Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EC8073 ME 2M QB IQ - by WWW - EasyEngineering.net 2M QB IQ 1
EC8073 ME 2M QB IQ - by WWW - EasyEngineering.net 2M QB IQ 1
Uploaded by
Cse -B.Dhivya BalakrishnanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EC8073 ME 2M QB IQ - by WWW - EasyEngineering.net 2M QB IQ 1
EC8073 ME 2M QB IQ - by WWW - EasyEngineering.net 2M QB IQ 1
Uploaded by
Cse -B.Dhivya BalakrishnanCopyright:
Available Formats
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.
net
ww
w.E
asy
E ngi
nee
rin
g.n
et
**Note: Other Websites/Blogs Owners Please do not Copy (or) Republish
this Materials, Students & Graduates if You Find the Same Materials with
EasyEngineering.net Watermarks or Logo, Kindly report us to
easyengineeringnet@gmail.com
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
EC8073 MEDICAL ELECTRONICS
UNIT –I ELECTRO-PHYSIOLOGY AND BIOPOTENTIAL RECORDING
PART-A
1. What are Bio electric potential?
The electric potentials that are generated due to chemical activity in
certain cells such as nerve cell or muscle cell are called as bio electric
potentials.
2. Name few bioelectric signals
Some of the bio electric signals are,
• ECG (Electrocardiogram)
ww
• EEG (Electroencephalogram)
• EOG (Electrooculogram)
w.E
• EMG (Electromyogram)
• PCG (Phonocardiogram)
3.
asy
What is Resting potentials? Or What is called as resting membrane
potential?
En
The membrane of excitable cells readily permits the entry of K+ ions and
Cl- ions, while it effectively blocks the entry of Na+ ions. Therefore the
gin
concentration of Na+ ions inside the cell becomes much lower than that outside
the cell. Since the Na+ ions are positive, the outside cells are more positive than
eer
the inside. Thus the charge balance is not achieved. Thus a potential difference
i
is developed across the membrane. This membrane potential caused by the
ng.
different concentration of ions is called the resting potential of the cell.
4. What is action potential? Or Define action Potential
When a cell membrane is excited by some form of externally applied
energy, the membrane changes its electrical characteristics and begins to allow
net
some of the Na+ ions to enter. The movement of Na+ ions into the cell
constitutes ionic current which further reduces the barrier of the membrane to
Na+ ions. The net result in Na+ ions rush into the cell and try to balance with
the ions outside. At the same time K+ ions present inside the cell try to leave
the cell. But they are unable to move as rapidly as Na+ ions. As a result the cell
has a slightly positive potential. This potential is called as action potential.
5. Write down the nernst equation.
Nernst equation is given as
E (mv) = 60 ln C o / C i
Where, E is the resting potential in millivolts
Co – Outside Concentration of the cell in moles/cm3
Ci – inside Concentration of the cell in moles/cm3
1
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
6. Draw action potential waveform.
7.
ww
What is meant by depolarization and repolarization of a cell?
DEPOLARIZATION:-
w.E
When the impulse reaches the muscle, the polarized condition (-90mv)
is altered. i.e., the resting membrane potential is abolished. The interior of the
muscle becomes positive and outside becomes negative. This condition is called
as depolarization.
asy (Or)
En
The process of changing from resting state to the action potential state
is called as depolarization.
REPOLARIZATION:-
gin
eer
With in a short period, the muscles obtain the resting electrical
i
potential once again. Interior of the muscle becomes negative and outside
ng.
becomes positive. So, the polarized state of the muscle is re-established. This
process is called as repolarization.
(Or)
The process of changing from action state to the resting potential state
is called as repolarization.
net
8. What is meant by Depolarization?
The process of changing from resting state to the action potential state
is called as depolarization.
9. What is absolute refractory period?
A short period of time during which the cell cannot respond to any
stimuli is called as absolute refractory period. The time period is about 1ms.
10. What is Relative refractory period?
The period followed by absolute refractory period is the relative
refractory period. during this period another action potential can be triggered,
but a much stronger stimulation is required.
2
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
11. State all or none law in respect of cell bio potential.
All or none law states that regardless of the method of excitation of cells
or by the intensity of the stimulus, the action potential is always the same for
any given cell.
12. What is known as the sodium potassium pump?
During depolarization of a cell, Na+ ions rush into the cell while K+ ions
attempt to leave the cell. After some time, the cell regains its original position
by an active process called sodium pump. By the action of sodium pump, the
Na+ ions are quickly transported to the outside of the cell and the cell again
becomes polarized.
13. What are unipolar and bipolar electrodes?
In bipolar electrode, the potential difference between two surface
ww
electrodes resting on the skin is measured.
In unipolar electrode, the reference surface electrode is placed on the
w.E
skin and the needle electrode which acts as active electrode, is inserted into
the muscle.
asy
14. List the types of Biopotential Electrode. (Or) What are the different types
of electrodes used in bipolar measurement? (Or) Classify Bipotential
electrodes
En
The types of biopotential electrodes are,
a. Surface Electrode
b. Micro Electrode and
gin
c. Needle Electrode
eer
i
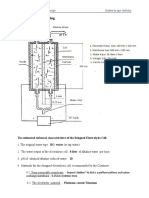
15. Draw the electrical equivalent circuit of a surface electrode
ng.
net
16. Differentiate micropipette and metal microelectrode
Metal microelectrodes are formed by electrolytically etching the tip of
fine tungsten or stainless steel wire to the desired size. Then the wire is coated
with an insulating material almost to the tip.
Glass micropipet microelectrodes are fabricated from glass capillaries.
The center region of the capillary is heated with a burner to the softening point,
and then the capillary is rapidly stretched to produce the constriction.
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
17. Name the electrodes used for recording EMG and ECG.
The electrodes used for recording EMG are,
• Surface electrode - Metal Disc electrode, Disposable electrode
• Needle electrode - Unipolar and Bi polar electrode
The electrodes used for recording ECG are,
• Surface electrode - Metal Disc electrode, Suction cup electrode, Disposable
electrode
18. What are the different types of electrodes used in bipolar measurement?
The types of biopotential electrodes are,
a. Surface Electrode
b. Micro Electrode and
c. Needle Electrode
ww
19. What is half cell potential?
w.E
The voltage developed at an electrode-electrolyte interface is called as
half cell potential or electrode potential.
asy
20. Draw a typical ECG waveform.
En
gin
eer
i ng.
net
21. What are the requirements for physiological signal amplifier?
1. The voltage gain should be more than 100dB.
2. The gain and frequency response should be uniform throughout the
required bandwidth.
3. Its input impedance should be very high
4. Its output impedance should be very low
5. Its CMRR should be very high (more than 80 dB)
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
22. Define Einthoven triangle
The closed path RA to LA to LL and back to RA is called as Einthoven
triangle. (RA - Right Arm, LA -Left Arm, LL - Left Leg)
23. Draw Einthoven triangle
ww
i)
w.E
24. Mention the various lead systems used in ECG recording
Bipolar limb leads or Standard Leads or Einthoven lead system
asy
1. Lead I
2. Lead II
ii)
3. Lead III
En
Unipolar limb leads or Wilson Lead System
a) Augmented unipolar limb lead
1. aVR
gin
2. aVL
3. aVF
eer
b) Unipolar chest leads
i ng.
25. Mention the important bands of frequencies in EEG and their importance
Alpha waves (8-13)Hz – to monitor the level of consciousness
Beta waves (13-30)Hz – to monitor cerebral and mental activity
net
Theta waves (4-8)Hz – to analyse the emotional stress in adults
Delta waves (0.5-4)Hz – to study sleep disorders and brain tumours
26. Define Phonocardiogram and Phonocardiography.
The Phonocardiogram is the graphical representation of the sound
recording connected with the pumping action of the heart.
Phonocardiography is a technique to measure the sounds generated
from opening and closure of heart valves.
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
27. Define the term Conduction velocity or propagation rate or nerve
conduction rate.
The rate at which an action potential moves down a fiber or is
propagated from cell to cell is called as propagation rate or nerve conduction
rate or conduction velocity.
28. Give the EMG signal characteristics. (Or) Mention the normal amplitude
and frequency of EMG signal
The EMG signal ranges from 0.1mV to 0.5mV. The frequency
components of the EMG signal vary from 20Hz to 10 KHz and they are
restricted to the frequency range of 20Hz to 200Hz for clinical purpose using a
low pass filter.
29. Define Latency as related to EMG
ww Latency is defined as the elapsed time between the stimulating impulse
and the muscles action potential. In other words it is the time delay between
w.E
stimulus and response.
30. What are the electrodes used for recording EMG?
asy
The electrodes used for recording EMG are,
Surface electrode
En
Metal Disc electrode, Disposable electrode
Needle electrode
Unipolar and Bi polar electrode
gin
31. What is the purpose of electrode paste?
eer
i
The outer skin of the body is highly conductive and it will not establish
ng.
a good electrical contact with an electrode so, some of the outer cells of the
skin is removed and the electrode paste is applied to reduce the contact
impedance and to avoid the movement artifacts.
net
PART-B
1. Explain the sources of Biopotential in detail. (Ans: Unit 1 Page No. 2-3)
2. Explain the origin of biopotential. (Ans: Unit 1 Page No. 3-8)
3. Draw the action potential waveform and explain the following terms. Resting
potential; Action potential; Absolute refractory period and Relative refractory
period. (Ans: Unit 1-Page No. 6-8)
4. Draw equivalent circuit of a biopotential electrode interface (Ans: Unit 1 Page
No. 10).
5. Discuss about the different types of electrode used in bio potential
measurement. (Or) Discuss in detail about various types of biopotential
electrodes. (Ans: Unit 1 Page No. 12-21)
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
6. Draw a typical ECG waveform and mark the important features and the
associated function of the heart. (Ans: Unit 1 Page No. 28-30)
7. With neat diagrams explain the 12 lead system in ECG measurement. (Or)
Draw and explain the different lead configuration and its significances in ECG.
(Ans: Unit 1 Page No. 30-33)
8. Explain the working principle of a ECG machine with a neat block diagram.(
Ans: Unit 1 Page No. 33-35)
9. Give the origin of brain waves and describe the 10-20 electrode system used in
EEG. (Ans: Unit 1 Page No. 35-38)
10. With a neat block schematic diagram, describe the principles involved in a
EEG recorder. (Ans: Unit 1 Page No. 39-40)
11. Explain the measurement of EMG. (Ans: Unit 1 Page No. 41-43)
ww PART-C
1. What should be the characteristics of biopotential amplifier? Explain with proper
w.E
justification. (Ans: Unit 1 Page No. 22-23)
2. Design a suitable amplifier that can be used in the front end of an ECG
machine. Justify by specifying the features of the selected amplifier. (Ans: Unit 1
Page No. 22-23)
asy
3. With neat diagrams, explain the schematic diagram of EEG machine. Also, show
En
the recording method of unipolar and bipolar EEGs. (Ans: Unit 1 Page No. 41-
43).
gin
eer
i ng.
net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
UNIT-II - BIO-CHEMICAL AND NON ELECTRICAL PARAMETER
MEASUREMENT
PART-A
1. What are the uses of gas analyzers? Or State the uses of Gas analyzers.
These are used to determine the quantitative composition of inspired and
expired gases and to asses the lung function.
These are mostly based on infra red absorption of CO2, paramagnetic
behavior of oxygen, thermal conductivity of CO2.
2. What is meant by pH value of blood?
The pH value of blood is defined as the logarithm of the reciprocal of H+
ion concentration in the blood.
pH = log 10 (1/[H+]) = -log 10 [H+]
3.
ww
What is a calorimeter?
Colorimeter is used to measure the transmitted and absorbed light as it
w.E
passes through a sample. The basic principle behind the colorimeter is that
many chemical compounds in solution appear coloured with the saturation of
asy
the colour depending on the concentration of the compound. By analyzing the
transmitted light through the sample or emitted light by the sample, the
En
concentration of the substance can be determined.
4.
S.No Colorimeter gin
Differentiate colorimeter and spectrophotometer
Spectrophotometer
1
Colorimeter uses filter as
eer
spectrophotometer uses
2
wavelength selector
It measures transmittance i
monochromator as wavelength selector.
It measures absorbance
ng.
5. State Beer and Lamberts Law
net
Beer and Lamberts law states that the absorption of light transmitted
through a medium is directly proportional to the concentration and length of
the medium.
6. What is a flame photometer?
A meter that is used to analyse urine or blood inorder to determine the
concentration of potassium (k), Sodium (Na), Calcium(ca) & Lithium (Li).
7. What is the use of Flame photometer?
Flame photometer is used to analyze urine or blood in order to
determine the concentration of potassium(K), Sodium (Na), Calcium(Ca) and
Lithium (Li).
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
8. Define Transmittance and Absorbance.
Transmittance is defined as the ratio of transmitted light intensity (I i ) to
incident light intensity (I 0 )
Transmittance, T = I 1 / I 0
Absorbance, A = -log(I 1 /I 0 )
9. What is an auto analyzer?
An auto analyzer is an instrument that sequentially measures the blood
chemistry and displays it on the graphic readout.
10. What is the disadvantage of Auto analyzer?
a. Patient data can be intermixed with that of other patient's data if care is
not taken.
b. Sterilization is also needed for samples, glassware and equipment parts
ww that are contaminated with disease.
w.E
11. Mention the application of auto analyzer
Auto analyzer is used to measure dozens of fluid samples an hour for a
variety of markers such as cholesterol, phosphate levels and proteins.
asy
12. What is the use of Electromagnetic Blood flow meter?
En
Electromagnetic Blood flow meter is used for measuring the flow
through blood vessels within the body
gin
13. What are the various types of blood flow meters?
1. Electromagnetic blood flow meter
eer
2. Ultrasonic (Doppler shift) blood flow meter
3. NMR blood flow meter and
4. Laser Doppler blood flow meter
i ng.
14. Name any four physical principles based on which blood flow meters are
constructed
net
Blood flow meters are constructed based on the following principles
a. Electromagnetic blood flow meter
b. Ultrasonic (Doppler shift) blood flow meter
c. NMR blood flow meter and
d. Laser Doppler blood flow meter
15. What is a cardiac output?
The amount of blood pumped out by the heart to the aorta per minute is
called as cardiac output.
16. Mention the methods of measurement of cardiac output.
The methods used to measure the cardiac output are,
• Indicator dilution method
9
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
• Fick’s method
• Dye dilution method
• Thermal dilution
• Impedance technique
17. Find the cardiac output of a patient whose heart rate is 80BPM and a
stroke volume of 80 millilitres per beat.
The cardiac output = heart rate x stroke volume
= 80 beats / min x 80 ml/beat
= 6.4 litres / minute
18. Define stroke volume. (Or) What is stroke volume?
Stroke volume is defined as the amount of blood that is ejected during each
heart beat.
wwStroke volume = Cardiac output / Number of heart beats per minute
w.E
19. Calculate the stroke volume in millilitres if the cardiac output is 5.2
litres/minute and heart rate is 76 beats/minute
Q = 5.2 litres/minute;
asy
HR = 76 beats/minute
Stroke volume = 𝑸𝑸/𝑯𝑯𝑯𝑯 = (5.2 𝑥𝑥 1000)/76 = 68.42 ml
En
gin
20. What are plethysmographs and plethysmography
Plethysmography is the process used to measure the volume changes in
eer
any part of the body that result from the pulsations of blood occurring with
each heart beat. These measurements are useful in the diagnosis of arterial
determine the heart rate. i
obstructions and pulse wave velocity measurement which may lead to
ng.
Plethysmograph produces a waveform that is similar to the arterial
pressure waveform.
21. What is the reason for decrease of cardiac output?
net
A bradycardia may be the primary cause of low cardiac output.
Hypothyroidism, hypothermia, drugs such as beta blockers and calcium
channels blockers, inferior myocardial ischemia and conduction system
dysfunction may all cause significant bradycardia
22. Define systolic and Diastolic Pressure.
Systolic pressure is the maximum blood pressure during contraction of
heart muscles. The range of systolic pressure is 95 to 140mmHg.
Diastolic pressure is the lowest blood pressure during dilation of the
heart cavities. The range of Diastolic pressure is 60 to 90mmHg.
10
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
23. What do you mean by systemic temperature?
systemic temperature is defined as the temperature of the internal
regions of the body. It is measured by temperature sensing devices placed in
the mouth. Normal systemic temperature of a healthy person is about 37°C.
Systemic temperature is not affected by the ambient temperature.
24. Define tidal volume
Tidal volume (TV) is the volume of gas inspired or expired during each
normal, quiet respiration cycle.
25. Define residual volume
Residual volume (RV) is the volume of gas remaining in the lungs at the
end of a maximal expiration.
ww
26. What is spirometer?
spirometer is a device used to measure the respiratory volume
w.E
measurements. By using this device, lung volume and capacities can be
determined by measuring the amount of gas inspired or expired under a given
set of conditions or during a given time interval.
asy
27. Name any two methods of respiration rate measurement
En
The methods used to measure respiration rate are,
• Thermistor method
• Impedance pneumography gin
• CO 2 method of respiration rate measurement
eer
28. How is the respiration rate measured?
Respiration rate is measured by one of the method
• Thermistor method
i ng.
• Impedance pneumography
• CO 2 method of respiration rate measurement
net
29. Name the parts of sphygmomanometer
Sphygmomanometer consists of inflatable rubber bladder which is
known as cuff, rubber squeeze-ball pump and valve assembly.
30. What is Kymograph?
It is an instrument for recording variations in pressure, as of the blood,
or in tension, as of a muscle, by means of a pen or stylus that marks a
rotating drum.
31. What are Korotkoff sounds?
Sounds produced by sudden pulsation of blood being forced through a
partially occluded artery and heard during ausculatory blood pressure
determination are called korotkoff sounds.
11
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
32. Write down the demerits of indirect method of blood pressure
measurement
The demerits of indirect method of blood pressure measurement
(Sphygmomanometer) are,
i. Does not provide continuous recording of pressure variations.
ii. Less repetition rate and
The measured value depends up on the experience of the doctor and
his hearing capability.
33. What is hypertension and hypotension?
High blood pressure is known as hypertension and Low blood pressure
is known as hypotension.
34. What is the principle used in pulse rate measurement?
ww Photo electric sensor is used to measure the pulse rate. It consists of
light source and LDR. During the contraction of the heart, the blood flow to the
w.E
finger tip will increase, will reduce the amount of light fall on LDR and during
relaxation the amount of light will increase. This change in resistance per
minute will be measured as pulse rate.
asy
35. How is the pulse rate measured?
En
The pulse rate is measured using one of the following methods:
• Electrical impedance method
• Strain gauge method
gin
• Photoelectric method
• Microphone method eer
36. Which transducer is used for measuring temperature?Why?
Thermister, High sensitivity.
i ng.
37. What is tachycardia and bradycardia?
Bradycardia: The heart beats slowly i.e., less than 60 beats per minute
net
Tachycardia: The heart beats fastly i.e., more than 100 beats per minute
38. List the functions of blood cells. (Or) Give the functions of Blood cell
Red Blood Cell (RBC): It is used for the transport of oxygen and carbon
dioxide.
White Blood Cell (WBC): It defenses against infections and foreign
substances.
39. Write the main function of Red Blood Cells.
Red Blood Cells transport oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. Oxygen
combines with carbohydrate, fat, protein to release the energy required for cell
function.
12
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
40. What is the basic principle behind the working of laser based blood cell
counter?
The basic principle behind the laser based blood cell counter is that the
angle of scattered light intensity is different for different sized particles.
PART-B
1. Describe the measurement of pH and pO 2 in blood. (Ans: Unit 2 - Page No. 4 -
6)
2. Discuss the working principle of colorimeter with a neat block diagram. (Ans:
Unit 2 - Page No. 7)
3. Explain the working principle of spectrophotometer with a neat diagram. (Ans:
Unit 2 - Page No. 8)
4. Explain the Blood flow measurement using following technique. (i)
Electromagnetic principle (ii) Thermo dilution iii) ultrasonic principle. (Ans:
5. ww
Unit 2 - Page No. 9-13)
Explain the working principle of electromagnetic blood flow meter. What are its
6. w.E
advantages and disadvantages?(Ans: Unit 2 - Page No. 9-11)
Define cardiac output. Discuss various techniques to determine cardiac
output. (Ans: Unit 2 - Page No. 14-18)
7.
asy
Explain the Direct and Indirect method of Blood pressure measurement (Ans:
Unit 2 - Page No. 26-29)
8.
En
Explain the working of a blood cell counter with a neat block diagram.
gin
(Or)Explain the principle of operation of coulter counter. What is its
application? (Ans: Unit 2 - Page No. 36-39)
9.
20-21) eer
Explain CO 2 method of Respiration rate measurement (Ans: Unit 2 - Page No.
10.
11.
Page No. 21-22) i
Explain spirometer method of Respiration rate measurement (Ans: Unit 2 -
Explain the indirect method of BP measurement using Sphygmomanometer
ng.
12.
(Ans: Unit 2 - Page No. 28)
Explain the following: i) Fick's method for the determination of cardiac output.
(16) ii) Ultrasonic blood flow meter (Ans: Unit 2 - Page No. 15)
net
13. Explain Transmittance and reflectance method of Pulse rate measurement
(Ans: Unit 2 - Page No. 34-36)
PART-C
1. What are the different types of ultrasonic blood flow meter? Explain each in
detail. (Ans: Unit 2 - Page No. 11-13)
2. Explain the working principle and calibration procedure followed in colorimeter
with neat diagram. (Ans: Unit 2 - Page No. 7), also Refer videos
3. Elucidate the detailed procedure to detect blood pressure using
Sphygmomanometer and ultrasonic method. (Ans: Unit 2 - Page No. 28),(
Ans: Unit 2 - Page No. 11-13)
4. Explain in detail about thermo dilution and dye dilution of cardiac output
measurement technique. (Ans: Unit 2 - Page No. 16-17)
13
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
UNIT – III - ASSIST DEVICES
PART-A
1. What is pacemaker?
Pacemaker is an electrical pulse generator for starting or maintaining
the normal heart beat.
2. Classify pacing modes
1. Competitive
a. Fixed Rate
2. Non Competitive
a. Ventricular Programmed
i) R-wave inhibited (Demand)
ii) R-wave Triggered (Stand by)
b. Atrial Programmed
ww i) R-wave Synchronized
3.
w.E
Which type of electrode is applied in the case of external stimulation and
what is the current range?
The paddle shaped electrodes are applied on the surface of the chest
asy
and the current range is 20-150mA.
4.
En
When is internal stimulation employed?
gin
Internal stimulation is employed in cases requiring long term pacing
because of permanent damage that prevents normal self triggering of heart.
5. eer
Which type of electrode is applied in the case of internal stimulation and
what is the current range?
i ng.
The electrodes in the form of fine wires of teflon coated stainless steel,
spoon like electrodes are used. The current range is 2 - 15 mA.
6. Mention the types of pacemaker based on modes of operation of the
net
pacemaker.
Based on modes of operation, the pacemaker are classified into 5 types,
a) Ventricular Asynchronous pacemaker (Fixed Rate Pacemaker)
b) Ventricular Synchronous pacemaker
c) Ventricular inhibited pacemaker (Demand pacemker)
d) Atrial synchronous pacemaker (Standby pacemaker)
e) Atrial Sequential ventricular inhibited pacemaker
7. Give two important factors that demand internal pacemakers usage
• These are mostly used for permanent heart damage.
• There is 100% percent safety for the internal circuits
14
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
8. Differentiate between internal and external pacemaker
S.No External Pacemaker Internal Pacemaker
The pacemaker is placed outside The pacemaker is miniaturized and
the body. It may be in the form of is surgically implanted beneath the
1 wrist watch or in the pocket, from skin near the chest or abdomen
that one wire will go into the with its output leads are connected
heart through the vein. directly to the heart muscle.
It does not need the open chest It requires a minor surgery to place
2
surgery the circuit.
Mostly these are used for Mostly these are used for
3
temporary heart irregularities permanent heart damages.
9. What is defibrillator?
ww A defibrillator is an electronic device that creates a sustained
myocardial depolarization of a patients heart in order to stop ventricular
w.E
fibrillation or atrial fibrillation
10. What is fibrillation?
asy
The heart is able to perform its important pumping function only
through precisely synchronized action of the heart muscle fibres. A condition in
En
which this necessary synchronism is lost is known as fibrillation.
11. What is ventricular fibrillation? gin
eer
Ventricular fibrillation is a serious cardiac emergency resulting from
asynchronous contraction of the heart muscle fibres. Ventricles are not able to
pump the blood.
12. What will happen during fibrillation?
i ng.
During fibrillation the normal rhythmic contractions of either the atria
or the ventricles are replaced by rapid irregular twitching of the muscular wall.
net
13. Which fibrillation is more dangerous?
Ventricular fibrillation is more dangerous. Under this condition, the
ventricles may not pump the blood so, it may lead to death.
14. Distinguish between internal and external Defibrillator
S.No Internal Defibrillator External Defibrillator
1 It is used when the chest is opened It is placed on the chest
Large spoon shaped electrodes are Paddle shaped electrodes are
2
used used.
Voltage is in the range of 50 – Voltage is in the range of 1000 –
3
1000v 10000v
15
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
15. What is defibrillator and list the electrodes used in defibrillator?
A defibrillator is an electronic device that creates a sustained
myocardial depolarization of a patients heart in order to stop ventricular
fibrillation or atrial fibrillation.
Large spoon shaped electrode is used for internal defibrillation and
Paddle shaped electrode id used for external defibrillation
16. What are the advantages of rectangular wave defibrillator?
• Efficient and quick recovery of the heart to beat in the normal manner.
• Atrial fibrillation is not introduced.
• No burning of skin
17. What is the disadvantage of AC defibrillator?
In AC defibrillator,
wwi) Large currents used in external defibrillations not only produces heart
muscle contraction but also produces burning of skin under the electrodes.
w.E
ii) Atrium fibrillation is introduced while arresting ventricular fibrillation
18. Calculate energy stored in a 16µf capacitor of a defibrillator that is
asy
charged to a potential of 5000V (dc)
Given: C = 16µF; V = 5000V
1 1
En
E = 2 CV2 = 2 x 16 x 10−6 x (5000)2 = 200 Joules.
gin
19. Classify the defibrillator based on applied voltage.
eer
Based on the nature of the voltage applied, the defibrillators can be
classified into 6 types.
• A.C Defibrillator
• D.C Defibrillator i ng.
• Synchronized D.C Defibrillator
• Square pulse Defibrillator
• Double square pulse Defibrillator
net
• Biphasic D.C Defibrillator
20. Draw the defibrillator output waveform and indicate the output energy
level. (Or) Draw the circuit of DC defibrillator and give its output
specifications.
16
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
21. What is Dialyser?
Dialyser is a machine that performs dialysis, It removes impurities from
the blood of patients with malfunctioning kidneys. It is also known as kidney
machine.
22. What is Dialysis or haemodialysis?
Dialysis is the process of removal of nitrogenous waste products that
are formed due to metabolism as a result of severe renal failure.
(Or)
Haemodialysis, or simply dialysis, is a process of purifying the blood of
a person whose kidneys are not working normally.
23. What is Dialysate? Mention its composition.
Dialysate solution is a nonsterile aqueous electrolyte solution that is
ww
similar to the normal levels of electrolyte found in ECF Dialysate solution is
almost isotonic solution. Dialysate solution commonly contains 6 electrolytes.
w.E
they are, Sodium (Na+), Magnesium (Mg++), Chloride (Cl-), Potasium (K+),
Calcium (Ca++) and bicarbonate (HCO3-). the 7th component, non-electrolyte
glucose or dextrose is invariably present in the dialysis.
asy
24. What are the membrane used for Haemodialysis?
En
Synthetic and natural membranes are commonly used for filtration
applications. Membrane materials most often used include regenerated
gin
cellulose, cellulose acetate, polysulfone, polycarbonate, polyethylene,
polyolefin, polypropylene, and polyvinylidene fluoride.
25. What is the Working Principle of Dialyser?
eer
i ng.
Works on Works on principles of diffusion of solutes and convection of
fluid across semi-permeable membrane.
Blood flows by one side of a semi-permeable membrane, and a dialysate
flows by the opposite side. net
26. What are the various components of Dialyser?
The various components of Dialysers are,
• Blood Compartment
• Dialysate Compartment
• Semipermeable membrane
• Membrane support structure
27. Give the difference between AV graft and AV fistula.
An AV fistula is created by directly connecting an artery to a vein,
usually in the wrist, forearm or upper arm. The AV fistula causes extra
pressure by increasing the blood flow into the vein, making it grow larger and
stronger and providing easy access to the blood vessels.
17
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
The AV graft is created by connecting an artery to a vein using a
synthetic tube implanted under the skin and providing needle placement
access for dialysis
28. List the types of Dialyser
Dialyser can be classified according to three basic design
considerations: Parallel plate, Coil and Hollow fiber
29. Compare haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
Extra Corporeal Dialysis Intra Corporeal Dialysis
S.No
(Hemodialysis) (Peritoneal Dialysis)
In this method, blood is purified
using hemodialyser, which acts
In this method, the abdomen of the
ww 1
as artificial kidney. Blood is
removed from the body. Waste
patient acts as semi permeable
membrane. The dialysate solution
w.E
products diffuse through the
semi – permeable membrane.
They are continuously rinsed
passes through it to remove the waste
from the blood.
asy
with dialysate solution.
It is more efficiently used for It is comparatively less efficiently
2
waste removal.
En used.
3
Since blood is taken out from the
body, the process is little gin
It does not involve removal of blood,
complex and risk.
eer
so simple and risk free.
The time taken for dialysis is 3 to The time taken for dialysis is 9 to 12
4
6 hours. hours.
i
Dialysis can be performed at Dialysis can be performed only in
ng.
5
6
home dialysis centres
Dialysis must be done every day Dialysis is done 3 times in a week
net
30. List the Advantages and disadvantages of AV fistula
The AV fistula is considered to be the best choice for vascular access.
Advantages:
1. An AV fistula uses your own arteries and veins without the need for artificial
material.
2. The risk of clotting or infection is significantly lower than with other forms of
vascular accesses.
3. AV fistula surgery is usually done on an outpatient basis, under local
anesthetic, allowing for a rapid and easy recovery.
4. AV fistulas last years longer than other forms of vascular access and can last
for decades.
5. AV fistulas are less expensive to maintain then AV Grafts or Venus catheters.
18
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Disadvantages:
1. The AV fistula requires several weeks to months to mature before it can be
used.
2. AV fistulas may not be suitable for people with small or weak veins.
3. Strengthening the AV fistula requires daily exercises.
4. Some AV fistulas fail to mature and process must be repeated.
5. AV Fistulas are visible on the forearm.
31. List the Advantages and disadvantages of AV graft
Advantages:
1. The AV graft provides a solution for small or weak veins.
2. The AV graft can be used as soon as 2-4 weeks after placement.
3. AV graft surgery is usually done on an outpatient basis, under local
anesthetic, allowing for a rapid and easy recovery.
ww Disadvantages:
1.
2.
3.
w.E
Use of synthetic material in the body.
With AV graft there is an increased risk of blood clotting, and infections.
AV graft tends to close more quickly than the fistula.
4.
5. asy
AV graft needs constant attention and upkeep.
AV graft does not last as long as a fistula and will probably need to be
replaced eventually.
En
32. What is ventilator?
gin
A ventilator is a machine that supports breathing
33. List the various types of ventilators.
eer
Positive and Negative pressure ventilator i ng.
34. What are the various applications of Ultrasonic imaging?
Some of the applications of ultrasonic imaging are, Gynecology,
cardiology and cancer detection
net
35. List the advantages and disadvantages of Ultrasonic imaging.
Advantages:
1. Ultrasonic imaging is a non-invasive imaging technique that does not use
any ionizing radiation
2. Ultrasonic imaging gives clear and detailed images of Soft tissues
structures of the body which cannot be seen through x-ray.
3. Ultrasonic imaging is cheaper than MRI imaging
Disadvantages:
1. Ultrasonic imaging is expensive than X-ray
2. Bone blocks ultrasound
3. Artifact is produced.
19
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
36. What are the various parts of Ultrasound machine?
Transducer probe, CPU, Display, Keyboard, printer, Disk storage
device, transducer control probe
37. What are the various probes used in Ultrasound machine?
The various probes are, Linear, Curvilinear, Phased array and
Endocavitary Probes
38. What are the various modes of display in ultrasound imaging system?
The various modes of display are,
1. A-mode
2. B-mode
3. M-mode Or T-M mode
ww
39. Compare the various probes used in ultrasonic imaging system
The various probes are, Linear, Curvilinear, Phased array and
w.E
Endocavitary Probes
40. What are the various applications of MRI?
MRI may be used to:
asy
1. Evaluate the structure of the heart and surrounding blood vessels
2. Assess abnormal heart rhythm
En
3. Assess blood flow to the heart muscle
gin
4. Diagnose developmental joint abnormalities in children
5. Diagnose sports related injuries
6. Detect hidden tumour or infection in joint
eer
7. Detect bone cancer
8. Diagnose problems with the pituitary gland and brainstemi
9. Determine the condition of nerve tissue within the spinal cord ng.
10. Detect brain abnormalities like cysts, tumours, bleeding, swelling
11. Detect damage to the brain caused by an injury or a stroke net
41. List the components of MRI scanner
A large magnet, 3 Gradient coils, a RF coils, a patient table and a computer.
42. What is the use of gradient coils in MRI scanner?
Gradient Coils are used to alter the homogenous magnetic field in 3
different axis x, y, z by producing smaller magnetic field (mTesla) for localizing
the RF signal in space.
43. List the advantages and disadvantages of MRI.
Advantages of MRI:
1. MRI is a non-invasive imaging technique that does not use any ionizing
radiation
20
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
2. MRI gives clear and detailed images of Soft tissues structures of the body
such as the heart, liver, brain, ligaments and cartilage.
3. MRI can cover large portion of the body
4. MRI can provide information about blood movement inside blood vessels.
Disadvantages of MRI:
1. MRI is expensive
2. Patient must remain still in an enclosed machine, which may be a problem
for claustrophobic patients.
3. A metal implant in a patient's body may be affected by the strong magnet of
the MRI unit
4. MRI scan does not show Bone and calcium. so, disease such as osteoporosis
cannot be detected using MRI scanning.
ww
44. Give difference between closed and opened MRI .
S.No Closed MRI Open MRI
1
2
w.E
High Field (Typical 1.5 T or 3T)
High SNR
Low Field (Typical 0.2 T – 0.4T)
Low SNR
3
asy
High image quality Low image quality
4
5
Fast imaging
Advanced Applications En Slow imaging
Limited Applications
6 Increased patient anxiety gin Less patient anxiety
7 Claustrophobic patient problems
eer
Claustrophobic patient handling
8 High acoustic noise levels
i
Lower acoustic noise levels
ng.
1.
PART-B
How pacemakers are classified based on the modes of operation? Explain its
net
working principle. (Ans: Unit 3 - Page No.3-6)
2. With neat diagram, Describe the function of ventricular inhibited pacemaker.
(Ans: Unit 3 - Page No. 10-11)
3. What are the different types of DC defibrillators? Explain the principle of DC
Defibrillator with neat diagram (Ans: Unit 3 - Page No.16, 17-19 )
4. With a neat diagram, illustrate the working of DC defibrillator. (Ans: Unit 3 -
Page No. 20-21 )
5. With a neat diagram, illustrate the working of Biphasic DC defibrillator. (Ans:
Unit 3 - Page No. 24-25 )
6. Discuss how the image is constructed using ultrasound with neat diagrams.
(Ans: Unit 3 - Page No. 17-19 )
7. Draw a block diagram of MRI system and explain the image reconstruction
using it. (Ans: Unit 3 - Page No. 22-26 )
21
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
8. Explain in detail the principle block diagram and working of peritoneal
dialyser. (Ans: Unit 3 - Page No. 6-7)
PART-C
1. With a neat block diagram explain the principle of operation of hemo dialyzer
machine. (Ans: Unit 3 - Page No. 8-9)
2. Explain the function of synchronized DC Defibrillator with neat block diagram.
(Ans: Unit 3 - Page No.20-21 )
3. Explain positive pressure ventilator with neat diagram. (Ans: Unit 3 - Page No.
14-15 )
ww
w.E
asy
En
gin
eer
i ng.
net
22
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
UNIT – IV PHYSICAL MEDICINE AND BIOTELEMETRY
PART-A
1. What is Diathermy? List its types
Diathermy is the treatment process by which cutting, coagulation,
Blending etc. of tissues are obtained.
Types: i) shortwave diathermy (ii) Microwave diathermy
(iii) Ultrasonic diathermy (iv) Surgical diathermy
2. Give the applications of diathermy
Diathermy is used to treat the following conditions:
arthritis neuralgia
back pain sprains and strains
fibromyalgia tenosynovitis
muscle spasms tendonitis
ww myositis bursitis
3.
w.E
What are the benefits of diathermy
Treating injuries with heat can increase blood flow and make connective
asy
tissue more flexible. It can also help minimize inflammation and reduce the
incidence of edema, or fluid retention.
En
By increasing blood flow to the site of an injury, the deep heat generated
with diathermy can accelerate healing.
4. gin
Compare shortwave, microwave and ultrasound diathermy.
S. eer
No
Shortwave diathermy
uses
Microwave diathermy
high-frequency uses microwaves to
iUltrasound diathermy
ng.
uses sound waves to heat
1 electromagnetic energy generate heat in the
to generate heat body
it can’t penetrate deep
deep tissues
net
muscles, it’s best suited
it can penetrate deep it can penetrate deep
2 for areas that are closer
muscles muscles
to the skin, such as the
shoulders
27.12 MHz at 11m 2450 MHz at 12.25cm 1 MHz or 3 MHz at 300m
3
wavelength wavelength or 100 wavelength
Using capacitive plate
Microwave is produced Ultrasound is produced
4 and cable
using Magnetron using Piezo electric cyrstal
electromagnetic energy
Maximum power Maximum power
5 3W/cm2
delivered is 500W delivered is 100W
Gel is applied to the
6 No gel is applied No gel is applied
affected area of the body
23
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
5. What are the risks of diathermy?
1. The electromagnetic energy used in shortwave and microwave diathermy
can cause extreme heat in metal devices such as:
bone pins
dental fillings
metal sutures
2. This could cause burns in the tissue near the implant. The procedure
should not be used over these areas to avoid the risk of burning.
6. List the advantages and disadvantages of shortwave diathermy.
Advantages:
When currents having very high frequencies, the motor or sensory
nerves are not stimulated and there is no contraction of the muscles. Thus
there is no discomfort to the patient.
wwDisadvantages:
Though most short-wave diathermy machines have output power
w.E
control, there is no indication of the amount converted and absorbed heat
within the body tissues. Therefore intensity of treatment depends on the
subjective sensation of warmth felt by the patient.
7. asy
Give the applications of ultrasonic diathermy
En
It is used where shortwave treatment failed and in cases where
localizing of heat is required. It is very useful in curing of diseases of peripheral
gin
nervous system like neuritis, skeletal muscle system like arthritis and skin like
ulcers
8. What are the advantages of ultrasonic diathermy?
eer
i ng.
a. Ultrasonic energy enables this massage to be carried out to greater depth
than when pressure cannot be exerted by hand because of intolerable pain
caused to the patient.
b. Unlike the operation of a short wave therapy unit, tuning is not needed
during treatment.
net
c. The operating frequency is also not very critical and may vary to the extent
±10%.
9. What is the frequency of operation of ultrasound diathermy? What is the
reason for this frequency selection?
The absorption of ultrasonics by the tissues is frequency dependent.
Higher the frequency, the quicker the energy loss and less is the penetration. A
frequency below 1MHz, the ultrasonic energy beams diffuse and there is no
efficient treatment. Therefore the frequency in the range of 800 KHz to 1MHz is
most widely adopted
24
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
10. What is the frequency of currents used in surgical diathermy units? Why?
The frequency of currents used in surgical diathermy units is in the
range of 1–3 MHz. This frequency is quite high in comparison with that of the
50 Hz mains supply. This is necessary to avoid the intense muscle activity and
the electrocution hazards which occur if lower frequencies are employed
11. Give the advantages of microwave diathermy
• The technique of application of microwave diathermy is very simple
• It does not require tuning for individual treatments. Since microwaves
are transmitted from an emitter and directed towards the portion of
the body to be treated directly.
• Better therapeutic results are obtained by using microwave diathermy
than short wave diathermy.
• There is no pad shaped electrode.
ww
12. What is electrosurgical diathermy?
w.E
An Electrosurgical diathermy is a generator capable of producing a
cutting and/or coagulating clinical effect on tissue by the use of alternating
current at a high frequency (RF - radio frequency, also known as radio
surgery).
asy
En
13. what are the various modes of electrosurgery?
gin
The different modes of electrosurgery that can be performed using
electrosurgical unit are,
1. Cutting (Or) Electrotomy
2. Coagulation eer
a. Fulguration
b. Desiccation
3. Blending (or) Haemostasis
i ng.
14. Give difference between cutting and coagulation in diathermy.
net
S.No Cutting Coagulation
1 Constant waveform is used Pulsed waveform is used
Current flows for 100% of the
2 Current flows only for 6% of the cycle
cycle
3 Low voltage (1300 – 2300)V High voltage (3500 – 9000)V
4 Produces intense heat Produces less heat
Cutting electrodes like needle,
5 Ball, Bipolar electrode is used
wire loop electrode is used
15. List some electrodes used in surgical diathermy
Needle electrode, Wire Loop electrode, Ball electrode, Patient plate electrode
25
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
16. Define Cutting and Coagulation (Or) What is cutting and Coagulation in
Electrosurgical diathermy?
Cutting:
When high frequency current flows through the sharp edge of a wire
loop or band loop or the point of a needle into the tissue, there is a high
concentration of current at this point. The tissue is heated to such an extent
that the cells which are immediately under the electrode, are torn apart by the
boiling of the cell fluid. The indifferent electrode establishes a large area
contact with the patient.
Coagulation:
Coagulation of tissue is caused by the high frequency current flowing
through the tissue and heating it locally so that it coagulates from inside. The
coagulation process is accompanied by a grayish-white discoloration of the
ww
tissue at the edge of the electrode.
There are two types of coagulation: 1) Desiccation (Or Pinpoint) and 2)
w.E
Fulguration (Or Spray).
17. Bring out the need for patient plate in surgical diathermy.
asy
The patient electrode or indifferent electrode establishes a large area
contact with the patient and the RF current is therefore, dispersed so that very
En
little heat is developed at this electrode.
18. Define Desiccation and Haemostasis.
gin
In desiccation, needle-point electrodes are stuck into the tissue and
eer
then kept steady. Depending upon the intensity and duration of the current, a
high local increase in heat will be obtained. The tissue changes due to drying
and limited coagulation.
i ng.
The concurrent use of continuous radio-frequency current for cutting
and a burst wave radiofrequency for coagulation is called Haemostasis mode.
19. What does the term fulguration refer to?
net
Fulguration is another type of coagulation. Fulguration can be defined
as non-contact coagulation in which current sparks or jumps from the active
electrode to the tissue.
The term ‘fulguration’ refers to superficial tissue destruction without
affecting deep-seated tissues.
20. Mention the advantages of a Bio-telemetry System
a. Major advantage of using biotelemetry is removing the cables from patient
and providing a more comfortable medium to patient. Patient needs to
carry only a small transmitter.
b. Isolation of patient from high voltage completely. Transmitters in the
patient side work with batteries without any danger of electrical shock
26
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
21. Draw the block diagram of Bio-telemetry System
22. List the applications of Bio-Telemetry.
• Monitoring ECG even under ergonomic conditions.
ww
• Monitoring the health of astronauts in space.
• Patient monitoring in an ambulance and other locations away from hospital.
w.E
• Research on unanaesthetized animals.
asy
23. What are the various modulation systems used in biotelemetry?
a. Double modulation : either AM/AM , AM/FM, FM/FM, FM/AM - to avoid
loading effect.
En
b. Pulse width modulation.: More than one bio signal can be transmitted
and recorded
gin
eer
24. What is the modulation techniques used for biotelemetry? Mention the
reason for adopting that modulation scheme.
i
• Double modulation : either AM/AM , AM/FM, FM/FM, FM/AM - to avoid
loading effect. ng.
• Pulse width modulation.: More than one bio signal can be transmitted and
recorded
net
Loading effect is avoided in double modulation.
More than one bio signal can be transmitted and recorded using pulse width
modulation.
25. Compare TDM and FDM Bio-telemetry System.
S.No TDM FDM
1 In FDM, Frequency sharing takes
In TDM, time sharing takes place
placee
2 In TDM, Synchronization pulse is
In FDM, Guard band is necessary
necessary
3 TDM works with digital as well as While FDM, works only with
analog signals analog signals
27
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
PART-B
1. Explain the simplified circuit diagram of a microwave diathermy machine. (Ans:
Unit 4 - Page No. 14-17)
2. Draw the block diagram of short wave diathermy unit and explain it. (Ans: Unit
4 - Page No. 4-7 )
3. Explain the basic principle of operation of an ultrasonic diathermy unit. List out
its applications. (Ans: Unit 4 - Page No. 12-14 )
4. Draw the block diagram of shortwave and microwave diathermy. Explain in
detail. (Ans: Unit 4 - Page No. 4-7, 14-17)
5. Discuss the working of a surgical diathermy unit with a neat block diagram
(Ans: Unit 4 - Page No. )
6. Explain the working of single channel ECG telemetry system. (Ans: Unit 4 -
Page No. )
7. Explain the working of a Multichannel Telemetry system with a neat block
ww
diagram. (Ans: Unit 4 - Page No. )
1.
w.E PART-C
With a neat block diagram, show the operation of a combined single channel
asy
telemetry system for ECG signal and respiration rate. (Ans: Unit 4 - Page
No.33-34 )
2.
En
Explain in detail the design requirements of an ECG telemetry receiver. Also,
gin
mention the role of IF amplifier in the receiver. use suitable illustration (Ans:
Unit 4 - Page No. 36-39 )
3.
eer
Draw the typical block diagram of electrosurgical unit and explain its
functioning. Mention the hazards that commonly occur in electrosurgical unit.
(Ans: Unit 4 - Page No. 17-26)
i ng.
net
28
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
UNIT – V RECENT TRENDS IN MEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION
PART-A
1. What is a radio pill?
Radio is a silicon-coated capsule containing a miniature radio
transmitter that can be swallowed by a patient. During its passage through the
digestive tract a radio pill transmits information about internal conditions
(acidity, etc.).
2. How the data are recorded using radio pill?
The radio pill is passed into the gastrointestinal tract like the normal pill. The
sensor in the pill collects the required parameter and transmits it through the
telemetry system. The data recorder picks up the transmitted signal, displays it
and stores the data in a solid-state memory until the data is downloaded into
the PC platform.
3. ww
Define telemedicine
w.E
• It is the application of tele communications and computer technology to
deliver health care from one location to other.
asy
• It involves the use of modern information to deliver timely health service to
those in need by the electronics transmission.
4. En
Explain the principle of telemedicine
gin
Telemedicine is a rapidly developing application of clinical medicine
where medical information is transferred via telephone, the internet or other
eer
networks for the purpose of consulting and sometimes remote medical
procedures or examinations.
5. State the applications of telemedicine i ng.
• Tele radiology.
• Tele cardiology.
• Tele education.
net
• Tele consultation.
6. What are the essential parameters of telemedicine
• Primary patient data.
• Patient history.
• Clinical information.
• Investigations
• Data and reports.
7. State the telemedicine concepts
• Store and forward concept
• Real time concept
29
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
8. What is the use of A/D converter in the transmitter of a biotelemetry
system?
A/D converter is used to convert analog signal to digital signal
9. What is insulin?
Insulin is a hormone created by pancreas that controls the amount of
glucose in the bloodstream at any given moment. It also helps to store glucose
in liver, fat, and muscles. Finally, it regulates body’s metabolism of
carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
10. What is insulin pump?
Insulin pumps are small, computerized devices that mimic the way the
human pancreas works by delivering small doses of short acting insulin
continuously
ww
11. What causes someone to be prescribed insulin?
w.E
• If the body doesn’t make insulin or doesn’t make enough, then the person
is diagnosed with type 1 diabetes.
• On the other hand, if the body doesn’t use insulin properly, then the
asy
person is diagnosed with type 2 diabetes.
En
12. What are the different types of insulin?
insulin gin
Rapid-acting, Short-acting, Intermediate-acting, Long-acting, Premixed
13. How do you take insulin? eer
i ng.
Many people with diabetes who use insulin self-administer it by
injecting it with a syringe. The outside of the syringe is marked with lines
denoting the amount of medication in the needle. There are different size
syringes that you can choose from with the help of your doctor. net
14. How do you take insulin without a syringe?
Insulin pens, Insulin pumps, Jet injection, Inhalable insulin
15. What are the disadvantages of using an insulin pump?
Disadvantages of Insulin Pumps
• Some people gain weight while using an insulin pump.
• people get into trouble if your pump stops working or your catheter comes
out.
• Pump has to be carried all the time.
30
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
16. What are the drawbacks to insulin treatment for diabetes? (Or) What are
the disadvantages of taking insulin?
The more common side effects that occur with insulin regular
(human) include:
• Swelling of your arms and legs.
• Weight gain.
• Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). This needs to be treated. ...
• Injection site reactions. ...
• Skin changes at the injection site (lipodystrophy)
17. Does an insulin pump check blood sugar?
The pump delivers insulin 24 hours a day through a catheter inserted
under the skin. Approved for people over the age of 18, the Vibe monitors
blood sugar levels every five minutes. The latest glucose readings, as well as
ww
glucose level trends over time, are visible on a built-in device screen
18.
w.E
Is insulin pump better than injections?
In the largest and longest study ever of an insulin pump with a
continuous glucose sensor, patients who used the device achieved better
asy
control of their blood sugar than patients taking insulin injections
19.
En
What are the side effects of insulin?
Insulin regular (human) side effects
• sweating.
• dizziness or lightheadedness.
gin
• shakiness.
eer
• hunger.
• fast heart rate.
• tingling in your hands, feet, lips, or tongue.
i ng.
• trouble concentrating or confusion.
• blurred vision. net
20. What is the difference between injecting insulin using a syringe vs an
insulin pump?
Injections are cheaper and take less training to use than insulin pumps.
A patient will have to test blood sugar levels before every injection. There is
the possibility a patient can develop resistant areas if injections are done too
frequently in the same spot.
21. What is endomicroscopy?
Endomicroscopy is a technique for obtaining histology like images from
inside the human body in real time by a process known as optical biopsy
22. List the applications of endomicroscopy.
The main clinical applications are,
31
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
• Imaging of the tumour margins of the brain and gastro-intestinal tract
• live imaging of cartilage and tendon
23. What is brain computer interface (BCI)?
Brain-computer interface (BCI) is a collaboration between a brain and
a device that enables signals from the brain to direct some external activity,
such as control of a cursor or a prosthetic limb. The interface enables a direct
communications pathway between the brain and the object to be controlled
24. Is brain computer interface real?
A brain-computer interface (BCI) is a computer-based system that acquires
brain signals, analyzes them, and translates them into commands that are
relayed to an output device to carry out a desired action. In principle, any type
of brain signal could be used to control a BCI system.
ww
25. What are brain computer interfaces used for?
w.E
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) allow their users to communicate
or control external devices using brain signals rather than the brain's
normal output pathways of peripheral nerves and muscles.
asy
26. What is brain computer interface (BCI)?
En
Brain-computer interface (BCI) is a collaboration between a brain and
a device that enables signals from the brain to direct some external activity,
gin
such as control of a cursor or a prosthetic limb. The interface enables a direct
communications pathway between the brain and the object to be controlled.
eer
PART-B i ng.
1. Explain how telemedicine helps the patients and medical practitioners. (Ans:
Unit 5 - Page No. 1-10)
2. Construct and discuss the working of endomicroscopy unit in detail (Ans: Unit 5
- Page No. 26-34)
net
3. Explain how insulin pump works in detail with suitable diagram. (Ans: Unit 5 -
Page No. 10-18)
4. What is radio pill? Explain in detail. (Ans: Unit 5 - Page No. 19-25 )
5. Explain in detail about Brain machine interface (Ans: Unit 5 - Page No. 35-48 )
6. Explain how Lab on chip (LOC) integrates several laboratory functions on a
single integrated chip. (Ans: Unit 5 - Page No. 35-48)
PART-C
1. Explain about the evolution and technologies involved in telemedicine and
discuss the application areas of telemedicine. (Ans: Unit 5 - Page No. 1-10 )
<<<<<<<< All the Best >>>>>>>
32
Downloaded From: www.EasyEngineering.net
You might also like
- MICEI Annual Report 2023Document40 pagesMICEI Annual Report 2023Hermes MATHEUSNo ratings yet
- Biology 13 QuestionsDocument4 pagesBiology 13 QuestionsAshmita Kumar33% (12)
- Unit 1 Bio Potential Generation and Electrode TypesDocument13 pagesUnit 1 Bio Potential Generation and Electrode TypesAleeshaNo ratings yet
- 35d PDFDocument8 pages35d PDFhuskerchamps0% (1)
- Medical Elec. QB With BT and AssignmentDocument50 pagesMedical Elec. QB With BT and AssignmentpavithrenNo ratings yet
- EI6704 - Biomedical Instrumentation Unit-IDocument9 pagesEI6704 - Biomedical Instrumentation Unit-Ikitcha5555No ratings yet
- Action Potential Electrodes Eeg Emg: L - T - P - S 3 - 0 - 2 - 0Document25 pagesAction Potential Electrodes Eeg Emg: L - T - P - S 3 - 0 - 2 - 0Ram MNo ratings yet
- Basic of Biomedical Instruments Mcqs (Set-1) : Chapter: Bio Potential and Electrodes TypesDocument8 pagesBasic of Biomedical Instruments Mcqs (Set-1) : Chapter: Bio Potential and Electrodes TypesdeborahNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Biopotential Generation and Electrodes TypesDocument19 pagesUnit - 1 Biopotential Generation and Electrodes Typespeta khyatheeswarNo ratings yet
- BiosignalDocument27 pagesBiosignalAurongo NasirNo ratings yet
- Ec8073-Medical Electronics Study MaterialDocument116 pagesEc8073-Medical Electronics Study Materialpurushothsatha100% (1)
- 03.resting Potential & Action PotentialDocument122 pages03.resting Potential & Action Potentialapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Electrooculography and It's ApplicationsDocument48 pagesElectrooculography and It's ApplicationsRose Edward50% (6)
- 4 - Neural Conduction and Synaptic TransmissionDocument10 pages4 - Neural Conduction and Synaptic TransmissionElmer SalazarNo ratings yet
- Origin of Bio PotentialDocument25 pagesOrigin of Bio Potential6115 Pratish MNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The History of Bioelectricity: Fundamentals of Neuroscience, Part 1: The Electrical Properties of The NeuronDocument4 pagesLesson 1: The History of Bioelectricity: Fundamentals of Neuroscience, Part 1: The Electrical Properties of The NeuronXyrille SantosNo ratings yet
- EC8073-LN NotesDocument220 pagesEC8073-LN NotesCse -B.Dhivya BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Action Potential: L - T - P - S 3 - 0 - 2 - 0Document12 pagesAction Potential: L - T - P - S 3 - 0 - 2 - 0Ram MNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Basic Physics of Galvanic Cells: I. Equivalent Circuit ModelsDocument7 pagesLecture 1: Basic Physics of Galvanic Cells: I. Equivalent Circuit Modelsanup chauhanNo ratings yet
- Biopotential 1Document17 pagesBiopotential 1Avinash GaikwadNo ratings yet
- III Year / V Semester - EEEDocument7 pagesIII Year / V Semester - EEEKarthikeyan GovindarajNo ratings yet
- Membrane PotentialDocument24 pagesMembrane Potentialubaid salimNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument32 pagesElectrochemistrySHOBHIT GAUTAM 2K21/A12/72No ratings yet
- Electricity 1Document42 pagesElectricity 1تصميم دعوات و تهنئة الكترونيةNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RMP ND APDocument78 pagesIntroduction To RMP ND APHariharanNo ratings yet
- OMD551-QB - 2mark With AnswerDocument17 pagesOMD551-QB - 2mark With AnswerKarthikeyan GovindarajNo ratings yet
- Basics of Biomedical Instrumentation OMD551Document22 pagesBasics of Biomedical Instrumentation OMD551Sri ArunaaNo ratings yet
- Omd 551 - Part A & Part BDocument17 pagesOmd 551 - Part A & Part Baarthir88100% (2)
- Ec1001 - Medical Electronics - Question Bank (2marks With Answer)Document26 pagesEc1001 - Medical Electronics - Question Bank (2marks With Answer)deepanece100% (1)
- Biomedical Instrumentation I: Lecture-5: The Origin of BiopotentialsDocument35 pagesBiomedical Instrumentation I: Lecture-5: The Origin of BiopotentialsNitin PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 4 - Membrane Potential N Action PotentialDocument7 pages4 - Membrane Potential N Action PotentialRaj KishoreNo ratings yet
- Electricity Within The Body Part 2Document31 pagesElectricity Within The Body Part 2ahmed husseinNo ratings yet
- Bio Potential and Bio ElectrodesDocument39 pagesBio Potential and Bio ElectrodesSiva NareshNo ratings yet
- K. Ramakrishnan College of Technology Ramakrishnan College of Technology Ramakrishnan College of TechnologyDocument48 pagesK. Ramakrishnan College of Technology Ramakrishnan College of Technology Ramakrishnan College of Technologyfaten emadNo ratings yet
- Lecure-5 The Origin of Biopotentials - 2Document34 pagesLecure-5 The Origin of Biopotentials - 2Noor Ahmed100% (1)
- Bioelectric Signals and ElectrodesDocument20 pagesBioelectric Signals and Electrodesنذير الشرعبيNo ratings yet
- 2M - BmiDocument48 pages2M - BmiAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- EI2311-Biomedical Instrumentation Question BankDocument20 pagesEI2311-Biomedical Instrumentation Question BankrajapandiyaNo ratings yet
- RestingMembranePotential JeffLindoDocument8 pagesRestingMembranePotential JeffLindoAbraham AberaNo ratings yet
- C 2.2 HL Neural SignalingDocument37 pagesC 2.2 HL Neural Signalingelizabeth.arockiadassNo ratings yet
- Basics of Biomedical Instrumentation NotesDocument24 pagesBasics of Biomedical Instrumentation NotesSteni GNo ratings yet
- RestingMembranePotential JeffLindoDocument8 pagesRestingMembranePotential JeffLindoClive NyabutiNo ratings yet
- Resting Membrane PotentialDocument8 pagesResting Membrane PotentialAhmad Atiq MalikiNo ratings yet
- Bmi Unit 1 To 5Document109 pagesBmi Unit 1 To 5sam08032004No ratings yet
- Action Potential: Axon Membrane Neuron Ion Channels Threshold Potential Depolarization RepolarizationDocument31 pagesAction Potential: Axon Membrane Neuron Ion Channels Threshold Potential Depolarization RepolarizationJennie KimNo ratings yet
- PleteDocument8 pagesPleteAnwesha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Generation and Conduction of Action PotentialsDocument19 pagesGeneration and Conduction of Action PotentialspuchioNo ratings yet
- Membrane Potential and Action Potential (1) - 1Document51 pagesMembrane Potential and Action Potential (1) - 1qvk8yy9pxcNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell EMF of A Cell Internal RDocument2 pagesElectrochemical Cell EMF of A Cell Internal RYashwant patelNo ratings yet
- Omd551 Part ADocument8 pagesOmd551 Part AArul50% (2)
- R.M.D. Engineering College - Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument17 pagesR.M.D. Engineering College - Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringVasanthakumar MariappanNo ratings yet
- Origin of Bioelectric Signal1Document65 pagesOrigin of Bioelectric Signal1SanathNo ratings yet
- الوحدة الأولىDocument16 pagesالوحدة الأولىHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- CHM031 Module 1 ReviewerDocument8 pagesCHM031 Module 1 ReviewerrainNo ratings yet
- Elec 1 RemovedDocument16 pagesElec 1 RemovedSaifan PlayzNo ratings yet
- Ent 311 - Medical Electronics and Bio-Instrumentation: WEEK: 4 & 5Document35 pagesEnt 311 - Medical Electronics and Bio-Instrumentation: WEEK: 4 & 5Nitin PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- f2 Chapter 7 Electricity and MagnetismDocument21 pagesf2 Chapter 7 Electricity and MagnetismLorza TigaBelasNo ratings yet
- Physiology Course: Dr. Velu M. RachelDocument18 pagesPhysiology Course: Dr. Velu M. RachelKunda JosephNo ratings yet
- Is Nuclear Energy Safe? -Nuclear Energy and Fission - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandIs Nuclear Energy Safe? -Nuclear Energy and Fission - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Quarantine Clearance Quarantine Clearance: Barangay Cato Barangay CatoDocument2 pagesQuarantine Clearance Quarantine Clearance: Barangay Cato Barangay CatoBarangay CatoNo ratings yet
- Motivation BisDocument20 pagesMotivation BishùhjgNo ratings yet
- Flow Sheet Writeup Gypsum DewateringDocument2 pagesFlow Sheet Writeup Gypsum DewateringKumarrathinamNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Public Transportation For Bus-Based Commuting in IndiaDocument8 pagesAn Analysis of Public Transportation For Bus-Based Commuting in IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Sex-Based Differences in Physiology: What Should We Teach in The Medical Curriculum?Document3 pagesSex-Based Differences in Physiology: What Should We Teach in The Medical Curriculum?Khaled Abdel-saterNo ratings yet
- IFR 150 GSM CoverallDocument4 pagesIFR 150 GSM CoverallBinay100% (1)
- Elecrolysis Cell DrawingDocument2 pagesElecrolysis Cell DrawingRimaNo ratings yet
- Essentials of PsychologyDocument519 pagesEssentials of PsychologyhodovskyNo ratings yet
- An Analysis On Maternity Benefit Laws of BangladeshDocument33 pagesAn Analysis On Maternity Benefit Laws of Bangladeshayesha.siddika.241No ratings yet
- Learning Challenges of Student Nurses in Virtual Learning QuestionnairesDocument8 pagesLearning Challenges of Student Nurses in Virtual Learning QuestionnairesJelaveil De VeraNo ratings yet
- Lipid Analysis: An Introduction ToDocument8 pagesLipid Analysis: An Introduction ToElaiza HerreraNo ratings yet
- Surgery 2Document27 pagesSurgery 2junaid4shaikhNo ratings yet
- Global Stem Cell Therapy Market IHealthcareAnalyst, IncDocument2 pagesGlobal Stem Cell Therapy Market IHealthcareAnalyst, InciHealthcareAnalyst, Inc.No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan of Education (MS (Document9 pagesLesson Plan of Education (MS (charanjit kaurNo ratings yet
- 5V6 DiodeDocument5 pages5V6 DiodeAchmad Rifdatul HisanNo ratings yet
- Server Room Cleaning ProcedureDocument3 pagesServer Room Cleaning ProcedureEmmanuel BorsariNo ratings yet
- Corticosteroids: Dr.R.Prameela, Assistant Professor of Pharmacology, GMC, SrikakulamDocument64 pagesCorticosteroids: Dr.R.Prameela, Assistant Professor of Pharmacology, GMC, SrikakulamRamadi PrameelaNo ratings yet
- CPG - Management of AcneDocument97 pagesCPG - Management of Acneumiraihana1No ratings yet
- Assessing Thorax and LungsDocument26 pagesAssessing Thorax and LungsTarah LedesmaNo ratings yet
- H05V-K H07V-KDocument2 pagesH05V-K H07V-Ktwo travellerNo ratings yet
- Definition of Biomedical Model of HealthDocument4 pagesDefinition of Biomedical Model of Healthتالیہ مرادNo ratings yet
- Imputed Income ChartDocument2 pagesImputed Income ChartclaokerNo ratings yet
- Business Plan AbmDocument42 pagesBusiness Plan AbmMikaela MassalangNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W7Document5 pagesDLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W7ADONNIS PESCASIONo ratings yet
- Equivalent Circuit of A Practical AutotransformerDocument8 pagesEquivalent Circuit of A Practical AutotransformerBT21EE017 Gulshan RajNo ratings yet
- Gadget Building 2016Document36 pagesGadget Building 2016Kelvin MsafiriNo ratings yet
- 2021 GKS-U Application FormDocument18 pages2021 GKS-U Application FormsheeryahNo ratings yet
- Thesis Chapter 1Document9 pagesThesis Chapter 1DaNica Tomboc JavierNo ratings yet