Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tuto A3 Relative Motion Tutorial 1
Tuto A3 Relative Motion Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
irvinelegoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tuto A3 Relative Motion Tutorial 1
Tuto A3 Relative Motion Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
irvinelegoCopyright:
Available Formats
School of Engineering University of Glasgow
Dynamics 1
TUTORIAL 4 (relative motion)
February 2014
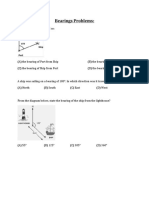
1 Aircraft A flies North at 300 km/h. Aircraft B flies North-West at 600 km/h.
Calculate the velocity of B relative to A.
[-424.3i+124.3j km/h]
2 Aircraft A flies North-East at 450 km/h. Aircraft B flies North-West at 250
km/h. Calculate the velocity of A relative to B.
[495i+141.4j km/h]
3 Aircraft A flies South-West at 700 km/h. Aircraft B flies East at 250 km/h.
Calculate the velocity of B relative to A.
[745i+495j km/h]
4 Aircraft A flies South-East at 125 km/h. Aircraft B flies South-West at 225
km/h. Calculate the velocity of A relative to B.
[247.5i+70.7j km/h]
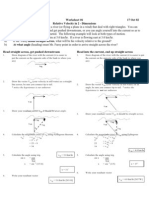
5 Aircraft A is flying a circular path at 275 km/h. aircraft B is heading South-West
at 300 km/h. Show that
v B / A = 165513 −116600(sin θ A − cos θ A )
2
where θ A is the angular position of A with respect to East.
6 Aircraft A is flying North-East at 400 km/h. Aircraft B is flying West. The speed
of A relative to B is 600 km/h. Calculate the speed of B.
[246.3 km/h]
7 Aircraft A is flying South-West at 300 km/h. Aircraft B has a speed of 250
km/h. The speed of B relative to A is 500 km/h. Estimate the heading of aircraft
B.
Dynamics 1 Relative motion
-1-
School of Engineering University of Glasgow
[approximately East – actually 094.5 deg relative to North]
8 Aircraft A is describing a circular flight path in and anti-clockwise direction at
125 km/h. Aircraft B is flying the same path but in the opposite direction at 225
km/h. If the radius of the flight path is 5 km, calculate the acceleration of A
relative to B when A is heading South-East, and B is heading South-West.
[0.7229i-0.3819j m/s^2]
Dynamics 1 Relative motion
-2-
You might also like
- TrigonometryDocument1 pageTrigonometryNisha KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Forces Acting On A PropellerDocument21 pagesForces Acting On A Propellercasandra joaquin100% (2)
- An Evaluation of Factors Significant To Lamellar TearingDocument7 pagesAn Evaluation of Factors Significant To Lamellar TearingpjhollowNo ratings yet
- Vector ApplicationsDocument17 pagesVector ApplicationsCYNo ratings yet
- Relative Velocity ProblemsDocument1 pageRelative Velocity Problemsthrow_away_5000No ratings yet
- Vector Word Problems Practice Worksheet 1Document1 pageVector Word Problems Practice Worksheet 1JNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Sheet 6 2023 2024Document2 pagesDynamics Sheet 6 2023 2024abdoayad1382005No ratings yet
- Worksheet 7 Relative MotionDocument7 pagesWorksheet 7 Relative MotionObsinet ObsinetNo ratings yet
- Clicker Questions For Vectors 1Document7 pagesClicker Questions For Vectors 1Gersson Alejandro LoperaNo ratings yet
- HW1 ch12Document1 pageHW1 ch12Rajib BaruaNo ratings yet
- Bearings Test Questions For Module 2Document8 pagesBearings Test Questions For Module 2Chet Jerry AckNo ratings yet
- Ch04 HWDocument2 pagesCh04 HWDilini Wijesinghe100% (1)
- Course and HeadingDocument11 pagesCourse and HeadingJowiNo ratings yet
- Phy 12 Relative Motion WS KeyDocument5 pagesPhy 12 Relative Motion WS KeyForever ApinkNo ratings yet
- Relative Motion NETDocument7 pagesRelative Motion NETR S.NagiNo ratings yet
- Plane Flying Due North at 325 KMDocument1 pagePlane Flying Due North at 325 KMFabeha KhanNo ratings yet
- Home Work-2Document1 pageHome Work-2عبدالرحمن الحازميNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicsBrentNo ratings yet
- 4 Navigation WKSTDocument2 pages4 Navigation WKSTJack RanollyNo ratings yet
- PLATES1 Tbes 8Document2 pagesPLATES1 Tbes 8Chris ChanNo ratings yet
- Ships Magnetic Compass PDFDocument215 pagesShips Magnetic Compass PDFJohn Snow100% (1)
- Tapas+ +Intro+to++Relative+Motion+in+1d+and+2d+Document74 pagesTapas+ +Intro+to++Relative+Motion+in+1d+and+2d+Gmail ManNo ratings yet
- Relative MotionDocument4 pagesRelative MotionHazim OmarNo ratings yet
- RelativeDocument1 pageRelativebisratNo ratings yet
- 15-07 Vector Application ProblemsDocument6 pages15-07 Vector Application ProblemsEvelyn LewisNo ratings yet
- 3HResultantVelocity SolutionscheckedDocument6 pages3HResultantVelocity SolutionscheckedRyan WNo ratings yet
- Bearings WSDocument7 pagesBearings WSFatmaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Vectors and Vector AdditionDocument47 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Vectors and Vector AdditionZeke MathiasNo ratings yet
- Relative VelocityDocument3 pagesRelative VelocityNadeem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Vector Applications Quiz ReviewDocument1 pageVector Applications Quiz ReviewJiho JunNo ratings yet
- Relative VelocityDocument40 pagesRelative VelocitybobNo ratings yet
- Bearings Group AssignmentDocument7 pagesBearings Group AssignmentSkyla DavisNo ratings yet
- Aircraft NavigationDocument11 pagesAircraft Navigationpinpit282No ratings yet
- Grade: 6 Subject: Science Topic: Force and MotionDocument5 pagesGrade: 6 Subject: Science Topic: Force and MotionAriel NgNo ratings yet
- 2.10 Worksheet 2Document1 page2.10 Worksheet 2Mario BuonocoreNo ratings yet
- 1-6 Relative VelocityDocument2 pages1-6 Relative VelocityKnowledgeIsTruePowerNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Assignment No. 2: KINEMATICS OF PARTICLE: Relative Motion, Dependent MotionDocument4 pagesEngineering Mechanics Assignment No. 2: KINEMATICS OF PARTICLE: Relative Motion, Dependent MotionshreyashNo ratings yet
- SPH4U 1.6 - Relative MotionDocument14 pagesSPH4U 1.6 - Relative MotionMatthew GreesonNo ratings yet
- Relative Motion: A With Respect To BDocument2 pagesRelative Motion: A With Respect To BAlecsia NuguidNo ratings yet
- 5.4 - Vector Sums: Find, To The Nearest Tenth, The Magnitude and Bearing of Each Resultant VectorDocument2 pages5.4 - Vector Sums: Find, To The Nearest Tenth, The Magnitude and Bearing of Each Resultant VectorJackson NewmanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics (Dynamics) Assignment 1Document4 pagesEngineering Mechanics (Dynamics) Assignment 1All in one EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section: (A) Relative Motion in One DimensionDocument5 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section: (A) Relative Motion in One DimensionAtulNo ratings yet
- Bearings NotesDocument4 pagesBearings Notesblackwoodjustin293No ratings yet
- Cse Distance Problem DrillDocument1 pageCse Distance Problem DrilllocanomelanieNo ratings yet
- Vector AdditionDocument1 pageVector AdditionDaniel WalshNo ratings yet
- Unit1 QuestionsDocument92 pagesUnit1 Questionsaadil249No ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document1 pageAssignment 3Ashrut AryalNo ratings yet
- Online%2Document6 pagesOnline%2jan12th2004No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 VectorsDocument47 pagesLesson 2 VectorsJimros CabigNo ratings yet
- Solve Curvilinear MotionDocument3 pagesSolve Curvilinear Motionصادق سلام محمود شوطNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Worksheet 5Document2 pagesDynamics Worksheet 5Jennifer Moore100% (1)
- EXERCISE 1 - Vector AdditionsDocument2 pagesEXERCISE 1 - Vector Additionsmuhammad haziqNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument218 pagesQuestionsAwdy AlgarniNo ratings yet
- KINEMATICS - Q 2 - EngDocument2 pagesKINEMATICS - Q 2 - Engboitshepomotsis4No ratings yet
- Dersnot - 5262 - 1695794963 2Document18 pagesDersnot - 5262 - 1695794963 2Soner InanNo ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument3 pagesKinema TicsSpammerNo ratings yet
- Lecture D11 - Relative Motion Using Translating Axes: Types of ObserversDocument6 pagesLecture D11 - Relative Motion Using Translating Axes: Types of ObserversFaiselNo ratings yet
- BANK OF QUESTIONS GoodDocument99 pagesBANK OF QUESTIONS GoodprinceNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Worksheet 1Document2 pagesKinematics Worksheet 1Hanh Vo100% (1)
- Midterm Science IvDocument1 pageMidterm Science IvKATHERINE JOY PAROCHANo ratings yet
- Exam 1 SolutionDocument5 pagesExam 1 SolutionIñigoAlberdiNo ratings yet
- Truck Unloading Station111Document4 pagesTruck Unloading Station111ekrem0867No ratings yet
- Inf Luence of Tip Clearance On The Flow Field and Aerodynamic Performance of The Centrif Ugal ImpellerDocument6 pagesInf Luence of Tip Clearance On The Flow Field and Aerodynamic Performance of The Centrif Ugal Impellerarm coreNo ratings yet
- Lin Cot 2005Document9 pagesLin Cot 2005londemonNo ratings yet
- Design - of - Soil - Nailed - Walls - According - To - AS4678 - CAB - 061117 - SMEC - ChrisBridges 1Document1 pageDesign - of - Soil - Nailed - Walls - According - To - AS4678 - CAB - 061117 - SMEC - ChrisBridges 1konsaljohn20No ratings yet
- DBMS Chapter 7Document5 pagesDBMS Chapter 7Nabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Motion and MomentumDocument6 pagesMotion and MomentumSyed TanveerNo ratings yet
- Examples Class LecturesDocument27 pagesExamples Class Lecturesnickthegreek142857No ratings yet
- WATER FILL UP Procedure - Rev.01Document6 pagesWATER FILL UP Procedure - Rev.01shivanshsovNo ratings yet
- FrictionDocument62 pagesFrictionchellamvNo ratings yet
- Introducing The Qest Broker: Scaling The Iot by Bridging MQTT and RestDocument6 pagesIntroducing The Qest Broker: Scaling The Iot by Bridging MQTT and RestM. A. BNo ratings yet
- Iec 364 4 41Document12 pagesIec 364 4 41Ramadan Dwiputra NurrachmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 (Cleaning and Fettling of Castings), 2003Document32 pagesChapter 9 (Cleaning and Fettling of Castings), 2003Desalegn DgaNo ratings yet
- 01 Poongavanam PDFDocument14 pages01 Poongavanam PDFAanand100% (1)
- High Voltage CablesDocument10 pagesHigh Voltage CableskhadijabugtiNo ratings yet
- AEC Drying Brochure AEC2-115.1Document12 pagesAEC Drying Brochure AEC2-115.1serdigital0No ratings yet
- Moisture BarriersDocument31 pagesMoisture BarriersraviciviltNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Speed of SoundDocument16 pagesModule 4 - Speed of SoundLaiza GranaNo ratings yet
- What Is Nelco N5000-3032 BT PCBDocument5 pagesWhat Is Nelco N5000-3032 BT PCBjackNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Chassis, Mast & OptionsDocument37 pagesService Manual: Chassis, Mast & OptionsIsos Cell0% (1)
- Manual YbportDocument105 pagesManual YbportMan GeekaaNo ratings yet
- L & T Catalogue 11Document3 pagesL & T Catalogue 11amulya00428No ratings yet
- Bikas 2015Document17 pagesBikas 2015Clint TcNo ratings yet
- Slimdek Pattern BookDocument40 pagesSlimdek Pattern BookBabak WSP GroupNo ratings yet
- Ultra Power Acb User ManualDocument138 pagesUltra Power Acb User ManualRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- InclinometerDocument5 pagesInclinometerAnis MulyaniNo ratings yet
- Excel - Lab - 1 - BasicsDocument4 pagesExcel - Lab - 1 - BasicsrahulNo ratings yet
- Text Hydraulics BasicDocument286 pagesText Hydraulics BasicGrigoris MpalitasNo ratings yet
- Inkjet RefillingDocument5 pagesInkjet RefillingpedroNo ratings yet