2 Months To 5 YearsDocument7 pagesCare of Child Aged 2 Months To 5 Yearsmg0% (1)
- For Drug Recitation 1Document33 pagesFor Drug Recitation 1Abigail LonoganNo ratings yet
- Kitir Proposal Penelitian 2014 SIDocument32 pagesKitir Proposal Penelitian 2014 SIclarazettiraNo ratings yet
- MCQ GastroenterologyDocument9 pagesMCQ GastroenterologyAhmed Magdy Youssif95% (19)
- Medication Classification Look Alike Sound Alike Medicines in Central StoresDocument30 pagesMedication Classification Look Alike Sound Alike Medicines in Central StoresAyuNo ratings yet
- Neurology 40 KochiDocument9 pagesNeurology 40 KochiSrirupa BiswasNo ratings yet
- Uncontrol Inventory UnitDocument69 pagesUncontrol Inventory Unithermina yanmedpwtNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat Oral Padat Berdasarkan Kelas FarmakoterapiDocument3 pagesDaftar Obat Oral Padat Berdasarkan Kelas Farmakoterapigampang lupaNo ratings yet
- Suboxone Brochure LKDDocument2 pagesSuboxone Brochure LKDJohn McconnellNo ratings yet
- Immunization in Children: Mary Beth F. Tanco, MD, FPPS Active Consultant Institute of Pediatrics and Child HealthDocument92 pagesImmunization in Children: Mary Beth F. Tanco, MD, FPPS Active Consultant Institute of Pediatrics and Child HealthPolychase Magaoay100% (1)
- Abilify Dosing GuideDocument2 pagesAbilify Dosing GuidemtassyNo ratings yet
- MSF Clinical Guidelines PDFDocument356 pagesMSF Clinical Guidelines PDFKirthinath BallalNo ratings yet
- GENIRICDocument2 pagesGENIRICŃtǿxNo ratings yet
- DKA Concept MapDocument2 pagesDKA Concept MapJanetNo ratings yet
- Promotion MCQDocument17 pagesPromotion MCQssamaddNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Patient With Digestive IndexDocument28 pagesNursing Care of Patient With Digestive IndexAngela FerrerNo ratings yet