Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 7+Composition+of+Functions
2 7+Composition+of+Functions
Uploaded by
Dolly PatelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 7+Composition+of+Functions
2 7+Composition+of+Functions
Uploaded by
Dolly PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
Foldable 2.7 Topic 2.
7 Composition of Functions
AP® Precalculus Notes for Topic 2.7 Combining functions in a manner where the output from
one function becomes the input for the next function is known
Source: AP® Precalculus Course as a Composition of Functions.
Notation:
and Exam Description f ( g ( x) ) g ( f ( x) )
or or
( f g ) ( x) ( g f ) ( x)
Print two-sided and fold. We read these as "f of g of x" or "g of f of x".
Example 1 – Analytical Representations:
Glue this side in the notebook.
1
Given:
= 2
f ( x) x= and g ( x)
x−4
Find: f ( g ( x) ) =
Created by Vicki Carter
Find: f ( g (6) ) =
Find : g ( f ( x ) )
Find : g ( f ( 3) )
What is the domain of the function given by h ( x ) = f ( g ( x ) ) ?
What is the domain of the function given by j ( x ) = g ( f ( x ) ) ?
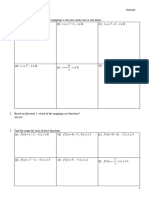
Example 2 – Analytical Representation: If h ( x ) = f g ( x ) , ( ) Example 5 – Combination of Representations:
decompose the function h into two less complicated functions Graphical: The piecewise-linear Numerical
f and g. function f is defined on [–5, 4]. x g ( x)
( x)
h= 3
2x − 5 –3 0
-1 1
Example 3 – Numerical Representations: 0 3
1 2
x f ( x) x g ( x) 2 4
–1 –4 –2 0 4 5
0 1 1 1
1 3 3 2
2 5 6 4
Find the value of:
Find: f ( g (3) ) = Find : g ( f (1) ) f ( g ( 2)) =
Example 4 – Combination of Representations: f ( g ( −3) ) =
Graphical: The piecewise-linear Analytical
function f is defined on [–5, 4]. g ( x )= x + 1
Find the value of:
g ( f ( 2)) =
f ( g ( 2)) =
g ( f ( −3) ) = g ( f ( −3) ) =
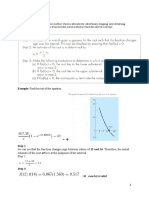
( )
For x = −1, find the value of f g ( x ) + f ( x ) .
(
Sketch the graph of f g ( x ) . ) (
Sketch the graph of g f ( x ) )
( )
For x = 0, find the value of g 2 f ( x ) − g ( x ) .
You might also like
- Form 4 Chapter 1 Functions (Topical Test)Document3 pagesForm 4 Chapter 1 Functions (Topical Test)SULIANI DANNY100% (17)
- TOPIC-4 Descriptive StatisticsDocument3 pagesTOPIC-4 Descriptive StatisticsRomina GravamenNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Homework: This Is A Preview of The Published Version of The QuizDocument7 pagesWeek 4 Homework: This Is A Preview of The Published Version of The QuizChaseNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesThermodynamicsvinovictory8571No ratings yet
- 4 Computing Derivatives, Product and Quotient Rules: Math 180 WorksheetsDocument3 pages4 Computing Derivatives, Product and Quotient Rules: Math 180 WorksheetsDeep PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3B - Combinations of FunctionsDocument33 pagesLesson 3B - Combinations of FunctionsLizbethHazelRiveraNo ratings yet
- 100 Ways To Motivate OthersDocument38 pages100 Ways To Motivate OthersonyejekweNo ratings yet
- Mat 121-FunctionsDocument45 pagesMat 121-Functionsakinleyedavid2007No ratings yet
- M3 Adv. AlgebraDocument4 pagesM3 Adv. AlgebraAngel Von Heart PandesNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-25 9 12-MorpheusDocument148 pagesChapter1-25 9 12-MorpheushauzhiNo ratings yet
- Gen-Math ReviewerDocument26 pagesGen-Math ReviewerElla DyNo ratings yet
- FunctionDocument17 pagesFunctionGoodness Nnesoma EMENIKENo ratings yet
- Functional Notation IgcseDocument17 pagesFunctional Notation IgcseAriyah SinghNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Add Maths NoteDocument9 pagesForm 4 Add Maths NoteLoh Chee WeiNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument17 pagesFunctionsMeiying LeeNo ratings yet
- Functions Assignment4Document6 pagesFunctions Assignment4AidanNo ratings yet
- C3 Chapter2 FunctionsQuestionsDocument9 pagesC3 Chapter2 FunctionsQuestionsWillie SalimNo ratings yet
- Functions 1Document7 pagesFunctions 1hannah10leahNo ratings yet
- Module 3 GenmathDocument3 pagesModule 3 GenmathJia BellesNo ratings yet
- W#2 M#1 Operation On FunctionsDocument6 pagesW#2 M#1 Operation On FunctionsIsabel PerezNo ratings yet
- F F F F: Centre For Pre-U Studies Mf012 Fundamental of Mathematics Tutorial 5Document2 pagesF F F F: Centre For Pre-U Studies Mf012 Fundamental of Mathematics Tutorial 5Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- C3 Functions H - QuestionsDocument2 pagesC3 Functions H - QuestionsvictorNo ratings yet
- Lesson No.1.LECTURE - MATH FOR ENGINEERS - Function and Algebraic Expression - OCT2021Document3 pagesLesson No.1.LECTURE - MATH FOR ENGINEERS - Function and Algebraic Expression - OCT2021MadagascarNo ratings yet
- S&Z 5.2Document19 pagesS&Z 5.2Jhe Hann BurcaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 1Document36 pagesExercise Chapter 1Samuel Sim Shien ShuangNo ratings yet
- Composite and Inverse FunctionsDocument12 pagesComposite and Inverse FunctionsAnonymous yPCsBWJG9No ratings yet
- 1 2 Functions HardDocument32 pages1 2 Functions HardShanayaNo ratings yet
- Sgi 2.1 Function Operations and Composition of FunctionsDocument2 pagesSgi 2.1 Function Operations and Composition of FunctionsKayNo ratings yet
- Skema LKM 7Document3 pagesSkema LKM 723005852No ratings yet
- Eda2f2ax Level3Document1 pageEda2f2ax Level3Yi-Sin Lin - OXF.StudentNo ratings yet
- Matematik Tambahan SoalanDocument137 pagesMatematik Tambahan SoalanDequeNo Mohd Noor100% (1)
- C3 Functions H Solving and Mixed Topics QuestionsDocument2 pagesC3 Functions H Solving and Mixed Topics QuestionsBONGLAV JemasonNo ratings yet
- Función InversaDocument6 pagesFunción InversacapsantinoNo ratings yet
- Composite FunctionDocument28 pagesComposite FunctionTANG PEI PEI100% (1)
- Ma1103 2NDWDocument12 pagesMa1103 2NDWDanur WendaNo ratings yet
- Gen. Math Chapter 1 4Document4 pagesGen. Math Chapter 1 4Jian BuenoNo ratings yet
- 3 3 PDFDocument2 pages3 3 PDFariel brightNo ratings yet
- COMOSITE AND INVERSE FUNCTIONS Worksheet IB Maths AA SLDocument7 pagesCOMOSITE AND INVERSE FUNCTIONS Worksheet IB Maths AA SLPraggu SwarnkarNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Exercise Inverse FunctionDocument5 pages2.3 Exercise Inverse FunctionNurshahiran sufyanNo ratings yet
- GenMath ADocument3 pagesGenMath AMariane Gayle CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Evaluating+a+Function GM+mod+2+unit+1docxDocument6 pagesEvaluating+a+Function GM+mod+2+unit+1docxKing HarlequinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Q55-Q75) - M35Document11 pagesChapter 1 (Q55-Q75) - M35sheshvar kumarNo ratings yet
- Let F (X) 2x + 1 and G (X) 3x - 4. Find (A) (X) (B) (G ° F) (-2) (C) (F ° G) (X)Document12 pagesLet F (X) 2x + 1 and G (X) 3x - 4. Find (A) (X) (B) (G ° F) (-2) (C) (F ° G) (X)Hadi AlnaherNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document6 pagesTutorial 1Muhd HafidzNo ratings yet
- IB Qns Functions Composite InvesrseDocument2 pagesIB Qns Functions Composite InvesrseDevNo ratings yet
- Math 169 - Worksheet 1Document2 pagesMath 169 - Worksheet 1Murat SahilliogluNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 NotesDocument34 pagesAlgebra 1 NotesALFRED TAIMONINo ratings yet
- Seminar Add Maths F4 1-4 PDFDocument18 pagesSeminar Add Maths F4 1-4 PDFAnonymous bwVxI8Y8WNo ratings yet
- Graphs, Functions, and ApplicationsDocument44 pagesGraphs, Functions, and ApplicationssaudNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - Student - 2021Document38 pagesCHAPTER 1 - Student - 2021M. Arief Fiqrie MuryadiNo ratings yet
- Functions Assignment3Document7 pagesFunctions Assignment3AidanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 Functions QuestionsDocument6 pagesTutorial 4 Functions Questionsaditya.khandelwal.2020No ratings yet
- Functions and Relations: RelationDocument4 pagesFunctions and Relations: RelationNurfadilah dilNo ratings yet
- Quiz Like Questions From Unit 6-10Document8 pagesQuiz Like Questions From Unit 6-10Lucie StudgeNo ratings yet
- (Total 6 Marks) : IB Questionbank Maths SL 1Document7 pages(Total 6 Marks) : IB Questionbank Maths SL 1agrbovic100% (1)
- 2006 AP Calculus BC A ReviewDocument9 pages2006 AP Calculus BC A ReviewHeNo ratings yet
- 1st Semester Final Exam ReviewDocument7 pages1st Semester Final Exam Reviewanimelovershipper101No ratings yet
- 10.WS-7 Inverse-Functions 14-09-2021 WorkDocument1 page10.WS-7 Inverse-Functions 14-09-2021 WorkYoosuf AiyasNo ratings yet
- Function Operations and CompositionDocument42 pagesFunction Operations and CompositionBenj Jamieson DuagNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chapter 1 Functions (Topical Test) (40 Marks) : X y Z H GDocument3 pagesForm 4 Chapter 1 Functions (Topical Test) (40 Marks) : X y Z H GMy fluffy Mochi100% (1)
- Form 4 Chapter 1 Functions Topical TestDocument3 pagesForm 4 Chapter 1 Functions Topical TestSed CatNo ratings yet
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson QuizDocument37 pagesWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson QuizEdal SantosNo ratings yet
- Goal Programming PPT SolvedDocument27 pagesGoal Programming PPT SolvedDika Virginia DevintasariNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification: Pedro S. Tolentino Memorial National High SchoolDocument4 pagesTable of Specification: Pedro S. Tolentino Memorial National High SchoolAngelica Manalo PerezNo ratings yet
- Integration Using Partial Fractions PDFDocument12 pagesIntegration Using Partial Fractions PDFStevenzel Eala EstellaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Acid and Base TitrationDocument17 pagesExperiment 3 - Acid and Base TitrationJoemer Absalon Adorna100% (3)
- Calculus DLL Week 7Document6 pagesCalculus DLL Week 7Gianmarie Sumagaysay HiladoNo ratings yet
- CFD VocabularyDocument10 pagesCFD VocabularyAmir LachrafNo ratings yet
- AMA1110 Exercise - 9Document9 pagesAMA1110 Exercise - 9Brian LiNo ratings yet
- Bms Project Shubham 4Document16 pagesBms Project Shubham 4Rishab Lohan100% (1)
- Time To Move On From Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) and Mean Time To Failure (MTTF)Document4 pagesTime To Move On From Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) and Mean Time To Failure (MTTF)aliNo ratings yet
- Anachem StudsDocument2 pagesAnachem StudsPrichebelle Gerona GrafiaNo ratings yet
- Quinton Buckner Math 1070 Excel ProjectDocument12 pagesQuinton Buckner Math 1070 Excel Projectapi-284827485No ratings yet
- Branch and Cut Algorithm IME 960 ProjectDocument23 pagesBranch and Cut Algorithm IME 960 ProjectAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Engineers (MAT2001) - SyllabusDocument3 pagesStatistics For Engineers (MAT2001) - SyllabusDiyali67% (3)
- If We Combine The MACD With The Stochastic IndicatorDocument1 pageIf We Combine The MACD With The Stochastic IndicatorMOHD TARMIZINo ratings yet
- Ongoing Visual Inspection (OVI)Document2 pagesOngoing Visual Inspection (OVI)NBNo ratings yet
- Standard Probability SpaceDocument8 pagesStandard Probability Spacedaniel656No ratings yet
- 02 The Potential Outcomes FrameworkDocument30 pages02 The Potential Outcomes FrameworkvrhdzvNo ratings yet
- ML Unit2 ClasspptDocument44 pagesML Unit2 Classpptriwag84842No ratings yet
- Mathematics Sample Paper Solutions Section-ADocument19 pagesMathematics Sample Paper Solutions Section-APoonamBhardwajNo ratings yet
- Determination of Acidity in Whole Raw MilkDocument3 pagesDetermination of Acidity in Whole Raw Milkpruebas123123No ratings yet
- Marketing Analytics NotesDocument3 pagesMarketing Analytics Notessumit SinghNo ratings yet
- LA - Lecture Notes Numerical AnalysisDocument25 pagesLA - Lecture Notes Numerical AnalysisAtalay SeçerNo ratings yet
- Btec Assignment HelpDocument12 pagesBtec Assignment HelpafmohuodeNo ratings yet
- Quarter Price Per Chip $ Forecast with α=.20 Forcast with α=.50Document3 pagesQuarter Price Per Chip $ Forecast with α=.20 Forcast with α=.50Robin LusabioNo ratings yet
- Statistics PDFDocument17 pagesStatistics PDFSauravNo ratings yet
- On Cleaning Validation Recovery Studies: Common MisconceptionsDocument9 pagesOn Cleaning Validation Recovery Studies: Common MisconceptionsMiguel Angel Pacahuala CristobalNo ratings yet
- PPA 691 - Seminar in Public Policy Analysis: Lecture 5 - Forecasting Policy FuturesDocument21 pagesPPA 691 - Seminar in Public Policy Analysis: Lecture 5 - Forecasting Policy Futureskuldip singhNo ratings yet