Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practical Task 2 Memo Revised
Practical Task 2 Memo Revised
Uploaded by
Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Krisis - Elisabeth Eybers1Document2 pagesKrisis - Elisabeth Eybers1Thato Moratuwa Moloantoa100% (1)
- Monster Genetics Lab 1Document2 pagesMonster Genetics Lab 1api-43711871350% (2)
- Alien Genetics Project FullDocument10 pagesAlien Genetics Project Fullapi-271665899No ratings yet
- Monster Genetics Lab 1Document2 pagesMonster Genetics Lab 1api-43811973250% (2)
- BLS PDFDocument6 pagesBLS PDFAyesha JadoonNo ratings yet
- Induction Testing of Bullet Magnet Installed at Flour Dispensing SystemDocument5 pagesInduction Testing of Bullet Magnet Installed at Flour Dispensing SystemMark Anthony Centeno100% (1)
- Human VariationDocument5 pagesHuman VariationChris F OrdlordNo ratings yet
- Create A Face Genetics Lab ActivityDocument3 pagesCreate A Face Genetics Lab Activityapi-2571879770% (1)
- The Genetics of ParenthoodDocument12 pagesThe Genetics of ParenthoodAqib Hussain SinaNo ratings yet
- Baby Face LabDocument8 pagesBaby Face LabMarleny TutNo ratings yet
- Genetics Activity 4 Mendelian Genetics and Punnett SquaresDocument11 pagesGenetics Activity 4 Mendelian Genetics and Punnett SquaresFe JanduganNo ratings yet
- Activity 1.9 (One For Each Teacher)Document9 pagesActivity 1.9 (One For Each Teacher)phathutshedzomudzanani24No ratings yet
- 50 Create A Face LabDocument10 pages50 Create A Face LabmrsginsburgNo ratings yet
- Islands 5º Tema 1Document10 pagesIslands 5º Tema 1PaskuatorNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Heredity NotesDocument20 pagesGenetics and Heredity NotesLaTonya RobertsNo ratings yet
- AlleleDocument7 pagesAlleleHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Week 3 DNA - The Genetic MaterialDocument9 pagesWeek 3 DNA - The Genetic MaterialCarl Brian L. MonteverdeNo ratings yet
- Contextualized Learners ModuleDocument23 pagesContextualized Learners ModuleSou MeiNo ratings yet
- Dihybrid Problems 1Document6 pagesDihybrid Problems 1Daniel De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Mendelian & Modern Genetics: General Biology 2Document51 pagesMendelian & Modern Genetics: General Biology 2sannsannNo ratings yet
- Create A Baby LabDocument7 pagesCreate A Baby LabAryaman KukalNo ratings yet
- NEW Term 2 Gr.12 PRACTICAL TASKDocument4 pagesNEW Term 2 Gr.12 PRACTICAL TASKThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Heredity: Mr. Rewey F. LavillesDocument45 pagesGenetics and Heredity: Mr. Rewey F. LavillesrenantevargasNo ratings yet
- Inheritance in Humans 2023Document3 pagesInheritance in Humans 2023Burning PhenomNo ratings yet
- BIOL 103 - Lab 8 - Genetics - StudentNameDocument11 pagesBIOL 103 - Lab 8 - Genetics - StudentNamegraham jarvis-lingardNo ratings yet
- Create A Baby LabDocument5 pagesCreate A Baby LabMariel LolincoNo ratings yet
- Steps in Solving Heredity Problems: Monohybrid CrossesDocument5 pagesSteps in Solving Heredity Problems: Monohybrid CrossesKlynt BasadreNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets - First QuarterDocument11 pagesActivity Sheets - First QuarterJohn Alvin YanezNo ratings yet
- COT DLL - Science G8 - Food ChainDocument4 pagesCOT DLL - Science G8 - Food ChainRAMIR BECOYNo ratings yet
- DEMO Law of SegregationDocument112 pagesDEMO Law of SegregationJESSIE SALINASNo ratings yet
- Genetics Notes - CANVAS 2019Document16 pagesGenetics Notes - CANVAS 2019Asian PersonNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q4 M4Document16 pagesScience8 Q4 M4Cristy VillamorNo ratings yet
- Probability and GeneticsDocument9 pagesProbability and GeneticsAnip,Fatima G.No ratings yet
- Heredity:: Sifat Yang Diturunkan Dari Tetua Ke KeturunannyaDocument17 pagesHeredity:: Sifat Yang Diturunkan Dari Tetua Ke Keturunannyayahya arifNo ratings yet
- Renaissance Science, Magic, and Medicine in Harry Potter's World Monster Genetics LabDocument2 pagesRenaissance Science, Magic, and Medicine in Harry Potter's World Monster Genetics LabPatience PenaNo ratings yet
- 21-22年3C班 英文 董凝 Book 7Document5 pages21-22年3C班 英文 董凝 Book 7y19978377No ratings yet
- ERI Monohybrid InheritanceDocument35 pagesERI Monohybrid Inheritancenanamd96No ratings yet
- How To Draw A Human FaceDocument11 pagesHow To Draw A Human FacePowerBitNo ratings yet
- Bio120 Labex12 Genetics 1Document30 pagesBio120 Labex12 Genetics 1api-525858524No ratings yet
- Q4 Science 8 Week3 - MAYSAGOTNADocument4 pagesQ4 Science 8 Week3 - MAYSAGOTNAsubidomaryjoy3025No ratings yet
- Lec2-Estimation of Genetic ParametersDocument22 pagesLec2-Estimation of Genetic ParametersRaed Al-AtiyatNo ratings yet
- GIVE ME FIVE 1 Pupil S BookDocument128 pagesGIVE ME FIVE 1 Pupil S BookMariana UrrozNo ratings yet
- Mendelian and Modern Genetics: General Biology IiDocument28 pagesMendelian and Modern Genetics: General Biology IiLesterNo ratings yet
- Jose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolDocument8 pagesJose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolEricha SolomonNo ratings yet
- SpacebugsDocument7 pagesSpacebugsdjhkang100% (1)
- Punnet Square Group 4a Ntot 2018Document9 pagesPunnet Square Group 4a Ntot 2018Daphnie Serate NunezNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Slk-Non-Mendelian-Week-4Document17 pagesGrade 9 Slk-Non-Mendelian-Week-4MilagrosBautistaNo ratings yet
- Pattern Air Pods Case UnicornDocument8 pagesPattern Air Pods Case UnicornAna María CastañoNo ratings yet
- Demonstration Lesson Plan in Genetics 8 Grade: I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesDemonstration Lesson Plan in Genetics 8 Grade: I. ObjectivesCherry MaeNo ratings yet
- New Destination ADocument89 pagesNew Destination AGeraldina UmañaNo ratings yet
- Lessons Plans Week 3 6-3 10 BCDocument4 pagesLessons Plans Week 3 6-3 10 BCapi-646133831No ratings yet
- My First English Adventure 1 Students Book ActivityDocument2 pagesMy First English Adventure 1 Students Book ActivityMantis100% (1)
- Beehive Scope and Sequence All LevelsDocument14 pagesBeehive Scope and Sequence All Levelsjan333100% (1)
- IS EspDocument5 pagesIS EspKIMBERLY PANTORILLANo ratings yet
- Aligned Assignment To ObjectiveDocument3 pagesAligned Assignment To ObjectiveJayson_HNo ratings yet
- Punnett Square Virtual LabDocument5 pagesPunnett Square Virtual LabJuan Luis Nevarez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Laws of Inheritance What's New Incomplete DominanceDocument5 pagesNon-Mendelian Laws of Inheritance What's New Incomplete DominanceChelleyOllitroNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Packet CompleteDocument35 pagesInheritance Packet Completeapi-356232366No ratings yet
- Step Ahead Document - Questions - 2020Document162 pagesStep Ahead Document - Questions - 2020sakhiletreemzerNo ratings yet
- CODOMINANCEDocument38 pagesCODOMINANCELerio AguharNo ratings yet
- Perry Modified MonstergeneticslabDocument4 pagesPerry Modified MonstergeneticslabShairamae RogelioNo ratings yet
- Business Studies Grade 12 Worksheet 8 Business EnvironmentsDocument3 pagesBusiness Studies Grade 12 Worksheet 8 Business EnvironmentsThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Measurement Measurement: Area & Perimeter Area & PerimeterDocument6 pagesMeasurement Measurement: Area & Perimeter Area & PerimeterThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Autocratic LeadershipDocument4 pagesAutocratic LeadershipThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 BaselineDocument3 pagesGrade 12 BaselineThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Phase 1 Report FinalDocument20 pagesPhase 1 Report FinalThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Provincial Examination Mathematics Literacy P1 (English) June 2023 AddendumDocument3 pagesGrade 12 Provincial Examination Mathematics Literacy P1 (English) June 2023 AddendumThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- A Business Studies Grade 12 Work Sheet 10 6 20Document4 pagesA Business Studies Grade 12 Work Sheet 10 6 20Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Business Studies Grade 12 Worksheet 15 Business OperationsDocument2 pagesBusiness Studies Grade 12 Worksheet 15 Business OperationsThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- 2024 GRADE 12 PROJECT REPLACEMENT - EnglishDocument9 pages2024 GRADE 12 PROJECT REPLACEMENT - EnglishThato Moratuwa Moloantoa100% (3)
- Phase 2 SpreadSheetDocument13 pagesPhase 2 SpreadSheetThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Talk To The Peach Tree - Contextual Questions-1Document1 pageTalk To The Peach Tree - Contextual Questions-1Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Measurement Worksheet 2Document3 pagesMeasurement Worksheet 2Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Programme of Assessment - English HL - GR 12Document2 pages2021 Programme of Assessment - English HL - GR 12Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- 1 - 1 Computers in Our Everyday Lives PDFDocument26 pages1 - 1 Computers in Our Everyday Lives PDFThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 StrategyDocument2 pagesPaper 1 StrategyThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Setting SBA Tasks in Life SciencesDocument20 pagesSetting SBA Tasks in Life SciencesThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Dicks Learner GuideDocument184 pagesDicks Learner GuideThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- World Coast TripDocument1 pageWorld Coast TripThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Phase 1 ReportDocument17 pagesPhase 1 ReportThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Sop Assignment 2023.09.22Document18 pagesSop Assignment 2023.09.22Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- 5-9 Western Cape - 240222 - 125959Document5 pages5-9 Western Cape - 240222 - 125959Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Mathematical Literacy Term 2Document1 pageGrade 12 Mathematical Literacy Term 2Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- The Child (Lines 16-23)Document5 pagesThe Child (Lines 16-23)Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- 2024 GP Eng LG Grade 12 Source - Based TaskDocument10 pages2024 GP Eng LG Grade 12 Source - Based TaskThato Moratuwa Moloantoa100% (1)
- CAT - Grade 12 T1 W6Document12 pagesCAT - Grade 12 T1 W6Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Finance Revision ManualDocument31 pagesFinance Revision ManualThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- BSTD GR 11 P1 Memo 2020Document29 pagesBSTD GR 11 P1 Memo 2020Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- At A Funeral Grade 12 Notes 1-2Document7 pagesAt A Funeral Grade 12 Notes 1-2Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Probability 1Document10 pagesProbability 1Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Safety & Rules in Biology LaboratoryDocument32 pages1.2 Safety & Rules in Biology LaboratoryasyuraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 8 Supermarket ShopDocument10 pagesLesson Plan 8 Supermarket ShopJo GregoryNo ratings yet
- UKA Athletics Coach Induction Pack v2 Jan 2013Document36 pagesUKA Athletics Coach Induction Pack v2 Jan 2013gpitbullNo ratings yet
- Prosecutor v. FurundzijaDocument1 pageProsecutor v. Furundzijacrlstinaaa100% (1)
- NRCan's Explosives Eservices - Authorized Products SearchDocument5 pagesNRCan's Explosives Eservices - Authorized Products SearchDiego VilaNo ratings yet
- Surfactant FloodingDocument13 pagesSurfactant FloodingVlassis SarantinosNo ratings yet
- 3att 1435070407870 Katura ResumeDocument2 pages3att 1435070407870 Katura Resumeapi-362299218No ratings yet
- Top 10 Tips From ZOE Science and NutritionDocument5 pagesTop 10 Tips From ZOE Science and NutritionGabaNo ratings yet
- Gobi ManchurianDocument3 pagesGobi ManchurianPriya JuligantiNo ratings yet
- Vaxigrip Tetra Pi Nh19-20Document2 pagesVaxigrip Tetra Pi Nh19-20A. shahizaNo ratings yet
- A Tale of Two CountriesDocument10 pagesA Tale of Two CountriesSandra BoteroNo ratings yet
- Solution Proposal Fleet ManagementDocument3 pagesSolution Proposal Fleet ManagementmasumidbNo ratings yet
- Gómez-López, Viejo, Ortega-Ruiz - 2019 - Well-Being and Romantic Relationships A Systematic Review in Adolescence and Emerging AdulthoodDocument31 pagesGómez-López, Viejo, Ortega-Ruiz - 2019 - Well-Being and Romantic Relationships A Systematic Review in Adolescence and Emerging AdulthoodCarmenNo ratings yet
- Solar Power For Beginners Basics Design and Installation of A Solar Panel System The Complete Guide For Your Off Grid HomeDocument96 pagesSolar Power For Beginners Basics Design and Installation of A Solar Panel System The Complete Guide For Your Off Grid HomeTek_nikkosNo ratings yet
- Overcome Emotional Eating by Healthy & Psyched PDFDocument74 pagesOvercome Emotional Eating by Healthy & Psyched PDFLarissa Veres100% (1)
- Vitamins & Minerals: Name: - DateDocument1 pageVitamins & Minerals: Name: - DateWiktoria StahlNo ratings yet
- Manual Usuario Smart LGDocument36 pagesManual Usuario Smart LGkarl CgcNo ratings yet
- Father's of Various FieldsDocument5 pagesFather's of Various FieldsAsad AliNo ratings yet
- MultiTherm OG-1® Tech DataDocument2 pagesMultiTherm OG-1® Tech DataSteranskoNo ratings yet
- Reasearch SummariesDocument12 pagesReasearch Summariesapi-508554918No ratings yet
- Proteomic Landscape Presents Cues For Vegetative To Reproductive Transition in MangoDocument7 pagesProteomic Landscape Presents Cues For Vegetative To Reproductive Transition in MangoShailendra RajanNo ratings yet
- Historia Tartarorum EcclesiasticaDocument4 pagesHistoria Tartarorum EcclesiasticaVladimir SaricNo ratings yet
- Binaural BeatsDocument8 pagesBinaural BeatsMitko100% (3)
- Ichi The KillerDocument7 pagesIchi The KillerShaul RechterNo ratings yet
- 2022 Fuenzalida Et Al 2022 New Records OfgigantolaelapswolffsohniDocument10 pages2022 Fuenzalida Et Al 2022 New Records OfgigantolaelapswolffsohniCarlos LandaetaNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Refining Notes 1Document5 pagesPetroleum Refining Notes 1api-304149645No ratings yet
- Nova Lista de Anabólicos VERÃODocument2 pagesNova Lista de Anabólicos VERÃOigorlaresNo ratings yet
- Suzumar Boat Engine PackagesDocument7 pagesSuzumar Boat Engine PackagesmarkoNo ratings yet
Practical Task 2 Memo Revised
Practical Task 2 Memo Revised
Uploaded by
Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Practical Task 2 Memo Revised
Practical Task 2 Memo Revised
Uploaded by
Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaCopyright:
Available Formats
MOPANI EAST DISTRICT
NATIONAL
SENIOR CERTIFICATE
GRADE 12
LIFE SCIENCES
REVISEDPRACTICAL TASK 2
MARKING GUIDELINE
04 MAY 2022
REVISED MARKING GUIDELINES
MARKS: 40
DATE: 04 MAY 2022
This Memo consists of 07 pages including the cover page.
Life Sciences Practical Task Grade 12 Page 2 Of 7 Mopani East /May 2022
NSC
QUESTION 1: Variations on a human face
In this activity, Learners learn about heredity and how traits are passed on to each
generation by creating a human face. Prior to creating the face, first discuss that
genes are units of heredity. There are two alleles, one is dominant and the other is
recessive. Dominant alleles have a capital letter. Recessive alleles have a lower case
letter. If both alleles are different, it is heterozygous (blending of traits). Genetic
makeup (letters) are called genotype. Physical characteristics are phenotype.
Material (What you need):
• Pencils
• 2 coins for each Learner
• Glue
• Crayons (dark brown; light brown; grey; light blue; green and dark blue)
Method (What you do):
In this activity both parents are hybrid (heterozygous). Give each of your learners two
coins to flip (one represents dad, the other mom). Heads = dominant / Tails =
recessive. Learners fill in the genetic chart to discover what their baby will look like.
Once their chart is filled, they look at the genotype and phenotype that represents
each trait and construct their baby out of construction paper.
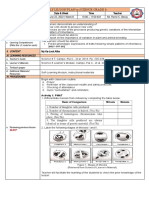
1.1. Complete the genetic chart below:
Trait Dad Mom Baby
Genotype Genotype
Genotype Phenotype
(Coin 1) (Coin 2) Coin1/Coin2
e.g Face Rr Rr Head/Head
Shape Round
RR
Hair Hh Hh HH Curly
Hh Wavy
hh Straight ()
Dimples Dd Dd DD; Dd Present
dd Absent ()
Eyebrows Qq Qq .QQ Qq Not connected
qq Connected
()
(3)
Please turn over
Life Sciences Practical Task Grade 12 Page 3 Of 7 Mopani East /May 2022
NSC
1.2. Polygenic Traits
– some traits are controlled by more than two genes and are called polygenic.
Hair, eye colour and skin colour are examples of polygenic traits.
Eye Colour –
Dark eyes are dominant over light eyes. To determine the colour of the offspring’s
eyes, assume there are two gene pairs involved, one which codes for depositing
pigment in the front of the iris, and one which codes for depositing pigment in the back
of the iris. Determine the genotype of the first pair (AA, Aa, or aa) Then flip again to
determine the genotype of the second pair (BB, Bb, or bb).
Use the chart below to find out what eye colour your offspring has and circle it.
If the genotype is… First pair coin toss//Second pair coin The eye colour is….
toss
AABB Head/Head // Head/Head dark brown
AABb Head/Head //Head/Tail or Tail/Head dark brown
AAbb Head/Head //Tail/Tail light brown
AaBB Head/Tail or Tail/Head // Head/Head light brown with green flecks
AaBb Head/Tail or Tail/Head // Head/Tail or light brown
Tail/Head
Aabb Head/Tail or Tail/Head // Tail/Tail grey-light blue
aaBB Tail/Tail // Head/Head green
aaBb Tail/Tail // Head/Tail or Tail/Head dark blue
aabb Tail/Tail // Tail/Tail light blue (hazel)
(1) Circle ()
1.3. Sex Determination
Is it a boy or a girl?
To determine the sex of your baby, flip the coin for the male parent. Heads would
represent X, while tails would be Y.
Parents Baby
Female Male Genotype Phenotype
(Coin 2) (Coin 1) Coin 1
. XX Female
X X X Y XY
Sex Male ()
(1)
Please turn over
Life Sciences Practical Task Grade 12 Page 4 Of 7 Mopani East /May 2022
NSC
1.4. Create your baby.
Now that you have determined all the traits of your child, draw a picture. Use
colours and try to make the sketch as accurate as possible given the traits your child
inherited. Make sure you name your child too!
(5)
Assessment criteria (Must be marked according to each individual learner’s answers)
Criteria Description of assessment
Heading Heading present ()
Indication of traits 1 traits correctly indicated ()
(3 traits as per 1.1.) 2 traits correctly indicated ()
3 traits correctly indicated ()
Colouring Eye coloured correctly as per 1.2.()
QUESTION 1: [10]
Please turn over
Life Sciences Practical Task Grade 12 Page 5 Of 7 Mopani East /May 2022
NSC
QUESTION 2: (Refer to genetic chart on question 1.1 above)
2.1 DD or Dd (2)
2.2 Hair (1)
2.3 P2 Phenotype Round Face x Square Face
Genotype Rr x rr
Meiosis
Gametes R r x r r
Fertilisation
F2 Genotype Rr; Rr; rr; rr
Phenotype Round face : 2 Square face
phenotype: 50% Round face and 50% Square face *
P2 and F2
Meiosis and fertilisation
*1 compulsory + any 4 (5)
OR
P2 Phenotype Round face x Square face
Genotype Rr x rr
Meiosis
Gametes R r
Fertilisation r Rr rr
r Rr rr
mark for correct gametes mark
for correct genotypes
F2 Phenotype 2 Round face: 2 Square face
% of phenotype: 50% Round face and 50% Square face *
P2 and F2
Meiosis and fertilisation
*1 compulsory + any 4 (5)
[8]
Please turn over
Life Sciences Practical Task Grade 12 Page 6 Of 7 Mopani East /May 2022
NSC
QUESTION 3
3.1 Why do you have to flip a coin to determine which allele each parent
would pass on to the offspring? (2)
Each parent has two alleles for each characteristic. Through
segregation one of the alleles from each parent will be in a gamete. /
There is a 50% chance (random assortment) of the offspring to receive
one of the two alleles from each parent
3.2 Why do you need to flip the male parent coin only to determine the sex
of your baby? (2)
The male determines the sex of the baby because the male gamete
has an X or Y allele and the female gamete only has an X
3.3 If you were to do this again, would your offspring be exactly alike?
Explain your answer. (2)
No/Yes (6)
For every characteristic there is a 50% chance to have a different allele
or the same allele from a parent.
QUESTION 2: [6]
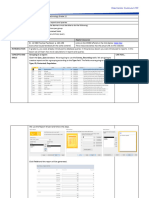
QUESTION 4
Phenotype: Rhanzu’s: Wavy and present x Lufuno’s : Wavy and present
4.1. Genotype: Rhanzu’s HhDd x Lufuno’s HhDd (2)
4.2.
Gametes HD Hd hD hd
HD HHDD HHDd HhDD HhDd
Hd e.g Curly and present (i) Curly and absent HhDd (ii) Hhdd
hD e.g Wavy and present (iii)Wavy and present
(vi)hhDD e.g Straight and
present
hd e.g Wavy and present e.g Wavy and absent e.g hhDd (v)Straight and
absent
(5)
4.1. 1. 3:1 (1)
4.1.2. X: Seed shape = 5474/1850= 2, 96: 1/2.95:1
Y: Seed colour = 6022/2001=3, 01:1
Closest: Seed colour / Y (3)
4.1.3. Y has the larger sample size (2)
Please turn over
Life Sciences Practical Task Grade 12 Page 7 Of 7 Mopani East /May 2022
NSC
4.1.4. Round Seeds (1)
QUESTION 4: [14]
GRAND TOTAL = [38]
TO BE CONVERTED TO 40 ON LEANERS’ SCRIPTS
Please turn over
You might also like
- Krisis - Elisabeth Eybers1Document2 pagesKrisis - Elisabeth Eybers1Thato Moratuwa Moloantoa100% (1)
- Monster Genetics Lab 1Document2 pagesMonster Genetics Lab 1api-43711871350% (2)
- Alien Genetics Project FullDocument10 pagesAlien Genetics Project Fullapi-271665899No ratings yet
- Monster Genetics Lab 1Document2 pagesMonster Genetics Lab 1api-43811973250% (2)
- BLS PDFDocument6 pagesBLS PDFAyesha JadoonNo ratings yet
- Induction Testing of Bullet Magnet Installed at Flour Dispensing SystemDocument5 pagesInduction Testing of Bullet Magnet Installed at Flour Dispensing SystemMark Anthony Centeno100% (1)
- Human VariationDocument5 pagesHuman VariationChris F OrdlordNo ratings yet
- Create A Face Genetics Lab ActivityDocument3 pagesCreate A Face Genetics Lab Activityapi-2571879770% (1)
- The Genetics of ParenthoodDocument12 pagesThe Genetics of ParenthoodAqib Hussain SinaNo ratings yet
- Baby Face LabDocument8 pagesBaby Face LabMarleny TutNo ratings yet
- Genetics Activity 4 Mendelian Genetics and Punnett SquaresDocument11 pagesGenetics Activity 4 Mendelian Genetics and Punnett SquaresFe JanduganNo ratings yet
- Activity 1.9 (One For Each Teacher)Document9 pagesActivity 1.9 (One For Each Teacher)phathutshedzomudzanani24No ratings yet
- 50 Create A Face LabDocument10 pages50 Create A Face LabmrsginsburgNo ratings yet
- Islands 5º Tema 1Document10 pagesIslands 5º Tema 1PaskuatorNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Heredity NotesDocument20 pagesGenetics and Heredity NotesLaTonya RobertsNo ratings yet
- AlleleDocument7 pagesAlleleHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Week 3 DNA - The Genetic MaterialDocument9 pagesWeek 3 DNA - The Genetic MaterialCarl Brian L. MonteverdeNo ratings yet
- Contextualized Learners ModuleDocument23 pagesContextualized Learners ModuleSou MeiNo ratings yet
- Dihybrid Problems 1Document6 pagesDihybrid Problems 1Daniel De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Mendelian & Modern Genetics: General Biology 2Document51 pagesMendelian & Modern Genetics: General Biology 2sannsannNo ratings yet
- Create A Baby LabDocument7 pagesCreate A Baby LabAryaman KukalNo ratings yet
- NEW Term 2 Gr.12 PRACTICAL TASKDocument4 pagesNEW Term 2 Gr.12 PRACTICAL TASKThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Heredity: Mr. Rewey F. LavillesDocument45 pagesGenetics and Heredity: Mr. Rewey F. LavillesrenantevargasNo ratings yet
- Inheritance in Humans 2023Document3 pagesInheritance in Humans 2023Burning PhenomNo ratings yet
- BIOL 103 - Lab 8 - Genetics - StudentNameDocument11 pagesBIOL 103 - Lab 8 - Genetics - StudentNamegraham jarvis-lingardNo ratings yet
- Create A Baby LabDocument5 pagesCreate A Baby LabMariel LolincoNo ratings yet
- Steps in Solving Heredity Problems: Monohybrid CrossesDocument5 pagesSteps in Solving Heredity Problems: Monohybrid CrossesKlynt BasadreNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets - First QuarterDocument11 pagesActivity Sheets - First QuarterJohn Alvin YanezNo ratings yet
- COT DLL - Science G8 - Food ChainDocument4 pagesCOT DLL - Science G8 - Food ChainRAMIR BECOYNo ratings yet
- DEMO Law of SegregationDocument112 pagesDEMO Law of SegregationJESSIE SALINASNo ratings yet
- Genetics Notes - CANVAS 2019Document16 pagesGenetics Notes - CANVAS 2019Asian PersonNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q4 M4Document16 pagesScience8 Q4 M4Cristy VillamorNo ratings yet
- Probability and GeneticsDocument9 pagesProbability and GeneticsAnip,Fatima G.No ratings yet
- Heredity:: Sifat Yang Diturunkan Dari Tetua Ke KeturunannyaDocument17 pagesHeredity:: Sifat Yang Diturunkan Dari Tetua Ke Keturunannyayahya arifNo ratings yet
- Renaissance Science, Magic, and Medicine in Harry Potter's World Monster Genetics LabDocument2 pagesRenaissance Science, Magic, and Medicine in Harry Potter's World Monster Genetics LabPatience PenaNo ratings yet
- 21-22年3C班 英文 董凝 Book 7Document5 pages21-22年3C班 英文 董凝 Book 7y19978377No ratings yet
- ERI Monohybrid InheritanceDocument35 pagesERI Monohybrid Inheritancenanamd96No ratings yet
- How To Draw A Human FaceDocument11 pagesHow To Draw A Human FacePowerBitNo ratings yet
- Bio120 Labex12 Genetics 1Document30 pagesBio120 Labex12 Genetics 1api-525858524No ratings yet
- Q4 Science 8 Week3 - MAYSAGOTNADocument4 pagesQ4 Science 8 Week3 - MAYSAGOTNAsubidomaryjoy3025No ratings yet
- Lec2-Estimation of Genetic ParametersDocument22 pagesLec2-Estimation of Genetic ParametersRaed Al-AtiyatNo ratings yet
- GIVE ME FIVE 1 Pupil S BookDocument128 pagesGIVE ME FIVE 1 Pupil S BookMariana UrrozNo ratings yet
- Mendelian and Modern Genetics: General Biology IiDocument28 pagesMendelian and Modern Genetics: General Biology IiLesterNo ratings yet
- Jose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolDocument8 pagesJose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolEricha SolomonNo ratings yet
- SpacebugsDocument7 pagesSpacebugsdjhkang100% (1)
- Punnet Square Group 4a Ntot 2018Document9 pagesPunnet Square Group 4a Ntot 2018Daphnie Serate NunezNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Slk-Non-Mendelian-Week-4Document17 pagesGrade 9 Slk-Non-Mendelian-Week-4MilagrosBautistaNo ratings yet
- Pattern Air Pods Case UnicornDocument8 pagesPattern Air Pods Case UnicornAna María CastañoNo ratings yet
- Demonstration Lesson Plan in Genetics 8 Grade: I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesDemonstration Lesson Plan in Genetics 8 Grade: I. ObjectivesCherry MaeNo ratings yet
- New Destination ADocument89 pagesNew Destination AGeraldina UmañaNo ratings yet
- Lessons Plans Week 3 6-3 10 BCDocument4 pagesLessons Plans Week 3 6-3 10 BCapi-646133831No ratings yet
- My First English Adventure 1 Students Book ActivityDocument2 pagesMy First English Adventure 1 Students Book ActivityMantis100% (1)
- Beehive Scope and Sequence All LevelsDocument14 pagesBeehive Scope and Sequence All Levelsjan333100% (1)
- IS EspDocument5 pagesIS EspKIMBERLY PANTORILLANo ratings yet
- Aligned Assignment To ObjectiveDocument3 pagesAligned Assignment To ObjectiveJayson_HNo ratings yet
- Punnett Square Virtual LabDocument5 pagesPunnett Square Virtual LabJuan Luis Nevarez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Laws of Inheritance What's New Incomplete DominanceDocument5 pagesNon-Mendelian Laws of Inheritance What's New Incomplete DominanceChelleyOllitroNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Packet CompleteDocument35 pagesInheritance Packet Completeapi-356232366No ratings yet
- Step Ahead Document - Questions - 2020Document162 pagesStep Ahead Document - Questions - 2020sakhiletreemzerNo ratings yet
- CODOMINANCEDocument38 pagesCODOMINANCELerio AguharNo ratings yet
- Perry Modified MonstergeneticslabDocument4 pagesPerry Modified MonstergeneticslabShairamae RogelioNo ratings yet
- Business Studies Grade 12 Worksheet 8 Business EnvironmentsDocument3 pagesBusiness Studies Grade 12 Worksheet 8 Business EnvironmentsThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Measurement Measurement: Area & Perimeter Area & PerimeterDocument6 pagesMeasurement Measurement: Area & Perimeter Area & PerimeterThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Autocratic LeadershipDocument4 pagesAutocratic LeadershipThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 BaselineDocument3 pagesGrade 12 BaselineThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Phase 1 Report FinalDocument20 pagesPhase 1 Report FinalThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Provincial Examination Mathematics Literacy P1 (English) June 2023 AddendumDocument3 pagesGrade 12 Provincial Examination Mathematics Literacy P1 (English) June 2023 AddendumThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- A Business Studies Grade 12 Work Sheet 10 6 20Document4 pagesA Business Studies Grade 12 Work Sheet 10 6 20Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Business Studies Grade 12 Worksheet 15 Business OperationsDocument2 pagesBusiness Studies Grade 12 Worksheet 15 Business OperationsThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- 2024 GRADE 12 PROJECT REPLACEMENT - EnglishDocument9 pages2024 GRADE 12 PROJECT REPLACEMENT - EnglishThato Moratuwa Moloantoa100% (3)
- Phase 2 SpreadSheetDocument13 pagesPhase 2 SpreadSheetThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Talk To The Peach Tree - Contextual Questions-1Document1 pageTalk To The Peach Tree - Contextual Questions-1Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Measurement Worksheet 2Document3 pagesMeasurement Worksheet 2Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Programme of Assessment - English HL - GR 12Document2 pages2021 Programme of Assessment - English HL - GR 12Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- 1 - 1 Computers in Our Everyday Lives PDFDocument26 pages1 - 1 Computers in Our Everyday Lives PDFThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 StrategyDocument2 pagesPaper 1 StrategyThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Setting SBA Tasks in Life SciencesDocument20 pagesSetting SBA Tasks in Life SciencesThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Dicks Learner GuideDocument184 pagesDicks Learner GuideThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- World Coast TripDocument1 pageWorld Coast TripThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Phase 1 ReportDocument17 pagesPhase 1 ReportThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Sop Assignment 2023.09.22Document18 pagesSop Assignment 2023.09.22Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- 5-9 Western Cape - 240222 - 125959Document5 pages5-9 Western Cape - 240222 - 125959Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Mathematical Literacy Term 2Document1 pageGrade 12 Mathematical Literacy Term 2Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- The Child (Lines 16-23)Document5 pagesThe Child (Lines 16-23)Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- 2024 GP Eng LG Grade 12 Source - Based TaskDocument10 pages2024 GP Eng LG Grade 12 Source - Based TaskThato Moratuwa Moloantoa100% (1)
- CAT - Grade 12 T1 W6Document12 pagesCAT - Grade 12 T1 W6Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Finance Revision ManualDocument31 pagesFinance Revision ManualThato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- BSTD GR 11 P1 Memo 2020Document29 pagesBSTD GR 11 P1 Memo 2020Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- At A Funeral Grade 12 Notes 1-2Document7 pagesAt A Funeral Grade 12 Notes 1-2Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Probability 1Document10 pagesProbability 1Thato Moratuwa MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Safety & Rules in Biology LaboratoryDocument32 pages1.2 Safety & Rules in Biology LaboratoryasyuraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 8 Supermarket ShopDocument10 pagesLesson Plan 8 Supermarket ShopJo GregoryNo ratings yet
- UKA Athletics Coach Induction Pack v2 Jan 2013Document36 pagesUKA Athletics Coach Induction Pack v2 Jan 2013gpitbullNo ratings yet
- Prosecutor v. FurundzijaDocument1 pageProsecutor v. Furundzijacrlstinaaa100% (1)
- NRCan's Explosives Eservices - Authorized Products SearchDocument5 pagesNRCan's Explosives Eservices - Authorized Products SearchDiego VilaNo ratings yet
- Surfactant FloodingDocument13 pagesSurfactant FloodingVlassis SarantinosNo ratings yet
- 3att 1435070407870 Katura ResumeDocument2 pages3att 1435070407870 Katura Resumeapi-362299218No ratings yet
- Top 10 Tips From ZOE Science and NutritionDocument5 pagesTop 10 Tips From ZOE Science and NutritionGabaNo ratings yet
- Gobi ManchurianDocument3 pagesGobi ManchurianPriya JuligantiNo ratings yet
- Vaxigrip Tetra Pi Nh19-20Document2 pagesVaxigrip Tetra Pi Nh19-20A. shahizaNo ratings yet
- A Tale of Two CountriesDocument10 pagesA Tale of Two CountriesSandra BoteroNo ratings yet
- Solution Proposal Fleet ManagementDocument3 pagesSolution Proposal Fleet ManagementmasumidbNo ratings yet
- Gómez-López, Viejo, Ortega-Ruiz - 2019 - Well-Being and Romantic Relationships A Systematic Review in Adolescence and Emerging AdulthoodDocument31 pagesGómez-López, Viejo, Ortega-Ruiz - 2019 - Well-Being and Romantic Relationships A Systematic Review in Adolescence and Emerging AdulthoodCarmenNo ratings yet
- Solar Power For Beginners Basics Design and Installation of A Solar Panel System The Complete Guide For Your Off Grid HomeDocument96 pagesSolar Power For Beginners Basics Design and Installation of A Solar Panel System The Complete Guide For Your Off Grid HomeTek_nikkosNo ratings yet
- Overcome Emotional Eating by Healthy & Psyched PDFDocument74 pagesOvercome Emotional Eating by Healthy & Psyched PDFLarissa Veres100% (1)
- Vitamins & Minerals: Name: - DateDocument1 pageVitamins & Minerals: Name: - DateWiktoria StahlNo ratings yet
- Manual Usuario Smart LGDocument36 pagesManual Usuario Smart LGkarl CgcNo ratings yet
- Father's of Various FieldsDocument5 pagesFather's of Various FieldsAsad AliNo ratings yet
- MultiTherm OG-1® Tech DataDocument2 pagesMultiTherm OG-1® Tech DataSteranskoNo ratings yet
- Reasearch SummariesDocument12 pagesReasearch Summariesapi-508554918No ratings yet
- Proteomic Landscape Presents Cues For Vegetative To Reproductive Transition in MangoDocument7 pagesProteomic Landscape Presents Cues For Vegetative To Reproductive Transition in MangoShailendra RajanNo ratings yet
- Historia Tartarorum EcclesiasticaDocument4 pagesHistoria Tartarorum EcclesiasticaVladimir SaricNo ratings yet
- Binaural BeatsDocument8 pagesBinaural BeatsMitko100% (3)
- Ichi The KillerDocument7 pagesIchi The KillerShaul RechterNo ratings yet
- 2022 Fuenzalida Et Al 2022 New Records OfgigantolaelapswolffsohniDocument10 pages2022 Fuenzalida Et Al 2022 New Records OfgigantolaelapswolffsohniCarlos LandaetaNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Refining Notes 1Document5 pagesPetroleum Refining Notes 1api-304149645No ratings yet
- Nova Lista de Anabólicos VERÃODocument2 pagesNova Lista de Anabólicos VERÃOigorlaresNo ratings yet
- Suzumar Boat Engine PackagesDocument7 pagesSuzumar Boat Engine PackagesmarkoNo ratings yet