Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Law of Reflection and Refraction - Activity
Law of Reflection and Refraction - Activity
Uploaded by
rosettereynanteCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Quam Dilecta (Peter Van Inwagen)Document14 pagesQuam Dilecta (Peter Van Inwagen)raccoonie81No ratings yet
- 11.6 Laws of Reflection WorksheetDocument6 pages11.6 Laws of Reflection WorksheetJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 - Law of ReflectionDocument2 pagesLab 10 - Law of Reflectionapi-408463795100% (1)
- Chapter 20 - Reflection and Refraction of Light: CommentsDocument14 pagesChapter 20 - Reflection and Refraction of Light: CommentsSalwa Mahbub0% (1)
- The Law of Reflection ActivityDocument4 pagesThe Law of Reflection ActivitymoggulreidNo ratings yet
- Law of Reflection AssignmentDocument5 pagesLaw of Reflection AssignmentJerry SungNo ratings yet
- 04 Reflected Ray WorksheetDocument4 pages04 Reflected Ray WorksheetWilma NichollsNo ratings yet
- Reflected Ray WorksheetDocument4 pagesReflected Ray WorksheetCalica Angelica100% (1)
- ReflectionsDocument2 pagesReflectionsMDNo ratings yet
- PS12 Week3 Las1Document2 pagesPS12 Week3 Las1Jeffry Centeno PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Shedding Light On Reflection The Law of Reflection Liacos Educational MediaDocument2 pagesShedding Light On Reflection The Law of Reflection Liacos Educational Mediaapi-428484559No ratings yet
- Law of ReflectionDocument4 pagesLaw of ReflectionEliNo ratings yet
- Reflection From A Plane MirrorDocument6 pagesReflection From A Plane MirrorHamidNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument25 pagesReflectionMarilyn Besawen CulanganNo ratings yet
- 2021-Ffflight - Reflection Lesson 3Document20 pages2021-Ffflight - Reflection Lesson 3Sheldon MusiinzaNo ratings yet
- Experiment Reflection of LightDocument6 pagesExperiment Reflection of Lightrizcst9759No ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction: Equipment ListDocument8 pagesReflection and Refraction: Equipment ListBABYNISHA N MNo ratings yet
- LightDocument72 pagesLighthelvimanojNo ratings yet
- S2-2nd Edit Unit-6 (6.1 Reflection)Document15 pagesS2-2nd Edit Unit-6 (6.1 Reflection)Kyaw Sit Nyein MaungNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Week 16Document6 pagesScience 10 - Week 16Mira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Law of ReflectionDocument2 pagesLaw of Reflectionanjali.oset.sinhaNo ratings yet
- 8 Science 16 Light TextBook QnADocument20 pages8 Science 16 Light TextBook QnAkumaran RNo ratings yet
- 3511 25040 Textbooksolution PDF PDFDocument9 pages3511 25040 Textbooksolution PDF PDFAshish GambhirNo ratings yet
- Unit I PDFDocument15 pagesUnit I PDFsrinivas0sai-10% (1)
- Science10 Q2 Mod4 v4Document11 pagesScience10 Q2 Mod4 v4Kim Taehyung100% (1)
- H1 Sxfoijozxr 8 Oi R6 NVDDocument56 pagesH1 Sxfoijozxr 8 Oi R6 NVDnaughtynaman420No ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity The Law of Reflection and RefractionDocument7 pagesLaboratory Activity The Law of Reflection and RefractionkionaNo ratings yet
- Let Us Entertain YouDocument1 pageLet Us Entertain YouReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab ReportJawad HaiderNo ratings yet
- Light IntensityDocument16 pagesLight IntensityJowesh Avisheik GoundarNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - Experiment No 1Document3 pagesLab Report - Experiment No 1Jawad HaiderNo ratings yet
- Thin LensesDocument21 pagesThin Lensesahmed mahamedNo ratings yet
- The Law of ReflectionDocument3 pagesThe Law of ReflectionKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- P102LN2324Document35 pagesP102LN2324Ayush Birla100% (1)
- Light NotesDocument7 pagesLight NotesSadiqa ArooshNo ratings yet
- Buenasher Learning Academy Inc.: Km.39 Cityland Ave., Pulong Buhangin, Sta. Maria, BulacanDocument9 pagesBuenasher Learning Academy Inc.: Km.39 Cityland Ave., Pulong Buhangin, Sta. Maria, BulacanEl CruzNo ratings yet
- 13 LightDocument38 pages13 LightDean Jezer100% (1)
- Qualitative Characteristics of Images: Absorbed Reflection Scatters TransmittedDocument6 pagesQualitative Characteristics of Images: Absorbed Reflection Scatters TransmittedMira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Archivos PASCO - CA-6787 PDF Files - 3 Thermo., WavDocument8 pagesArchivos PASCO - CA-6787 PDF Files - 3 Thermo., WavChess ManNo ratings yet
- Light NotesDocument8 pagesLight NotesSherazNo ratings yet
- Reflection Refraction DispersionDocument5 pagesReflection Refraction DispersionPi PoliNo ratings yet
- QA LightDocument7 pagesQA LightDomino CreationsNo ratings yet
- Law of ReflectionDocument3 pagesLaw of ReflectionAlyssum Marie100% (2)
- Properties of Light: Polarization Reflection Refraction Dispersion Diffraction InterferenceDocument5 pagesProperties of Light: Polarization Reflection Refraction Dispersion Diffraction InterferenceRobert Ocariza IINo ratings yet
- Properties of Light: Polarization Reflection Refraction Dispersion Diffraction InterferenceDocument5 pagesProperties of Light: Polarization Reflection Refraction Dispersion Diffraction InterferenceRobert Ocariza IINo ratings yet
- Properties of Light: Polarization Reflection Refraction Dispersion Diffraction InterferenceDocument5 pagesProperties of Light: Polarization Reflection Refraction Dispersion Diffraction InterferenceRobert Ocariza IINo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 LightDocument5 pagesChapter 16 Lightkalash iyerNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument28 pagesSolutionDebayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- AP Physics B - Refraction and LensesDocument20 pagesAP Physics B - Refraction and Lensesorngmn77No ratings yet
- Week 24 - Day 3 - Reflection of LightDocument21 pagesWeek 24 - Day 3 - Reflection of Lightnouran alsaadanyNo ratings yet
- Phy 1.2Document16 pagesPhy 1.2Kurisu KokoneNo ratings yet
- Light: S.No Regular Reflection Diffused Reflection 1. 2Document6 pagesLight: S.No Regular Reflection Diffused Reflection 1. 2bharat patelNo ratings yet
- Igcse 33 LightwavesDocument36 pagesIgcse 33 LightwavesMuhammad Ahsan Ali KharalNo ratings yet
- Reflection & Refraction of LightDocument43 pagesReflection & Refraction of Lightgbokoyiayomide17No ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument11 pagesRay OpticsxkryxxzNo ratings yet
- TERM+4+Ppt +Reflection+of+LightDocument22 pagesTERM+4+Ppt +Reflection+of+LightSolinaNo ratings yet
- 7 - Reflection of Light PDFDocument28 pages7 - Reflection of Light PDFprash_hingeNo ratings yet
- Refraction of LightDocument6 pagesRefraction of LightlibertymarongaNo ratings yet
- Reflection & RefractionDocument17 pagesReflection & Refractionlaraibhamza804No ratings yet
- Unit 16 (Light) : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Document8 pagesUnit 16 (Light) : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Narsi KumarNo ratings yet
- Phong Reflection Model: Understanding Light Interactions in Computer VisionFrom EverandPhong Reflection Model: Understanding Light Interactions in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- To Focus On Physics: Form 4Document1 pageTo Focus On Physics: Form 4Mugeshini RauNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification SampleDocument5 pagesTable of Specification SampleMichael John F GalsimNo ratings yet
- PHYS1600 Assignment On TelescopeDocument6 pagesPHYS1600 Assignment On TelescopeMuhamad Nur FarhanNo ratings yet
- IOM Model Exam 2068-03-11Document8 pagesIOM Model Exam 2068-03-11Dylan Bob50% (2)
- Scienc 1Document25 pagesScienc 1LYDIA Villalon-AyingNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1: (A) Determine Focal Length of A Given Concave MirrorDocument10 pagesExperiment No.1: (A) Determine Focal Length of A Given Concave MirrorLeyah Mary ThomasNo ratings yet
- 102 Lab 9. Reflection and RefractionDocument9 pages102 Lab 9. Reflection and RefractionAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Konica Minolta 7050 Service ManualDocument290 pagesKonica Minolta 7050 Service ManualBen JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Z Notes PDFDocument22 pagesZ Notes PDFHarshdeep Kaur DhillonNo ratings yet
- Mox Profile Systems Wholesale Price List - 09.05.2022-MinDocument52 pagesMox Profile Systems Wholesale Price List - 09.05.2022-MinAli oseniNo ratings yet
- Concave Mirror: REFERENCE: Science 10 Learner's Material, Pp. 181 - 189Document3 pagesConcave Mirror: REFERENCE: Science 10 Learner's Material, Pp. 181 - 189KentNo ratings yet
- OPTICSDocument29 pagesOPTICSPremalatha R ShettigarNo ratings yet
- Rahul Sardana - Optics and Modern Physics PDFDocument573 pagesRahul Sardana - Optics and Modern Physics PDFRajendraNo ratings yet
- HyperStar C14 HD InstructionsDocument7 pagesHyperStar C14 HD InstructionsHugoGustavoNo ratings yet
- Laws of Refraction of LightDocument5 pagesLaws of Refraction of Lightpadmja4purohitNo ratings yet
- UD100 Users Guide:: Illustration A Illustration BDocument1 pageUD100 Users Guide:: Illustration A Illustration BSta. Rita Elementary SchoolNo ratings yet
- MCQs For Class 10 PhysicsDocument21 pagesMCQs For Class 10 PhysicsKRISH VIMALNo ratings yet
- 5989 9712 PDFDocument14 pages5989 9712 PDFAbraham ThomasNo ratings yet
- Astigmatism-Free Czerny-Turner Compact Spectrometer With Cylindrical MirrorsDocument5 pagesAstigmatism-Free Czerny-Turner Compact Spectrometer With Cylindrical MirrorsEduardo GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Physics For Entertainment - Yakov Isidorovich Perelman PDFDocument221 pagesPhysics For Entertainment - Yakov Isidorovich Perelman PDFLucius Thales da SilvaNo ratings yet
- B.SC Optometry SyllabusDocument90 pagesB.SC Optometry SyllabusMαρία ΚολέδαNo ratings yet
- Applications of Laser Interferometry in Providing Traceable Vibration Measurements in IndiaDocument14 pagesApplications of Laser Interferometry in Providing Traceable Vibration Measurements in Indiasunit.kumarNo ratings yet
- physicsEM-eenadu Prathiba PDFDocument156 pagesphysicsEM-eenadu Prathiba PDFraghu ramNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Geometric Optics PDFDocument36 pagesLecture 3 Geometric Optics PDFPuja KasmailenNo ratings yet
- Duchamp Notes Inframince EnglishDocument9 pagesDuchamp Notes Inframince EnglishHenrique XavierNo ratings yet
- Module 2-Lesson 1Document11 pagesModule 2-Lesson 1Cindy BononoNo ratings yet
- M & M MCQ QPDocument12 pagesM & M MCQ QPPrabin MahatoNo ratings yet
- 7th LightDocument29 pages7th Lightsmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- 1-KONE Materials and Accessories SOC 21-1Document8 pages1-KONE Materials and Accessories SOC 21-1immeshNo ratings yet
Law of Reflection and Refraction - Activity
Law of Reflection and Refraction - Activity
Uploaded by
rosettereynanteOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Law of Reflection and Refraction - Activity
Law of Reflection and Refraction - Activity
Uploaded by
rosettereynanteCopyright:
Available Formats
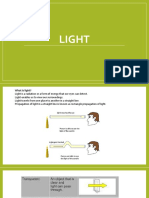
The Law of Reflection
The law of reflection works perfectly with light and the smooth surface of a mirror. However, you can
apply this law to other situations. It can help you win a game of pool or pass a basketball to a friend on
the court.
In this skill sheet you will review the law of reflection and perform practice problems that utilize this law.
Use a protractor to make your angles correct in your diagrams.
The law of reflection states that when an object
hits a surface, its angle of incidence will equal the
angle of reflection. This is true when the object is
light, and the surface is a flat, smooth mirror.
When the object and the surface are larger and
lack smooth surfaces (like a basketball and a gym
floor), the angles of incidence and reflection are
nearly but not always exactly equal. The angles
are close enough that understanding the law of
reflection can help you improve your game.
Example:
A light ray strikes a flat mirror with a 30-degree angle of incidence. Draw a ray diagram to show how the
light ray interacts with the mirror. Label the normal line, the incident ray, and the reflected ray.
Solution:
When we talk about angles of incidence and reflection, we
often talk about the normal. The normal to a surface is an
imaginary line that is perpendicular to the surface. The
normal line starts where the incident ray strikes the mirror.
A normal line is drawn for you in the sample problem.
a. Draw a diagram that shows a mirror with a normal
line and a ray of light hitting the mirror at an angle of
incidence of 60 degrees.
b. In the diagram, label the angle of reflection. How
many degrees is this angle of reflection?
The Law of Reflection
I. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING:
1. Label the diagram below using the following terms: reflected ray, angle of reflection, angle of
incidence, incident ray, normal line, reflecting surface.
a. Measure the angle of incidence with your protractor and record. _______________
b. Measure the angle of reflection with your protractor and record. _______________
c. Compare the sizes of the angles of incidence and reflection. Explain how they relate to each
other.
2. In your own words, clearly distinguish between the terms: normal, angle of incidence and
angle of reflection.
NORMAL:
ANGLE OF INCIDENCE:
ANGLE OF REFLECTION:
3. Draw a diagram that shows a mirror with a normal line and a ray of light hitting the mirror at
an angle of incidence of 60° degrees.
The Law of Reflection
You might also like
- Quam Dilecta (Peter Van Inwagen)Document14 pagesQuam Dilecta (Peter Van Inwagen)raccoonie81No ratings yet
- 11.6 Laws of Reflection WorksheetDocument6 pages11.6 Laws of Reflection WorksheetJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 - Law of ReflectionDocument2 pagesLab 10 - Law of Reflectionapi-408463795100% (1)
- Chapter 20 - Reflection and Refraction of Light: CommentsDocument14 pagesChapter 20 - Reflection and Refraction of Light: CommentsSalwa Mahbub0% (1)
- The Law of Reflection ActivityDocument4 pagesThe Law of Reflection ActivitymoggulreidNo ratings yet
- Law of Reflection AssignmentDocument5 pagesLaw of Reflection AssignmentJerry SungNo ratings yet
- 04 Reflected Ray WorksheetDocument4 pages04 Reflected Ray WorksheetWilma NichollsNo ratings yet
- Reflected Ray WorksheetDocument4 pagesReflected Ray WorksheetCalica Angelica100% (1)
- ReflectionsDocument2 pagesReflectionsMDNo ratings yet
- PS12 Week3 Las1Document2 pagesPS12 Week3 Las1Jeffry Centeno PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Shedding Light On Reflection The Law of Reflection Liacos Educational MediaDocument2 pagesShedding Light On Reflection The Law of Reflection Liacos Educational Mediaapi-428484559No ratings yet
- Law of ReflectionDocument4 pagesLaw of ReflectionEliNo ratings yet
- Reflection From A Plane MirrorDocument6 pagesReflection From A Plane MirrorHamidNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument25 pagesReflectionMarilyn Besawen CulanganNo ratings yet
- 2021-Ffflight - Reflection Lesson 3Document20 pages2021-Ffflight - Reflection Lesson 3Sheldon MusiinzaNo ratings yet
- Experiment Reflection of LightDocument6 pagesExperiment Reflection of Lightrizcst9759No ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction: Equipment ListDocument8 pagesReflection and Refraction: Equipment ListBABYNISHA N MNo ratings yet
- LightDocument72 pagesLighthelvimanojNo ratings yet
- S2-2nd Edit Unit-6 (6.1 Reflection)Document15 pagesS2-2nd Edit Unit-6 (6.1 Reflection)Kyaw Sit Nyein MaungNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Week 16Document6 pagesScience 10 - Week 16Mira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Law of ReflectionDocument2 pagesLaw of Reflectionanjali.oset.sinhaNo ratings yet
- 8 Science 16 Light TextBook QnADocument20 pages8 Science 16 Light TextBook QnAkumaran RNo ratings yet
- 3511 25040 Textbooksolution PDF PDFDocument9 pages3511 25040 Textbooksolution PDF PDFAshish GambhirNo ratings yet
- Unit I PDFDocument15 pagesUnit I PDFsrinivas0sai-10% (1)
- Science10 Q2 Mod4 v4Document11 pagesScience10 Q2 Mod4 v4Kim Taehyung100% (1)
- H1 Sxfoijozxr 8 Oi R6 NVDDocument56 pagesH1 Sxfoijozxr 8 Oi R6 NVDnaughtynaman420No ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity The Law of Reflection and RefractionDocument7 pagesLaboratory Activity The Law of Reflection and RefractionkionaNo ratings yet
- Let Us Entertain YouDocument1 pageLet Us Entertain YouReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab ReportJawad HaiderNo ratings yet
- Light IntensityDocument16 pagesLight IntensityJowesh Avisheik GoundarNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - Experiment No 1Document3 pagesLab Report - Experiment No 1Jawad HaiderNo ratings yet
- Thin LensesDocument21 pagesThin Lensesahmed mahamedNo ratings yet
- The Law of ReflectionDocument3 pagesThe Law of ReflectionKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- P102LN2324Document35 pagesP102LN2324Ayush Birla100% (1)
- Light NotesDocument7 pagesLight NotesSadiqa ArooshNo ratings yet
- Buenasher Learning Academy Inc.: Km.39 Cityland Ave., Pulong Buhangin, Sta. Maria, BulacanDocument9 pagesBuenasher Learning Academy Inc.: Km.39 Cityland Ave., Pulong Buhangin, Sta. Maria, BulacanEl CruzNo ratings yet
- 13 LightDocument38 pages13 LightDean Jezer100% (1)
- Qualitative Characteristics of Images: Absorbed Reflection Scatters TransmittedDocument6 pagesQualitative Characteristics of Images: Absorbed Reflection Scatters TransmittedMira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Archivos PASCO - CA-6787 PDF Files - 3 Thermo., WavDocument8 pagesArchivos PASCO - CA-6787 PDF Files - 3 Thermo., WavChess ManNo ratings yet
- Light NotesDocument8 pagesLight NotesSherazNo ratings yet
- Reflection Refraction DispersionDocument5 pagesReflection Refraction DispersionPi PoliNo ratings yet
- QA LightDocument7 pagesQA LightDomino CreationsNo ratings yet
- Law of ReflectionDocument3 pagesLaw of ReflectionAlyssum Marie100% (2)
- Properties of Light: Polarization Reflection Refraction Dispersion Diffraction InterferenceDocument5 pagesProperties of Light: Polarization Reflection Refraction Dispersion Diffraction InterferenceRobert Ocariza IINo ratings yet
- Properties of Light: Polarization Reflection Refraction Dispersion Diffraction InterferenceDocument5 pagesProperties of Light: Polarization Reflection Refraction Dispersion Diffraction InterferenceRobert Ocariza IINo ratings yet
- Properties of Light: Polarization Reflection Refraction Dispersion Diffraction InterferenceDocument5 pagesProperties of Light: Polarization Reflection Refraction Dispersion Diffraction InterferenceRobert Ocariza IINo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 LightDocument5 pagesChapter 16 Lightkalash iyerNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument28 pagesSolutionDebayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- AP Physics B - Refraction and LensesDocument20 pagesAP Physics B - Refraction and Lensesorngmn77No ratings yet
- Week 24 - Day 3 - Reflection of LightDocument21 pagesWeek 24 - Day 3 - Reflection of Lightnouran alsaadanyNo ratings yet
- Phy 1.2Document16 pagesPhy 1.2Kurisu KokoneNo ratings yet
- Light: S.No Regular Reflection Diffused Reflection 1. 2Document6 pagesLight: S.No Regular Reflection Diffused Reflection 1. 2bharat patelNo ratings yet
- Igcse 33 LightwavesDocument36 pagesIgcse 33 LightwavesMuhammad Ahsan Ali KharalNo ratings yet
- Reflection & Refraction of LightDocument43 pagesReflection & Refraction of Lightgbokoyiayomide17No ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument11 pagesRay OpticsxkryxxzNo ratings yet
- TERM+4+Ppt +Reflection+of+LightDocument22 pagesTERM+4+Ppt +Reflection+of+LightSolinaNo ratings yet
- 7 - Reflection of Light PDFDocument28 pages7 - Reflection of Light PDFprash_hingeNo ratings yet
- Refraction of LightDocument6 pagesRefraction of LightlibertymarongaNo ratings yet
- Reflection & RefractionDocument17 pagesReflection & Refractionlaraibhamza804No ratings yet
- Unit 16 (Light) : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Document8 pagesUnit 16 (Light) : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Narsi KumarNo ratings yet
- Phong Reflection Model: Understanding Light Interactions in Computer VisionFrom EverandPhong Reflection Model: Understanding Light Interactions in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- To Focus On Physics: Form 4Document1 pageTo Focus On Physics: Form 4Mugeshini RauNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification SampleDocument5 pagesTable of Specification SampleMichael John F GalsimNo ratings yet
- PHYS1600 Assignment On TelescopeDocument6 pagesPHYS1600 Assignment On TelescopeMuhamad Nur FarhanNo ratings yet
- IOM Model Exam 2068-03-11Document8 pagesIOM Model Exam 2068-03-11Dylan Bob50% (2)
- Scienc 1Document25 pagesScienc 1LYDIA Villalon-AyingNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1: (A) Determine Focal Length of A Given Concave MirrorDocument10 pagesExperiment No.1: (A) Determine Focal Length of A Given Concave MirrorLeyah Mary ThomasNo ratings yet
- 102 Lab 9. Reflection and RefractionDocument9 pages102 Lab 9. Reflection and RefractionAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Konica Minolta 7050 Service ManualDocument290 pagesKonica Minolta 7050 Service ManualBen JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Z Notes PDFDocument22 pagesZ Notes PDFHarshdeep Kaur DhillonNo ratings yet
- Mox Profile Systems Wholesale Price List - 09.05.2022-MinDocument52 pagesMox Profile Systems Wholesale Price List - 09.05.2022-MinAli oseniNo ratings yet
- Concave Mirror: REFERENCE: Science 10 Learner's Material, Pp. 181 - 189Document3 pagesConcave Mirror: REFERENCE: Science 10 Learner's Material, Pp. 181 - 189KentNo ratings yet
- OPTICSDocument29 pagesOPTICSPremalatha R ShettigarNo ratings yet
- Rahul Sardana - Optics and Modern Physics PDFDocument573 pagesRahul Sardana - Optics and Modern Physics PDFRajendraNo ratings yet
- HyperStar C14 HD InstructionsDocument7 pagesHyperStar C14 HD InstructionsHugoGustavoNo ratings yet
- Laws of Refraction of LightDocument5 pagesLaws of Refraction of Lightpadmja4purohitNo ratings yet
- UD100 Users Guide:: Illustration A Illustration BDocument1 pageUD100 Users Guide:: Illustration A Illustration BSta. Rita Elementary SchoolNo ratings yet
- MCQs For Class 10 PhysicsDocument21 pagesMCQs For Class 10 PhysicsKRISH VIMALNo ratings yet
- 5989 9712 PDFDocument14 pages5989 9712 PDFAbraham ThomasNo ratings yet
- Astigmatism-Free Czerny-Turner Compact Spectrometer With Cylindrical MirrorsDocument5 pagesAstigmatism-Free Czerny-Turner Compact Spectrometer With Cylindrical MirrorsEduardo GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Physics For Entertainment - Yakov Isidorovich Perelman PDFDocument221 pagesPhysics For Entertainment - Yakov Isidorovich Perelman PDFLucius Thales da SilvaNo ratings yet
- B.SC Optometry SyllabusDocument90 pagesB.SC Optometry SyllabusMαρία ΚολέδαNo ratings yet
- Applications of Laser Interferometry in Providing Traceable Vibration Measurements in IndiaDocument14 pagesApplications of Laser Interferometry in Providing Traceable Vibration Measurements in Indiasunit.kumarNo ratings yet
- physicsEM-eenadu Prathiba PDFDocument156 pagesphysicsEM-eenadu Prathiba PDFraghu ramNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Geometric Optics PDFDocument36 pagesLecture 3 Geometric Optics PDFPuja KasmailenNo ratings yet
- Duchamp Notes Inframince EnglishDocument9 pagesDuchamp Notes Inframince EnglishHenrique XavierNo ratings yet
- Module 2-Lesson 1Document11 pagesModule 2-Lesson 1Cindy BononoNo ratings yet
- M & M MCQ QPDocument12 pagesM & M MCQ QPPrabin MahatoNo ratings yet
- 7th LightDocument29 pages7th Lightsmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- 1-KONE Materials and Accessories SOC 21-1Document8 pages1-KONE Materials and Accessories SOC 21-1immeshNo ratings yet