Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson Plan G7 June-July
Lesson Plan G7 June-July
Uploaded by
sunitak1150 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Lesson plan G7 June-July
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesLesson Plan G7 June-July
Lesson Plan G7 June-July
Uploaded by
sunitak115Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Grade 5
School: CAGS, LR
Teachers’ Initials: Sunita Kumari
Subject/age group: 10 years, Science Date: 3rd – 28th April 2024
Learning objectives (Cambridge curriculum Framework):
This unit covers all aspects of flowering plants: parts and functions, life cycle
including pollination and germination, seed and fruit production, and dispersal.
Learners then study the features of plants that attract pollinators, how seeds
disperse.
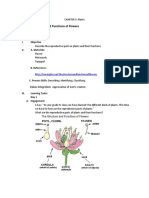
Topic/Sesson/ Learning Intentions: Success
Unit/Lesson 1. Learn that some plants have Criteria:
flowers and other plants do not 1. Can identify
have flowers. the parts of
1.1 Flowering
2. Identify parts of a flower and flower and
and non
describe their functions. describe their
flowering
3. Learn about the stages in the life functions.
plants
cycle of a flowering plant. 2. Can say
4. Identify types of pollination and sort what the
1.2 Pollination, flowers into groups according to stages are in
fruits and how they are pollinated. the life cycle of
seeds 5. Collect and record observations of a flowering
pollination in a table. plant.
6. Sort seeds into groups according to 3. Can identify
1.3 How seeds
the way they are dispersed. factors seeds
are spread
7. Say how flowering plants are need to
adapted for seed dispersal. germinate.
1.4 Seed 8. Identify the conditions needs to 4. Can
germination germinate. describe seed
germination.
5. Can
describe how
flowering
plants are
adapted for
seed dispersal.
6. Can say
how flowers
are adapted to
attract
pollinators.
1 Resources: Images of flowering and non-flowering plants, video of
pollination, learner’s book, images of fruits and seeds, packets of seeds
and their instructions for planting.
2 Language Support, including any subject-specific vocabulary:
Absorb, Conditions, germination, shrivels, explode, seed dispersal,
seedlings, spongy, fertilization, fertilize, pollination, pollinate, pollinator,
anther, carpel, filament, sepals, scent, stamen, stigma, ovary, ovule.
3 Introducing the lesson- Timings:
3rd - 5th Bridging the gap 35
8th- 28th April- Getting started questions from the learner’s book minutes
of every topic in the first Unit. each
Main activities: Timing: 13 lectures/ 35 minutes.
4 Discussion whether all plants
produce flowers or not using
images of flowering and non-
flowering plants.
Explain stages in the lifecycle of
flowering plant with the help of
diagram.
Describe the parts of flower with
help of real flower/ picture of
flower.
Explain the process of pollination,
pollinators, seed dispersal and
seed germination.
7 Assessment Opportunities:
To monitor learner’s understanding, learners will be orally assessed in
the form of quiz. Mark diagrams to determine how well learners
understand the process of gaseous exchange, summarizing the topic
and class test on the topic will be conducted
8 Differentiation opportunities:
Learners will be asked to draw the diagrams in the notebooks, can be
provided extra guidance, encouraged them to participate more in the
activities and discussion.
9 Plenary and reflection:
10 Homework (if required)
Exercise questions from learner’s book.
Topic worksheet
11 Notes:
You might also like
- P Science 5 Learners Book AnswersDocument22 pagesP Science 5 Learners Book AnswersEman100% (10)
- SCIENCE-5-Q2-Module 4Document16 pagesSCIENCE-5-Q2-Module 4Mary Ann Gabion100% (11)
- Flora of Ethiopia and Eritrea - Aeonium 20200512 PDFDocument7 pagesFlora of Ethiopia and Eritrea - Aeonium 20200512 PDFCarles JiménezNo ratings yet
- Science 5: Quarter 2 Week 5 Module 5Document20 pagesScience 5: Quarter 2 Week 5 Module 53tj internetNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 21 1Document9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 21 1femie hemilgaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in ScienceRegine MalanaNo ratings yet
- LB ANSWERS STAGE 5 Cambridge Primary ScienceDocument22 pagesLB ANSWERS STAGE 5 Cambridge Primary ScienceChi AmNo ratings yet
- Classification of PlantsDocument57 pagesClassification of PlantsELLA EATANo ratings yet
- Science 5 SLEM Week5 2nd Q V2 QATEAMDocument10 pagesScience 5 SLEM Week5 2nd Q V2 QATEAMlea eduardoNo ratings yet
- What Is This Module About?: What Would Life Be Without Plants? and Think GreenDocument52 pagesWhat Is This Module About?: What Would Life Be Without Plants? and Think Greennageen198475% (4)
- Malee DLL For COT Q2 WK 6 Science Part of A FlowerDocument9 pagesMalee DLL For COT Q2 WK 6 Science Part of A FlowerMARIE LEE BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Classification of PlantsDocument54 pagesClassification of PlantsAngeline Panaligan AnselaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument8 pagesScienceBryl MedrozoNo ratings yet
- LP ScienceDocument4 pagesLP Sciencejoshuaborral0No ratings yet
- DownloadScience 5 Q2 Week 5Document10 pagesDownloadScience 5 Q2 Week 5Zukalu ZoldyckNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan SCIENCE 5 (WEEK 6, DAY 3)Document3 pagesLesson Plan SCIENCE 5 (WEEK 6, DAY 3)Angel rose reyesNo ratings yet
- Malee DLL For COT Q2 WK 4 ScienceDocument11 pagesMalee DLL For COT Q2 WK 4 ScienceMARIE LEE BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science Lesson Plan 1Document3 pagesGrade 10 Science Lesson Plan 1Shamshad ShaheerNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Sciences Week 6Document5 pagesEarth and Life Sciences Week 6Ma. Jhysavil ArcenaNo ratings yet
- Board Plan: Session 2023-24 Class-V Subject - ScienceDocument5 pagesBoard Plan: Session 2023-24 Class-V Subject - SciencebhartiNo ratings yet
- Final Science (LP) - Beed 2aDocument18 pagesFinal Science (LP) - Beed 2aTrisha MedidasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan SCIENCE 5 (WEEK 7, DAY 2)Document3 pagesLesson Plan SCIENCE 5 (WEEK 7, DAY 2)Angel rose reyes100% (1)
- Plants and Seeds: A 1st Grade Unit On Plants, Seeds, and How They Survive and GrowDocument8 pagesPlants and Seeds: A 1st Grade Unit On Plants, Seeds, and How They Survive and Growapi-337085136No ratings yet
- How Plant Grow and ReproduceDocument6 pagesHow Plant Grow and ReproduceFrinces Mae CristalNo ratings yet
- Science-Grade 5: Different Modes of Reproduction in Flowering and Non-Flowering PlantsDocument6 pagesScience-Grade 5: Different Modes of Reproduction in Flowering and Non-Flowering PlantsJocel AlicanteNo ratings yet
- DLP Demo Science 5Document4 pagesDLP Demo Science 5maricrisgerona650No ratings yet
- DLL For DemoDocument3 pagesDLL For Demosarah100% (3)
- Cot Filipino 5Document2 pagesCot Filipino 5Jesusa Franco DizonNo ratings yet
- Ashely Jade Domalanta - Checked-SPLM-4-for-Gen-BiologyDocument5 pagesAshely Jade Domalanta - Checked-SPLM-4-for-Gen-BiologyAshley Jade DomalantaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Parts of A PlantDocument5 pagesReproductive Parts of A PlantMelyn BustamanteNo ratings yet
- K 2 Fun With FlowersDocument2 pagesK 2 Fun With FlowersMiriam MilaneloNo ratings yet
- College of Teacher: Don Carlos Polytechnic CollegeDocument9 pagesCollege of Teacher: Don Carlos Polytechnic CollegeAiraj YlnNo ratings yet
- DLL in SCIENCE 5 Q2W5Document4 pagesDLL in SCIENCE 5 Q2W5Junelle Joy CatbaganNo ratings yet
- How Plant Grow and ReproduceDocument6 pagesHow Plant Grow and ReproduceFrinces Mae CristalNo ratings yet
- Sci PPTX q2wk6 Day 1-5Document74 pagesSci PPTX q2wk6 Day 1-5Junrel Canete100% (1)
- Science5 - q2 - Mod4 - The Reproductive Parts in Plants and Their Functions - v3Document19 pagesScience5 - q2 - Mod4 - The Reproductive Parts in Plants and Their Functions - v3Teacher Lhor BaturiNo ratings yet
- GR6 Tle Q1 W5 D1-D5Document10 pagesGR6 Tle Q1 W5 D1-D5Erdell BaronNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument8 pagesPlant ReproductionExceil Matthew Carpio100% (1)
- Sample Lesson Plan DemoDocument2 pagesSample Lesson Plan DemoNeveen KarimaNo ratings yet
- Board Plan: Session 2023-24 Class-V Subject - ScienceDocument7 pagesBoard Plan: Session 2023-24 Class-V Subject - SciencebhartiNo ratings yet
- Virtual Science Cambridge 3rd Grade COMPLETED - CompressedDocument193 pagesVirtual Science Cambridge 3rd Grade COMPLETED - CompressedJonatan Roberto Santos FloresNo ratings yet
- S5LT 11f 6Document8 pagesS5LT 11f 6Kristine Joy PitaNo ratings yet
- G5 Q2W5 DLL SCIENCE MELCsDocument10 pagesG5 Q2W5 DLL SCIENCE MELCsma cristina cabaya cunananNo ratings yet
- Science7 Q2 Module 5 Reduced FileDocument12 pagesScience7 Q2 Module 5 Reduced FileKei SparksNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan SCIENCE 5 (WEEK 7, DAY 1)Document3 pagesLesson Plan SCIENCE 5 (WEEK 7, DAY 1)Angel rose reyesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 6 Q2 WK7Document9 pagesLesson Plan in Science 6 Q2 WK7Jannah100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Science 3 PlantsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Science 3 PlantsCaren Pogoy ManiquezNo ratings yet
- Agr 516 - Laboratory ManualDocument20 pagesAgr 516 - Laboratory ManualAiman WafiyNo ratings yet
- Pasay-Lsen-Science-Q2-W4 - D1-5Document16 pagesPasay-Lsen-Science-Q2-W4 - D1-5Nomar CapoyNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument3 pagesReproduction in PlantsKavyaranjan “Ranju”No ratings yet
- DLL Demo Science 5Document4 pagesDLL Demo Science 5Marie Fe Jambaro80% (5)
- Curriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningDocument11 pagesCurriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningMerce Tojino ManigosNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 LPDocument7 pagesGrade 5 LPJuhanna Lizl GustiloNo ratings yet
- LP in Science VIDocument5 pagesLP in Science VIJudy C. BelardoNo ratings yet
- Lycopersicum Esculentum Antocarpus HeterophyllusDocument2 pagesLycopersicum Esculentum Antocarpus HeterophyllusAbegail Bantilan ConiendoNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 PPT Science Q2 W6 Day 1-5Document75 pagesGrade 5 PPT Science Q2 W6 Day 1-5gerelyn matuteNo ratings yet
- Observation Sept 30Document25 pagesObservation Sept 30TeacherJoie DioNo ratings yet
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- Monocot vs. DicotDocument2 pagesMonocot vs. DicotRonalynNo ratings yet
- Llista HerbesDocument5 pagesLlista HerbesIfariKu Guanabacoa EshuOmoNo ratings yet
- Botany Exp2Document7 pagesBotany Exp2SarthakNo ratings yet
- Adinandra Hongiaoensis (Theaceae), A New Species From Lam Dong, VietnamDocument5 pagesAdinandra Hongiaoensis (Theaceae), A New Species From Lam Dong, VietnamPlant VietNo ratings yet
- Den Hartog, 1970 - The Seagrass of The WorldDocument21 pagesDen Hartog, 1970 - The Seagrass of The WorldfurkonableNo ratings yet
- Universal Herbal or Botanical, Medical and Agricultural Containing An Account of All Known Plants in The World. 1824Document1,062 pagesUniversal Herbal or Botanical, Medical and Agricultural Containing An Account of All Known Plants in The World. 1824Guillermo BenítezNo ratings yet
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument22 pagesPerpetuation of Lifemarizel salcedoNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives:: 4. Appreciate The Purpose and Importance of ClassificationDocument7 pagesI. Objectives:: 4. Appreciate The Purpose and Importance of ClassificationBethymay EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Lessonplan How Plants SurviveDocument8 pagesLessonplan How Plants SurviveEllen DispoNo ratings yet
- Botany 5 Root System PDFDocument31 pagesBotany 5 Root System PDFZyreeneNicoleNo ratings yet
- CH 21Document16 pagesCH 21wallace120No ratings yet
- Herbal and Complementary Medicine Dr. Denise K. DaleyDocument92 pagesHerbal and Complementary Medicine Dr. Denise K. DaleyMarquel CulmerNo ratings yet
- Plant Unit Test Answer KeyDocument2 pagesPlant Unit Test Answer Keyapi-375119310No ratings yet
- Transpiration Experiments Basis Demonstration & Measurement - EmbibeDocument9 pagesTranspiration Experiments Basis Demonstration & Measurement - EmbibeLakshmyNo ratings yet
- 12th STD Bio-Botany Video LinksDocument3 pages12th STD Bio-Botany Video Linksnaina10691No ratings yet
- EphedraDocument7 pagesEphedraJhon SmithNo ratings yet
- Cacti: Astrophytum MyriostigmaDocument7 pagesCacti: Astrophytum MyriostigmaBahar AliNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument2 pagesNutrition in PlantsroopamsNo ratings yet
- Angio Sperm AsDocument19 pagesAngio Sperm AsLuis Diego Obando PaniaguaNo ratings yet
- Plant Transpiration: Objectives: Describe The Process of Transpiration in Vascular PlantsDocument2 pagesPlant Transpiration: Objectives: Describe The Process of Transpiration in Vascular PlantsSheen Angcla MiraNo ratings yet
- List of Single Drug Monographs Published in API, Part I, Vol. V Sl. No. Name of The Drug Botanical Name Part UsedDocument2 pagesList of Single Drug Monographs Published in API, Part I, Vol. V Sl. No. Name of The Drug Botanical Name Part Usedaparna tiwariNo ratings yet
- موسوعة فسيولوجيا النبات للدكتور ادريسDocument241 pagesموسوعة فسيولوجيا النبات للدكتور ادريسbelhoucinetouhamiNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of Flowering PlantsDocument3 pagesLife Cycle of Flowering PlantsAnonymous HMlygCCNo ratings yet
- Review JurnalDocument6 pagesReview JurnalWahyu ArifNo ratings yet
- Solanumdiphylluml. (Solanaceae) - A New Record To The Flora of Gujaratstate, IndiaDocument5 pagesSolanumdiphylluml. (Solanaceae) - A New Record To The Flora of Gujaratstate, IndiaIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants: CPP Vii ClassDocument2 pagesNutrition in Plants: CPP Vii ClassJ SoujanyaNo ratings yet
- GenBioL Mod 8 Leaf PDFDocument3 pagesGenBioL Mod 8 Leaf PDFKimNo ratings yet
- Biology Review ExemplarDocument8 pagesBiology Review ExemplarPeggy DominicoNo ratings yet
- 2 Growth Stages of The Rice PlantDocument35 pages2 Growth Stages of The Rice PlantJONATHAN CACAYURINNo ratings yet