Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsCVA Impaired Physical Mobility
CVA Impaired Physical Mobility
Uploaded by
johnnyferry03TRANS_MS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Mystical Stitches Downloadable PDFDocument51 pagesMystical Stitches Downloadable PDFJudit Lozano Peiró67% (3)
- NCP For MyomectomyDocument3 pagesNCP For Myomectomyyasira100% (2)
- Ischemic Stroke NCPDocument11 pagesIschemic Stroke NCPJohannah DaroNo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute Pain - FractureDocument1 pageNCP - Acute Pain - Fracturemawel73% (22)
- Il RN Nclex RequirementsDocument14 pagesIl RN Nclex RequirementsJin RiddlerNo ratings yet
- Behaviorally Anchored Rating ScalesDocument5 pagesBehaviorally Anchored Rating ScalesAarti Bhoria100% (2)
- Business Plan of MushroomsDocument29 pagesBusiness Plan of MushroomsMahamudul Hasan80% (5)
- CVA Impaired Physical MobilityDocument3 pagesCVA Impaired Physical MobilityJasmineNo ratings yet
- NCP GbsDocument2 pagesNCP GbsChristine Lebico100% (2)
- NCP Mics11 MedwardDocument7 pagesNCP Mics11 MedwardAbegail ReyesNo ratings yet
- Case IcuDocument5 pagesCase IcuTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: West Visayas State University College of NursingDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: West Visayas State University College of NursingRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- NCP Orif Right Femur Post OpDocument2 pagesNCP Orif Right Femur Post OpCen Janber CabrillosNo ratings yet
- CuesDocument2 pagesCuesKay DiancoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesNursing Care PlanCatherine Joy VillapandoNo ratings yet
- NCP ImmobilityDocument1 pageNCP ImmobilityBcoi QuilacioNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical Mobility. Impaired CommunicationDocument5 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility. Impaired CommunicationJovania Liza R. Baguilat100% (2)
- Impaired MobilityDocument3 pagesImpaired MobilityYeana AlonNo ratings yet
- NCP CVA ImmoblityDocument3 pagesNCP CVA ImmoblityAnalyn FloresNo ratings yet
- Names: MANIRAHO Cyprien Reg. Numbers: 020/04/GN/933 Individual AssignimentDocument70 pagesNames: MANIRAHO Cyprien Reg. Numbers: 020/04/GN/933 Individual AssignimentCyprien Silencer ManirahoNo ratings yet
- Icu NCPDocument8 pagesIcu NCPClaire Nicole ApostolNo ratings yet
- NCP FractureDocument2 pagesNCP Fracturemawel50% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Physical Mobility Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Impaired Physical Mobility Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationSheril Sularte CasanesNo ratings yet
- NCP StrokeDocument6 pagesNCP StrokeIrish TatelNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - FractureDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - FractureAbdallah Alasal100% (1)
- Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Independent: 1. Monitor Patient's Vital Signs. 2. Determine Diagnosis That Short Term GoalDocument3 pagesSubjective Data: Short Term Goal: Independent: 1. Monitor Patient's Vital Signs. 2. Determine Diagnosis That Short Term GoalGeralyn KaeNo ratings yet
- Geria NCP, Dela CruzDocument7 pagesGeria NCP, Dela CruzStephany Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NCM1023 NursingCarePlan Group2new2Document4 pagesNCM1023 NursingCarePlan Group2new2Akio OzaragaNo ratings yet
- CT TractionDocument3 pagesCT TractionLaira CañeteNo ratings yet
- 3CNCPDocument7 pages3CNCPHelen MontesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- Gumalaw, Higa Lang. Hindi Pwede Umupo,"Document3 pagesGumalaw, Higa Lang. Hindi Pwede Umupo,"chiknerrNo ratings yet
- NCP of Impaired MobilityDocument3 pagesNCP of Impaired MobilityHazel Cabrera0% (1)
- NCP Impaired MobilityDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired MobilityLouis LazaroNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocument1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNo ratings yet
- FHP & NCP - FractureDocument14 pagesFHP & NCP - FractureFrancis AdrianNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlansAvonne SabileNo ratings yet
- NCP For Pain - Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument5 pagesNCP For Pain - Rheumatoid Arthritisveorjan100% (1)
- Nag Lilinis NG Sugat Ko, Hindi Ko Kasi Kaya. Mahina Kasi Kalahati NG Katawan Ko" AsDocument4 pagesNag Lilinis NG Sugat Ko, Hindi Ko Kasi Kaya. Mahina Kasi Kalahati NG Katawan Ko" AsNursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- TractionDocument2 pagesTractionRogelyn PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- Prognosis and Health Teaching NCPDocument4 pagesPrognosis and Health Teaching NCPJanine Mae MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Subjective: The PatientDocument2 pagesSubjective: The PatientRoscoe ParaanNo ratings yet
- NCP (BD)Document5 pagesNCP (BD)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageCues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Planaprilrosehibaya100% (1)
- ORTHO NCPsDocument5 pagesORTHO NCPsSophia A. GoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan-1 Age: 50Y Medical Diagnoses: Fracture Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Scientific Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan-1 Age: 50Y Medical Diagnoses: Fracture Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Scientific Rationale EvaluationBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Pasien Pra Dan Pasca Bedah Rekonstruksi SendiDocument8 pagesPasien Pra Dan Pasca Bedah Rekonstruksi SendiAnonymous WTf5q6J7znNo ratings yet
- NCP VergelDocument3 pagesNCP VergelKelly Vergel de DiosNo ratings yet
- Impaired Mobility NCPDocument1 pageImpaired Mobility NCPAmal Bacaraman MauteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument15 pagesNursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationEina TandincoNo ratings yet
- CDC 74349 DS1Document11 pagesCDC 74349 DS1AlinaNo ratings yet
- Assessmen T Nursing Diagnosi S Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Cues: Independent IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessmen T Nursing Diagnosi S Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Cues: Independent IndependentKim Glaidyl BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature: Motor Vehicle AccidentDocument8 pagesReview of Related Literature: Motor Vehicle AccidentJ. TSNo ratings yet
- NCP 5 A 2Document2 pagesNCP 5 A 2api-3825388No ratings yet
- FractureDocument1 pageFractureReechie TeasoonNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesComprehensive Nursing Care PlanJustine Joy SolanoNo ratings yet
- 4 Amputation Nursing Care Plans - Nurseslabs-1 PDFDocument12 pages4 Amputation Nursing Care Plans - Nurseslabs-1 PDFsaidi MwanamongaNo ratings yet
- NCP CSDocument4 pagesNCP CSJM UncianoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Fascial Training For More Flexibility, Suppleness and Vitality: This Is How You Get Your Fascias Into Top Form! (10 Minutes Fascia Workout For Home)From EverandFascial Training For More Flexibility, Suppleness and Vitality: This Is How You Get Your Fascias Into Top Form! (10 Minutes Fascia Workout For Home)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Ageless Flexibility: The Ultimate Guide to Stretching Your Body after 60From EverandAgeless Flexibility: The Ultimate Guide to Stretching Your Body after 60No ratings yet
- Fascial Training For More Flexibility, Suppleness and Vitality: This Is How You Get Your Fascias Into Top Form!From EverandFascial Training For More Flexibility, Suppleness and Vitality: This Is How You Get Your Fascias Into Top Form!No ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing: 3 Quarter Week 1Document7 pagesComputer Systems Servicing: 3 Quarter Week 1Romnick PortillanoNo ratings yet
- PMBOK Guide 5th Edition - NotesDocument50 pagesPMBOK Guide 5th Edition - NotesJoaoCOS100% (1)
- Unit 10: Values: Lesson A Objective: Learn To Talk About Moral DilemmasDocument7 pagesUnit 10: Values: Lesson A Objective: Learn To Talk About Moral DilemmasLiss PeñafielNo ratings yet
- Periodic Answer Key (Editable)Document44 pagesPeriodic Answer Key (Editable)coleenmaem.04No ratings yet
- Regular Income Tax: Exclusions From Gross IncomeDocument11 pagesRegular Income Tax: Exclusions From Gross IncomeAngelica PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Fungal NutritionDocument3 pagesFungal NutritionArtemishaMtzNo ratings yet
- Creation Centered HymnsDocument4 pagesCreation Centered HymnsJoshua DanielNo ratings yet
- BTEC Assignment Brief: (For NQF Only)Document2 pagesBTEC Assignment Brief: (For NQF Only)mlmihjazNo ratings yet
- Financing Model-Understanding Startup Studio Structures - by John Carbrey - FutureSight - MediumDocument12 pagesFinancing Model-Understanding Startup Studio Structures - by John Carbrey - FutureSight - MediummberensteinNo ratings yet
- STAT115 Questions 5Document6 pagesSTAT115 Questions 5Jom NicolasNo ratings yet
- SBP - Pengenalan, Induksi RulesDocument37 pagesSBP - Pengenalan, Induksi RulesTU ElektroNo ratings yet
- Rape of The LockDocument8 pagesRape of The LockKomal PurbeyNo ratings yet
- Mti and Pulsed DopplerDocument33 pagesMti and Pulsed DopplerWaqar Shaikh67% (3)
- IJCRT2202407Document9 pagesIJCRT2202407Harsh.s13No ratings yet
- Lexical Concepts, Cognitive Models and Meaning-Construction: Vyvyan EvansDocument44 pagesLexical Concepts, Cognitive Models and Meaning-Construction: Vyvyan EvansДарья БелокрыльцеваNo ratings yet
- Levels and Trends of MortalityDocument192 pagesLevels and Trends of MortalityvthiseasNo ratings yet
- Interchange - 5ed - 1 - Students - Book CONTESTADODocument166 pagesInterchange - 5ed - 1 - Students - Book CONTESTADORodrigoNo ratings yet
- 720U2301 Rev 07 - Minimate Pro Operator ManualDocument126 pages720U2301 Rev 07 - Minimate Pro Operator ManualCristobalKlingerNo ratings yet
- Social Cognitive Theory and Physical ActivityDocument13 pagesSocial Cognitive Theory and Physical ActivityMega AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- People v. Sy Pio, G.R. No. L-5848. April 30, 1954Document3 pagesPeople v. Sy Pio, G.R. No. L-5848. April 30, 1954Anna BarbadilloNo ratings yet
- Real Numbers 40 Marks Test PaperDocument4 pagesReal Numbers 40 Marks Test Paperdinesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Lhamo Lomagyonma PracticeDocument4 pagesLhamo Lomagyonma Practicemozollis22No ratings yet
- 2 OWA310005 GSM UMTS Softswitch Core Network Principle ISSUE 3 2Document59 pages2 OWA310005 GSM UMTS Softswitch Core Network Principle ISSUE 3 2abu bakrNo ratings yet
- Isaiah 61 CommentaryDocument77 pagesIsaiah 61 CommentaryВолодимир БурдилякNo ratings yet
- PDF Abstrak-20335667Document1 pagePDF Abstrak-20335667hirukihealNo ratings yet
- Resilience Definitions Theory and ChallengesDocument14 pagesResilience Definitions Theory and ChallengesRaji Rafiu BoyeNo ratings yet
CVA Impaired Physical Mobility
CVA Impaired Physical Mobility
Uploaded by
johnnyferry030 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesTRANS_MS
Original Title
394657438-CVA-Impaired-Physical-Mobility
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTRANS_MS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesCVA Impaired Physical Mobility
CVA Impaired Physical Mobility
Uploaded by
johnnyferry03TRANS_MS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Republic of the Philippines
Bicol University Polangui Campus
NURSING AND HEALTH SCIENCES DEPARTMENT
S.Y 2018-2019
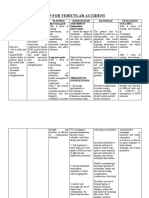
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
INDEPENDENT:
OBJECTIVE: After 8 hours of nursing 1. Change positions at Reduces risk of After 8 hours of nursing
+ impaired coordination “Impaired Physical intervention, the patient least every 2 hours tissue ischemia and intervention, the patient
+ decreased muscle Mobility r/t perceptual or will (supine, side lying) injury. Affected was able to maintain or
strength cognitive impairment as and possibly more side has poorer increase strength and
+ poor motor control evidenced by impaired often if placed on circulation and function of affected or
coordination and decreased affected side. reduced sensation compensatory body part.
muscle strength and and is more
control” predisposed to skin
breakdown and
pressure ulcers.
2. Place pillow under Prevents adduction
axilla to abduct arm. of shoulder and
flexion of elbow.
3. Elevate arm and hand. Promotes venous
return and helps
prevent edema
4. Place knee and hip in formation.
extended position. Maintains
5. Observe affected side functional position.
for color, edema, or Edematous tissue is
other signs of more easily
compromised traumatized and
circulation. heals more slowly.
Minimizes muscle
atrophy, promotes
6. Begin active or passive circulation, and
ROM to all extremities helps prevent
(including contractures.
splinted) on admission.
Encourage exercises,
such as
quadriceps or gluteal
exercise, squeezing
rubber ball, and
extension of fingers Aids in retraining
and legs and feet. neuronal pathways,
7. Assist client to develop enhancing
sitting balance (such as proprioception
raise head of and motor
bed; assist to sit on response.
edge of bed, having
client use the
strong arm to support
body weight and strong
leg to move
affected leg; increase
sitting time) and
standing balance—
put flat walking shoes
on client, support
client’s lower back
with hands while
positioning own knees
outside client’s
knees, and assist in
using parallel bars and
walker.
8. Set goals with
client/significant other
(SO) for increasing
participation Promotes sense of
in activities, exercise, expectation of
and position changes. progress and
improvement,
COLLABORATIVE and provides some
1) Consult with physical sense of control
therapist regarding and independence.
active, resistive
exercises and client
ambulation. Individualized
program can be
developed to meet
particular
needs and deal with
2) Administer muscle deficits in balance,
relaxants and coordination, and
antispasmodics as strength.
indicated, May be required to
such as baclofen relieve spasticity in
(Lioresal) and affected
dantrolene (Dantrium). extremities.
You might also like
- Mystical Stitches Downloadable PDFDocument51 pagesMystical Stitches Downloadable PDFJudit Lozano Peiró67% (3)
- NCP For MyomectomyDocument3 pagesNCP For Myomectomyyasira100% (2)
- Ischemic Stroke NCPDocument11 pagesIschemic Stroke NCPJohannah DaroNo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute Pain - FractureDocument1 pageNCP - Acute Pain - Fracturemawel73% (22)
- Il RN Nclex RequirementsDocument14 pagesIl RN Nclex RequirementsJin RiddlerNo ratings yet
- Behaviorally Anchored Rating ScalesDocument5 pagesBehaviorally Anchored Rating ScalesAarti Bhoria100% (2)
- Business Plan of MushroomsDocument29 pagesBusiness Plan of MushroomsMahamudul Hasan80% (5)
- CVA Impaired Physical MobilityDocument3 pagesCVA Impaired Physical MobilityJasmineNo ratings yet
- NCP GbsDocument2 pagesNCP GbsChristine Lebico100% (2)
- NCP Mics11 MedwardDocument7 pagesNCP Mics11 MedwardAbegail ReyesNo ratings yet
- Case IcuDocument5 pagesCase IcuTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: West Visayas State University College of NursingDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: West Visayas State University College of NursingRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- NCP Orif Right Femur Post OpDocument2 pagesNCP Orif Right Femur Post OpCen Janber CabrillosNo ratings yet
- CuesDocument2 pagesCuesKay DiancoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesNursing Care PlanCatherine Joy VillapandoNo ratings yet
- NCP ImmobilityDocument1 pageNCP ImmobilityBcoi QuilacioNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical Mobility. Impaired CommunicationDocument5 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility. Impaired CommunicationJovania Liza R. Baguilat100% (2)
- Impaired MobilityDocument3 pagesImpaired MobilityYeana AlonNo ratings yet
- NCP CVA ImmoblityDocument3 pagesNCP CVA ImmoblityAnalyn FloresNo ratings yet
- Names: MANIRAHO Cyprien Reg. Numbers: 020/04/GN/933 Individual AssignimentDocument70 pagesNames: MANIRAHO Cyprien Reg. Numbers: 020/04/GN/933 Individual AssignimentCyprien Silencer ManirahoNo ratings yet
- Icu NCPDocument8 pagesIcu NCPClaire Nicole ApostolNo ratings yet
- NCP FractureDocument2 pagesNCP Fracturemawel50% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Physical Mobility Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Impaired Physical Mobility Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationSheril Sularte CasanesNo ratings yet
- NCP StrokeDocument6 pagesNCP StrokeIrish TatelNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - FractureDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - FractureAbdallah Alasal100% (1)
- Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Independent: 1. Monitor Patient's Vital Signs. 2. Determine Diagnosis That Short Term GoalDocument3 pagesSubjective Data: Short Term Goal: Independent: 1. Monitor Patient's Vital Signs. 2. Determine Diagnosis That Short Term GoalGeralyn KaeNo ratings yet
- Geria NCP, Dela CruzDocument7 pagesGeria NCP, Dela CruzStephany Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NCM1023 NursingCarePlan Group2new2Document4 pagesNCM1023 NursingCarePlan Group2new2Akio OzaragaNo ratings yet
- CT TractionDocument3 pagesCT TractionLaira CañeteNo ratings yet
- 3CNCPDocument7 pages3CNCPHelen MontesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- Gumalaw, Higa Lang. Hindi Pwede Umupo,"Document3 pagesGumalaw, Higa Lang. Hindi Pwede Umupo,"chiknerrNo ratings yet
- NCP of Impaired MobilityDocument3 pagesNCP of Impaired MobilityHazel Cabrera0% (1)
- NCP Impaired MobilityDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired MobilityLouis LazaroNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocument1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNo ratings yet
- FHP & NCP - FractureDocument14 pagesFHP & NCP - FractureFrancis AdrianNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlansAvonne SabileNo ratings yet
- NCP For Pain - Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument5 pagesNCP For Pain - Rheumatoid Arthritisveorjan100% (1)
- Nag Lilinis NG Sugat Ko, Hindi Ko Kasi Kaya. Mahina Kasi Kalahati NG Katawan Ko" AsDocument4 pagesNag Lilinis NG Sugat Ko, Hindi Ko Kasi Kaya. Mahina Kasi Kalahati NG Katawan Ko" AsNursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- TractionDocument2 pagesTractionRogelyn PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- Prognosis and Health Teaching NCPDocument4 pagesPrognosis and Health Teaching NCPJanine Mae MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Subjective: The PatientDocument2 pagesSubjective: The PatientRoscoe ParaanNo ratings yet
- NCP (BD)Document5 pagesNCP (BD)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageCues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Planaprilrosehibaya100% (1)
- ORTHO NCPsDocument5 pagesORTHO NCPsSophia A. GoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan-1 Age: 50Y Medical Diagnoses: Fracture Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Scientific Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan-1 Age: 50Y Medical Diagnoses: Fracture Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Scientific Rationale EvaluationBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Pasien Pra Dan Pasca Bedah Rekonstruksi SendiDocument8 pagesPasien Pra Dan Pasca Bedah Rekonstruksi SendiAnonymous WTf5q6J7znNo ratings yet
- NCP VergelDocument3 pagesNCP VergelKelly Vergel de DiosNo ratings yet
- Impaired Mobility NCPDocument1 pageImpaired Mobility NCPAmal Bacaraman MauteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument15 pagesNursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationEina TandincoNo ratings yet
- CDC 74349 DS1Document11 pagesCDC 74349 DS1AlinaNo ratings yet
- Assessmen T Nursing Diagnosi S Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Cues: Independent IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessmen T Nursing Diagnosi S Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Cues: Independent IndependentKim Glaidyl BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature: Motor Vehicle AccidentDocument8 pagesReview of Related Literature: Motor Vehicle AccidentJ. TSNo ratings yet
- NCP 5 A 2Document2 pagesNCP 5 A 2api-3825388No ratings yet
- FractureDocument1 pageFractureReechie TeasoonNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesComprehensive Nursing Care PlanJustine Joy SolanoNo ratings yet
- 4 Amputation Nursing Care Plans - Nurseslabs-1 PDFDocument12 pages4 Amputation Nursing Care Plans - Nurseslabs-1 PDFsaidi MwanamongaNo ratings yet
- NCP CSDocument4 pagesNCP CSJM UncianoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Fascial Training For More Flexibility, Suppleness and Vitality: This Is How You Get Your Fascias Into Top Form! (10 Minutes Fascia Workout For Home)From EverandFascial Training For More Flexibility, Suppleness and Vitality: This Is How You Get Your Fascias Into Top Form! (10 Minutes Fascia Workout For Home)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Ageless Flexibility: The Ultimate Guide to Stretching Your Body after 60From EverandAgeless Flexibility: The Ultimate Guide to Stretching Your Body after 60No ratings yet
- Fascial Training For More Flexibility, Suppleness and Vitality: This Is How You Get Your Fascias Into Top Form!From EverandFascial Training For More Flexibility, Suppleness and Vitality: This Is How You Get Your Fascias Into Top Form!No ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing: 3 Quarter Week 1Document7 pagesComputer Systems Servicing: 3 Quarter Week 1Romnick PortillanoNo ratings yet
- PMBOK Guide 5th Edition - NotesDocument50 pagesPMBOK Guide 5th Edition - NotesJoaoCOS100% (1)
- Unit 10: Values: Lesson A Objective: Learn To Talk About Moral DilemmasDocument7 pagesUnit 10: Values: Lesson A Objective: Learn To Talk About Moral DilemmasLiss PeñafielNo ratings yet
- Periodic Answer Key (Editable)Document44 pagesPeriodic Answer Key (Editable)coleenmaem.04No ratings yet
- Regular Income Tax: Exclusions From Gross IncomeDocument11 pagesRegular Income Tax: Exclusions From Gross IncomeAngelica PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Fungal NutritionDocument3 pagesFungal NutritionArtemishaMtzNo ratings yet
- Creation Centered HymnsDocument4 pagesCreation Centered HymnsJoshua DanielNo ratings yet
- BTEC Assignment Brief: (For NQF Only)Document2 pagesBTEC Assignment Brief: (For NQF Only)mlmihjazNo ratings yet
- Financing Model-Understanding Startup Studio Structures - by John Carbrey - FutureSight - MediumDocument12 pagesFinancing Model-Understanding Startup Studio Structures - by John Carbrey - FutureSight - MediummberensteinNo ratings yet
- STAT115 Questions 5Document6 pagesSTAT115 Questions 5Jom NicolasNo ratings yet
- SBP - Pengenalan, Induksi RulesDocument37 pagesSBP - Pengenalan, Induksi RulesTU ElektroNo ratings yet
- Rape of The LockDocument8 pagesRape of The LockKomal PurbeyNo ratings yet
- Mti and Pulsed DopplerDocument33 pagesMti and Pulsed DopplerWaqar Shaikh67% (3)
- IJCRT2202407Document9 pagesIJCRT2202407Harsh.s13No ratings yet
- Lexical Concepts, Cognitive Models and Meaning-Construction: Vyvyan EvansDocument44 pagesLexical Concepts, Cognitive Models and Meaning-Construction: Vyvyan EvansДарья БелокрыльцеваNo ratings yet
- Levels and Trends of MortalityDocument192 pagesLevels and Trends of MortalityvthiseasNo ratings yet
- Interchange - 5ed - 1 - Students - Book CONTESTADODocument166 pagesInterchange - 5ed - 1 - Students - Book CONTESTADORodrigoNo ratings yet
- 720U2301 Rev 07 - Minimate Pro Operator ManualDocument126 pages720U2301 Rev 07 - Minimate Pro Operator ManualCristobalKlingerNo ratings yet
- Social Cognitive Theory and Physical ActivityDocument13 pagesSocial Cognitive Theory and Physical ActivityMega AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- People v. Sy Pio, G.R. No. L-5848. April 30, 1954Document3 pagesPeople v. Sy Pio, G.R. No. L-5848. April 30, 1954Anna BarbadilloNo ratings yet
- Real Numbers 40 Marks Test PaperDocument4 pagesReal Numbers 40 Marks Test Paperdinesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Lhamo Lomagyonma PracticeDocument4 pagesLhamo Lomagyonma Practicemozollis22No ratings yet
- 2 OWA310005 GSM UMTS Softswitch Core Network Principle ISSUE 3 2Document59 pages2 OWA310005 GSM UMTS Softswitch Core Network Principle ISSUE 3 2abu bakrNo ratings yet
- Isaiah 61 CommentaryDocument77 pagesIsaiah 61 CommentaryВолодимир БурдилякNo ratings yet
- PDF Abstrak-20335667Document1 pagePDF Abstrak-20335667hirukihealNo ratings yet
- Resilience Definitions Theory and ChallengesDocument14 pagesResilience Definitions Theory and ChallengesRaji Rafiu BoyeNo ratings yet