Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Def and Formula Electricity
Def and Formula Electricity
Uploaded by
ISI ALPHACopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Def and Formula Electricity
Def and Formula Electricity
Uploaded by
ISI ALPHACopyright:
Available Formats
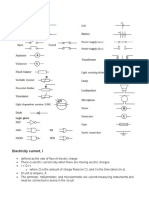
Electric line of force or field line: The path a free test charge follows due to source charge is called
a line
of force or field line.
Electric field: It is a region around a charged particle within which a force would be exerted on other
charged particle. The direction of an electric field line is the direction a positive test charge would move
along.
Electric field strength: It is defined as the force due to source charge per unit positive test charge.
Electric current: It is the rate of flow of charge due to the passage of charge carriers.
Resistance: Resistance of a component in a circuit is the measure of the difficulty of making current
pass through the component.
p . d across the component
Resistance of any component =
current thorugh¿ ¿
Ohms law:It states that the potential difference across a metallic conductor is proportional to the
current through it provided that temperature does not change.
Ohm : Resistance in a conductor will be 1 ohm if potential difference of 1 volt is across it when current
through it 1 ampere.
Volt : If work done of 1 Joule is done by charge of 1 Coulomb across a load, the potential difference is 1
volt.
Charge : It is the product of electric current and time.
Coulomb : If current of 1 Ampere flows through a conductor in time of 1 second , the charge flowing will
be 1 Coulomb.
emf : It is defined as the energy supplied per unit charge by the source to drive the charge round a
complete circuit including the internal battery. It represents the conversion of chemical energy to
electrical energy per unit charge.
p.d : It is defined as the energy spent per unit charge between two points across the load .It represents
the conversion of electrical energy to non-electrical energy per unit charge .
Formulas Q=xt W= V x Q V= x R P= x V E=V x x t
E= 2 x R x t E= V 2 xt / R P=V2/R P = 2x R
For series R= R1 + R2 , stays same , V= V1 + V2 , V and R are directly proportional
For parallel R=product /sum, V stays same , = 1 + 2 , and R are Inversely proportional
Resistance of wire is directly proportional to length
Resistance of wire is inversely proportional to area
Resistance of wire is inversely proportional to square of diameter
Resistance of wire is inversely proportional to square of radius
You might also like
- Current and Resistance Current and Current DensityDocument20 pagesCurrent and Resistance Current and Current Densityminhajul.cse.diuNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Electricity: ChargeDocument6 pagesRevision Notes On Electricity: ChargeJahnavi MeharNo ratings yet
- Direct Current D.C.Document10 pagesDirect Current D.C.Puran BistaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electric CircuitsDocument78 pagesPrinciples of Electric CircuitsEvbaruNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module 1Document48 pagesUnit 2 Module 17sky7harveyNo ratings yet
- Electricity NotesDocument10 pagesElectricity NotesCarlos KasambiraNo ratings yet
- X Class Physics ElectricityDocument7 pagesX Class Physics ElectricityPaarth BansalNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 12Document11 pagesElectricity Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 12vatnik100% (1)
- Current ElectricityDocument7 pagesCurrent ElectricityMakrand ShirsatNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument87 pagesElectricityayushk68863No ratings yet
- CH1L1 DCCDocument75 pagesCH1L1 DCCjoshikartiknatubhai73No ratings yet
- ' ElectricityDocument98 pages' Electricitya9758127118No ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities 1 ReviewerDocument20 pagesEngineering Utilities 1 ReviewerBaby John lystier NadayaoNo ratings yet
- Physics STPM Sem 2 DefinitionDocument2 pagesPhysics STPM Sem 2 DefinitionBen100% (4)
- Chapter ELECTRICITYDocument21 pagesChapter ELECTRICITYunknown072006No ratings yet
- Unit 02 - 1Document3 pagesUnit 02 - 1raghg2005No ratings yet
- Applied Physics II - Module III - Part IDocument17 pagesApplied Physics II - Module III - Part Ikannankarthi3002No ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument5 pagesCurrent ElectricityKamesh RajputNo ratings yet
- 09 CurrentElectricity IDocument9 pages09 CurrentElectricity ILearner PointNo ratings yet
- UnitNo1DCCircuitspptx 2022 10 08 15 08 30pptx 2022 11 03 21 34 27Document66 pagesUnitNo1DCCircuitspptx 2022 10 08 15 08 30pptx 2022 11 03 21 34 27DUSHIMIMANA ROBIN mefgiNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics M3 M4 2021RVNDocument35 pagesApplied Physics M3 M4 2021RVNkannankarthi3002No ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Grade 10 2024Document6 pagesElectric Circuit Grade 10 2024ontha619No ratings yet
- Physics Ch5 NotesDocument20 pagesPhysics Ch5 NotesAli GorganiNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity (Edited)Document41 pagesCurrent Electricity (Edited)paperNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Chapter 9 Unit 2 (Class Ix Week29)Document10 pagesPresentation On Chapter 9 Unit 2 (Class Ix Week29)SpideyPro23No ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument7 pagesElectricitypranjaltyagi61No ratings yet
- Chapter - 12: ElectricityDocument22 pagesChapter - 12: ElectricityAgrasen SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 12 ElectricityDocument10 pagesCH 12 ElectricityMohammed SafwanNo ratings yet
- Science Notes Chapter 12 Electricity: Electricity:Electric Current, Electric Circuit, Voltage orDocument23 pagesScience Notes Chapter 12 Electricity: Electricity:Electric Current, Electric Circuit, Voltage orAayushiNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITYDocument5 pagesELECTRICITYminakshi tiwariNo ratings yet
- Study Material and Notes of CH 12 Electricity Class 10th. Topics in The ChapterDocument5 pagesStudy Material and Notes of CH 12 Electricity Class 10th. Topics in The ChapterSavita ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Electrical+thermal PhysicsDocument20 pagesElectrical+thermal PhysicsTaha YousafNo ratings yet
- Notes ElectricityDocument10 pagesNotes ElectricityDivyanshu BaghelNo ratings yet
- Elecrticity PDFDocument8 pagesElecrticity PDFmrneetgamerNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit SymbolsDocument38 pagesElectrical Circuit Symbolsanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Current-Electricity NotesDocument4 pagesCurrent-Electricity NotesPiyush RoyNo ratings yet
- A Level Electric Current Slides 001Document43 pagesA Level Electric Current Slides 001markwelly367No ratings yet
- Charge and Electric Field: Online Learning Resources For Malaysia StudentsDocument0 pagesCharge and Electric Field: Online Learning Resources For Malaysia StudentsJia HuiNo ratings yet
- RRB NTPC - Physics - Electricity-EnglishDocument2 pagesRRB NTPC - Physics - Electricity-EnglishAkella LokeshNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Unit: The Unit of Current Is AmpereDocument3 pagesElectricity: Unit: The Unit of Current Is Amperejspragati273No ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument16 pagesCurrent Electricitysukaina fatimaNo ratings yet
- Current ElecricityDocument131 pagesCurrent ElecricityD SiddaiahNo ratings yet
- Electricity at HomeDocument10 pagesElectricity at HomeWilliam HaNo ratings yet
- 10 ElectricityDocument4 pages10 ElectricitySunil SeerviNo ratings yet
- gbbcvbcvDocument18 pagesgbbcvbcvravenbeaconiteNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Latest 2023 - 17aa175d 3382 4a65 9ad5 Bad8694c983aDocument9 pagesCurrent Electricity Latest 2023 - 17aa175d 3382 4a65 9ad5 Bad8694c983asnigdha varshaNo ratings yet
- Electricity (Main)Document16 pagesElectricity (Main)Sarthak KapoorNo ratings yet
- Charge (Q) : STD - X Topic-Electricity - Part-1Document12 pagesCharge (Q) : STD - X Topic-Electricity - Part-1ᴀᴛʜᴀʀᴠ ʟᴇɴɢᴜʀᴇツツNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Electric CurrentDocument4 pagesElectricity: Electric CurrentSuman DasNo ratings yet
- 3.Current ElectricityDocument17 pages3.Current ElectricityThomas WatsonNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument112 pagesCurrent Electricitymkg_met2391No ratings yet
- 10 Chapter-12-: Electricity CBSE Study NotesDocument11 pages10 Chapter-12-: Electricity CBSE Study Notesrucha BNo ratings yet
- 10th Electricity Study Notes For Chapter - 12 Ncert PDFDocument11 pages10th Electricity Study Notes For Chapter - 12 Ncert PDFNaseeb YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 NotesDocument21 pagesChapter 18 NotesaliNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Electric Current (I) : ElectronDocument12 pagesCurrent Electricity Electric Current (I) : ElectronMichael LeungNo ratings yet
- Electricity NotesDocument10 pagesElectricity NotesTictacNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitDocument26 pagesAC CircuitSukanta MallickNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 ElectricityDocument3 pagesChapter 12 ElectricityShashank SharmaNo ratings yet