Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DRUG-STUDY - Potassium Chloride
DRUG-STUDY - Potassium Chloride
Uploaded by
ameerurmatan21Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DRUG-STUDY - Potassium Chloride
DRUG-STUDY - Potassium Chloride
Uploaded by
ameerurmatan21Copyright:
Available Formats
DRUG STUDY
Patient (Initials only): J.R.A Age: 88 Gender: Male Ward/Room/Bed: Bed # 2
Impression: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) in Acute Exacerbation Allergy to: N/A
Generic Name: Potassium Chloride Brand Name: K – Tab Dosage & Route: 600mg through PEG tube
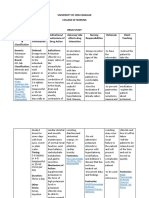
CLASSIFICATION: MECHANISM OF ACTION: PHARMACOKINETICS
Pharmacologic Class: Mineral, electrolyte Maintains acid-base balance, isotonicity, and electrophysiologic balance throughout body tissues; crucial to Onset: Unknown
nerve impulse transmission and contraction of cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle. Also essential for normal
Therapeutic Class: Electrolyte replacement, nutritional supplement Peak: 1-2 hr
renal function and carbohydrate metabolism.
Pregnancy Category: Category C Duration: Unknown
CATEGORY NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES / CONSIDERATIONS RATIONALE PATIENT / FAMILY EDUCATION
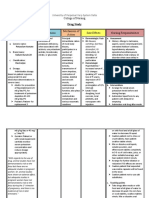
INDICATION
potassium depletion Monitoring Potassium Levels Potassium chloride is often prescribed to treat Educate the patient about the importance of taking
potassium depletion, a condition where the body potassium chloride as prescribed by their healthcare
lacks an adequate amount of potassium. provider.
CONTRAINDICATIONS / PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity to tartrazine or alcohol (with some products) Before administering potassium chloride, assess the patient's Identifying and avoiding these components helps Educate the patient about the potential presence of
medical history and allergies, specifically checking for prevent adverse reactions. tartrazine or alcohol in certain potassium chloride
hypersensitivity to tartrazine or alcohol. formulations.
Acute dehydration Evaluate the patient's fluid status, electrolyte levels, and renal Potassium chloride supplementation is commonly Teach the patient about the importance of maintaining
function before administering potassium chloride, especially in used to replenish potassium levels in individuals proper hydration, especially during periods of illness,
cases of acute dehydration. experiencing electrolyte imbalances due to physical activity, or environmental heat exposure.
conditions like dehydration.
Heat cramps Monitor patients with heat cramps closely for signs of electrolyte Heat cramps, often occurring due to excessive Educate the patient about the role of electrolytes,
imbalances and consider potassium chloride supplementation if sweating and fluid/electrolyte losses during including potassium, in muscle function and heat
indicated. prolonged physical exertion in high temperatures, regulation.
can lead to potassium depletion.
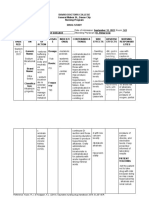
DRUG INTERACTIONS (Drug-Drug / Drug-Food / Drug-Diagnostics / Drug-Herb)
Drug-food. Salt substitutes containing potassium Monitor and educate the patient on their dietary intake of Potassium chloride is commonly prescribed to Instruct the patient to avoid or limit the use of salt
potassium-rich foods, including salt substitutes. patients with low potassium levels. substitutes unless otherwise instructed by their
healthcare provider.
Drug-herbs. Dandelion, Licorice Assess and monitor the patient for signs and symptoms of Dandelion and licorice are herbs known to have Encourage the patient to maintain regular follow-up
hypokalemia or hyperkalemia when potassium chloride is taken diuretic effects and may alter potassium levels in appointments with their healthcare provider to monitor
concurrently with dandelion or licorice. the body. electrolyte levels and adjust treatment as necessary.
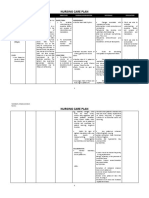
SIDE EFFECTS / ADVERSE REACTIONS / ADVERSE EFFECTS (By System)
CNS: confusion, unusual fatigue, restlessness, asthenia, flaccid paralysis, paresthesia, absent Regularly monitor the patient for signs of CNS disturbances Potassium chloride plays a vital role in nerve Educate the patient on the importance of reporting any
reflexes impulse transmission and muscle function. changes in mental status or unusual sensations promptly.
CV: ECG changes, hypotension, arrhythmias, heart block, cardiac arrest Continuously monitor the patient's cardiovascular status Abnormal potassium levels can disrupt the Instruct the patient to report any palpitations, dizziness, or
electrical impulses in the heart, leading to chest pain immediately.
potentially life-threatening arrhythmias or cardiac
arrest.
GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, flatulence Assess and manage gastrointestinal symptoms Potassium chloride supplements can irritate the Suggest dividing the daily dose into smaller, more
gastrointestinal tract, leading to these symptoms. frequent doses if tolerated to reduce the risk of GI upset.
Metabolic: hyperkalemia Monitor serum potassium levels regularly to prevent hyperkalemia. Potassium chloride supplementation aims to Instruct the patient to adhere strictly to the prescribed
correct hypokalemia dosage and avoid taking additional potassium
supplements without consulting a healthcare provider.
Musculoskeletal: weakness and heaviness of legs Assess the patient for weakness and heaviness of legs Potassium is essential for muscle contraction, and Emphasize the importance of maintaining adequate
imbalance can lead to weakness and fatigue. hydration and balanced nutrition to support muscle
function.
Respiratory: respiratory paralysis Monitor respiratory status for signs of respiratory paralysis Severe hyperkalemia can affect respiratory Instruct the patient to seek immediate medical attention if
muscles, leading to respiratory paralysis. they experience difficulty breathing or shortness of
breath.
Other: irritation at I.V. site Monitor the infusion site for signs of irritation or infiltration. Potassium chloride can cause irritation or tissue Encourage the patient to report any discomfort or
damage if administered incorrectly or at a high changes at the infusion site promptly.
concentration.
You might also like
- Mapeh 6 1st Quarter ExamDocument7 pagesMapeh 6 1st Quarter ExamRalph Fael Lucas93% (57)
- MiraLax (Polyethylene Glycol)Document1 pageMiraLax (Polyethylene Glycol)E100% (2)
- Drug Potassium Chloride KCLDocument1 pageDrug Potassium Chloride KCLSrkocher100% (3)
- Vitamin DDocument2 pagesVitamin DAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug Potassium ChlorideDocument1 pageDrug Potassium ChlorideSrkocherNo ratings yet
- ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT PLANNING DhavalDocument143 pagesORTHODONTIC TREATMENT PLANNING DhavalAshish Mathew100% (2)
- CaCO3 Drug StudDocument2 pagesCaCO3 Drug StudAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Laurente DrugstudyDocument3 pagesLaurente DrugstudyPao LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Potassium Chloride (Ktab)Document2 pagesPotassium Chloride (Ktab)Marlisha D. BrinkleyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Andrea Albester GarinoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry Lecture KayzardnDocument3 pagesClinical Chemistry Lecture KayzardnHenry QuimbaNo ratings yet
- Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesPotassium ChlorideAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY - Sodium BicarbonateDocument2 pagesDRUG-STUDY - Sodium Bicarbonateameerurmatan21No ratings yet
- Potassium Supplements ParenteralDocument3 pagesPotassium Supplements Parenteralcarl meiNo ratings yet
- KCL TabDocument3 pagesKCL TabGermin CesaNo ratings yet
- Icu Jendrugiee2Document6 pagesIcu Jendrugiee2Jennifer AlamonNo ratings yet
- Potassiumchlorideoral PDFDocument2 pagesPotassiumchlorideoral PDFShaira TanNo ratings yet
- Arshi Zeb Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesArshi Zeb Nursing Care Planarshi khanNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Kate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesKate Drug StudyShiehan Mae ForroNo ratings yet
- Department of Nursing: Tarlac State University College of ScienceDocument11 pagesDepartment of Nursing: Tarlac State University College of ScienceDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationChamelli RobinNo ratings yet
- Inborn Error of MetabolismDocument55 pagesInborn Error of MetabolismRahil singh chauhanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Kalium DuruleDocument2 pagesDrug Study Kalium DuruleMva AgueroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studyfaula rocamoraNo ratings yet
- Micro K (Potassium Chloride)Document2 pagesMicro K (Potassium Chloride)ENo ratings yet
- KaliumDocument2 pagesKaliumJustine Kaye Iballa HarligaNo ratings yet
- Output For CASE STUDY 4Document10 pagesOutput For CASE STUDY 4Chelsy Sky SacanNo ratings yet
- Salazar DsDocument4 pagesSalazar DsDjayNo ratings yet
- MLS 111B Endterm LectureDocument41 pagesMLS 111B Endterm LectureJohanna MarieNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDYDocument6 pagesDRUGSTUDYMauriceNo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy in Various ConditionsDocument62 pagesFluid Therapy in Various ConditionsAndy F MonroeNo ratings yet
- Base-Icu Drug-Study-FormDocument27 pagesBase-Icu Drug-Study-FormJennifer AlamonNo ratings yet
- Adime 2 UchcDocument9 pagesAdime 2 Uchcapi-307029735100% (1)
- Drug Study - Potassium ChlorideDocument6 pagesDrug Study - Potassium ChlorideBalloonsRus PHNo ratings yet
- Potassium GluconateDocument2 pagesPotassium GluconateFika AmaliaNo ratings yet
- BSN 3a Drug StudyDocument16 pagesBSN 3a Drug StudyACOB, Jamil C.No ratings yet
- Zaroxolyn MetolazoneDocument1 pageZaroxolyn MetolazoneCassieNo ratings yet
- Activity # 7 Fluid and Electrolyte Balance (WITH NCP)Document15 pagesActivity # 7 Fluid and Electrolyte Balance (WITH NCP)Louise OpinaNo ratings yet
- GI: Gastric: Distention, Belching, FlatulenceDocument8 pagesGI: Gastric: Distention, Belching, FlatulenceAjie ZamNo ratings yet
- Pastel Colorful Cute Group Project PresentationDocument18 pagesPastel Colorful Cute Group Project Presentationglori-annetmorteraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Vitamin DDocument1 pageDrug Study Vitamin DErica VelascoNo ratings yet
- Case ScenarioDocument9 pagesCase ScenarioKM DelantarNo ratings yet
- Journal of Translational Medicine: Practical Aspects in The Management of Hypokalemic Periodic ParalysisDocument8 pagesJournal of Translational Medicine: Practical Aspects in The Management of Hypokalemic Periodic ParalysisAndi Besse Ummu AmalyahNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument4 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityFaye Andrea FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument6 pagesDrug Study FinalJade HemmingsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Santiago, J. L. 243-D Dr. E. de Lunas Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Santiago, J. L. 243-D Dr. E. de Lunas Liver CirrhosisNathalia CabalseNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJennirose JingNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY PesebreDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY PesebreFrancoise Nicolette PesebreNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Learning Activities (Semis)Document12 pagesNCM 106 Learning Activities (Semis)Kimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Potassium ChlorideDocument5 pagesDrug Study Potassium ChlorideKenneth Mark B. TevesNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate: (Kal-See-Um Gloo-Koh-Nate)Document3 pagesCalcium Gluconate: (Kal-See-Um Gloo-Koh-Nate)govind_soni_15No ratings yet
- Comprehensive Drug Study Ketoanalogue PDF FreeDocument2 pagesComprehensive Drug Study Ketoanalogue PDF FreeYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- Hypokalemia Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypokalemia Nursing Care PlanIan Lelis100% (1)
- System Disorder DehydrationDocument1 pageSystem Disorder Dehydrationmax20020821No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyFelizandra MicuNo ratings yet
- Lactated RingersDocument3 pagesLactated RingersE100% (5)
- Hyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanRenie Serrano100% (1)
- Potassium Nutrition: In Heart Disease, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Gout, Diabetes, and Metabolic ShockFrom EverandPotassium Nutrition: In Heart Disease, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Gout, Diabetes, and Metabolic ShockRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hypercalcemia, (High Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypercalcemia, (High Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Hypocalcemia, (Low Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypocalcemia, (Low Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Chapter II Group 2 CheckedDocument17 pagesChapter II Group 2 CheckedeeynaNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet Q1W7Document26 pagesActivity Sheet Q1W7cristineann.arandiaNo ratings yet
- 12 MRCP 2 Opthalmology NOTES PassmedicineDocument30 pages12 MRCP 2 Opthalmology NOTES PassmedicineHussein GhannamNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum Care For Healthy Women and Babies PDF 35109866447557Document96 pagesIntrapartum Care For Healthy Women and Babies PDF 35109866447557Lakshmi DheviNo ratings yet
- Rtc-Eeng Protocol IV Iron DextranDocument11 pagesRtc-Eeng Protocol IV Iron DextranUp ApNo ratings yet
- Management of SheetapittaDocument8 pagesManagement of Sheetapittadrsibaprasad7755100% (1)
- Monsoon Advisory 22 - United Way MumbaiDocument9 pagesMonsoon Advisory 22 - United Way MumbaiSwati Silver DoeNo ratings yet
- Malaria: DR Mohammedyassin RediDocument63 pagesMalaria: DR Mohammedyassin Redimiki amareNo ratings yet
- Samar: Superstitious Beliefs in Allen, Northern SamarDocument5 pagesSamar: Superstitious Beliefs in Allen, Northern SamarBeverly ManaloNo ratings yet
- Choose The Word Whose Stress Pattern Is Different From The RestDocument3 pagesChoose The Word Whose Stress Pattern Is Different From The RestKim Ngân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Gastrointestinal DisordersDocument11 pagesPediatric Gastrointestinal DisordersANGELTHERESE CANDIANo ratings yet
- 172 Anatomy Resp SystemDocument24 pages172 Anatomy Resp Systemharvin95No ratings yet
- CBC With Differential, BMPDocument3 pagesCBC With Differential, BMPMrRightNo ratings yet
- Team Project SlidesDocument10 pagesTeam Project Slidesapi-545982271No ratings yet
- ML Minor MayDocument5 pagesML Minor Maygovind kumarNo ratings yet
- Final Report LT 13 SeptDocument21 pagesFinal Report LT 13 SeptScrubin UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Obgyn: History Taking and Examination DR Musa Marena ObgynDocument94 pagesObgyn: History Taking and Examination DR Musa Marena ObgynnidoNo ratings yet
- Hypothermia PDFDocument6 pagesHypothermia PDFLizbeth Gianella Egusquiza VicenteNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension #4Document2 pagesReading Comprehension #4María Cristina Tobón SotoNo ratings yet
- Kursk State Medical University: Department of PathophysiologyDocument42 pagesKursk State Medical University: Department of PathophysiologyNaseer SareenaNo ratings yet
- Status of Curfew Implementation in Selected Barangays of San Jorge, Samar During The COVID 19 PandemicDocument53 pagesStatus of Curfew Implementation in Selected Barangays of San Jorge, Samar During The COVID 19 PandemicJackielielai CabiloganNo ratings yet
- Where Is The Evidence For The Existence of The Coronavirus FinalDocument13 pagesWhere Is The Evidence For The Existence of The Coronavirus FinalTim Brown0% (1)
- Evaluate of The Physical Performance of Patients Undergoing HemodialysisDocument9 pagesEvaluate of The Physical Performance of Patients Undergoing HemodialysisAhmed AlkhaqaniNo ratings yet
- THERAP COMM QuizletDocument28 pagesTHERAP COMM QuizletMary Margareth GonzalesNo ratings yet
- @ebookmedicin 2018 Cardiology Consult ManualDocument18 pages@ebookmedicin 2018 Cardiology Consult Manualعلي الكوافيNo ratings yet
- Drug De-Addiction and Rehabilitation Center: "A Project For The People in Need"Document69 pagesDrug De-Addiction and Rehabilitation Center: "A Project For The People in Need"El JayNo ratings yet
- Icu Skills Assessment ExamDocument5 pagesIcu Skills Assessment ExamJona AureNo ratings yet
- Acute Pyelonephritis Treatment & Management: Approach ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesAcute Pyelonephritis Treatment & Management: Approach ConsiderationsPeter InocandoNo ratings yet