Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsGB2 Cell Cycle
GB2 Cell Cycle
Uploaded by
sja254677Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- MS - Worthy of It All - Key of A & GDocument6 pagesMS - Worthy of It All - Key of A & GDianne HorarioNo ratings yet
- 13 Principles of Wiccan BeliefDocument7 pages13 Principles of Wiccan BeliefWayne100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - Part2Document32 pagesChapter 8 - Part2Youssef MoustafaNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)Document2 pagesWORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)gyeojib aeNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)Document2 pagesWORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)gyeojib aeNo ratings yet
- Biology Anomalies and MeiosisDocument11 pagesBiology Anomalies and MeiosisJodi Kryztel JosolNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument12 pagesBiologyfloresstephaniejoycNo ratings yet
- Meiosis (: ListenDocument13 pagesMeiosis (: ListenmuhammadismailNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument25 pagesMeiosisAnjelica BucasasNo ratings yet
- GeneticDocument34 pagesGeneticDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument7 pagesMitosis Vs MeiosisJD DX100% (1)
- 2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument21 pages2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisKinjNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument4 pagesMitosis and MeiosisMicah Porcal ArelladoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document15 pagesUnit 2Jhon Rey RodeoNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Cell DivisionDocument12 pagesMeiosis and Cell DivisionAD-MQNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 With Arabic Words 2Document36 pagesChapter 13 With Arabic Words 2jadjaffal01No ratings yet
- Cell-Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell-Cycle and Cell DivisionToby TrollyNo ratings yet
- Botany Module 3Document6 pagesBotany Module 3Yaz VergaraNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Chapter 13 NotesDocument5 pagesAP Bio Chapter 13 NotesAndrew SongNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction SlidesDocument29 pagesMeiosis and Sexual Reproduction Slidesmysticgalaxy2823No ratings yet
- 2 MeiosisDocument36 pages2 MeiosisnthabiisengNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument21 pagesMitosis and MeiosisJuLie Ann DeGuzman Geslani100% (1)
- MeiosisDocument34 pagesMeiosisJared CoyagboNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument3 pagesMeiosisSachintha JayamahaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notebook: 03.02 Meiosis: Key Questions and Terms Notes Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument4 pagesBiology Notebook: 03.02 Meiosis: Key Questions and Terms Notes Asexual and Sexual ReproductionCameron LightbourneNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 1Document37 pagesMeiosis 1Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Chapter 19 Pages 651 - 663Document20 pagesMeiosis: Chapter 19 Pages 651 - 663María SalazarNo ratings yet
- 2.meiosis 1Document36 pages2.meiosis 1taskmask37No ratings yet
- (Unit 2) Cell Division - MeiosisDocument9 pages(Unit 2) Cell Division - MeiosisHanif AlfarizkiNo ratings yet
- Science HW MM Compare and ConstrastDocument1 pageScience HW MM Compare and ConstrastjiNo ratings yet
- Meiosis - Clay ModellingDocument4 pagesMeiosis - Clay ModellingAlexandra M.No ratings yet
- JajajaDocument2 pagesJajajaLouie BarrientosNo ratings yet
- MEIOSIS and MITOSISDocument4 pagesMEIOSIS and MITOSISHannaj May De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- ComparisonDocument2 pagesComparisonMary Rose AllinegNo ratings yet
- La Meiosis en Distintos Tipos de Ciclos Vitales: Ciclo de Vida de ChlamydomonasDocument21 pagesLa Meiosis en Distintos Tipos de Ciclos Vitales: Ciclo de Vida de ChlamydomonasLENNI DAYARA HERNANDEZ GARCIANo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument1 pageMitosis Vs Meiosisgovicky565No ratings yet
- CH.10 Meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesDocument5 pagesCH.10 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cyclesdidua08No ratings yet
- Biology (Form 4)Document25 pagesBiology (Form 4)Aloysius RajNo ratings yet
- Meiosis - WikipediaDocument89 pagesMeiosis - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 - Meiosis NotesDocument3 pagesBio 1 - Meiosis NotesJayson RiveraNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 2Document6 pagesMeiosis 2Areefa MohamedNo ratings yet
- 2nd MT Biology ReviewerDocument4 pages2nd MT Biology ReviewerAliah HernandezNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Online Study GuideDocument6 pagesCH 13 Online Study Guideюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument62 pagesMeiosisEMANUEL PAGAN-VELEZNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument13 pagesMeiosistaylorNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesCell Divisionlelejfintlskia1we39No ratings yet
- Meiosis Meiosis Halves The Number of Chromosomes in The Parent Cell. The Half Number of ChromosomesDocument4 pagesMeiosis Meiosis Halves The Number of Chromosomes in The Parent Cell. The Half Number of ChromosomesTracia WalcottNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PDFDocument22 pagesMeiosis PDFEbook DownloadNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment 1: BY: Sucheta Patnaik 15Bbt0122 Harshita Agarwal 15BBT0083Document10 pagesDigital Assignment 1: BY: Sucheta Patnaik 15Bbt0122 Harshita Agarwal 15BBT0083Melanie Tagudin TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Sexual ReproductionDocument8 pagesMeiosis: Sexual ReproductionVivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- MEIOSIS OnlineDocument42 pagesMEIOSIS OnlineAltheaNo ratings yet
- 9 Meiosis Notes KeyDocument2 pages9 Meiosis Notes Keydancelora6No ratings yet
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument1 pageMeiosis and MitosisnmrasaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Theme: "Meiosis." - Presentation TranscriptDocument3 pagesPresentation On Theme: "Meiosis." - Presentation TranscriptSharmaine Claire VillondoNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 2Document2 pagesMeiosis 2Hans Hanji ZoeNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument8 pagesMitosis and MeiosisShiela BelandresNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument2 pagesMeiosisjeline raniNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Evan Walker - 17 Meiosis-SDocument8 pagesKami Export - Evan Walker - 17 Meiosis-Sevan.walker621No ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To GeneticsDocument3 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Geneticsrizza reyesNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes: Karyotype of A Male HumanDocument7 pagesChromosomes: Karyotype of A Male HumanKEITHLYN EIZEL RAMITERRENo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles: Urry - Cain - Wasserman - Minorsky - ReeceDocument92 pagesMeiosis and Sexual Life Cycles: Urry - Cain - Wasserman - Minorsky - ReeceJiyo ChangNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - TAD-DT5Document17 pagesUnit 2 - TAD-DT5Nguyễn Văn HòaNo ratings yet
- Computer Application Unit 1Document9 pagesComputer Application Unit 1Yubraj Chaudhary100% (1)
- Boronizing AVIONDocument37 pagesBoronizing AVIONManwi Khandelwal100% (1)
- Olive BookletDocument83 pagesOlive Bookletcobrabr83% (6)
- A Brief History of The Corinth CanalDocument2 pagesA Brief History of The Corinth Canalangeliki1992No ratings yet
- Medfordsun 062911Document16 pagesMedfordsun 062911elauwitNo ratings yet
- Pages From WRC - 452 - 2000 - , - Recommended - Practices PDFDocument1 pagePages From WRC - 452 - 2000 - , - Recommended - Practices PDFabhisheks5987No ratings yet
- Grade 6 - Science (သိပ္ပံ)Document160 pagesGrade 6 - Science (သိပ္ပံ)Khin Nyein100% (9)
- Branches of Aerodynamics: Conservation LawsDocument2 pagesBranches of Aerodynamics: Conservation LawsKarthiNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument3 pagesMCQEkta ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Cal2K Operating Manual: Dds CalorimetersDocument123 pagesCal2K Operating Manual: Dds CalorimetersHilario ZanardiNo ratings yet
- 1.5.1 The Lattice Dynamics Model: Dynamical MatrixDocument4 pages1.5.1 The Lattice Dynamics Model: Dynamical MatrixLuis SerranoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibria of Aqueous Solutions: Che 401: Analytical ChemistryDocument31 pagesChemical Equilibria of Aqueous Solutions: Che 401: Analytical ChemistryScrappy WellNo ratings yet
- Iteration Question'sDocument17 pagesIteration Question'sAyra MujibNo ratings yet
- 5130 - 02 5G Network Architecture and Key TechnologiesDocument96 pages5130 - 02 5G Network Architecture and Key TechnologiesMauricio SantosNo ratings yet
- FOSG Quality StandardsDocument1 pageFOSG Quality Standardspandey008No ratings yet
- Swot Analysis For SubmissionDocument6 pagesSwot Analysis For Submissionapi-502888276No ratings yet
- Teacher Resource Bank: GCE Physics A Sample A2 ISA: Damped Harmonic Motion - Question PaperDocument9 pagesTeacher Resource Bank: GCE Physics A Sample A2 ISA: Damped Harmonic Motion - Question PaperAbdul-Ahad LockhartNo ratings yet
- Development of A Two-Wheeled Mobile Tilting & Balancing (MTB) RobotDocument6 pagesDevelopment of A Two-Wheeled Mobile Tilting & Balancing (MTB) RobotAs'ad Syamsul ArifinNo ratings yet
- BF 3Document8 pagesBF 3Abella Septiana PutriNo ratings yet
- AI Tech Agency - by SlidesgoDocument9 pagesAI Tech Agency - by SlidesgoSULOCHNA KUJURNo ratings yet
- Post Assesment Question 1Document7 pagesPost Assesment Question 1Ganesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- SANDVIK CH660:01: Wear Parts CatalogDocument18 pagesSANDVIK CH660:01: Wear Parts CatalogEduardoNo ratings yet
- Chocolate Bar by Venelopa ToysDocument29 pagesChocolate Bar by Venelopa ToysMarcela Murillo100% (2)
- Practical Manual Hort 382Document112 pagesPractical Manual Hort 382Dr.Eswara Reddy Siddareddy100% (1)
- Replacement Certification LabelsDocument2 pagesReplacement Certification LabelsTung NguyenNo ratings yet
- 350 EXC-F USA 2012: Spare Parts Manual: ChassisDocument36 pages350 EXC-F USA 2012: Spare Parts Manual: ChassischarlesNo ratings yet
- IATA Certification CEIV WhitepaperDocument14 pagesIATA Certification CEIV WhitepaperMario Vazquez BNo ratings yet
GB2 Cell Cycle
GB2 Cell Cycle
Uploaded by
sja2546770 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views9 pagesOriginal Title
GB2-Cell-Cycle
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views9 pagesGB2 Cell Cycle
GB2 Cell Cycle
Uploaded by
sja254677Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 9
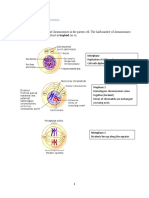
Normal human somatic cells have 46 chromosomes, half
from each parent.
Each of the 22 maternal autosomes has a homologous
paternal chromosome.
Single , haploid(n) sets of chromosomes in ovum and
sperm unite during fertilization to form a diploid(2n) single
– celled zygote , which develops into a multi-cellular
organism by mitosis.
At sexual maturity , ovaries and testes produce haploid
gametes by meiosis.
Sexual life cycles differ in the timing of meiosis in relation
to fertilization.
Multicellular organisms may be diploid(as animals) , or
haploid(as in most fungi) , or may alternate between
haploid and diploid generations (as in plants) .
EVENTS MITOSIS MEIOSIS
DNA Replication occurs during Occurs once,
Interphase before during the
nuclear division interphase before
begins. meiosis I begins.
Number of One , including Two , each
Divisions prophase , including
metaphase , prophase ,
anaphase , and metaphase ,
telophase. anaphase , and
telophase.
EVENTS MITOSIS MEIOSIS
Synapsis of Does not occur. Synapsis is unique
homologous to meoisis:During
chromosomes prophase I, the
homologous
chromosomes join
along their length,
forming
tetrads;synapsis is
associated with
crossing over
between nonsister
chromatids.
EVENTS MITOSIS MEIOSIS
Number of Two, each Four, each
daughter cells and diploid(2n) and haploid(n)
genetic genetically containing half as
composition identical to the many
parent cell. chromosome as
the parent cell,
genetically
nonidentical to the
parent cell and to
each other.
EVENTS MITOSIS MEIOSIS
Role in the animal Enables multi- Produces
body cellular adult to gametes; reduces
arise from zygote; chromosome
produces cells for number by half
growth and tissue and introduces
repair. genetic variability
among the
gametes.
You might also like
- MS - Worthy of It All - Key of A & GDocument6 pagesMS - Worthy of It All - Key of A & GDianne HorarioNo ratings yet
- 13 Principles of Wiccan BeliefDocument7 pages13 Principles of Wiccan BeliefWayne100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - Part2Document32 pagesChapter 8 - Part2Youssef MoustafaNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)Document2 pagesWORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)gyeojib aeNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)Document2 pagesWORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)gyeojib aeNo ratings yet
- Biology Anomalies and MeiosisDocument11 pagesBiology Anomalies and MeiosisJodi Kryztel JosolNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument12 pagesBiologyfloresstephaniejoycNo ratings yet
- Meiosis (: ListenDocument13 pagesMeiosis (: ListenmuhammadismailNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument25 pagesMeiosisAnjelica BucasasNo ratings yet
- GeneticDocument34 pagesGeneticDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument7 pagesMitosis Vs MeiosisJD DX100% (1)
- 2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument21 pages2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisKinjNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument4 pagesMitosis and MeiosisMicah Porcal ArelladoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document15 pagesUnit 2Jhon Rey RodeoNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Cell DivisionDocument12 pagesMeiosis and Cell DivisionAD-MQNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 With Arabic Words 2Document36 pagesChapter 13 With Arabic Words 2jadjaffal01No ratings yet
- Cell-Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell-Cycle and Cell DivisionToby TrollyNo ratings yet
- Botany Module 3Document6 pagesBotany Module 3Yaz VergaraNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Chapter 13 NotesDocument5 pagesAP Bio Chapter 13 NotesAndrew SongNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction SlidesDocument29 pagesMeiosis and Sexual Reproduction Slidesmysticgalaxy2823No ratings yet
- 2 MeiosisDocument36 pages2 MeiosisnthabiisengNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument21 pagesMitosis and MeiosisJuLie Ann DeGuzman Geslani100% (1)
- MeiosisDocument34 pagesMeiosisJared CoyagboNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument3 pagesMeiosisSachintha JayamahaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notebook: 03.02 Meiosis: Key Questions and Terms Notes Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument4 pagesBiology Notebook: 03.02 Meiosis: Key Questions and Terms Notes Asexual and Sexual ReproductionCameron LightbourneNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 1Document37 pagesMeiosis 1Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Chapter 19 Pages 651 - 663Document20 pagesMeiosis: Chapter 19 Pages 651 - 663María SalazarNo ratings yet
- 2.meiosis 1Document36 pages2.meiosis 1taskmask37No ratings yet
- (Unit 2) Cell Division - MeiosisDocument9 pages(Unit 2) Cell Division - MeiosisHanif AlfarizkiNo ratings yet
- Science HW MM Compare and ConstrastDocument1 pageScience HW MM Compare and ConstrastjiNo ratings yet
- Meiosis - Clay ModellingDocument4 pagesMeiosis - Clay ModellingAlexandra M.No ratings yet
- JajajaDocument2 pagesJajajaLouie BarrientosNo ratings yet
- MEIOSIS and MITOSISDocument4 pagesMEIOSIS and MITOSISHannaj May De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- ComparisonDocument2 pagesComparisonMary Rose AllinegNo ratings yet
- La Meiosis en Distintos Tipos de Ciclos Vitales: Ciclo de Vida de ChlamydomonasDocument21 pagesLa Meiosis en Distintos Tipos de Ciclos Vitales: Ciclo de Vida de ChlamydomonasLENNI DAYARA HERNANDEZ GARCIANo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument1 pageMitosis Vs Meiosisgovicky565No ratings yet
- CH.10 Meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesDocument5 pagesCH.10 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cyclesdidua08No ratings yet
- Biology (Form 4)Document25 pagesBiology (Form 4)Aloysius RajNo ratings yet
- Meiosis - WikipediaDocument89 pagesMeiosis - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 - Meiosis NotesDocument3 pagesBio 1 - Meiosis NotesJayson RiveraNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 2Document6 pagesMeiosis 2Areefa MohamedNo ratings yet
- 2nd MT Biology ReviewerDocument4 pages2nd MT Biology ReviewerAliah HernandezNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Online Study GuideDocument6 pagesCH 13 Online Study Guideюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument62 pagesMeiosisEMANUEL PAGAN-VELEZNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument13 pagesMeiosistaylorNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesCell Divisionlelejfintlskia1we39No ratings yet
- Meiosis Meiosis Halves The Number of Chromosomes in The Parent Cell. The Half Number of ChromosomesDocument4 pagesMeiosis Meiosis Halves The Number of Chromosomes in The Parent Cell. The Half Number of ChromosomesTracia WalcottNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PDFDocument22 pagesMeiosis PDFEbook DownloadNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment 1: BY: Sucheta Patnaik 15Bbt0122 Harshita Agarwal 15BBT0083Document10 pagesDigital Assignment 1: BY: Sucheta Patnaik 15Bbt0122 Harshita Agarwal 15BBT0083Melanie Tagudin TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Sexual ReproductionDocument8 pagesMeiosis: Sexual ReproductionVivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- MEIOSIS OnlineDocument42 pagesMEIOSIS OnlineAltheaNo ratings yet
- 9 Meiosis Notes KeyDocument2 pages9 Meiosis Notes Keydancelora6No ratings yet
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument1 pageMeiosis and MitosisnmrasaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Theme: "Meiosis." - Presentation TranscriptDocument3 pagesPresentation On Theme: "Meiosis." - Presentation TranscriptSharmaine Claire VillondoNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 2Document2 pagesMeiosis 2Hans Hanji ZoeNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument8 pagesMitosis and MeiosisShiela BelandresNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument2 pagesMeiosisjeline raniNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Evan Walker - 17 Meiosis-SDocument8 pagesKami Export - Evan Walker - 17 Meiosis-Sevan.walker621No ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To GeneticsDocument3 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Geneticsrizza reyesNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes: Karyotype of A Male HumanDocument7 pagesChromosomes: Karyotype of A Male HumanKEITHLYN EIZEL RAMITERRENo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles: Urry - Cain - Wasserman - Minorsky - ReeceDocument92 pagesMeiosis and Sexual Life Cycles: Urry - Cain - Wasserman - Minorsky - ReeceJiyo ChangNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - TAD-DT5Document17 pagesUnit 2 - TAD-DT5Nguyễn Văn HòaNo ratings yet
- Computer Application Unit 1Document9 pagesComputer Application Unit 1Yubraj Chaudhary100% (1)
- Boronizing AVIONDocument37 pagesBoronizing AVIONManwi Khandelwal100% (1)
- Olive BookletDocument83 pagesOlive Bookletcobrabr83% (6)
- A Brief History of The Corinth CanalDocument2 pagesA Brief History of The Corinth Canalangeliki1992No ratings yet
- Medfordsun 062911Document16 pagesMedfordsun 062911elauwitNo ratings yet
- Pages From WRC - 452 - 2000 - , - Recommended - Practices PDFDocument1 pagePages From WRC - 452 - 2000 - , - Recommended - Practices PDFabhisheks5987No ratings yet
- Grade 6 - Science (သိပ္ပံ)Document160 pagesGrade 6 - Science (သိပ္ပံ)Khin Nyein100% (9)
- Branches of Aerodynamics: Conservation LawsDocument2 pagesBranches of Aerodynamics: Conservation LawsKarthiNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument3 pagesMCQEkta ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Cal2K Operating Manual: Dds CalorimetersDocument123 pagesCal2K Operating Manual: Dds CalorimetersHilario ZanardiNo ratings yet
- 1.5.1 The Lattice Dynamics Model: Dynamical MatrixDocument4 pages1.5.1 The Lattice Dynamics Model: Dynamical MatrixLuis SerranoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibria of Aqueous Solutions: Che 401: Analytical ChemistryDocument31 pagesChemical Equilibria of Aqueous Solutions: Che 401: Analytical ChemistryScrappy WellNo ratings yet
- Iteration Question'sDocument17 pagesIteration Question'sAyra MujibNo ratings yet
- 5130 - 02 5G Network Architecture and Key TechnologiesDocument96 pages5130 - 02 5G Network Architecture and Key TechnologiesMauricio SantosNo ratings yet
- FOSG Quality StandardsDocument1 pageFOSG Quality Standardspandey008No ratings yet
- Swot Analysis For SubmissionDocument6 pagesSwot Analysis For Submissionapi-502888276No ratings yet
- Teacher Resource Bank: GCE Physics A Sample A2 ISA: Damped Harmonic Motion - Question PaperDocument9 pagesTeacher Resource Bank: GCE Physics A Sample A2 ISA: Damped Harmonic Motion - Question PaperAbdul-Ahad LockhartNo ratings yet
- Development of A Two-Wheeled Mobile Tilting & Balancing (MTB) RobotDocument6 pagesDevelopment of A Two-Wheeled Mobile Tilting & Balancing (MTB) RobotAs'ad Syamsul ArifinNo ratings yet
- BF 3Document8 pagesBF 3Abella Septiana PutriNo ratings yet
- AI Tech Agency - by SlidesgoDocument9 pagesAI Tech Agency - by SlidesgoSULOCHNA KUJURNo ratings yet
- Post Assesment Question 1Document7 pagesPost Assesment Question 1Ganesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- SANDVIK CH660:01: Wear Parts CatalogDocument18 pagesSANDVIK CH660:01: Wear Parts CatalogEduardoNo ratings yet
- Chocolate Bar by Venelopa ToysDocument29 pagesChocolate Bar by Venelopa ToysMarcela Murillo100% (2)
- Practical Manual Hort 382Document112 pagesPractical Manual Hort 382Dr.Eswara Reddy Siddareddy100% (1)
- Replacement Certification LabelsDocument2 pagesReplacement Certification LabelsTung NguyenNo ratings yet
- 350 EXC-F USA 2012: Spare Parts Manual: ChassisDocument36 pages350 EXC-F USA 2012: Spare Parts Manual: ChassischarlesNo ratings yet
- IATA Certification CEIV WhitepaperDocument14 pagesIATA Certification CEIV WhitepaperMario Vazquez BNo ratings yet